Pharm 2 - E2: Opioids
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
all opioids are based off of? what is it?
opium = brownish residue from the dried juice
opiate is =
the drug derived from opium
how do opioid agonists work
blocks the ascending pathway via 1st and 2nd order neuron and engages the descending pathway via agonizing GABA (increasing cl)
what are the 2 main chemical classification groups of opioids?
what is their structure?
benzylisoquinoline alkaloid: benzene ring not fused together
phenanthrenes: 3 fused benzene rings = phenanthrene ring
benzene ring pic
phenanthrene ring pic
what class does papaverine belong to?
what are its properties?
what does its chemical structure look like?
benzylisoquinoline alkaloid
non-analgesic and antispasmodic properties
3 benzene rings but they are NOT fused together
what class does morphine belong to?
what is its significance? (2)
where does it come from?
phenanthrene
principle active compound from opium used for pain
used as a comparison for all other agents when judging strength
naturally occuring and comes from opium!
substitution of an ether for an alcohol of the phenanthrene nucleus of morphine =
codeine
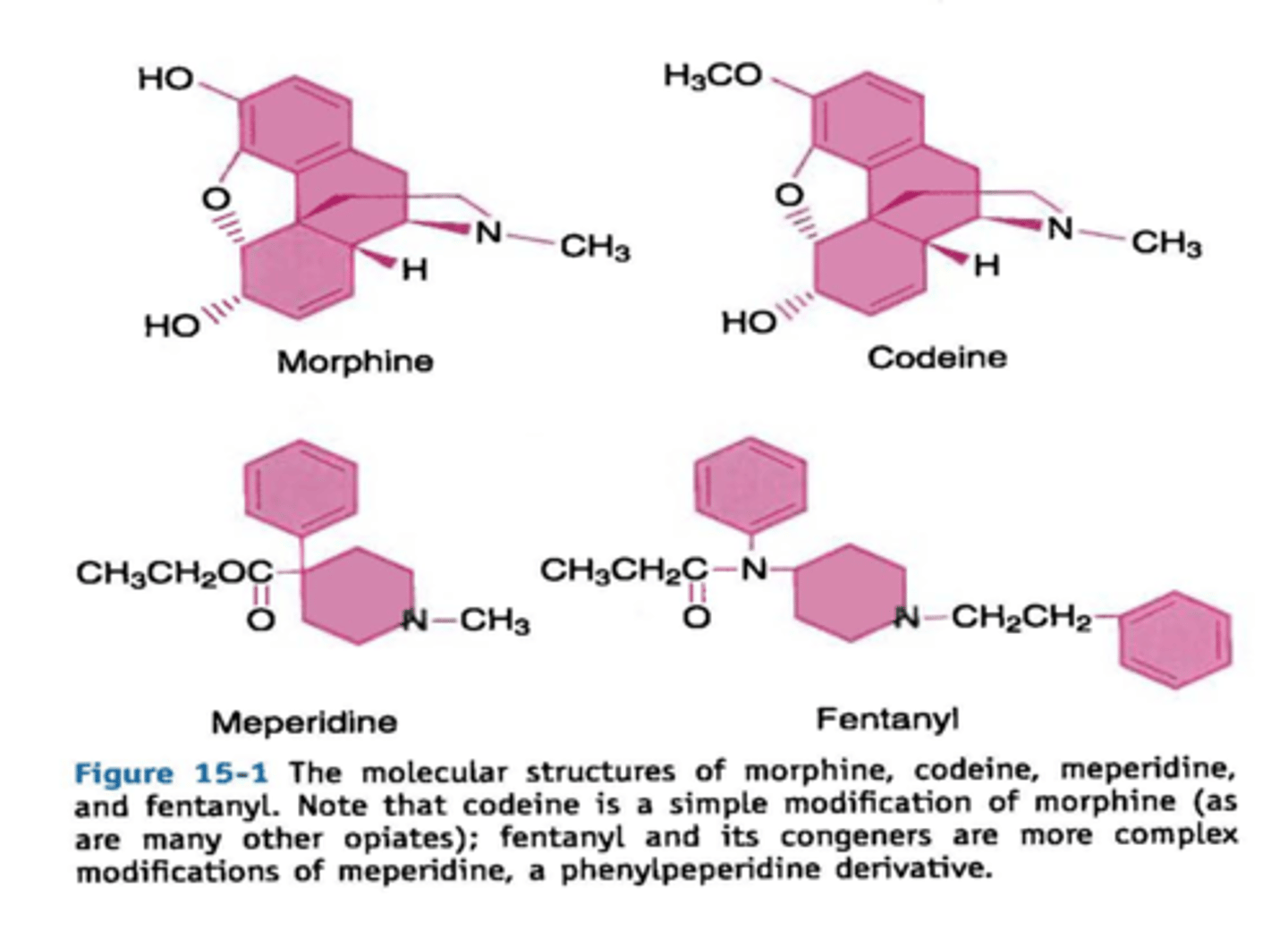
what was the 1st synthetic opioid?
