Behavioral Science I Lesson 7: Cognitive Development
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Put Piaget's Four Stages of Cognitive Development in order from earliest to latest stage:
I. Pre-Operational
II. Formal Operational
III. Sensorimotor
IV. Concrete Operational
(A) I > II > III > IV
(B) I > III > IV > II
(C) III > I > IV > II
(D) III > IV > II > I
(C) III > I > IV > II
Piaget's Four Stages of Cognitive Development in order from earliest to latest stage:
1. Sensorimotor (0-2 years)
2. Preoperational (2-7 years)
3. Concrete Operational (7-11 years)
4. Formal Operational (12+ years)
CRB At which of Piaget's stages of Cognitive Development would an infant be able to babble or learn one word a month?
(A) Pre-Operational
(B) Formal Operational
(C) Sensorimotor
(D) Concrete Operational
(C) Sensorimotor
An infant would be babbling around 9-12 months old and learning a word a month from 12-18 months. These both fall squarely within the Sensorimotor Stage.
CRB At which of Piaget's stages of Cognitive Development would a child have language rules largely mastered?
(A) Pre-Operational
(B) Formal Operational
(C) Sensorimotor
(D) Concrete Operational
(A) Pre-Operational
In terms of language acquisition, a 5-year-old will have language rules largely mastered. 5-year-olds are in the Pre-Operational stage.
At the end of the Sensorimotor stage (0-2 years) of Piaget's stages of development, toddlers would fully understand and utilize:
(A) Pretend play
(B) Symbolic representation
(C) Operational thought
(D) Object Permanence
(D) Object Permanence
Object permanence is the main mental trait that is developed during the Sensorimotor stage of development.

True or False? Object Permanence describes how older children can know that two cups hold equal volumes of water, even if the cups are different shapes, if the water is poured in front of them.
False. CONSERVATION describes how older children can know that two cups hold equal volumes of water, even if the cups are different shapes, if the water is poured in front of them.

Which of the following combination of activities can a child in the preoperational stage perform?
I. Symbolic/Pretend Play
II. Reversible actions
III. Mental math
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(A) I only
A child in the preoperational stage can perform symbolic/pretend play. Both reversible actions and mental math are traits of operational thought, which are not developed until later.

True or False? Children in the Pre-operational Stage are often egocentric, not allowing them to consider other's perspectives.
True. Children in the Pre-operational Stage are often egocentric, not allowing them to consider other's perspectives.
An adolescent is presented with a nuanced story of how a lady stole medication she couldn't afford from a pharmacy to live. When asked about it, the adolescent understood it was a complex situation, not black and white. Which stage would this adolescent belong to?
(A) Preoperational
(B) Formal Operational
(C) Concrete Operational
(D) Sensorimotor
(B) Formal Operational
Since the adolescent was able to examine the situation from multiple angles instead of simply right or wrong, they are clearly in that final stage of Cognitive Development: Formal Operational.

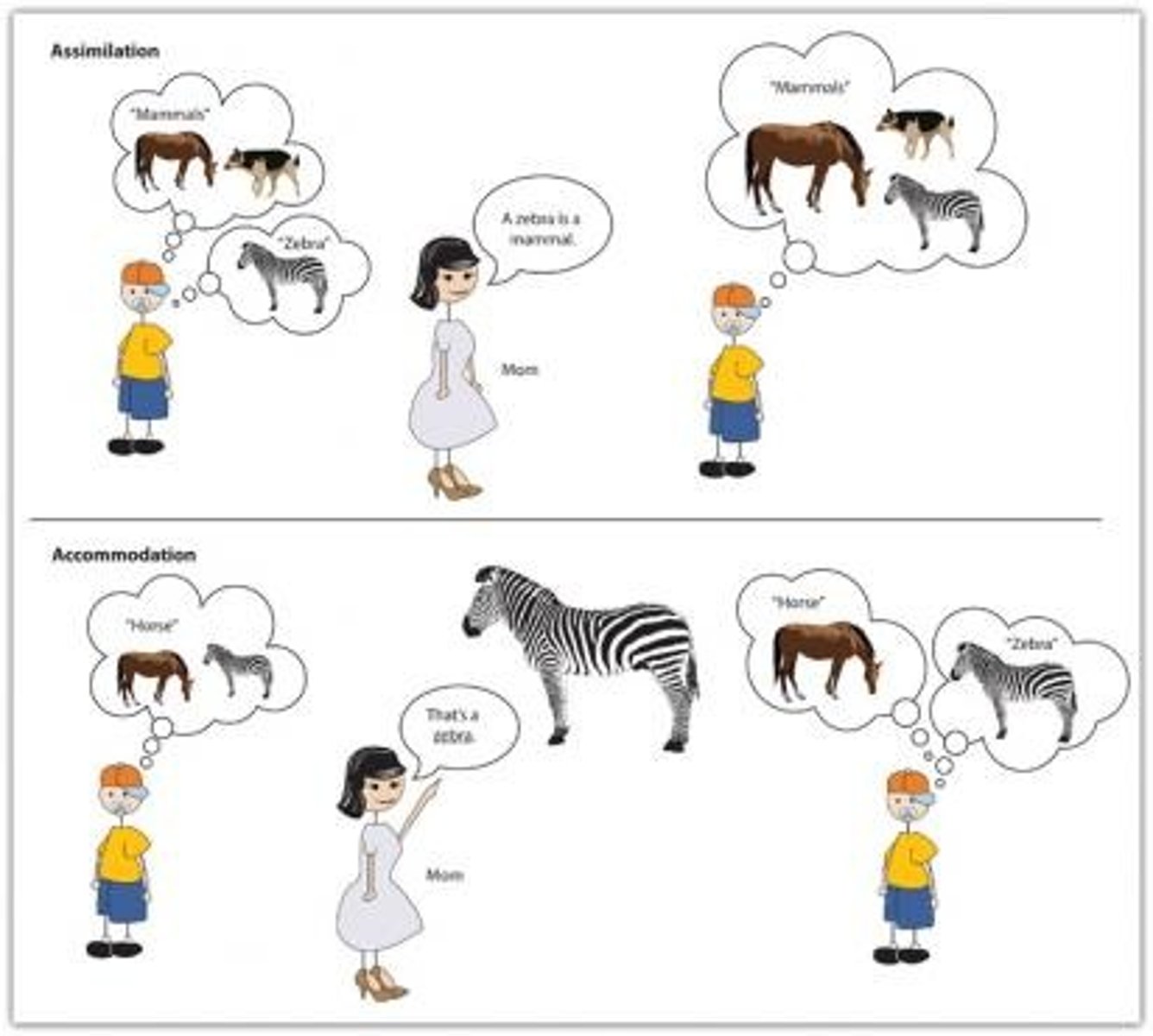
Compare Assimilation and Accommodation, in terms of mental Schema.
