V Biology EOY
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
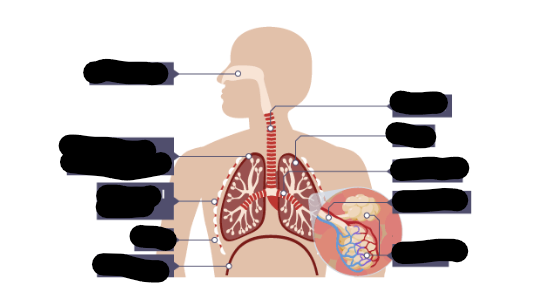
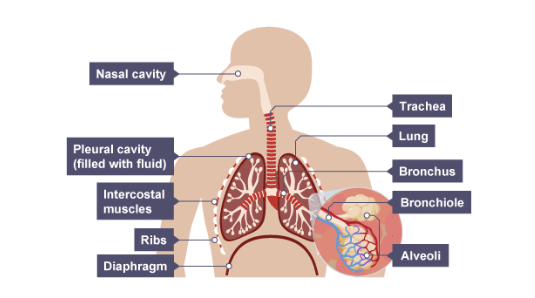
Structure of the Thorax
Intercostal Muscles in Inhalation
contract
Intercostal Muscles in Exhalation
Relax
Diaphragm in Inhalation
Muscles contract: diaphragm raised
Diaphragm in Exhalation
Muscles: relax - diaphragm lowers
Alveoli Adaptations
Large SA: More oxygen/CO2 can diffuse per second
Thin barrier: Short diffusion distance - walls 1 cell thick
Large network of capillaries: maintains a high concentration gradient
Moist lining: so gases can dissolve
Ventilation: Allows the organism to maintain a concentration gradient
3 Main Components of Cigarettes
Nicotine
Tar
Carbon Monoxide
Biological consequences of Smoking
Mimics action of neurotransmitters at synapses and makes smoker feel more alert
Stimulates the release of adrenaline (increase heart rate etc.)
Settles on lining of airways and alveoli:
Increases diffusion distance
Chemicals cause muscles to contract narrowing airways
Cause excess mucus production
Combines with haemoglobin irreversibly:
Reduces oxygen carrying of blood
Damages lining of arteries
Coronary heart disease from Smoking
Chronic Bronchitis: Overproduction of mucus and inflimation of lining of airways
Emphysema: Cause alveoli to burst
Lung Cancer
Names of different trophic levels:
Producer
Primary consumer
Secondary consumer
Tertiary consumer
Apex predator
Decomposers
Producer
An organism that makes its own food via photosynthesis
Consumer
An organism that retrieves its energy from consuming another organism
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down organic material such as the remains of a dead organism
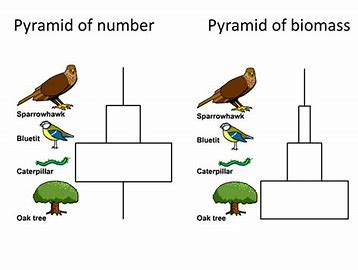
Pyramids of Number
Total number of each organism at each trophic level
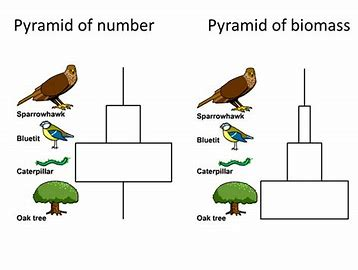
Pyramids of Biomass
Total dry mass of each organism at each trophic level
Why is only 10% of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next?
Not all of the materials are transferred from one level to the next (bones are not eaten etc.)
Some parts of the organism are not digested so not absorbed
Some of the materials absorbed form excretory products
Many are respired to release energy - loss of CO2, water and thermal energy
Why can unicellular organisms rely on diffusion for movement of substances in and out of the cell?
Unicellular organisms have very large SA : V ratio meaning that the distance between the surface of the organism to its centre is very small
Why do multicellular organisms need a transport system?
They consist of many cells that differentiate to take on specialized functions.
They have a small surface area to volume ratio, so transport systems are needed to get substances to the correct place.
