NUTR 120 - Midterm 2
4.9(14)
4.9(14)
Card Sorting
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
1
New cards
What is a Carbohydrate?
Contains C,H,O with O in the same proportions as water
2
New cards
Two kinds of CHO
Simple, Complex
3
New cards
Three kinds of Monosaccharides
Glucose, Galactose, Fructose
4
New cards
Three kinds of disacharides
* maltose
* lactose
* sucrose
* lactose
* sucrose
5
New cards
Maltose
glucose + glucose
* maltase
* maltase
6
New cards
Sucrose
Glucose+ Fructose
* sucrase
* sucrase
7
New cards
Lactose
Glucose+ Galactose
* lactase
* lactase
8
New cards
Hydrolysis
add water to break disaccharides
9
New cards
Condensation Reaction
release water to form disaccharides (impossible in humans)
10
New cards
2 Simple Sugars
Mono and disaccharides
11
New cards
Oligosaccharides
* prebiotics- growth of healthy gut microbes
* 3-12 monosaccharides linked together (not simple, not poly)
* legumes
* raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
* 3-12 monosaccharides linked together (not simple, not poly)
* legumes
* raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
12
New cards
Polysaccharides
-many monosaccharides linked
- 100-1000
- 100-1000
13
New cards
Complex CHO
starch, glycogen and fibre
14
New cards
Glycogen
CHO made of many glucose molecules linked together in a highly branched structure.
storage form of of CHO in animals
storage form of of CHO in animals
15
New cards
Starch
CHO made of many close molecules linked in straight or branched chains
storage form of CHO in plants
storage form of CHO in plants
16
New cards
Glycogen VS Starch
* very similar in structure and their function is the same ( store glucose)
* glycogen in animals, starch in plants
* glycogen in animals, starch in plants
17
New cards
glycogen and starches are ________,__ where as __ is broken down via ___ breakdown
* digestible
* fibre
* bacterial (fermentation)
* fibre
* bacterial (fermentation)
18
New cards
DRI Values of CHO
Carb: 45-65% calories
Fibre: 14g/ 1000 kcal
Fibre: 14g/ 1000 kcal
19
New cards
Name types of carbohydrates in food across all food categories
Meat and Alternative
* meat: not a source of CHO
* alternatives: legumes, nuts are rich in starch
Milk and Alternative
* Milk: has Lactose
* Alternatives: added sugars/starch like soy beverage
Grain Products- starch
* wheat
* rice
* barely
Vegetable- starch
* potatoes
* corn
* carrots
* peas
Fruit
* Simple sugars
* meat: not a source of CHO
* alternatives: legumes, nuts are rich in starch
Milk and Alternative
* Milk: has Lactose
* Alternatives: added sugars/starch like soy beverage
Grain Products- starch
* wheat
* rice
* barely
Vegetable- starch
* potatoes
* corn
* carrots
* peas
Fruit
* Simple sugars
20
New cards
CHO Digestion and Absorption from mouth to liver
1. mouth: salivary amylase breaks some starch into maltose
2. stomach: HCl inactivates salivary amylase and no digestion occurs
3. small intestine: starch broken down by pancreatic amylase to form disaccharides, disaccharides broken down by digestive enzymes (maltase, sucrase, lactase) to form monosaccharides
4. Mucosal cell: monosaccharides absorbed into mucosal cell
5. hepatic portal vein
6. liver
21
New cards
Discuss metabolism of absorbed monosaccharides in the liver. What are the various paths/roles glucose may take once it reaches the liver?
* remaining monosaccharides that aren’t already glucose (fructose and galactose) converted to glucose
* Glucose used in different ways:
* Used by liver cells for Kcal
* Liver glycogen (storage)
* Nonessential amino acid synthesis
* Conversion to fat } VLDL to adipose tissue
* bloodstream
* Glucose used in different ways:
* Used by liver cells for Kcal
* Liver glycogen (storage)
* Nonessential amino acid synthesis
* Conversion to fat } VLDL to adipose tissue
* bloodstream
22
New cards
Once glucose is released from the liver into the bloodstream, it can be used as?