Mental Schema are what organize categories of information and the relationships among them. If newly acquired information is similar enough to the schema to simply be added in, that new information is Assimilated and the Schema is relatively unchanged.
If the newly acquired information is too different to fit the schema as is, the schema must be altered accordingly. The Schema is changing to Accommodate the new information.
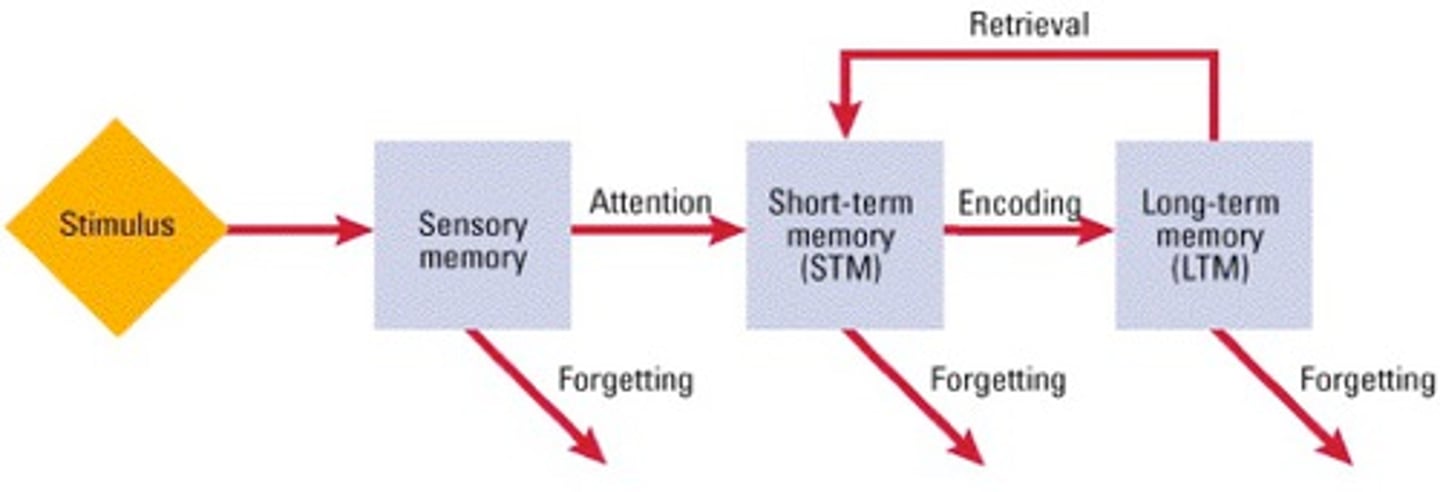
CRB Recall the information processing models. Which of the following is NOT one of the series of steps in this model?
(A) Attention
(B) Perception
(C) Accommodation
(D) Storage into memory
(C) Accommodation
Three of the main steps involved in the Information-processing model are Attention, Perception and Storage into Memory.
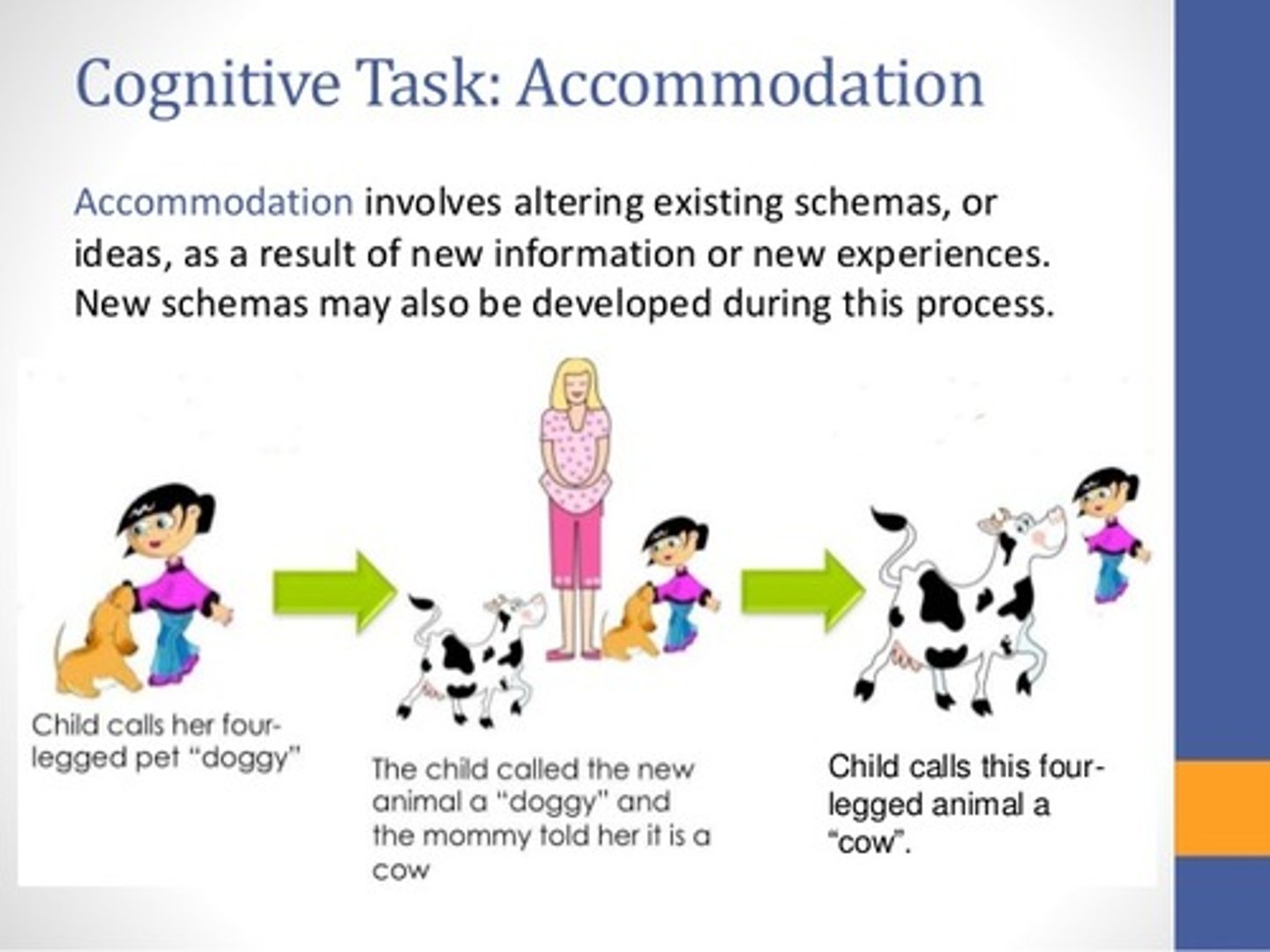
True or false? An example of accommodation would be introducing a foreigner to darts as a competitive sport, and the foreigner altering their Schema related to sports to include a less physically involved sport.
True. An example of accommodation would be introducing a foreigner to darts as a competitive sport, and the foreigner altering their Schema related to sports to accommodate this new idea.
Right now, you are preparing for the MCAT. Is the MCAT a Well-Defined or Ill-Defined problem, and why?
The MCAT is a well-defined problem, because it has a clear beginning and end. Especially with the structure and organization of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse! ;)
An Ill-defined problem lacks that clarity.
Why is Trial and Error typically not used when other problem solving methods are feasible?
(A) Trial and Error is a methodical approach, but non-methodical approaches are easier.
(B) Trial and Error is a resource-intensive approach, and can drain the problem solver
(C) Trial and Error is not a methodical approach, and therefore an inefficient approach and does not guarantee a correct solution.
(D) None of the above because Trial and Error is the superior problem solving method.
(C) Trial and Error is not a methodical approach, and therefore an inefficient approach and does not guarantee a correct solution.
Compare and contrast heuristics and algorithms in terms of processing speed and guarantee of correctness.