meperidine “demerol”
what is the prototype for phenylpeperidine?
meperidine
fentanyl cogeners means:
“cousins” of fentanyl
what class of opioids is created when morphine is split btwn the 12th and 13th carbon to get a benzene connected to a 5 ring structure?
phenylpiperidine
what is the relation btwn synthetic opioids and the basic morphine molecule?
they only have 2 of the original 5 rings
Opioid Drug Classes Chart
NATURAL | SEMI-SYN. | SYNTHETIC | |
|---|---|---|---|
AGONIST |
|
|
|
PARTIAL-AGONIST | buprenorphine | butorphanol (stadol) | |
AG-ANTAG | nalbuphine (nubane) | ||
ANTAGONIST |
| nalmefene |
which semi-synthetics are "morphine derivatives"? (3)
(i.e. synthesized by making small changes to morphine molecule)
heroine
oxymorphone
hydromorphone
what is the highlight effect of codeine?
cough suppression
what does a "synthetic" opioid mean?
it contains the phenanthrene nucleus of morphine and is manufactured by synthesis instead of a chemical modification of morphine
general principles of opioids: (5)
highly lipid soluble & protein bound
mostly central acting
weak base
largely ionized at physiologic pH
pKa usually > 7.45
what are the 3 opioid receptor classes?
what kind of receptors are they in general?
GPCRs
mu (mop)
kappa (kop)
delta (dop)
what are the endogenous opioid agonists? (6)
enkephalins
endorphins
dynorphins
nociceptin
endomorphin 1
endomorphin 2
________________ are individual peptides that have their own specific precursors and share a common _________ with a small variation
opioid agonists (endogenous & exogenous)
amino acid terminal sequence
what is the shared amino acid terminal sequence all opioid agonists?
what is this sequence labeled as?
why is it necessary?
what part makes it an agonists on a receptor level?
try-gly-gly-phe-met or leu
met or leu will be at the C-terminus
labeled as “opioid motif” or “opioid message”
necessary for the endo agonists action w/ the receptor
terminus
what other drug/structure is enkephalin similar to?
morphine
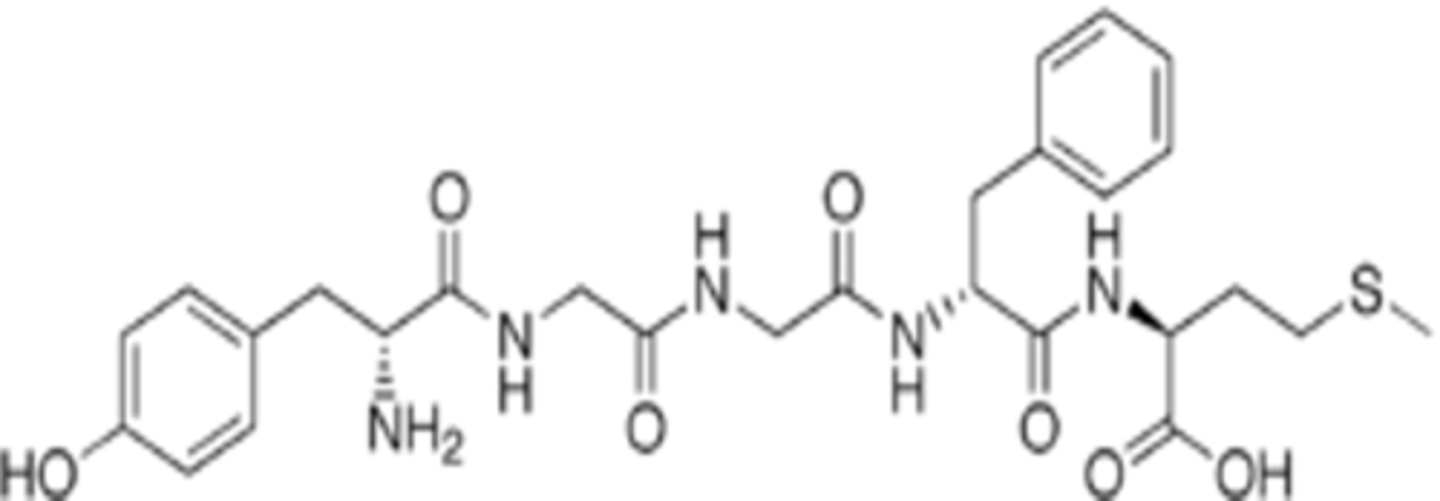
G protein coupled receptor includes a ____membrane loop that is both _______ and ________
7
intra and extracellular
3 opioid receptor subtypes share ___-___% sequence homology (same structure) but diversity is greatest in the _______ of the protein
55-58
extracellular loops/external portions
what is thought to be the importance of the external loops of an opioid receptor?