Transport systems supply cells with useful substances (e.g. glucose and oxygen) and remove waste products.
Eg. Circulatory system in humans
Composition of Blood
Red blood cells, White blood cells, Platelets and Plasma
The Role of Plasma
Transporting dissolved carbon dioxide, digested food molecules, urea and hormones; distributing heat
Adaptations of Red Blood cells so they are suitable for the transport of oxygen
Contain haemoglobin: Haemoglobin can combine reversibly with oxygen. This means that it can combine with oxygen as blood passes through the lungs, and release the oxygen when it reaches the cells.
They have no nucleus so they can contain more haemoglobin.
They are small and flexible so that they can fit through narrow blood capillaries.
They have a biconcave shape to maximise their surface area for oxygen absorption.
They are thin, so there is only a short distance for the oxygen to diffuse to reach the centre of the cell.
Phagocytes
Engulf and destroy unwanted microorganisms that enter the blood, by the process of phagocytosis.
(Part of the immune system)
Lymphocytes
Produce antibodies when a foreign body such as a microorganism enters the body:
they bind to pathogens and damage or destroy them
they coat pathogens, clumping them together so that they are easily ingested by phagocytes
they bind to the pathogens and release chemical signals to attract more phagocytes
Lymphocytes may also release antitoxins that stick to the toxins that the microorganism makes, which stops it damaging the body.
(Part of the immune system)
How do vaccines work?
Allow a dead or altered form of the disease causing pathogen to be introduced into the body, which contain a specific antigen. This causes the immune system, specifically the white blood cells, to produce complementary antibodies, which target and attach to the antigen.
Platelets
They have proteins on their surface that enable them to stick to breaks in a blood vessel and clump together
They secrete proteins that result in a series of chemical reactions that make blood clot, which plugs a wound
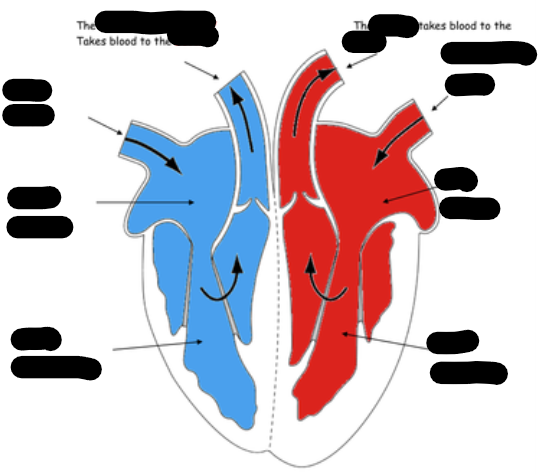
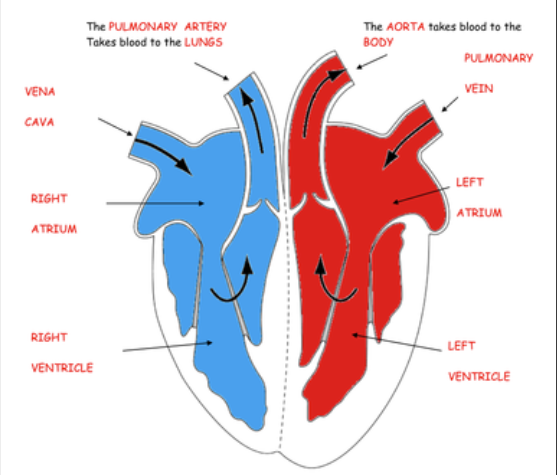
Structure of the Heart
How and what factors may increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease?