Heuristics are mental tricks used to break complex problems into simpler problems using mental tricks, but do not guarantee right answers.
Algorithms are methodical approaches that are guaranteed to get the correct answer, but can take a very long time.

CRB Using heuristics in language can often lead to mistakes, like misspelling words like "Neighbor" or making the past tense of run "runned". Which of the following describes when a child misapplies one of these grammar rules?
(A) Loose Lips
(B) Misapplication
(C) Mistaken integration
(D) Errors of Growth
(D) Errors of Growth
Errors of growth are when a child applies some grammatical rule where it doesn't apply.
Which of the following are examples of heuristics?
I) Availability
II) Representativeness
III) Means-end analysis
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and III
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Availability (of examples that come to mind), Representativeness (using prototypes), and Means-end Analysis (breaking large problems into smaller ones) are all heuristics, or mental shortcuts used in problem solving. Working backwards is another common heuristic.
When trying to first solve a Rubik's Cube, someone could be incorrectly focused on trying to solve all horizontal rows first. What is this an example of?
(A) Fixation
(B) Representativeness
(C) Means-End Analysis
(D) Insight
(A) Fixation
Because the solver is stuck on a wrong approach, this is an example of fixation.
CRB True or false? Fixation is often the result of a tendency to focus on novel solutions to solve new problems, called a Mental Set.
False. Fixation is often the result of a tendency to focus on Solutions that worked previously to solve new problems (even though they will not work).
A Mental Set describes a person's approach to solving a problem, often based in previous experience.
After a long time of trying to solve the Rubik's Cube, the solver takes a break and later has an "aha" moment and solves it rather quickly. What is this an example of?
(A) Fixation
(B) Representativeness
(C) Means-End Analysis
(D) Insight
(D) Insight
The solver underwent Incubation by taking a break from the problem, which led to Insight when the solution popped into their head.