* Fuel for most body cells 4 Kcal/g
* Storage as glycogen in Muscle
* Storage as glycogen in Muscle
23
New cards
Name body tissues that rely mainly or solely on glucose for energy
Brain, red blood cells, kidney cortex, CNS
24
New cards
What happens to glucose when it is released from the liver?
* increases blood glucose levels which activates pancrea
25
New cards
Effects of insulin
* facilitate uptake of glucose from blood into cells (kinda like an escort)
* stimulate the production of liver glycogen (turning glucose into storage)
* return of blood glucose levels to 'normal' ( baseline or basal value)
* stimulate the production of liver glycogen (turning glucose into storage)
* return of blood glucose levels to 'normal' ( baseline or basal value)
26
New cards
What happens when blood glucose levels begin to fall?
1. Insulin production decreases and glucagon increases (glucagon = hormone stimulates conversion glycogen to glucose)
2. Liver glycogen converted into Glucose which will be released into bloodstream
3. Blood glucose levels should return to basal levels, providing essential glucose as fuel to tissues
27
New cards
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. What is wrong in the body? Treatment? Cause?
* pancreases cannot produce insulin
* Treatment: taking insulin
* Cause: genetic: in utero/infancy autoimmune reaction , viral infection destruction of beta cells
* Treatment: taking insulin
* Cause: genetic: in utero/infancy autoimmune reaction , viral infection destruction of beta cells
28
New cards
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. What is wrong in the body? Treatment? Cause?
* body cells become 'resistant' to insulin (cell will not take up the insulin-glucose pair, so glucose remains in blood)
* Treatment: exercise, diet, medications (increase insulin sensitivity)
* Cause: genetic and environment, correlated to overweight/obesity
\
* Treatment: exercise, diet, medications (increase insulin sensitivity)
* Cause: genetic and environment, correlated to overweight/obesity
\
29
New cards
What is Glucose Tolerance
a measure of a persons ability to remove excess blood glucose following meals
30
New cards
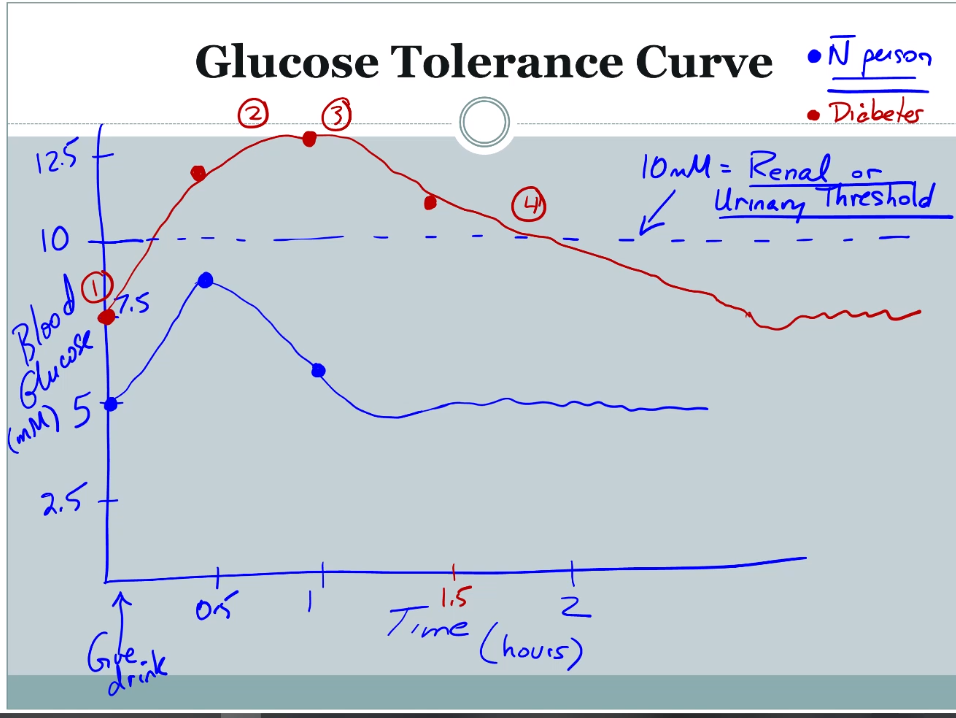
4 characteristics used when analyzing a glucose tolerance test graph to determine if a patient has per-diabetes or diabetes
1. higher basal glucose level
2. higher peak
3. delayed peak
4. levels stay higher longer
31
New cards
Renal urinary threshold
* 10 mili moles blood glucose concentration
* concentration where kidney transporters can absorb glucose out of blood stream
* over 10 mM all transporters in use so glucose in urine
* concentration where kidney transporters can absorb glucose out of blood stream
* over 10 mM all transporters in use so glucose in urine
32
New cards
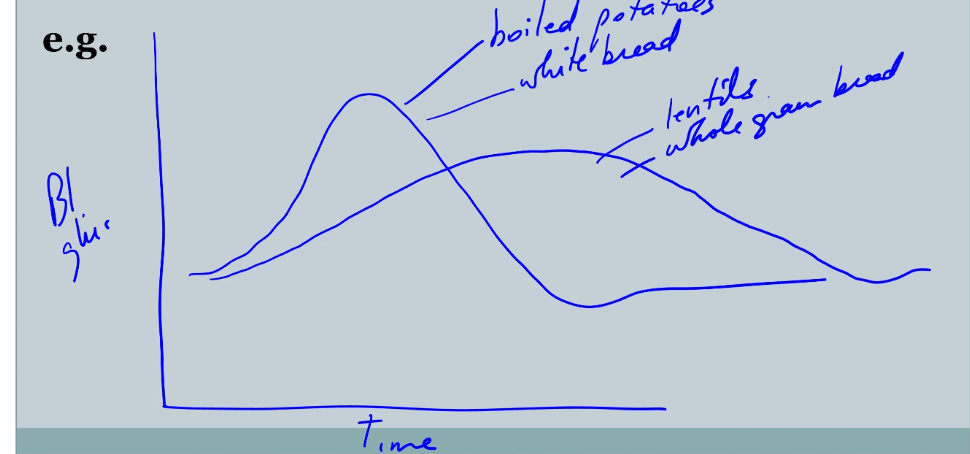
Glycemic Response
- blood glucose response following eating certain foods