poor diet – eating more saturated fat tends to increase cholesterol levels
stress and smoking – increases blood pressure
salt – eating too much causes high blood pressure
lack of exercise
genetic factors
Arteries: Adaptations
Have thick muscular and elastic walls to accommodate and pump blood and withstand high pressures and stretch + recoil
Have connective tissue to provide strength
Veins: Adaptations
Have thin walls
Have valves to prevent backflow of blood
Large lumen as there are low pressures
Capillaries: Adaptations
Walls one cell thick: therefore allow the exchange of molecules between the blood and the body's cells - molecules can diffuse across their walls
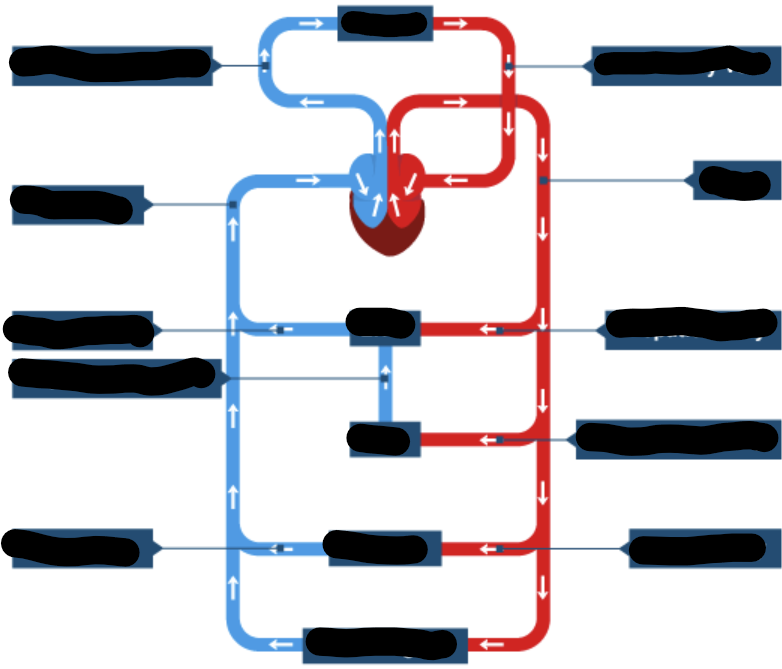
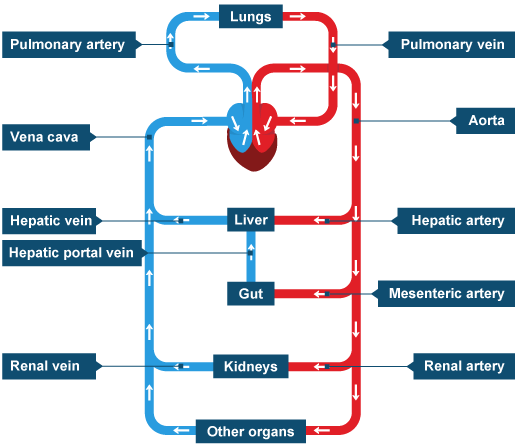
General structure of circulation system
Production of ATP is via:
Process of Respiration
What does ATP provide for cells?
Energy
Aerobic Respiration
Occurs with the use of Oxygen
Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs when Oxygen is not present
Word Equation for Aerobic Respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)
Balanced Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H20
Word Equation for Anaerobic Respiration
glucose → lactic acid (+ energy)
Mitochondria
Aerobic respiration
Nucleus
Contains DNA
Ribosome
Protein synthesis
Cytoplasm
Many chemical reactions
Cell membrane
Controls what enters and leaves
Cell wall
Support and strength
Vacuole
Contains cell sap
Chloroplast
Photosynthesis/ Absorbs light
carbohydrate elements
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (CHO)
lipid elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO)
protein elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON)
storage for carbohydrates in: plants
starch: polysaccharide
storage for carbohydrates in: animals
glycogen: made of glucose (monosaccharide)
lipids are made of:
fatty acids and glycerol (meaning they are triglycerides)
proteins are made of:
long chains of amino acid monomers (meaning they are polymers)
test for: starch
iodine: brown → blue
test for: glucose
benedicts test: blue → brick red
test for: lipids
ethanol emulsion: white emulsion
test for: proteins
biruet: blue → lilac
Word equation for Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water —> glucose + oxygen
Balanced chemical equation for Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
The process of Photosynthesis
Light energy is used to split water, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions.
Carbon dioxide gas combines with the hydrogen to make glucose.