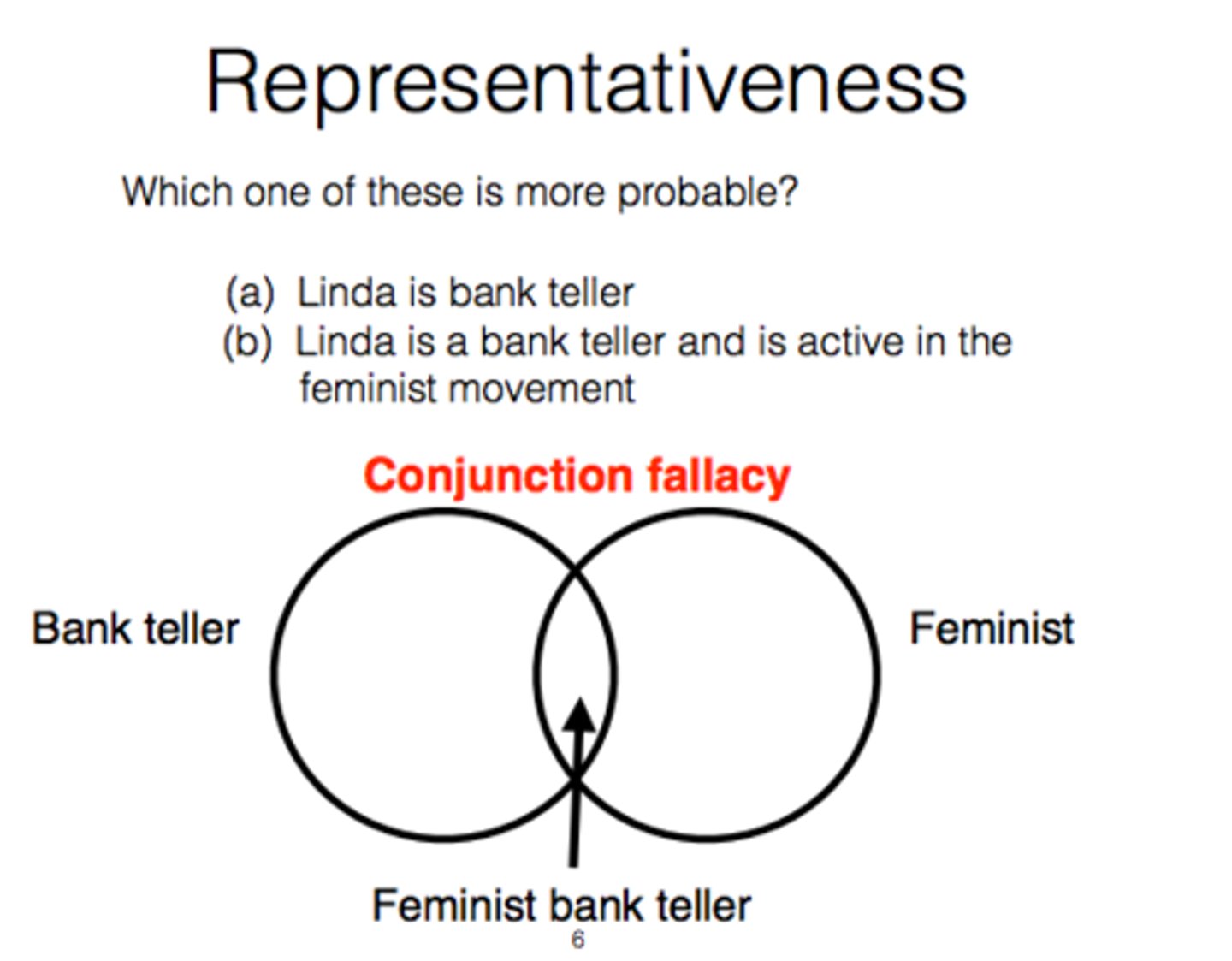
A man comes into the ER room wearing steel-toed boots, a mesh hat and a RAM 1500 t-shirt, and is carrying his detached finger with him in a toolbox. Is it more likely that he is a construction worker, or a truck-driving construction worker? How might this be an example of the Conjunction Fallacy?
Despite any context clues, it is statistically more likely that the patient falls under just the label of "construction worker" than both "construction worker" and "truck driver". This is a clear example of the Conjunction Fallacy.
Which of the following is not a bias that can impair decision making?
(A) Confirmation Bias
(B) Overconfidence
(C) Heuristics
(D) Belief Perserverance
(C) Heuristics
Confirmation Bias, Overconfidence, and Belief Perserverance are all biases that can impair decision making.

Explain the difference between Belief Perseverance and Confirmation Bias.
Belief Perseverance is maintaining old, incorrect beliefs by ignoring or rationalizing against the dis-confirming facts presented to you.
Confirmation Bias is when you intentionally seek out only facts to support your current opinion/decision.
CRB A young sociologist student reads two statements: "Drug usage is higher in low-income areas" and "Crime rates are higher in low-income areas". If the sociologist draws the conclusion that "Drug usage is causing higher crime rates in low income areas", which of the following errors is the sociologist committing?
(A) Confirmation Bias
(B) Belief Bias
(C) Heuristics
(D) Belief Perserverance
(B) Belief Bias
In belief bias, a person may judge arguments based on what they personally believe, as opposed to the statements' logical conclusions. In this case, drawing the conclusion that the drug usage is causing the higher crime rates is NOT a strictly logical conclusion.
Give an example of how framing a decision can change the choice a person will make.
Take the flu vaccine as an example. If I ask someone if they want to be protected from the flu, they would be likely to get vaccinated; if I ask if they want to receive a shot, they are less likely to get vaccinated. Framing makes a big difference in how someone views their choices!

Generally define "intelligence", and what IQ stands for.
IQ = Intelligence Quotient
Generally, intelligence gives the abilities to learn from experience, solve problems and adapt to new situations.
After running various intelligence tests on subjects, Charles Spearman found that students who score highly in one area tend to score very well in other categories too. Which intelligence theory does his data support?
(A) Multiple Intelligences
(B) General Intelligence
(C) Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
(D) Seven Types Theory of Intelligence
(B) General intelligence
The overlap of high scores in many areas supports the existence of a "g factor", or a general intelligence factor.