- some foods will give you quick response some will enter slowly ( white bread is higher index then whole grains and legumes)
- area under the curves are the same
- some foods will give you quick response some will enter slowly ( white bread is higher index then whole grains and legumes)
- area under the curves are the same
33
New cards
Fructose
* fruit sugar, honey
* less cariogenic (cavity causing) than sucrose
* high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in pop, condiments
* less cariogenic (cavity causing) than sucrose
* high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in pop, condiments
34
New cards
How is HFCS contributing to obesity epidemic ?
body uses fructose differently than other sugars
* does not stimulate insulin or leptin production (leptin tells you when you are full) HFCS makes you remain hungry … overeat
* stimulates liver fat synthesis = increase blood TG
* may promote high blood pressure increasing risk CHD
* does not stimulate insulin or leptin production (leptin tells you when you are full) HFCS makes you remain hungry … overeat
* stimulates liver fat synthesis = increase blood TG
* may promote high blood pressure increasing risk CHD
35
New cards
Sucrose
* table sugar
* isolated from sugar beet/ sugar cane
* sweetness value 1 ( low compared to aspartame 200)
* isolated from sugar beet/ sugar cane
* sweetness value 1 ( low compared to aspartame 200)
36
New cards
what is the only certainly true consequence of consuming sucrose
dental caries
37
New cards
Does high sucrose cause glucose intolerance?
no
38
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause type 2 diabetes?
no
39
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause coronary heart disease?
No, dependent on overall calories not just sugar
40
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause ADHD?
no, sugar does not cause hyper activity
41
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause obesity?
dependent on overall calories, not just sugar
42
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause dyslipidemia (increased TG, and decreased HDL
no
43
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause malabsorption
no
44
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause gallstones
no
45
New cards
Does high sucrose intake cause carcinogens
no
46
New cards
Explain how diets high in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates contribute to obesity
1. people replaced fat with low fat foods = replaced with more overall Kcal from sugar = increased Kcal = increased weight gain
2. Form of CHO affects satiety
1. beverages are not detected in the same way as solid foods, so less filling
2. simple sugars are less filling than complex CHO and fibre
3. Sugars have no nutrional values other than the k cal " empty calories"
47
New cards
Do sugars cause Heart Disease ie metabolic syndrome?