discriminating btwn ligands
what are the steps/effects of when an opioid agonist binds with a receptor?
opioid agonist binds w/ receptor (endo or exo; doesnt matter)
3 distinct subunits of the g-protein become activated
produces inhibitory effects
results in membrane hyperpolarization and reduction of neuron excitability
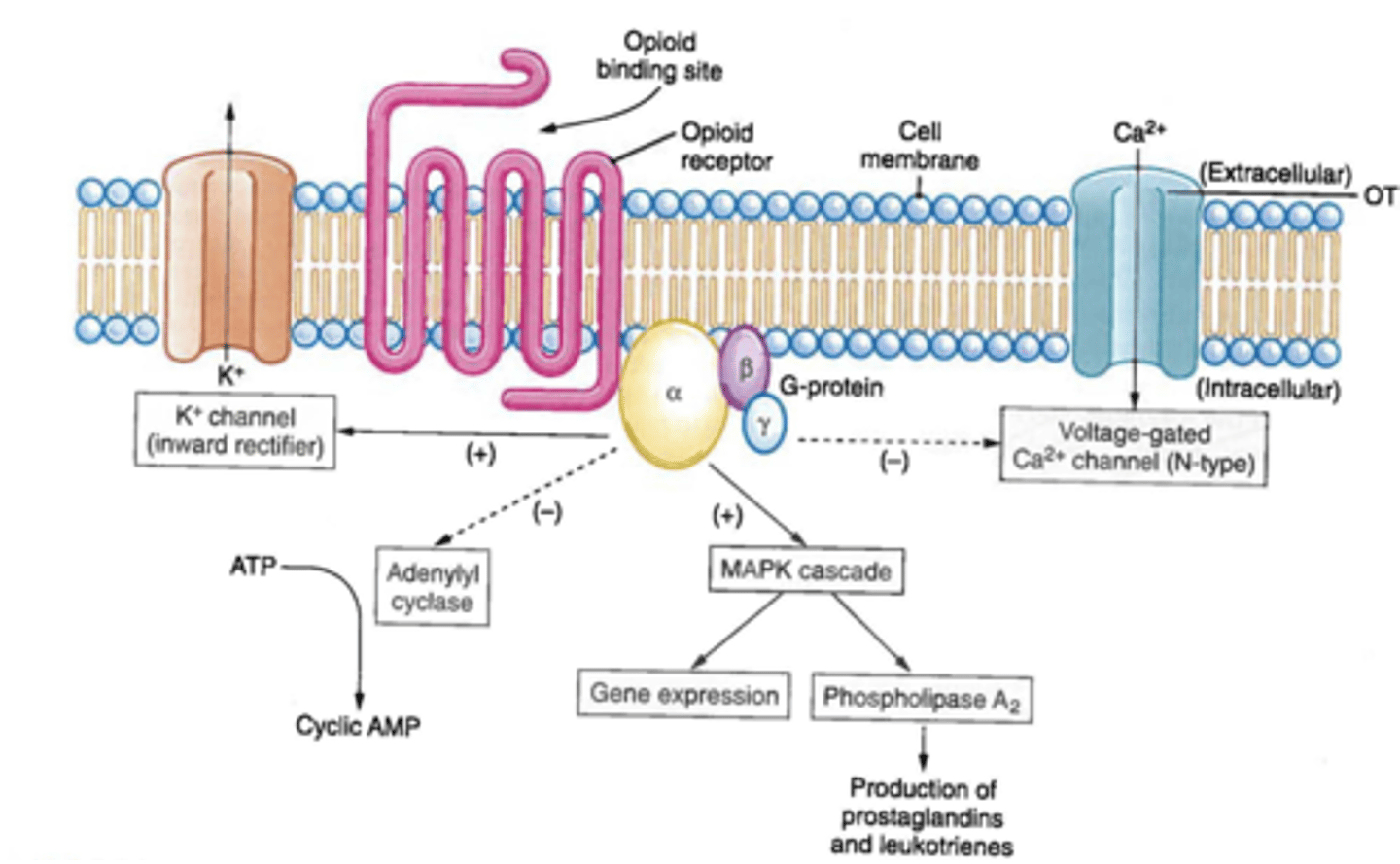
what are the inhibitory effects that are produced from the g-protein activation?