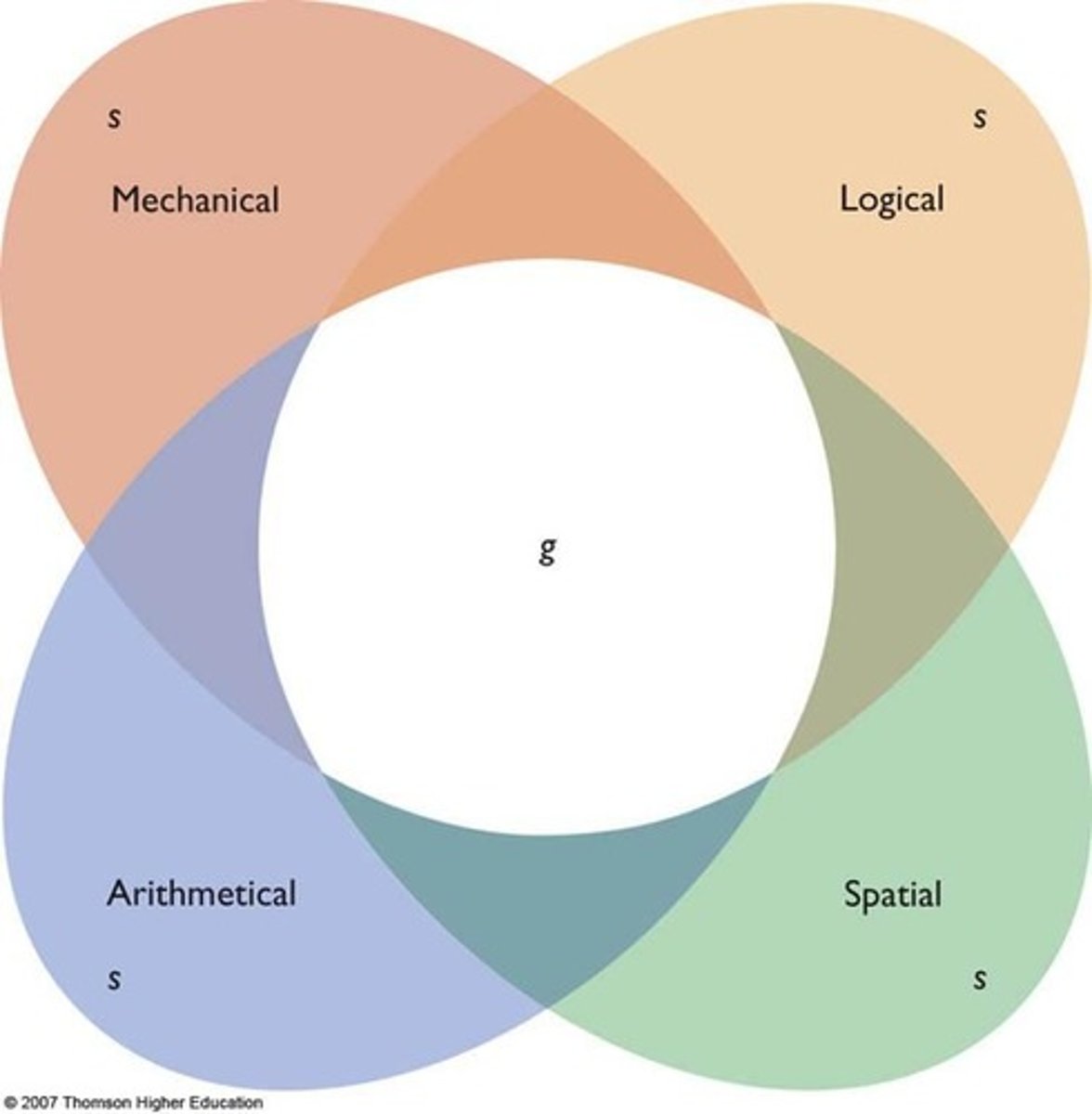
Robert Sternberg found that people's intelligences could be broadly grouped into a few well-defined, separated groups. Which intelligence theory is based off of this?
(A) Multiple Intelligences
(B) General Intelligence
(C) Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
(D) Seven Types Theory of Intelligence
(C) Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
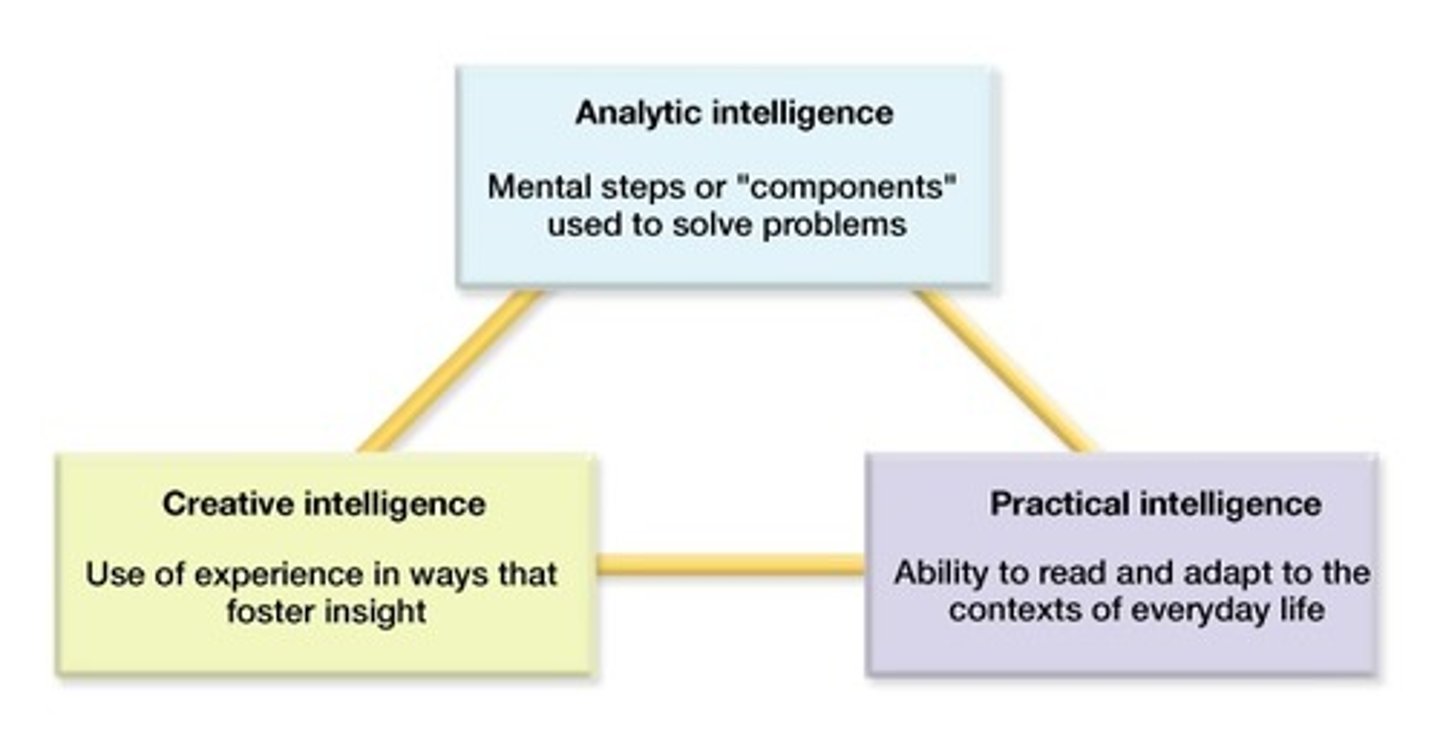
Which of the following is not a component of the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence?