5 features of Metabolic syndrome (disturbances that can lead to CHD)
1. abdominal obesity
2. increased fasting blood glucose
3. increase in TG
4. Decrease in HDL
5. High blood pressure
Having 3 features classifies as having metabolic syndrome, which can lead to CHD
* increased intake of sugars and refined CHO increase prevalence of features
1. abdominal obesity
2. increased fasting blood glucose
3. increase in TG
4. Decrease in HDL
5. High blood pressure
Having 3 features classifies as having metabolic syndrome, which can lead to CHD
* increased intake of sugars and refined CHO increase prevalence of features
48
New cards
Lactase Deficiency
* all infants and children possess enzymes lactase to break down lactose
* lactase deficiency is the drop in ability to make lactase enzyme (4-16 yrs)
* lactase deficiency is the drop in ability to make lactase enzyme (4-16 yrs)
49
New cards
Lactose Intolerance
* describes symptoms associated with being lactase deficient
* consequences of undigested lactose:
* small intestine: attracts water = bloating, cramps
* colon: diarrhea, bacterial fermentation = gas
* consequences of undigested lactose:
* small intestine: attracts water = bloating, cramps
* colon: diarrhea, bacterial fermentation = gas
50
New cards
Milk Allergy
* exaggerated immune response to protein
* milk protein broken into amino acids in small intestine, **but amino acid gets into bloodstream** which causes immune response, antibodies, anaphylaxis… impaired breathing
* milk protein broken into amino acids in small intestine, **but amino acid gets into bloodstream** which causes immune response, antibodies, anaphylaxis… impaired breathing
51
New cards
sugar alcohols
xylitol, sorbitol
* sugar free gum
* sugar free gum
52
New cards
dextrin
* short chains of starch
* used for thickening
* used for thickening
53
New cards
resistant starch
* non digestible
* oats
* barley
* cooled potatoes/rice
* oats
* barley
* cooled potatoes/rice
54
New cards
Soluble Fibre examples, names, fraction of fibre intake, effect on digestion
* oatbran, citrus, insides legumes, psyllium
* names: pectins, gums, carageenin
* 1/3 fibre intake
* slows digestion
* names: pectins, gums, carageenin
* 1/3 fibre intake
* slows digestion
55
New cards
Insoluble fibres examples, names, fraction of fibre intake, effect on digestion
* legumes skin, veggie and fruit skin, psyllium
* cellulose, lignan
* 2/3 fibre intake
* increases speed of movement of digestion through small intestine
* cellulose, lignan
* 2/3 fibre intake
* increases speed of movement of digestion through small intestine
56
New cards
What does Soluble Fibre (loose mesh) do in the colon?
* slows digestion, lots of fermentation = production of gases and short chain fatty acids
* proprionate (3:0) absorbed, to liver → decreased cholesterol synthesis = decreased CHD
* Butyrate (4:0) preferred energy source of colon cells = decreased colorectal cancer
* proprionate (3:0) absorbed, to liver → decreased cholesterol synthesis = decreased CHD
* Butyrate (4:0) preferred energy source of colon cells = decreased colorectal cancer
57
New cards
What does insoluble Fibre do in the colon?