This is important in order for the plant to maintain/ gain energy and continue to grow
Use of Magnesium Ions
Chlorophyll
Magnesium Deficiency
Plant leaves appear yellow
Use of Nitrate Ions
Amino acids
Nitrate Deficiency
Poor growth and yellow leaves
Use of Mineral Ions
Growth
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation occurs when toxins build up - or accumulate - in a food chain. The animals at the top of the food chain are affected most severely.
Biomagnification
The rise or increase in the contaminated substances caused by the intoxicating environment.
Causes of Eutrophication
Some pollutants affect the environment by disrupting the equilibrium in food chains:
Sewage
Nitrate Fertilisers
Pesticides
Adaptations of the leaf for Photosynthesis
Adaption | Large surface area |
|---|---|
Purpose | To absorb more light |
Adaption | Thin |
|---|---|
Purpose | Short distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf cells |
Adaption | Chlorophyll |
|---|---|
Purpose | Absorbs sunlight to transfer energy into chemicals |
Adaption | Network of veins |
|---|---|
Purpose | To support the leaf and transport water, mineral ions and sucrose (sugar) |
Adaption | Stomata |
|---|---|
Purpose | Allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen to diffuse out |
Adaption | Epidermis is thin and transparent |
|---|---|
Purpose | To allow more light to reach the palisade cells |
Adaption | Thin cuticle made of wax |
|---|---|
Purpose | To protect the leaf from infection and prevent water loss without blocking out light |
Adaption | Palisade cell layer at top of leaf |
|---|---|
Purpose | To absorb more light and increase the rate of photosynthesis |
Adaption | Spongy layer |
|---|---|
Purpose | Air spaces allow gases to diffuse through the leaf |
Adaption | Palisade cells contain many chloroplasts |
|---|---|
Purpose | To absorb all the available light |
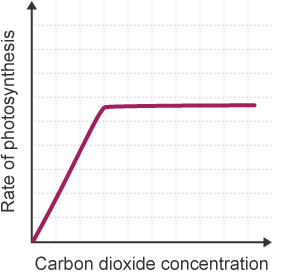
Effect of Carbon Dioxide on rate of photosynthesis
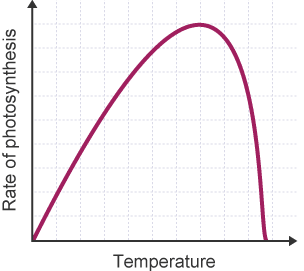
Effect of Temperature on rate of photosynthesis
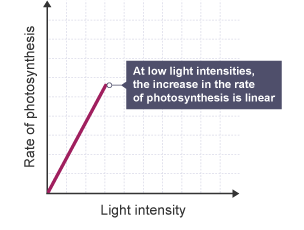
Effect of Light Intesity on rate of photosynthesis
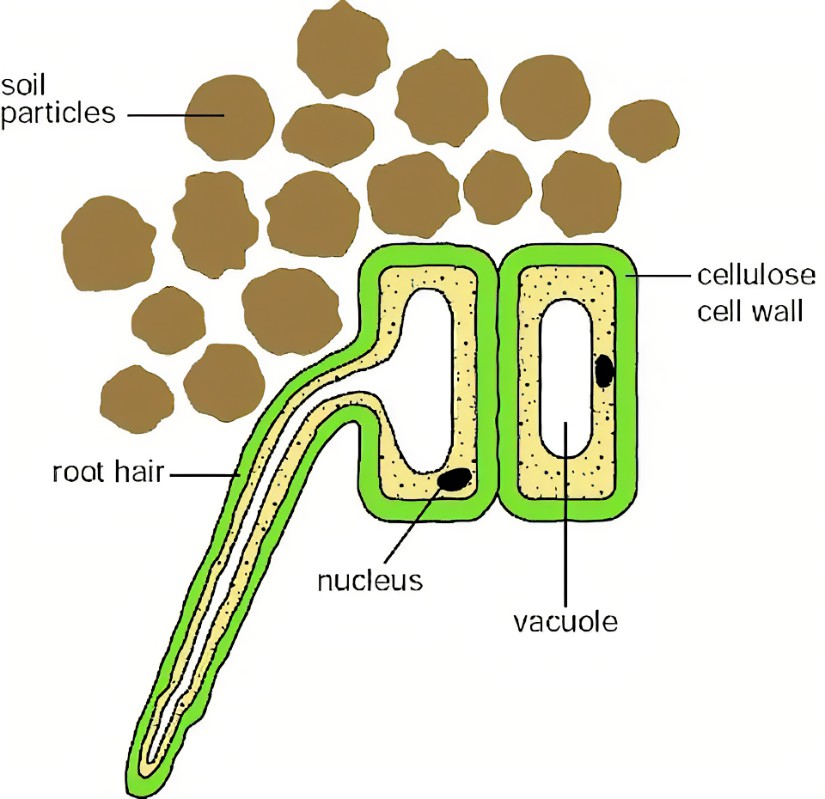
Root hair cell adaptations
Elongated: large surface area
Short diffusion distance because the wall is one cell thick
Lots of mitochondria for respiration to release ATP for active transport
Absorption of water into plants by root hair cells
The water in the soil diffuses into the roots by osmosis from an area of high water concentration to a low water concentration across a partially permeable membrane and travels up the roots into the stem and travels up the stem into the leaves.