(A) Analytical
(B) Emotional
(C) Creative
(D) Practical
(B) Emotional
Analytical, Creative and Practical intelligences are the three in the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence.
Emotional intelligence is suggested as a counter to this theory, because the triarchic theory does not account for better marriages/relationships and interactions with others.
Quick and abstract reasoning is _______ Intelligence, whereas accumulated knowledge is ______ Intelligence.
(A) Fluid, Crystallized
(B) Fluid, Fluid
(C) Crystallized, Fluid
(D) Crystallized, Crystallized
(A) Fluid, Crystallized
Quick and abstract reasoning is Fluid Intelligence, whereas accumulated knowledge is Crystallized Intelligence.
Which of the following affect intelligence?
(A) Nature
(B) Nurture
(C) Both Nature and Nurture
(D) Neither
(C) Both Nature and Nurture
Based on twin studies, intelligence has been shown to be influenced by nature and nurture.
True or False? The original IQ tests are completely independent of and not affected by the culture of the test-taker.
False. The original IQ tests' results were affected by the culture of the test-taker. Cultural barriers are still an issue in this field.
Which of the following theories is incorrectly described?
(A) The theory of general intelligence states that a "g factor" could apply to various tests of intelligence.
(B) The Theory of Primary Mental Abilities suggests there are seven specific factors that combine to make up all of intelligence.
(C) The Theory of Multiple Intelligences is another 7-9 specific factors of intelligence that rely on each other.
(D) The Triarchic Theory of Intelligence limits itself to 3 independent intelligences that will directly lead to real-world success.
(C) The Theory of Multiple Intelligences suggests that there are 7-9 specific factors of intelligence that ARE INDEPENDENT OF each other.
Which of the following examples best represents cognitive dissonance?
(A) Jessica spends lots of time alone with her boyfriend instead of socializing, and would rather spend time with him than other friends.
(B) Raven telling others that her gastroparesis means she cannot eat meat, but she eats hamburgers.
(C) Jason knows Paul is manipulating all their mutual friends, but convinces himself that Paul wouldn't manipulate him.
(D) Matt believes everything Raven says because he is blinded by love.
(C) Jason knows Paul is manipulating all their mutual friends, but convinces himself that Paul wouldn't manipulate him.
(B) is simply lying
(A) shows no dissonance
(D) is only one thought, so there cannot be dissonance
Which of the following is not a coping mechanism for Cognitive Dissonance?
(A) Removing the Cognitions
(B) Modifying the Cognitions
(C) Trivializing the Cognitions
(D) Denying the relation between the Cognitions
(A) Removing Cognitions
The main strategies of reconciling cognitive dissonance is modifying the cognitions, trivializing the cognitions, or adding more cognitions to confound the first two, and denying the relation between the cognitions.
Compare the differences in symptoms between patients with Broca's aphasia, Wernicke's aphasia, and conductive aphasia.
Broca's aphasia will exhibit broken speech, but comprehension is preserved.
Wernicke's aphasia (fluent aphasia) will exhibit fluent speech, but loss of meaning, almost like a word salad.
Conductive aphasia exhibits having a tough time expressing the correct thoughts from Wernicke's area to Broca's Area, but with enough time patients will correctly get their point across.