* increased speed of movement, so less fermentation = increase elimination in stool and increased bowel movement regularity
* decreases diverticulosis - small bulging pouches develop in digestive tract
* decreases diverticulosis - small bulging pouches develop in digestive tract
58
New cards
Gold Standard for insoluble fibre
Wheat Bran
59
New cards
Kernel Structure
Bran- outer protective layer, insoluble fibre (concentrated source of dietary fibre)
Allerome layer - Fe, B vitamins
Endosperm-largest portion of the grain, starch and protein
Germ- embryo or sprouting portion of the grain, B Vitamins, Fe, fat soluble vitamins E
Allerome layer - Fe, B vitamins
Endosperm-largest portion of the grain, starch and protein
Germ- embryo or sprouting portion of the grain, B Vitamins, Fe, fat soluble vitamins E
60
New cards
How does soluble fibre decrease the risk of colorectal Cancer
· production of butyric acid (4:0) - preferred energy source of colon cells
· lowers PH (acidic) by decreasing amount of NH3 = good
· stimulates growth of beneficial microbes
· lowers PH (acidic) by decreasing amount of NH3 = good
· stimulates growth of beneficial microbes
61
New cards
How does insoluble fibre decrease the risk of colorectal Cancer
* because of bulking effect, dilutes colon content
* provides surface for adsorption (stick to) for NH3 by products
* decrease transit time (mouth to anus)
* altered bile acid metabolism (less secondary bile acids that are cancer promoters)
* provides surface for adsorption (stick to) for NH3 by products
* decrease transit time (mouth to anus)
* altered bile acid metabolism (less secondary bile acids that are cancer promoters)
62
New cards
How does soluble fibre lower blood cholesterol
1. Binds Bild acids in small interline and physically prevents reabsorption/ recycling
2. propionic acid (3:0) reduced liver cholesterol synthesis
2. propionic acid (3:0) reduced liver cholesterol synthesis
63
New cards
How might fibre increase weight loss?
* Increases satiety
* delays gastric emptying
* takes longer to eat (beneficial because there is a delay between time we are full, and time it takes to feel full)
* delays gastric emptying
* takes longer to eat (beneficial because there is a delay between time we are full, and time it takes to feel full)
64
New cards
Calculate dietary fibre requirements, given an adults daily Kcal intake. What is the dietary fibre requirement for men consuming 2500 kcal/day?
memorize: 14 g/1000kcal
* 2500 kcal x (14g/1000 kcal) = 35 g fibre/day
* 2500 kcal x (14g/1000 kcal) = 35 g fibre/day
65
New cards
\n Complex carbohydrate is also known as
starch
66
New cards
Plants are able to synthesize disaccharides such as maltose in a ___ reaction, which _______water.
Plants are able to synthesize disaccharides such as maltose in a condensation reaction, which releases water.
67
New cards
Animals and humans store glucose as ___ whereas plants store glucose as _____
* glycogen
* starch
* starch
68
New cards
A 252 kcal bowl of chili provides 24 g protein, 8 g fat. What percentage of the kcal in this chili is coming from \n carbohydrate?
24 g pro x 4 kcal/g = 96 kcal protein
8 g fat x 9 kcal/g = 72 kcal fat
\
96 + 72 kcal = 168 kcal
252 kcal total – 168 kcal from pro and fat = 84 kcal carbohydrate
\
84kcal CHO/252 kcal total = 33% of kcal in this chili are from CHO
8 g fat x 9 kcal/g = 72 kcal fat
\
96 + 72 kcal = 168 kcal
252 kcal total – 168 kcal from pro and fat = 84 kcal carbohydrate
\
84kcal CHO/252 kcal total = 33% of kcal in this chili are from CHO
69
New cards
An individual who is maintaining a healthy weight by consuming 1800 kcal per day should aim for no less than \n ______ g carbohydrate each day.
a) DRI recommendations for CHO: 45-65% total kcal \n b) 45% of 1800 kcal is: 45 x 1800/100 = 810 kcal \n c) 810 kal/4 kcal per g = 203 g CHO
70
New cards
When ____ is released from the pancreas, blood glucose concentrations increase.
glucagon
71
New cards
Does insulin lead to the storage or the breakdown of liver glycogen?
storage
72
New cards
The key factor leading to Type 1 Diabetes is: \n a) insulin resistance \n b) overweight /obesity \n c) pancreas unable to synthesize insulin \n d) sedentary (inactive) lifestyles
c ) pancreas unable to synthesize insulin
73
New cards
‘Pre-diabetes’ is also known as ___ __,__ and is an indication that an individual is on the way to developing ________
* glucose intolerance
* type 2 diabetes
* type 2 diabetes
74
New cards
Which of the following higher starch foods will result in the highest ‘glycemic curve’ (sharp elevation in blood \n glucose concentrations)? \n a) peeled, boiled potatoes \n b) lentil soup \n c) whole wheat bran muffin \n d) black bean and white rice pilaf
a. peeled, boiled potatoes
75
New cards
How can you make your potatoes higher in ‘resistant starch’?