↓ cAMP (alpha) = adenyl cyclase is inhibited → ATP cant be converted into cAMP → ↓ cAMP ⇨ relaxes smooth muscle
↓ Ca influx (alpha, beta & gamma) = ↓ neuronal excitation
↑ K efflux (beta & gamma) = hyper-polarization
overall, what does ↓ cAMP cause?
↓ conductance of Ca channels & opened K+ channels ⇨ ↓ neuronal excitation and inhibition of neurotransmitter/neuropeptide release
what is the result of abrupt opioid withdrawal?
rebound dis-inhibition of cAMP ⇨
abd. pain
chills
diarrhea
muscle cramps
mydriasis
restlessness
sweating
tremors
↑ irritability & HR
where are the different opioid receptors located in the CNS?
brain 🧠
periaquaductal gray
area postrema
limbic system
cerebral cortex
thalamus
spine
substantia geletanosa of dorsal horn
where are the different opioid receptors located in the PNS?
intestines
what are the 4 additional locations of opioid receptors?(4)
vaculature
🫀
🫁
immune system 🦠
what is the anatomy related action of the brain and opioid receptors?
the brainstem modulates nociceptive transmission via inhibitory pathways of the spinal cord
what is the anatomy related action of the spine and opioid receptors?
inhibits the release of substance P
blocks transfer of pain upwards
what is the anatomy related action of GI/GU and opioid receptors?
constipation/post op ileus
↑ urinary sphincter tone
how does supra-spinal analgesia occur?
through activation of opioid receptors in brain that cause inhibition of nerves involved in pain pathways ⇨ message cant be propagated anymore
how does spinal analgesia occur?
via activation of presynaptic opioid receptors in spine, ↓ing release of the neurotransmitters of the nociception
supraspinal analgesia + spinal analgesia = _________
synergistic pain relief
what kind of analgesia will mu and kappa both cause? supra-spinal, spinal, both, none?
supra-spinal & spinal
what are the CV effects of mu receptors?
↓ HR
what are the respiratory effects of mu and kappa receptors?
mu = respiratory depression
kappa = possible depression if high dose
dose dependent resp depression!!!
what are the CNS effects of mu receptors? (6)
euphoria
sedation
prolactin release
mild hypothermia
catalepsy
indifference to environmental stimulus
what are the CNS effects of kappa receptors? (3)
sedation
dysphoria
psychomimetic reactions (delirium, hallucinations)
what are the pupil effects of mu and kappa receptors?
miosis
which opioid receptor will inhibit peristalsis and cause N/V?
mu
what are the GU effects of mu and kappa receptors?
mu = urinary retention
kappa = diuresis d/t inhibition of vasopressin release
which opioid receptors can cause pruritus?
mu and delta
what is the difference in physical dependence btwn mu and kappa receptors?
mu = high abuse potential
kappa = low abuse potential
what opioid receptor is involved with antishivering?
kappa
what are the effects of the delta receptors?
resp depression
urinary retention
pruritus
physical dependence
which endogenous opioid ligands agonize mu receptors?
B-endorphin
endomorphin
which endogenous opioid ligand agonizes kappa receptors?
dynorphin
which endogenous opioid ligand agonizes delta receptors?
Leu- Enkephalin
Met-Enkephalin
what are the routes of opioid admin? (7)
epidural
IM/IV
intrathecal
nasal
oral
suppository
transdermal
how would you describe opioid absorption orally?
modest
do opioids have a 1st pass effect?
yes, a big one
are opioids mainly lipophilic or hydrophilic?
how does this affect absorption?
↑ lipophillic = ↑ absorption through nasal and oral mucosa and skin
how are opioids distributed throughout the body? via the _________ compartment model
via the 2 compartment model (vessel rich group)
how are opioids metabolized?
do they have active metabolites?
what is the exception? explain
CYP450
some
remifentanil → metabd in blood by esterase
how are opioids excreted?
1° = kidney
2° = biliary system & GI tract
what are the differences in use of opioids r/t anesthesia practice?