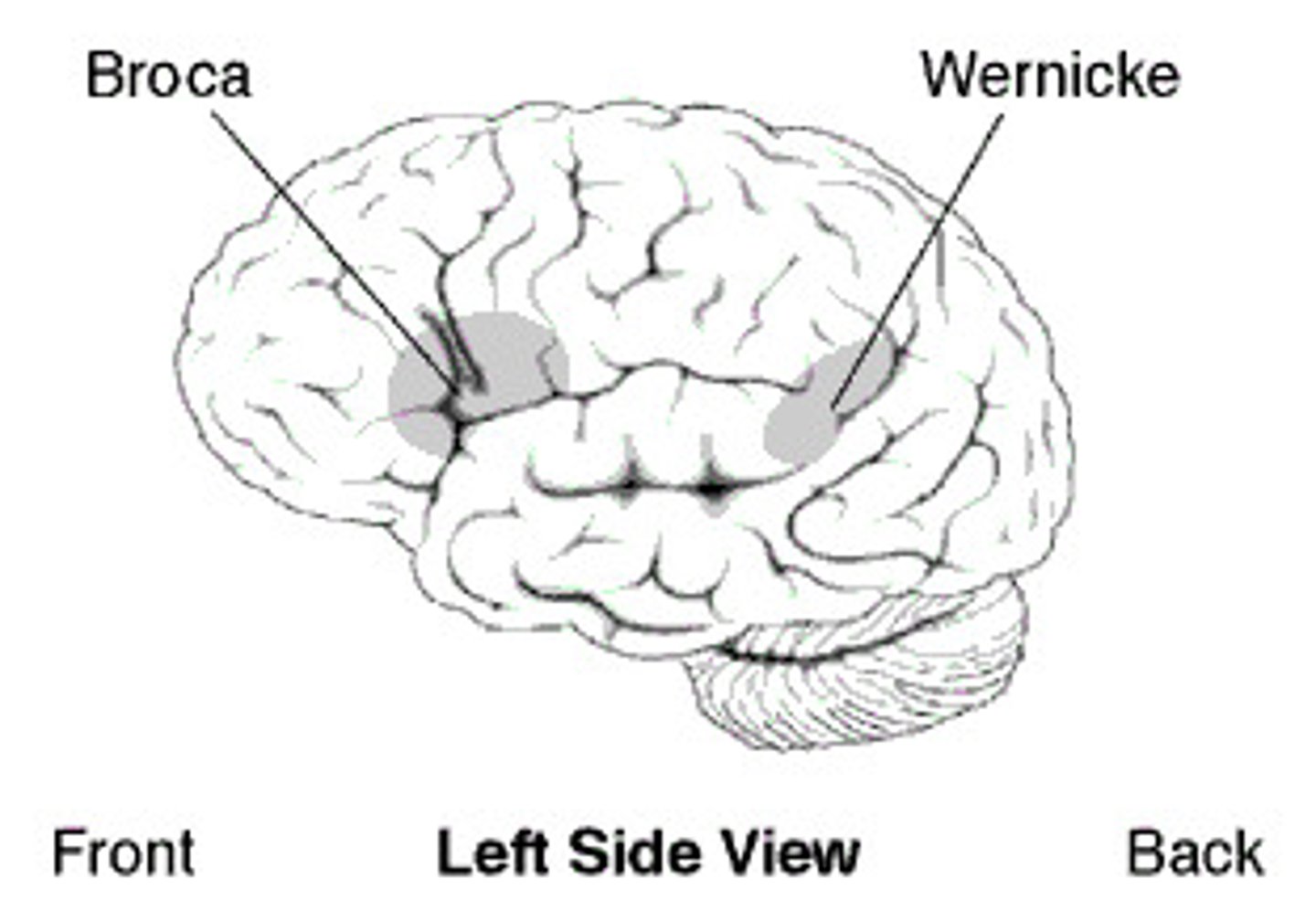
Which of the following are damaged if a patient is suffering from Global Aphasia?
(A) Broca's Area
(B) Wernicke's Area
(C) Both A and B
(D) Arcuate Fasciculus
(C) Both A and B
Global Aphasia occurs when both Broca's Area and Wernicke's Area are damaged.
Which of the following are damaged if a patient is suffering from Conduction Aphasia?
(A) Broca's Area
(B) Wernicke's Area
(C) Both A and B
(D) Arcuate Fasciculus
(D) Arcuate Fasciculus
The Arcuate Fasciculus is the connection between Wernicke's Area and Broca's Area, so damaging the Arcuate Fasciculus will affect how the two areas interact.
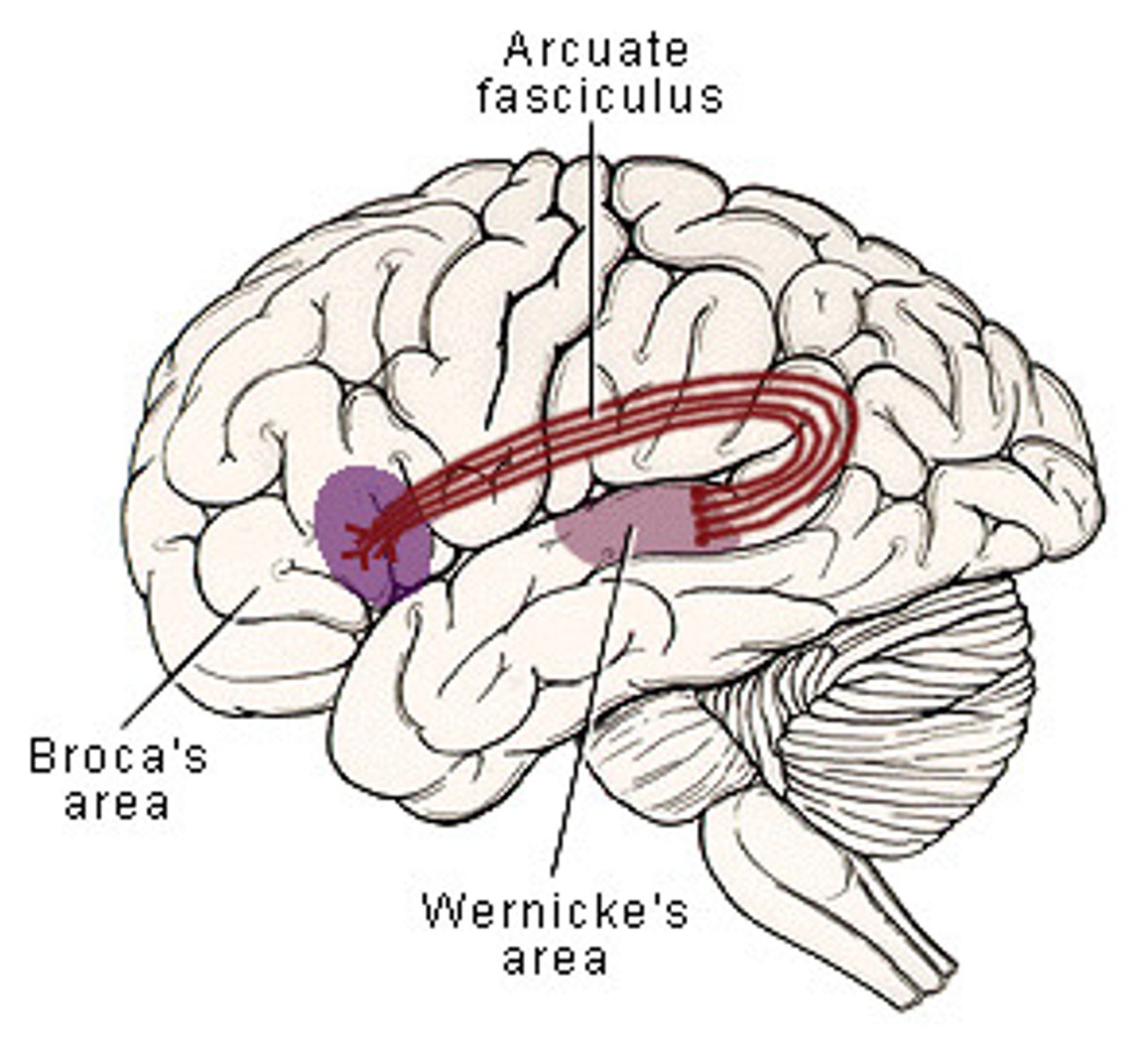
Which of the following properly describes a Split Brain patient?
