Unit 4: Chapter 9 - The Contemporary Political Map
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Political geography
the study of the ways in which the world is organized as a reflection of the power that different groups hold over territory.
Political maps
Show countries, their borders, and capital cities
Political maps express different interpretations of the world.
Ex:
U.S. maps include Taiwan as a separate country, but Chinese maps do not.
State
an area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government that has control over its internal and foreign affairs.
STATE = COUNTRY
How are some regions unique?
Some regions test the definition of a state because multiple actors lay claim to the same piece of territory.
Ex:
Kashmir (India/Pakistan/China Conflict)
West Bank (Israeli/Palestinian Conflict)
Sovereignty
the right to control and defend its territory and determine what happens within its borders.
How do the number of states fluctuate over time?
In 1945, the UN had 49 'MEMBER STATES.' Today, it has 193. These states cover virtually the entire surface of the Earth.
Is a state the same thing as a nation?
NO.
Nation (like nationality from Unit 3)
a cultural entity made up of individuals who have forged a common identity through a shared language, religion, ethnicity, or heritage.
People of a nation share a common vision of the future and having a feeling of togetherness.
Ex:
Native Hawaiians and the Navajo Nation
Nation-state
a territory in which a group that views itself as a nation is the same as the politically recognized boundaries the state calls its own.
Is nation-state an ideal or reality?
Nation-state is an ideal because there is no nation on Earth that is purely one race or ethnicity.
What are some nation-states that come close?
Estonia, Japan, Iceland, Iran
Multi-state nation
consists of a population that shares a cultural or ethnic background but lives in more than one country.
How do multi-state nations happen?
when people feel a stronger affinity for a neighboring state that is home to others of their ethnic group than to their own state.
Ex:
Russia. People living in former Soviet Union countries have deep ties and pride for Russia.
Irredentism
an attempt to acquire territories in neighboring states inhabited by people of the same nation.
Ex:
Russia captured the Crimea region of Ukraine. They justified taking this area by pointing out the predominant ethnically Russian population
Multinational state
a country with various ethnicities and cultures living inside its borders
What is a problem within multinational states?
Multinational states typically struggle with creating a sense of unity across the state.
Ex:
Yugoslavia. The three dominant ethnicities constantly fought each other for dominance until eventually the country broke apart into Croatia, Serbia, and Bosnia.
Autonomous and semi-autonomous regions
regions given some authority to govern their own territories within the larger state/country.
Stateless nation
a people united by culture, language, history, and traditions but not possessing a state.
Ex:
Palestinians and the Kurds
Territoriality
-An expression of a group's historic and personal links to a place.
-The connection of people, their culture, and their economic systems to the land.
It is the basis for the power that people try to exert and the political spaces they create. This leads to sovereignty.
Colonization
the practice of claiming and dominating overseas territories.
Neocolonialism
the use of economic, political, cultural, or other pressures to control or influence other countries, especially former dependencies.
Ex:
Kenya and its dependence on foreign money to rebuild its failing infrastructure.
What are the 3 G's (or reasons) of Colonization?
Gold, God, and Glory.
To gain money, spread religion, and gain territory.
Chokepoints
a narrow, strategic passageway to another place through which it is difficult to pass.
Chokepoints are straits, canals, or other restricted passages.
Ex:
The Suez Canal, The Strait of Gibraltar, The Strait of Hormuz, and the Panama Canal.
What is the most important resource that goes through these chokepoints?
The most important resource that goes through these chokepoints is OIL.
Controlling one of these chokepoints gives you a tremendous amount of power over the global supply of oil.
Shatterbelt
*important*
a region with ongoing political instability.
States will form, join, break up, and then form again. This cycle is repeated until one group or power takes complete control and suppresses the other groups.
What are causes of instability?
Instability can be caused by religious, ethnic, and linguistic conflicts.
Self-Determination
the right of all people to choose their own political status.
Some states have self determination but are not completely sovereign; Cuba depended on the Soviet Union because they were cut off from the rest of the world due to the US Embargo.
Imperialism
the push to create an empire by exercising force or influence to control other peoples or nations.
BRITISH and DUTCH colonies were purely economic (wealth-producing)
The SPANISH, PORTUGUESE, and FRENCH sought to impose their culture (language and religion) on their colonies.
How do countries establish boundaries?
Countries establish boundaries by defining, delimiting, demarcating, and defending them.
Defining Boundaries
explicitly stating in legally binding documentation such as a treaty where borders are located.
This usually happens after a battle or war. The victor creates the borders. "To the victors go the spoils".
Ex:
Treaty of Paris 1783
Delimiting Boundaries
Drawing boundaries on a map in accordance with a legal agreement
This usually happens when one country purchases land from another.
Ex:
Louisiana Purchase
Demarcating Boundaries
marking a boundary with stones, pillars, walls, fences, or other physical objects.