Absorption of mineral ions into plants by root hair cells
The mineral ions move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration across a partially permeable membrane using ATP from respiration into the roots via active transport and travels through the roots and stem into the leaves.
Role of the Xylem
Water and dissolved mineral ions travel in these vessels from root to shoots and leaves in one direction.
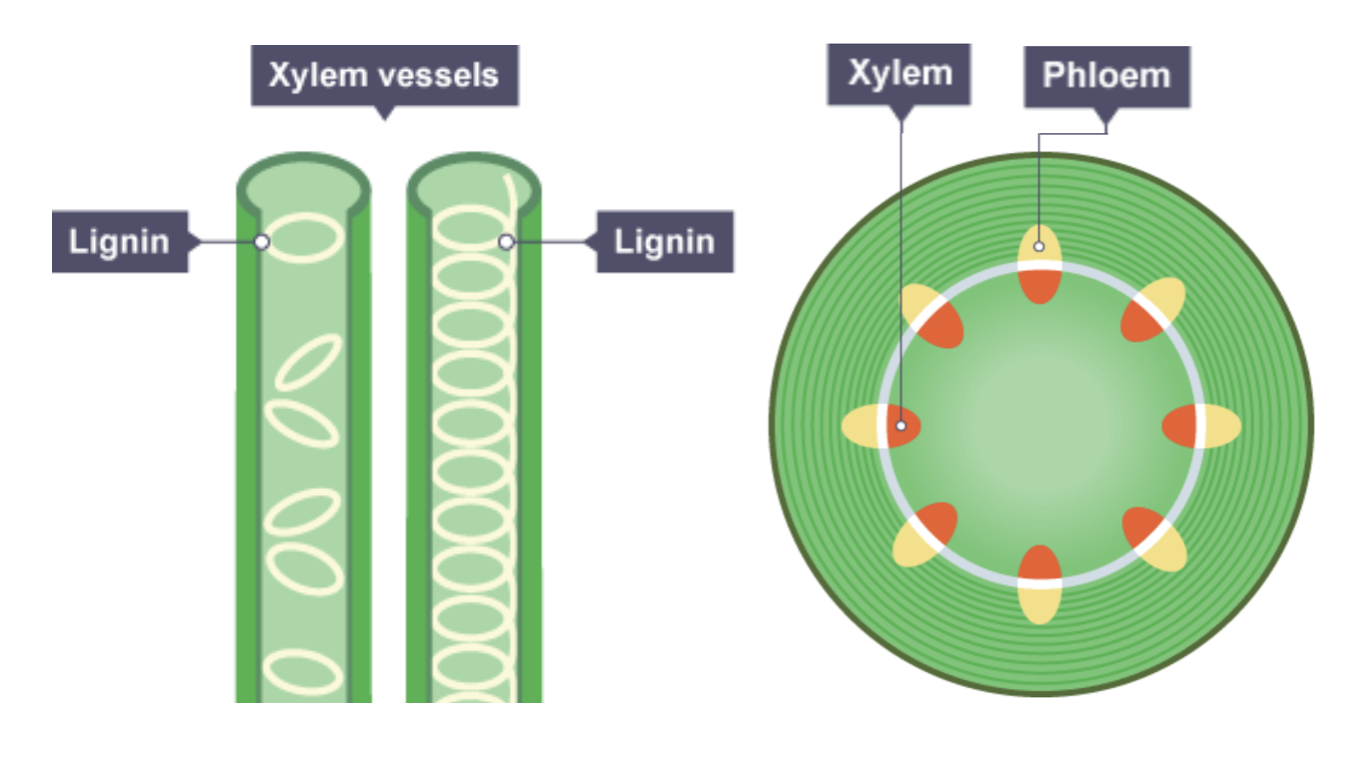
Xylem Vessels
Have thick cellulose cell walls, strengthened by lignin. Once xylem cells have formed the xylem, they die making long, thin, hollow vessels for water to move through. The thick walls also help support plants.