(A) The connection between the occipital and temporal lobes is severed
(B) The Arcuate Fasciculus is severed
(C) The Corpus Callosum is severed
(D) The Central Sulcus is severed.
(C) The Corpus Callosum is severed
This produces a Split Brain patient, where the right and left hemispheres do not interact with one another.
If a Split Brain patient looks at an object on their right visual field, could they verbally describe the object? Why or why not?
Yes, if a Split Brain patient sees an object in their right visual field, it will be processed on the left side of their brain, where the language center is found.
If the object were on the left side, however, the patient could not verbally express the object!
After a 2 year old still has not started speaking, worried parents go to see a specialist. The specialist suggests that they start bringing their child to a popular park. Which language development theory would this specialist most agree with?
(A) Nativist approach
(B) Learning reinforcement
(C) Interactionist approach
(D) Universal approach
(C) Interactionist approach
This therapist would support the interactionist approach because his recommended course of action is to increase the child's interaction with other children.

Lamar comes from a technologically superior culture to Jane. Both are asked to describe a new Tablet, and although Lamar can use specific tech words, Jane can only describe it as "shiny" and "bright". A specialist claims that Jane must not have thought about the Tablet in the same sense that Lamar did based on her response. Which theory of Language Development would this specialist most agree with?
(A) Nativist Approach
(B) Learning Reinforcement
(C) Interactionist Approach
(D) Universal Approach
(D) Universal Approach
The Universal Approach states that thoughts precede and dictate language, so Jane not being able to come up with words to describe the advanced technology means her thoughts about them were also under-developed.
Another three-year-old has not acquired any language abilities yet, and the specialist keeps referring to a Language Acquisition Device in the child's brain. Which theory of Language Development would this specialist most agree with?
(A) Nativist approach
(B) Learning reinforcement
(C) Interactionist approach
(D) Universal approach
(A) Nativist Approach
The Nativist Approach claims infants have a Language Acquisition Device (LAD) in their brains to allow them to learn and understand any language, and that there is a critical/sensitive period where it is easiest to learn a language. That LAD only operates during that sensitive period.

Another two-year-old has learned to say female words like "mama", but has not learned "dada" or any other male words. The specialist insists it is because those masculine sounds/words are not being rewarded enough by the parents. Which theory of Language Development would this specialist most agree with?
(A) Nativist approach
(B) Learning reinforcement
(C) Interactionist approach
(D) Universal approach
(B) Learning Reinforcement
Learning Reinforcement states that the infant learns to make and put together certain sounds because specific sounds will make the individuals around them will react positively to them, reinforcing those sounds.
CRB B.F. Skinner led the Behaviorist Approach for language, which emphasizes imitation and reinforcement, and supports why an infant will learn their second word quicker than their first and their second 100-words faster than their first 100-words. Which theory of Language Development would this most align with?
(A) Nativist approach
(B) Learning reinforcement
(C) Interactionist approach
(D) Universal approach
(B) Learning reinforcement
Because of the focus on imitation and Reinforcement to facilitate learning language, the Behaviorist Approach is most similar to Learning Reinforcement.
CRB Opposing the findings of Universal Grammar and a LAD, which of the following hypotheses claims that cognition and perception are shaped by the language someone speaks?
(A) Linguistic Relativity
(B) Linguistic Constancy
(C) Cognitive Relativity
(D) Universalism
(A) Linguistic Relativity
The Linguistic Relativity Hypothesis claims that cognition and perception are shaped by the language someone speaks.
This can also be called the Whorfian Hypothesis.
CRB True or false? Linguistic Determinism is considered the strong form of Linguistic Relativity, claiming that that language can actually limit or determine thoughts and perceptions, rather than just shape or influence those thoughts and perceptions.
True. Linguistic Determinism is considered the strong form of Linguistic Relativity, claiming that that language can actually limit or determine thoughts and perceptions, rather than just shape or influence those thoughts and perceptions.
CRB When comparing areas of mental ability and decline, Recall and Recognition are typically separated. Compare the two terms.
Both Recall and Recognition involve retrieving information. Recall is retrieving information without context clues, whereas Recognition will use context clues.