Enzymes
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
\-work because they have the correct shape to fit the substrate
\-reactions are reversible like a lock in a key
\-Involved in anabolic and catabolic reactions
\-amylase (enzyme)
\
Amylase is an enzyme that breakdown starch down into maltose
\-DNA polymerase: found in plants and animals that forms and repairing DNA
\-Enzymes involved in photosynthesis(water and CO2 into glucose)
\-In plants best at 20-30°C
\-Enzymes cannot function at very low temperatures
\-Above a certain temp enzymes behind to loose their shape and become denatured
\-Optimal pH for enzymes is neutral
\-An exception is pepsin: a digestive enzyme in the stomach that works in acidic conditions
* When this happens enzymes are said to be denatured
\-Recently used for antibiotics, drugs and vaccines
\-Enzymes in bioprocessing are often reused to prevent waste
\-This is due to immmobilising them
\-Bioreactors are vessels where living cells are used to create products
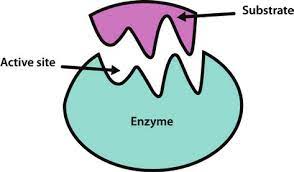
\-enzyme is a biological catalyst made if protein
Enzymes work because they have the 3-D shape to fit a particular molecule
They will neatly fit into the substrate.
They will neatly fit into the substrate because they are the same shape
Reversible like a key in a lock
\-a drop of washing up liquid
\-2 ml of hydrogen peroxide
\-easy to separate from the product
\-cheaper
\-convert penicillin to different forms
\-produce sweet tasting sugars from lactose
\-when the substrate enters the active site, it changes the enzyme shape slightly.
\-enzyme fits more percisely
1. sodium alginate
2. calcium chloride
1. magnesium
2. chlorophyll production
1. fatty acids
2. glycerol
1. Enzyme and a certain substrate come together (specificity\`)
2. The substrate fits snugly in the active site, since the active site does not have a rigid shape (Induced Fit model)
3. The enzyme and substrate as one is called the Enzyme-Substrate Complex
4. The products are formed
5. The enzymes shape is unchanged
__-enzyme__: catalase (from celery)
\
1. Boil 5g chopped celery in a water bath
2. Use the unheated chopped celery as a control
3. Place both in water bath
4. Add hydrogen peroxide
5. No activity in denatured enzyme
6. Record volume of foam produced
7. Measure the result of the control
8. Compare the results
9. pH and temperature were maintained constant
\-base adenine, 5 carbon sugar (ribose), 2 phosphate groups
\-low energy molecule
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
-if another phosphate is added to ADP
-extra energy, since extra bond
-rich energy molecule
-stores and carries energy around cell
A vessel used to carry out enzyme controlled reactions.
1. Enzyme
2. Substrate
3. Product
4. Application
1. Enzyme: Sucrase
2. Substrate: Sucrose
3. Product: Glucose
4. Application: sweetener
Give an example of an anabolic reaction
protein synthesis, DNA synthesis
Explain enzyme specificity with reference to the active site
Specificity means that enzymes can act on certain substrates. This means that only one substrate fits the shape of an active site
Name two processes that occur in plant or animal cells that require the use of enzymes
When immobilising an enzyme, you used a gel substance to trap the enzyme. A second substance was also used to make gel insoluble. Name first and second substance
Gel- sodium alginate
second substance- calcium chloride
In relation to investigation into heat denaturation of an enzyme, name the products formed
oxygen and water
What is adsorption
When enzymes are physically attached to inactive supports
Name two processes that occur in plant or animal cells that require the use of enzymes
Plants = Respiration and photosynthesis
Animals = Respiration and DNA replication
Some biological washing powders contain enzymes similar to the ones found in our digestive system. Many of these enzymes are extracted from bacteria. Why is 40°C the recommended temperature for these washing powders?
40°C is these enzymes' optimum temperature
Write notes on metabolism
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions that take place within an organism.
2. It is controlled by enzymes.
3. Catabolic and anabolic enzymes are involved in metabolism.
4.a) A catabolic enzyme is amylase which converts starch into maltose.
4.b) It is catabolic because it breaks down a substance into simpler parts.
5.a) An anabolic enzyme is DNA ligase which is used in genetic engineering.
5.b) It is an anabolic enzyme because it converts simpler molecules into a more complex form.
Write notes on ADP
1. ADP stands for adenosine diphosphate.
2. It is a low energy molecule.
3. It is found in the cells of all organisms.
4. ADP + P ——> ATP
5. ADP + energy ——> ATP + water
“Enzymes are essential for metabolism” Explain why this statement is true
Enzymes are biological catalysts and they control the rate of metabolic reactions
State one way by which an enzyme may be denatured
high temp, too low or too high pH
Give two features of a denatured enzyme
change of shape
loss of function
Give an example of a reducing sugar
glucose/maltose