After cooking, allow them to cool – reheat for next meal: the process of cooling cooked potatoes converts some starch into ‘resistant starch’, which resembles soluble fibre physiologically and confers some of the same health benefits as soluble fibre.
76
New cards
proteins are about __% nitrogen by weight. Protein intake (g)= Nitrogen x ___
\
* every AA contains nitrogen, proteins are about 16% N by weight
* Protein intake (g)= Nitrogen x 6.25
* every AA contains nitrogen, proteins are about 16% N by weight
* Protein intake (g)= Nitrogen x 6.25
77
New cards
Peptide Bonds:
* Bond between 2 amino acids to form dipeptide
* Formed through condensation/dehydration reaction
* Formed through condensation/dehydration reaction
78
New cards
How many peptide bonds in a tripeptide?
\- 2
79
New cards
Primary Structure
\- linear order of AA in a string
80
New cards
Secondary structure
* shapes within the protein
* alpha helix (spiral) & beta pleated sheets (stairs)
* alpha helix (spiral) & beta pleated sheets (stairs)
81
New cards
tertiary structure
final 3-D shape of protein
82
New cards
What happens when a protein undergoes denaturation
* adding chemicals or heat denatures protein and it loses it’s final 3D shape
* protein’s shape critical to function so denaturation changes function
* protein’s shape critical to function so denaturation changes function
83
New cards
Explain why sickle cell anemia occurs, with respect to protein sequence
* occurs because of 1 AA change in hemoglobin
* changes polypeptide shape -> hemoglobin shape -> causing long chains of molecules (instead of individual molecules) -> sickle shaped
* results: decrease O2 carrying capacity
* changes polypeptide shape -> hemoglobin shape -> causing long chains of molecules (instead of individual molecules) -> sickle shaped
* results: decrease O2 carrying capacity
84
New cards
Examples of proteins that regulate body processes:
* hormones: insulin
* enzymes: trypsin, pepsin
* neurotransmitters: serotonin
* enzymes: trypsin, pepsin
* neurotransmitters: serotonin
85
New cards
Examples of proteins that help in the growth and repair of tissues:
* muscle protein: collagen (structure), actin/ myosin (muscle contraction)
* normal “turnover” – breakdown and replacement of all body tissues and organs
* normal “turnover” – breakdown and replacement of all body tissues and organs
86
New cards
What protein is made of immune defence?
antibodies
87
New cards
What are two transport proteins?
Hemoglobin- transports oxygen
Transferrin - transport iron
Transferrin - transport iron
88
New cards
Explain the process of protein digestion. Include stomach, pancreas, small intestine. What are the uses of trypsin?
Stomach
* HCL denatures protein
* protein is converted to shorter peptides by __**pepsin**__
Pancreas
* Pancreas releases pancreatic pre-enzymes trypsinogen and chymotrysinogen
Small Intestine
* Produces intestinal __**enterokinase**__ which converts trypsinogen into __***trypsin***__
* Trypsin can activate various intestinal __**pre-peptidases**__ -> Various peptidases (to active form)
* Trypsin can convert chymotrypsinogen to active form chymotrypsin
* Trypsin can cleave peptides into smaller peptide
* __**Peptidase, chymotrypsin, and trypsin**__ breakdown proteins into di and tri peptides
* Di and tri peptides enter mucosal cell -> broken down into AA
* AA into bloodstream to portal vein to liver
* HCL denatures protein
* protein is converted to shorter peptides by __**pepsin**__
Pancreas
* Pancreas releases pancreatic pre-enzymes trypsinogen and chymotrysinogen
Small Intestine
* Produces intestinal __**enterokinase**__ which converts trypsinogen into __***trypsin***__
* Trypsin can activate various intestinal __**pre-peptidases**__ -> Various peptidases (to active form)
* Trypsin can convert chymotrypsinogen to active form chymotrypsin
* Trypsin can cleave peptides into smaller peptide
* __**Peptidase, chymotrypsin, and trypsin**__ breakdown proteins into di and tri peptides
* Di and tri peptides enter mucosal cell -> broken down into AA
* AA into bloodstream to portal vein to liver
89
New cards
Outline various pathways amino acids entering the liver from the portal vein may take
AA from body tissue breakdown (endogenous) and AA from diet (exogenous) enters a liver cell and create an AA pool. Follows through to two processes:
1. Synthesis of body proteins: (enzymes, antibodies, lean body mass)
2. Breakdown of AA: (deamination)
1. Amino group:
1. Amino group NH2 is removed from carbon skeleton as free ammonia NH3+
2. NH3+ is toxic to body so is converted to urea in liver
3. Sent to kidney and excreted in urine
2. Carbon skeleton
1. Used directly by cells for Kcal (4 Kcal/g)
2. Converted to glucose (gluconeogenesis)
3. Converted to fat - stored in adipose (most likely pathway for people eating a lot)
1. Synthesis of body proteins: (enzymes, antibodies, lean body mass)
2. Breakdown of AA: (deamination)
1. Amino group:
1. Amino group NH2 is removed from carbon skeleton as free ammonia NH3+
2. NH3+ is toxic to body so is converted to urea in liver
3. Sent to kidney and excreted in urine
2. Carbon skeleton
1. Used directly by cells for Kcal (4 Kcal/g)
2. Converted to glucose (gluconeogenesis)
3. Converted to fat - stored in adipose (most likely pathway for people eating a lot)
90
New cards
What would force the body to use protein as a source for energy?