Role of the Phloem
Carries dissolved sucrose and amino acids from the leaves to the growing and storage parts of the plants. Transports sucrose up the plants from stores of starch e.g. in root tubes.
Phloem cells
These cells are alive - if they are damaged they cannot work properly. Phloem are made of companion cells and sieves. Cells are joined by small tubes in the cell wall at the end of each cell, forming a continuous system. The end walls are called sieve plates.
Sieve tubes
Nearly empty - allow sap (sucrose) to move easily
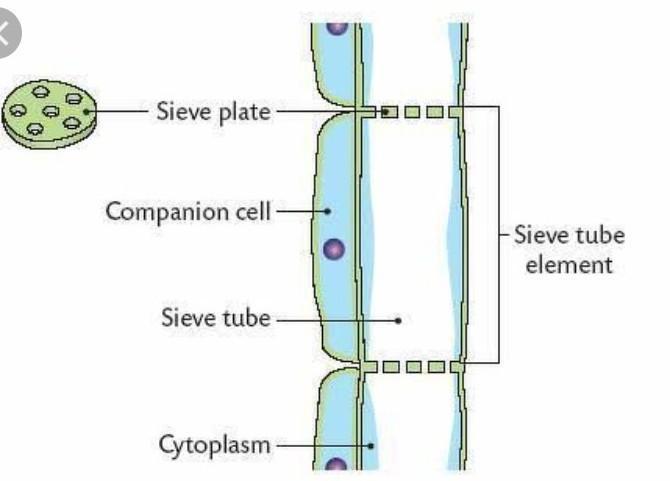
Companion cells
Have normal cell contents including lots of mitochondria
Transpiration
The loss of water by evaporation from the plants - they lose water when they open the stomata in the leaves for gas exchange.
Stomata
Small holes located on the underside of the leaves to allow for the exchange of gases. Water also evaporates through the stomata.
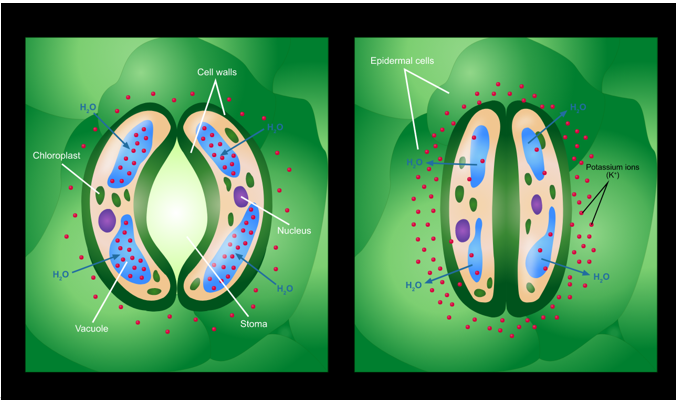
Guard cells
Each stoma is surrounded by two guard cells, which control the opening and closing of the stoma. The guard cells gain water and become more turgid. They curve out opening the stoma and allowing gases in and out.
Stage 1 of the Opening of the Stomata
Accumulate solutes in their vacuoles which lowers the water potential. Water moves in by osmosis. The guard cells swell up which changes their shape - opening the stomata.