Typically used to keep citizens in or invaders out.
Ex:
Great Wall of China, Berlin Wall, the U.S-Mexican Wall
Administrated Boundaries
countries manage the way borders are maintained and how goods and people will cross them.
Most of the world's borders are restricted, meaning you need official documentation like a passport or visa to cross them.
Some countries have completely closed borders like North and South Korea.
Antecedent Boundaries
boundaries that are established before many people settle in an area.
"Ante" means before
Ex:
The border between the United States and Canada runs across the 49th parallel was created before people lived in North Dakota, Montana, and Washington state.
Subsequent Boundaries
drawn in areas that have been settled by people and where cultural landscapes already exist or are in the process of being created.
"Subsequent" means after
The Berlin wall created a border between the Soviet East and Democratic West. It was created to keep people in.
Consequent Boundaries
a type of subsequent boundaries.
It takes into account differences within an existing cultural landscape, separating groups that have distinct languages, religions, ethnicities, or other traits.
Ex:
In India the border between India and Pakistan is ethnic and established by the British as they exited the country.
Superimposed Boundaries
boundaries drawn over existing borders by an outside or conquering force.
The Berlin Conference where European nations divided up the continent of Africa without thought for the people or their cultures is an example.
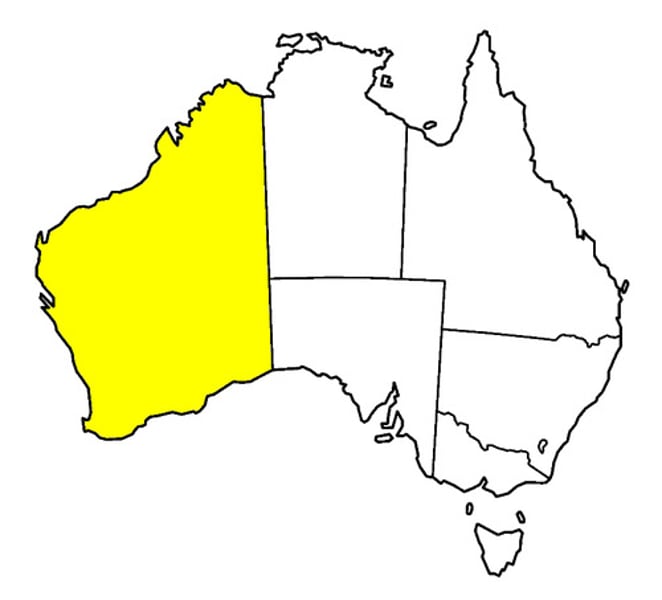
Geometric Boundaries
Mathematical. They follow lines of latitude and longitude or are straight-line arcs between two points.
Ex:
Australia is divided geometrically. The interior of the country is divided into 6 states or territories reflecting political rather than cultural divides.
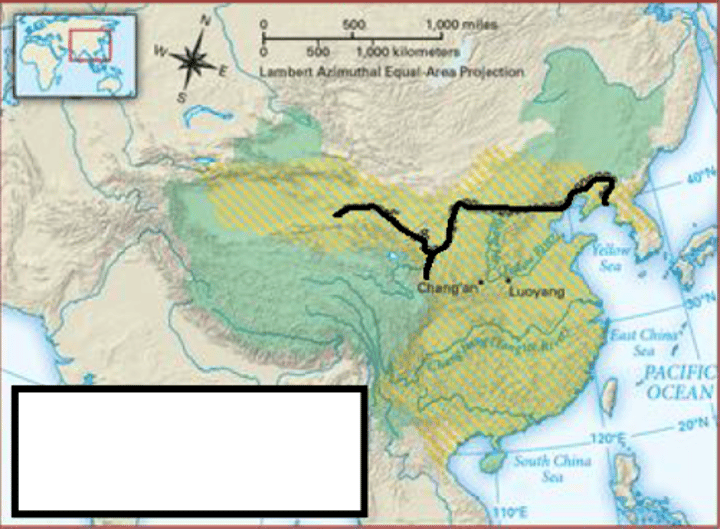
Relic Boundaries
former boundaries that once existed but no longer have an official function.
Ex:
The Great Wall of China was the boundary between the Ch'in Dynasty and the Mongols to the west. The wall is no longer the boundary but it remains as a reminder of human innovation.
Maritime Boundaries
allow countries to access offshore resources such as oil and marine life (fish and other animals).
States have complete sovereignty over their territorial seas. This includes all the space below and above the surface.
Boundary disputes happen because some waters are full of resources.
What is the advantage of having maritime boundaries?
Countries with maritime boundaries are often more economically developed than those that are landlocked because of the advantages granted by having ports to facilitate trade.
What is the structure of maritime boundaries?
A country's territorial seas extend 12 nautical miles off its coast.
A country's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) extends 200 nautical miles off its coast.