Chemistry: Ionic and Metallic Bonding
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
few
Metal atoms have a lot/few valence electrons.
partially
Metals have many partially/fully filled orbitals
delocalized electrons
These are not confined to a bond between two atoms, but instead, able to move freely between three or more atoms.
False
True or False: In metals, valence electrons are stationary.
sea
In metals, cations are suspended in a ___ of valence electrons
electrostatic
Metallic bonding results from __________ attraction between metal cations and the surrounding electrons.
alloy
Mixture of metals
substitution alloy
Atoms are roughly the same size when this alloy occurs
interstitial alloy
Atoms are different sizes so they fit in between each other when this alloy occurs
brass
What metal is this: Cu+Zn
bronze
What metal is this: Cu+Sn
varies
Solder _____ from the metals in it
steel
What metal is this: Fe+C
stainless steel
What metal is this: Fe+Co or Fe+Mn
ternary ionic compound
formed (usually) from a metal plus a polyatomic ion
ammonium ion
This ion is the exception to the usual way ternary ionic compounds are formed because it replaces the metal
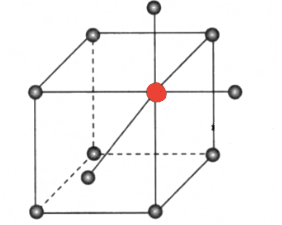
coordination number
the number of ions that surround each ion of opposite charge in a crystal lattice
6
What is the coordination number of the element highlighted in red?
water of hydration
the water molecules that are bound into a hydrate
hydrate
an ionic solid that has H20 molecules loosely bound to it’s crystals
anhydrous
a compound that has its water of hydration removed, usually by heating
hydrated compound
This formula is an example of what type of compound?
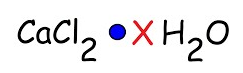
mono
What is the prefix for 1
di
What is the prefix for 2
tri
What is the prefix for 3
tetra
What is the prefix for 4
penta
What is the prefix for 5
hexa
What is the prefix for 6
hepta
What is the prefix for 7
octa
What is the prefix for 8
nona
What is the prefix for 9
deca
What is the prefix for 10
multivalent ion
An ion that has more than one cationic charge
Copper (I)
What is the stock name for this ion

cuprous ion
What is the common name for this ion

stock system
This naming technique was developed by Alfred Stock in 1919, roman numerals are used to show the different charge of each ion
common name
This naming technique was developed by Lavoisier, it uses different suffixes to show the charge of the ion
lower
In common names, the suffix “-ous” is added to the lower/higher valence
higher
In common names, the suffix “-ic” is added to the lower/higher valence
copper (II)
What is the stock name for this ion
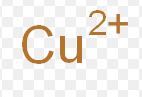
cupric ion
What is the common name for this ion
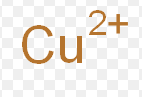
mercury (I)
What is the stock name for these ions
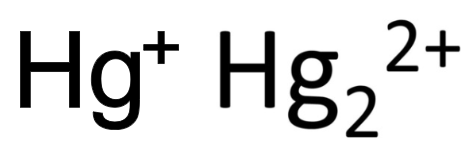
mercurous ion
What is the common name for these ions
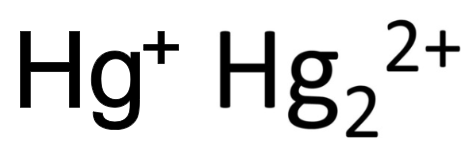
mercury (II)
What is the stock name for this ion
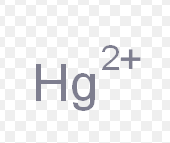
mercuric ion
What is the common name for this ion
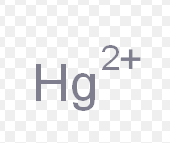
cobaltous ion
What is the common name for this ion
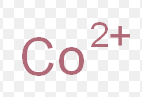
cobalt (II)
What is the stock name for this ion
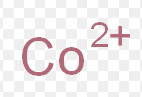
cobalt (III)
What is the stock name for this ion
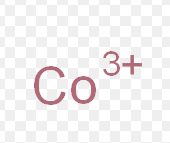
cobaltic ion
What is the common name for this ion
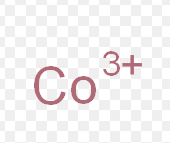
iron (II)
What is the stock name for this ion
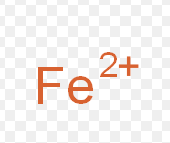
Ferrous ion
What is the common name for this ion
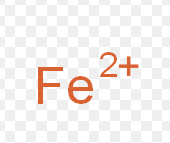
Ferrric ion
What is the common name for this ion
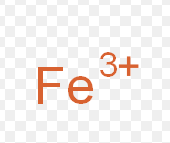
Iron (III)
What is the stock name for this ion
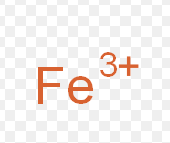
lead (II)
What is the stock name for this ion
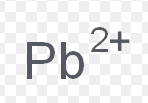
Plumbous ion
What is the common name for this ion
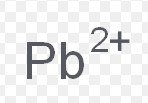
plumbic ion
What is the common name for this ion
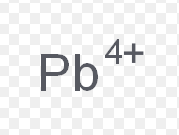
lead (IV)
What is the stock name for this ion
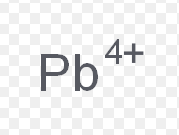
tin (II)
What is the stock name for this ion
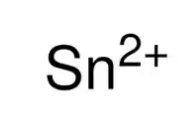
stannous ion
What is the common name for this ion
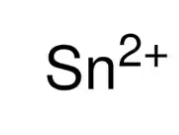
stannic ion
What is the common name for this ion
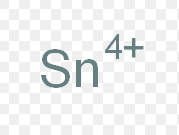
tin (IV)
What is the stock name for this ion
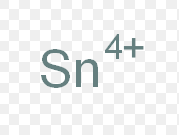
True
True or False: A binary ionic bond can be formed between either a monovalent cation and an anion or a multivalent cation and an anion
positive
A positive/negative ion is formed when an electron is taken away
negative
A positive/negative ion is formed when an electron is received
cation
a positively charges particle
anion
a negatively charged particle
electrostatic attraction
opposite charges attract
metals
Cations are metals/nonmetals
nonmetals
Anion are metals/nonmetals
chemical bonds
a strong force of attraction that holds atoms together in a molecule or crystal, resulting from sharing or transfer of electrons
ionic bond
a chemical bond formed by electrostatic attraction between cations and anions
metallic bond
a chemical bond formed by electrostatic attraction between cations and a sea of electrons
covalent bond
electronegativity
the ability of atoms in a molecule to attract electrons to itself
polar covalent
How is this electronegativity difference described: 0.4—1.7
i
properties/reactivity
What are valence electrons primarily responsible for?
Elements have the same lewis dot structure as their period/group
electron affi
endothermi
exothermic
If energy is released then it is an _____ reaction
0—4.0
The relative scale for electron affinity
4.0
The electron negativity for fluorine
The electron negativity for francine
This elemen
This element has the losw
isoelectric series
atoms and ions with the same number of electrons