Stage 2 of the Opening of the Stomata
The stomata are open for gas exchange. During this time water is lost as water vapour moves out of the leaf down the water potential gradient.

Stage 3 of the Opening of the Stomata
At night the guard cells lose water so becoming flaccid and close the stomata.

Closing at Night is a Useful Adaptation because:
The guard cells are the only cells in the lower epidermis to contain chloroplasts and so the opening and closing of the stomata is caused by light intensity.
There is no light so no need for photosynthesis
No need to cool the plant
Stage 1 of the Transpiration Stream
Water leaves the cells of the mesophyll and evaporates into the air spaces. This water vapour diffuses out through the stomata down the water vapour potential gradient
Stage 2 of the Transpiration Stream
The loss of water from the mesophyll cells reduces the water potential of these cells so water moves by osmosis from the surrounding cells into these cells down the water potential gradient.
Stage 3 of the Transpiration Stream
Water from the xylem moves into the mesophyll cells down the water potential gradient.
Stage 4 of the Transpiration Stream
The loss of water from the xylem causes water to be pulled up the xylem in the stem and the roots in a continuous flow, called the ‘transpiration stream’
Transpiration stream functions
Supplies water to the palisade mesophyll for photosynthesis
Carries mineral ions dissolved in the water to cells in the plants
Provides water to cells to keep cells turgid
Allows evaporation from the leaf surface, which cools the leaf in a similar way to sweating cooling the skin
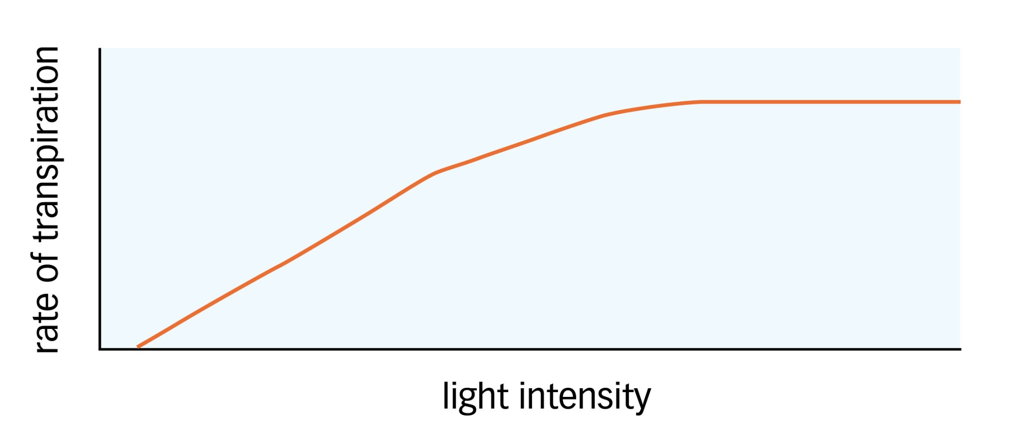
Effect of Light Intensity on the Rate of Transpiration
The rate of transpiration increases as light intensity increases because of the opening of the stomata for gas exchange for photosynthesis
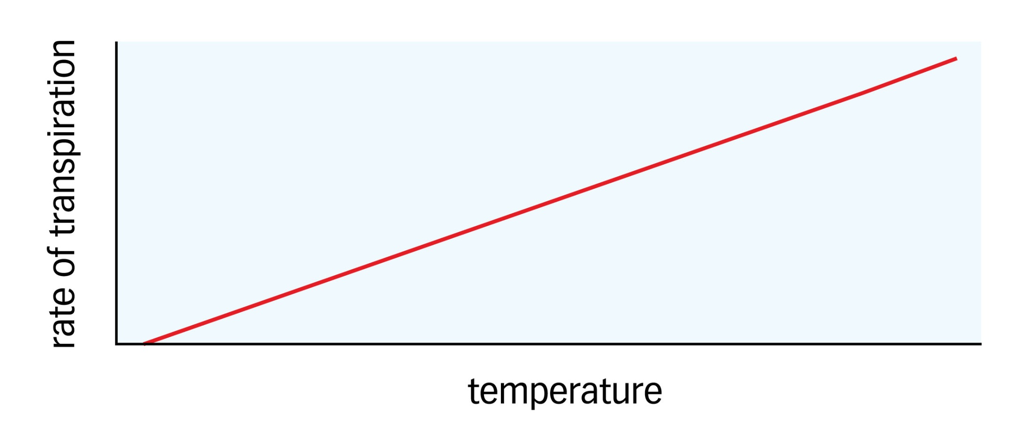
Effect of Temperature on the Rate of Transpiration
Higher temperatures increase the rate of transpiration by increasing the rate of evaporation from the mesophyll cells
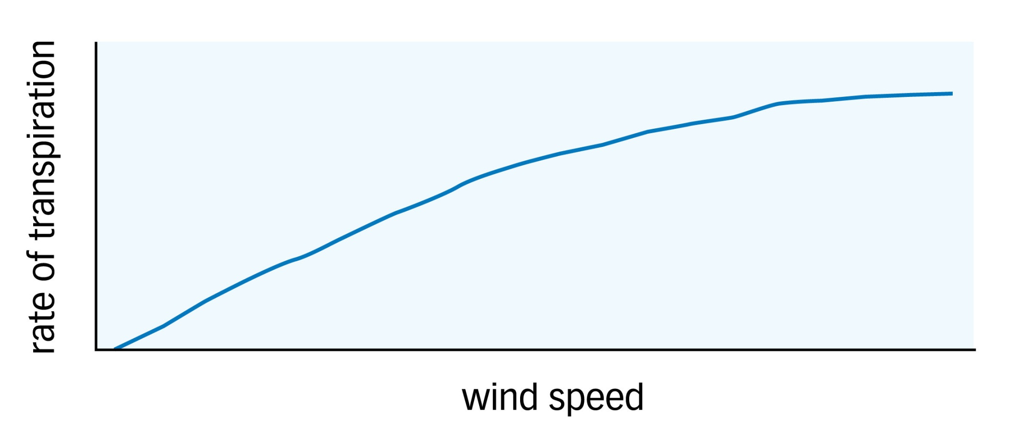
Effect of Wind Speed on the Rate of Transpiration
The rate of transpiration increases with faster air movements across the surface of the leaf as the moving air removes any water vapour which might have been near the stomata so increasing the water vapour potential gradient
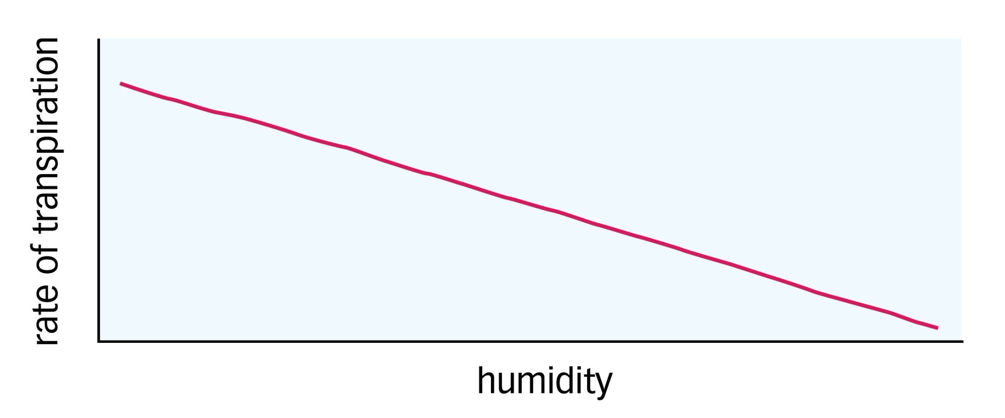
Effect of Humidity on the Rate of Transpiration
The rate of transpiration is higher when the air is less humid as there is an increased water vapour potential gradient.
Organ
A collection of tissues that work together to perform a particular function
Nervous System
Uses electrical impulses for faster, shorter lined responses
Endocrine System
Uses hormones for longer lasting and slower responses