Quizzes 5-6
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
An example of a task that can be used to demonstrate holistic face processing is:
Face Composite task
Thrombotic and embolic strokes are subtypes of":
Ischemic stroke
Visual fibers originating from the left nasal retina ___ at the optic chiasm and end up in the ___
do cross over; right hemisphere
With regard to the 2 main output pathways from the occipital lobe, ___ is to ___ as dorsal is to ventral.
where; what
It is dramatically more difficult to recognize pictures of faces when they are:
shown as a photo negative (with contrast polarity reversal)
The following is true of congenital prosopagnosia:
it is accompanied by severe neurological impairments and intellectual deficits
it is characterized by severe visual deficits and near-blindness
it is present from early childhood, suggesting familial predisposition
it is usually caused by a sudden lesion, such as a stroke
it is present from early childhood, suggesting familial predisposition
People can still recognize faces very well even when the pictures are:
compressed into a pancake (down to 25% of height)
Retinal fibers go directly to all of these structures EXCEPT:
lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
hippocampus
superior colliculus
suprachiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus
hippocampus
Area MT is necessary for the processing of:
motion
The left eye gets information from:
both visual hemifields
Dendritic spines are characterized by the following:
they are present only in non-human primates
they release glutamate
they generate action potentials
they host most synaptic contacts (with axon terminals)
they host most synaptic contacts (with axon terminals)
If the cell is NOT sufficiently depolarized and the EPSPs do not reach the firing threshold, then the following happens:
an action potential is generated
there is a dopamine influx into the cell
nothing happens
GABA is released at its axon terminal
nothing happens
Extracellular fluid is similar to ___ in it chemical composition. It mostly contains: ___
seawater; sodium and chloride
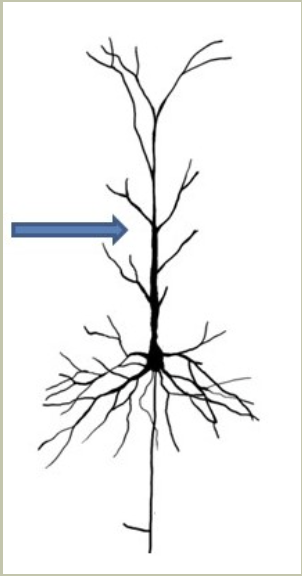
The arrow marks the following feature of the pyramidal cell:
apical dendrite
GABA is an ____ neurotransmitter which causes ____ of the cell membrane
inhibitory; hyperpolarization
Synaptic release of an excitatory neurotransmitter (glutamate) does NOT result in:
hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
opening of postsynaptic Na+ channels
depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
excitatory postsynaptic potentials
hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
Sodium-potassium pumps move ___
sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell
The synapse is characterized by the following:
a neurotransmitter is released
A cell is likely to fire if the following happens near the axon hillock (the trigger zone):
the membrane is sufficiently depolarized
The most common types of cells in the cerebral cortex are:
pyramidal neurons