16.5 Gibbs free energy
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the equation for Gibbs free energy?
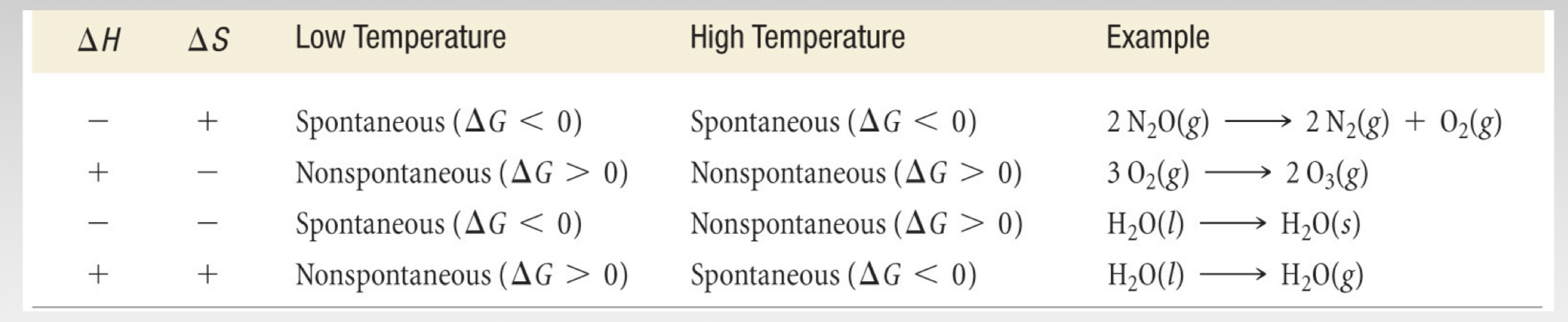
For a spontaneous process: ∆G __ 0
For a non-spontaneous process: ∆G __ 0
A process at equilibrium: ∆G __ 0
Gibbs free energy represents the _____________; it is a ______ function
< , > , = , energy available to do work , state

State the equation for calculating the ∆H of a chemical reaction.
∆H = ∑∆Hproducts - ∑∆Hreactants
State the equation for calculating the ∆S of a chemical reaction.
∆S = ∑∆Sproducts - ∑∆Sreactants
The entropy of a perfect crystal of a pure substance approaches 0 as the temperature approaches 0 K.
Every substance that’s not a perfect crystal at _________ has _________ from entropy → absolute entropy of a substance is always ________.
3rd Law of Thermodynamics
Ans: absolute zero, some energy, positive
Conditions for standard state:
Standard entropy (Sº): _______
∆Gº (∆G = ∆Gº only when reactants and products are in their standard states): _______
Entropies for 1 mole at 298 K (25º C) for a particular state, particular allotrope, particular molecular complexity, particular molar mass, and a particular degree of dissolution
Normal state at that temperature, partial pressure of gas = 1 atm, concentration = 1 M
∆G and ∆S are ______ properties.
extensive (dependent upon the amount of substance)
What is are the equations for ∆Greaction at 298 K and temperatures other than 298 K (i.e. calculating Gibbs free energy of a reaction using ∆Gºf for both situations)?
∆Gºreaction = ∑n∆Gºf(products) - ∑n∆Gºf(reactants)
∆Gºf is the Gibbs free energy of formation: the energy associated with forming 1 mole of a compound from its components in their standard state
Assuming the change in ∆Hºreaction and ∆Sºreaction is negligble: ∆Gºreaction = ∆Hºreaction - T∆Sºreaction
determine ∆Hºrxn and ∆Sºrxn separately to determine ∆Gºrxn
What is the equation for ∆G under non-standard conditions (hint: related to equilibrium constant K)?