1. higher analgesic requirement
2. co-admin of potent anesthetics and sedative agents
3. require the ability to support respirations until emergence
what effect does small dose opioids have on the DOA?
terminates it via redistribution into peripheral compartments
what effect does larger doses/multiple doses/continuous infusions of opioids have on the DOA?
becomes more dependent on metabolism
what is the key factor in the effect of an opioid being therapeutic or adverse?
clinical setting ⇨ sedation from mu receptor may be part of therapeutic intent (OR) versus being an adverse effect (ER)
what other factors are opioids dependent on? (5)
body weight
renal and hepatic failure
CABG
acid-base changes
hemorrhagic shock
what are the pharmacokinetic considerations of opioids? (7)
narrow therapeutic index
balance btwn optimizing pain control and sedation
resp depression
variability btwn patients (dose & DOA)
patients perception of pain (hx of chronic pain, opioid use? etc.)
severity and duration of pain
lifestyle (smoking? etoh? illicit drug use?)
what are the therapeutic effects of mu agonists?
pain relief (spinal and supraspinal)
sedation
anti-tussive
mu agonists are good for txing ___________ pain sensations, but less effective for ___________ pain sensations
2° (c-fibers); 1° (a-delta)
mu agonists have a _________ effect on drowsiness/sleep
dose dependent
T/F: opioids can be used as a sole anesthetic
FALSE: they do not reliably produce unresponsiveness and are not an anesthetic
explain the antitussive effect of mu agonists?
suppresses the cough center of the medulla (↓ the stimulation) but does NOT take away the cough
what is the risk a/w bolus doses of opioids?
a paradoxical rxn causing ↑ coughing
what are the adverse effects of opioid agonists? (12)
↓ HR and cellular immunity
↑ biliary pressures
constipation/ileus
delayed gastric empty
euphoria (abuse)
miosis
muscle rigidity
N/V
pruritus
urinary retention
vaso-d
ventilatory depression ****mu****
what are the CNS effects of opioids? (5)
sedation and eupohoria → mu
*both dependent on agent and receptor*
dysphoria → kappa receptors or opioids taken in absence of pain
analgesia
minimal effect of neuromonitoring
potential for ↑ ICP → respiratory induced hypercarbia
describe the analgesic MOA of opioid within the CNS
inhibit ascending transmission of nociceptive stimuli from dorsal horn of SC
activate pain control pathways from midbrain via rostral ventromedial medulla to spinal cord dorsal horn
what kind of pain are opioids most effective for?
continuous visceral dull pain
list the undesired CNS effects of opioids (4)
dependence
tolerance/cross tolerance
awareness
hyperalgesia
dependence of opioids can be ________ &________
*they need the drug to fxn properally*
physical and psychological
tolerance to opioids begins with _______ followed by ________
↓ in DOA
↓ in effect
what are the 5 theories r/t tolerance?
not d/t altered receptor #
receptor internalization
activation of NMDA-Rs
2nd messenger changes
G-protein uncoupling (changes in binding sites)
do high dose opioids ↓ the risk of awareness?
NO
hyperalgesia r/t opioids include what? what drug can cause it?
↑ sensitivity to pain
damage to nociceptors or periph nerves (ex: degloving)
**Remifentanil can cause this**
what is the most significant adverse effect of opioids?
depression of ventilation
what are risk factors for respiratory depression with use of opioids? (6)
high doses
advanced age
CNS depression
renal insufficiency
morphine
sleep
what breathing mechanism is altered by resp depression w/ opioids?
what does it ultimately result in?
the natural response to ↑↓ CO2 → RIGHT SHIFT in CO2 CURVE = ↓ resp drive to breath
when is resp depression d/t opioids potentially life threatening?
post-op in morbidly obese or OSA pts
can opioid tolerance be r/t miosis?
NO
what is thought to cause miosis w/ opioid use?
opiate depression of GABA →
stimulation of edinger-westphal nucleus →
PNS signals via ciliary ganglion
stimulation of oculomotor n. to constrict
can miosis be reversed? how so?
YES w/ narcan
where does miosis occur?
pupillary reflex arc
is miosis a qualitative or quantitative sign?
quaLitative
what are the best opioids for cough suppression?
codeine
heroine
how do opioids cause cough suppression?
they depress the cough center in the medulla but PRESERVE/PROTECT glottic reflexes
*just making it less reactive*
how does the antitussive effects of opioids affect tolerance w/ induction/intubation?
↑ tolerance to intubation and ETTs
what are the 5 receptors that cause PONV?
5-HT3
dopamine
H1 & 2
M1
NK 1
would patients typically rather have pain or N/V?
N/V!!!!
what kind of pts is PONV r/t opioids higher in?
ambulatory! we dont know why maybe because of quick movement or vestibular component
opioids cause N/V by acting where?
CTZ in the area postrema in the floor of 4th ventricle