low carb diet, starvation
91
New cards
Explain two ways how dietary protein may be used for energy
* When energy is deficient, body proteins, such as enzymes and muscle proteins, are broken down into amino acids that can then be used to generate ATP or synthesize glucose.
* Excess protein converted to fat which can be used for energy
* Excess protein converted to fat which can be used for energy
92
New cards
Explain why taking enzymes orally are worthless unless they are specially encapsulated for medical purposes.
Enzyme activity is deactivated by HCl in the stomach
93
New cards
What are some problems with taking amino acid supplements?
1. Absorption and Transport Issues:
1. GI Tract: AAs share transporters, and they compete for absorption. If excess AA, transporters get overwhelmed with only 1 AA, preventing other AA from getting from GI to body. Causes an imbalance of absorption
2. Brain: similar to GI tract, AA share Transporters in “Blood Brain Barrier”. Will take excess of one AA in, and lack of other AAs. AA imbalance can lead to changes in mood because AAs used to make brain chemical (ex. Tryptophan makes serotonin)
3. Di and tri peptides absorb better than individual AA
2. N-retention:
1. N retention better after eating protein, rather than one
2. bottom line: get protein from food
94
New cards
What are the 6 concerns with consuming too much protein?
1. Increased Kcal intake – contributor to overweight
2. High protein foods often high in fat and Kcal (meat, cheese, saturated fats)
3. Calcium loss in urine increases which might affect bone health?
1. Animal proteins high in sulfur (methionine). Sulfur converted to acidic compound that body has to balance, so draws Ca+ out of bones.
4. Overworked liver and kidney? (work harder to extract extra urea, not a concern for healthy person)
5. Cancer? – diets high in red meat and processed meat linked to cancer
6. Gut microbiome (no idea the impact)
95
New cards
What is ' protein quality" determined by
- digestibility of a protein
- types of amino acids
- proportion of amino acids (compared to ideal protein source which is a chicken egg)
- types of amino acids
- proportion of amino acids (compared to ideal protein source which is a chicken egg)
96
New cards
percent of protein digested for animals, plant and soy protein
animals 90-99%
plants 70-90%
soy +90%
plants 70-90%
soy +90%
97
New cards
What is the difference between complete and incomplete dietary protein sources?
* Complete: contain all 9 essential AAs. Usually animal origin
* Incomplete: low in at least 1 essential AA. Usually plant origin.
* Incomplete: low in at least 1 essential AA. Usually plant origin.
98
New cards
Examples of incomplete protein sources
* Foods from plant origins
* Grains (Low in Lysine)
* Legumes (Low in methionine)
* Grains (Low in Lysine)
* Legumes (Low in methionine)
99
New cards
Examples of Complete protein sources
* Chicken
* Egg
* Dairy products
* Egg
* Dairy products
100
New cards
Limiting Amino acid
* The essential amino acid that is available in the lowest concentration relative to the body’s needs
* Lack of this amino acid limits the ability to make protein
* Lack of this amino acid limits the ability to make protein