Head, Neck, and Thorax For Lecture
1/281
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
282 Terms
What is the cranial made of?
frontal, temporal, and occipital
What is the posterior neck called?
nuchal
What is the anterior neck called?
cervical
What is the ear called?
auricular
What is the eye called?
orbit
What is the cheek called?
buccal
What is the part of the face with the eyebrow called?
superciliary arch
What is the eyelid called?
superior palpebra
What are the 6 auditory ossicles in the ear?
malleus, incis, stapes
How many bones make up the cranial vault?
8
How many facial bones are there?
14
How many bones make up the skull?
28
What are the groups of bones that make up the skull?
auditory ossicles, cranium, sutures
Where is the hyoid bone?
superior aspect of the neck, just below the mandible
What is the function of the hyoid bone?
provide attachment for the tongue muscles and the muscles that elevate the larynx during speech or swallowing
What muscles make the strap of the hyoid bone?
infra and supra hyoid muscles
What is CN I?
olfactory
What is the function of CN I?
smell
What is CN II?
optic
What is the function of CN II?
vision
What is CN III?
oculomotor
What is the function of CN III?
moves eye up, down, medial, raises upper eyelid, constricts pupil, adjusts shape of the lens of the eye
What is CN IV?
trochlear
What is the function of CN IV?
moves eyelid medially and down
What is CN V?
trigeminal
What is the function of CN V?
facial sensation, chewing, sensation from TMJ
What is CN VI?
abducens
What is the function of CN VI?
abducts eye
What is CN VII?
facial
What is the function of CN VII?
facial expression, close eye, tears, salivation, taste
What is CN VIII?
vestibulococholear
What is the function of CN VIII?
sensation of head position relative to gravity and head movement, hearing
What is CN IX?
glossopharyngeal
What is the function of CN IX?
swallowing, salivation, taste
What is CN X?
vagus
What is the function of CN X?
regulates viscera, swallowing, speech, taste
What is CN XI?
accessory
What is the function of CN XI?
elevates shoulders, turns head
What is CN XII?
hypoglossal
What is the function of CN XII?
move tongue
What nerve innervates the muscles of expression?
CN VII
What nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
CN V and V3
What are the cutaneous nerves of the face?
lesser and greater occipital from cervical plexus, and CN V
Where is trigeminal nerve V1 found on the face?
skin of scalp, superior eyelid, forehead, top portion of nose to the tip of it
Where is trigeminal nerve V2 found on the face?
skin of inferior eyelid, cheek, anterior part of temples, lateral nose, superior lip
Where is trigeminal nerve V3 found on the face?
skin anterior to ear, posterior portion of the temples, posterior skin of cheek, inferior lip to chin
Where is the lesser occipital from the cervical plexus found on the face?
scalp of posterior auricle
Where is the greater occipital from the cervical plexus found on the face?
scalp of occipital region

What muscles make this expression?
occipitofrontalis

What muscles make this expression?
corrugator supercilii

What muscles make this expression?
procerus, transverse part of nasalis

What muscles make this expression?
orbicularis oculi

What muscles make this expression?
lev. labii sup. alaeque nasi, alar part of naslis
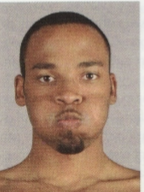
What muscles make this expression?
buccinator, orbiculais oris

What muscles make this expression?
zygomatic major and minor

What muscles make this expression?
risorius

What muscles make this expression?
risorius, depressor labii inferioris
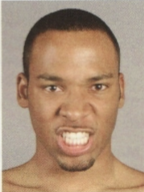
What muscles make this expression?
levator labii superioris, depressor labii
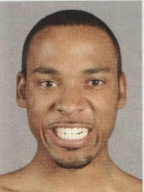
What muscles make this expression?
risorius, levator laii superioris, depressor labii inferioris

What muscles make this expression?
orbicularis oris

What muscles make this expression?
depressor anguli oris

What muscles make this expression?
mentalis
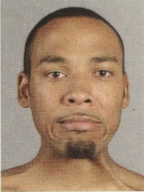
What muscles make this expression?
platysma
What is the facial canal a passage for?
CN VII
Where does the parotid gland pass?
pierce buccinator into oral cavity
What type of fibers innervate the parotid gland?
sympathetic and parasympathetic
What is unique about the sympathetic innervation to the parotid gland?
from cervical ganglia, with heavy breathing, it creates thick saliva
What is unique about the parasympathetic innervation to the parotid gland?
from CN IX and greater auricular nerve (C2-C3), it aids to chew and digest by producing thin saliva
What are the branches of the external carotid artery?
facial, occipital, superficial temporal
What are the branches of the superficial temporal artery of the external carotid?
frontal, parietal, temporal
What are the lymph nodes that do lymphatic drainage of the face?
submental, submandibular, parotid, mastoid, occipital
Where is the lacrimal gland?
superolateral corner of orbit
What is the pathway of the lacriaml apparatus?
orbital/palpebral to lacrimal lake to punctum to canaliculi, to lacrimal duct to nasal lacrimal duct
What are the tunics of the eye?
fibrous, vascular, nervous
What is in the firbous tunic?
outer sclera (white of eye), cornea (translucent)
What is in the vascular tunic?
choroid, ciliary body, iris (color of eye/controls light), provides blood to other vessels of eye
What is in the nervous tunic?
retina (most interior)
What are the chambers of the eye?
anterior and posterior
Where is the anterior chamber of the eye?
between cornea and iris
What is in the anterior chamber of the eye?
aqueous humor
Where is the posterior chamber of the eye?
between iris and lens
What is in the posterior chamber of the eye?
small % of aqueous humor, viteous body, viteous humor (structure of eyeball)
What is the function of the sclera?
maintain shape of eye, provide structure, provide attachment for muscles that move eye
What is the function of the cornea?
permit light to enter the eye
What is the choroid of the eye?
thin membrane
What is the function of the ciliary body of the eye?
secrete aqueous humor, the muscles attach to lens
What is the function of the iris?
colored and surround the pupil
What is the function of the retina?
respond to light
What is in the retina?
rods, cones, macula lutea, fovea centralis, optic disc, blind spot
What does the macula lutea do?
control peripheral vision
What does the fovea centralis do?
control focal vision
What does the optic disc do?
optic nerve to retina, visual blind spot
How do the rectus muscles move?
linear
How do the oblique eye muscles move?
spin
How do the oblique and rectus muscles move?
rotation
What actions does the superior rectus do?
elevate, adduct, medially rotate
What actions does the inferior rectus do?
depresses, adducts, laterally rotates
What actions does the medial rectus do?
adducts
What actions does the lateral rectus do?
abducts
What actions does the inferior oblique do?
elevate medially rotated eye, abducts, laterally rotates