∆G = ∆Gº + RT ln(Q)
∆G = non-standard Gibbs free energy (J / mol)
∆Gº = standard Gibbs free energy (J / mol)
R = ideal gas constant
T = temperature in K
Q = reaction quotient (note: at EQ, Q = K and ∆G = 0)
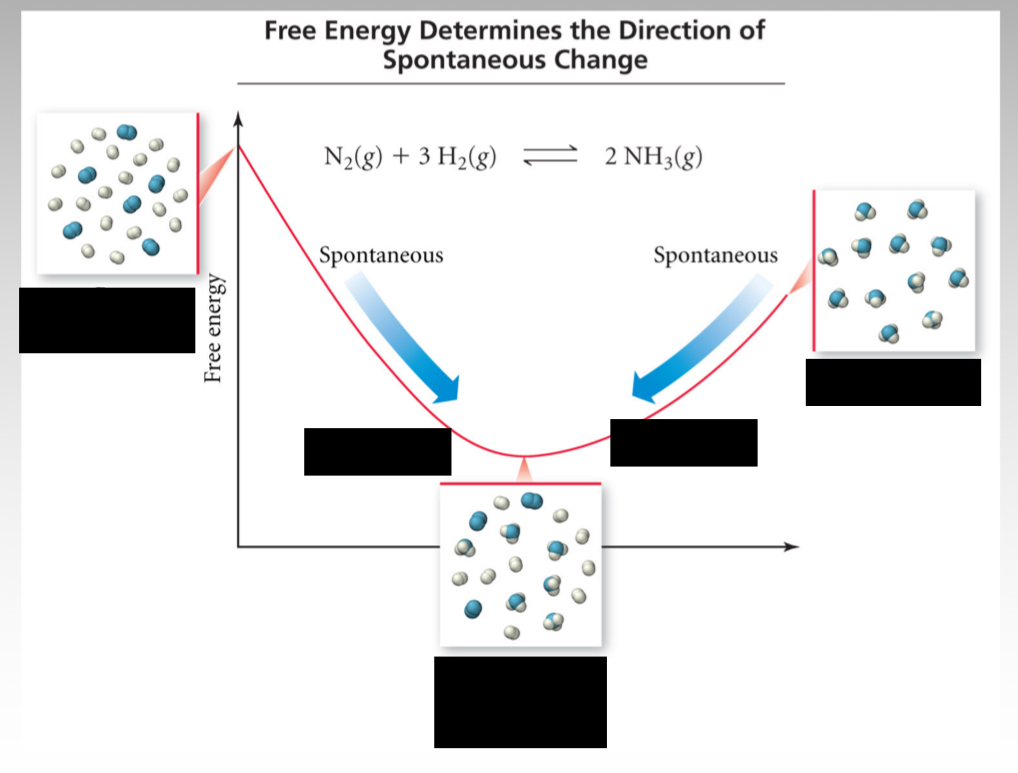
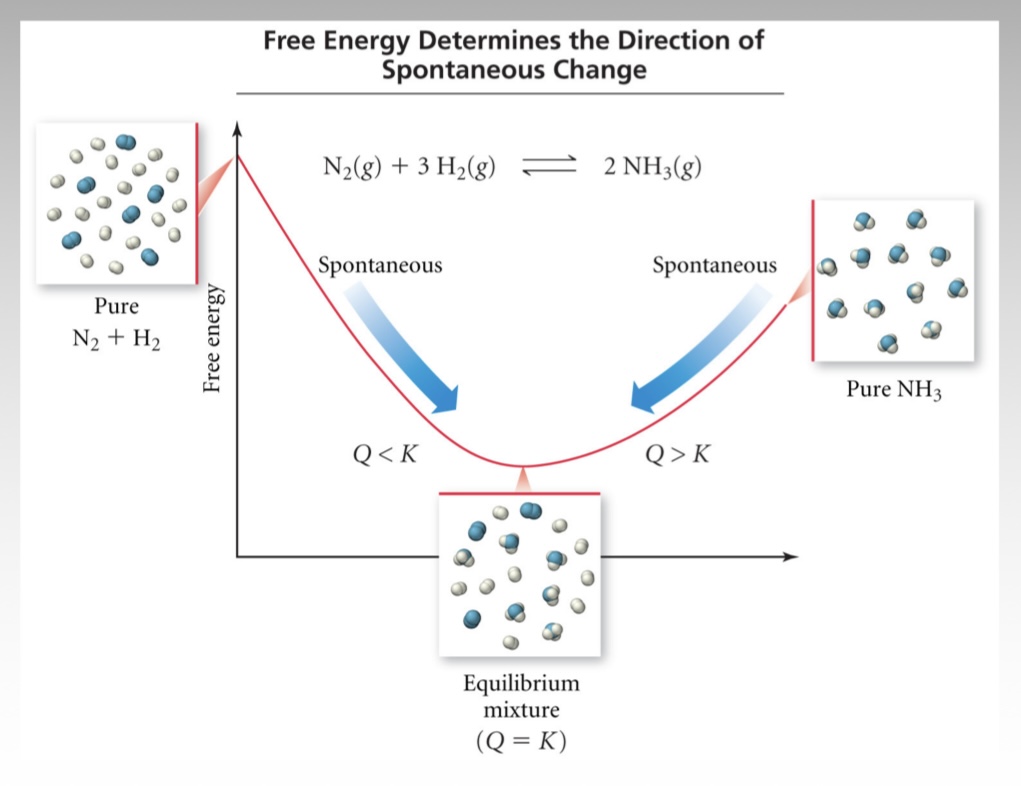

At equilibrium, what is the relationship between standard Gibbs free energy and the equilibrium constant?
At equilibrium, ∆G = 0, so ∆G = ∆Gº + RTln(K) → ∆Gº = -RTln(K)
What is the significance of ∆Gº = 0?
The reaction is at equilibrium under standard conditions. This means that the concentrations of all reactants and products = 1 M (or 1 atm for gas-phase reactions).
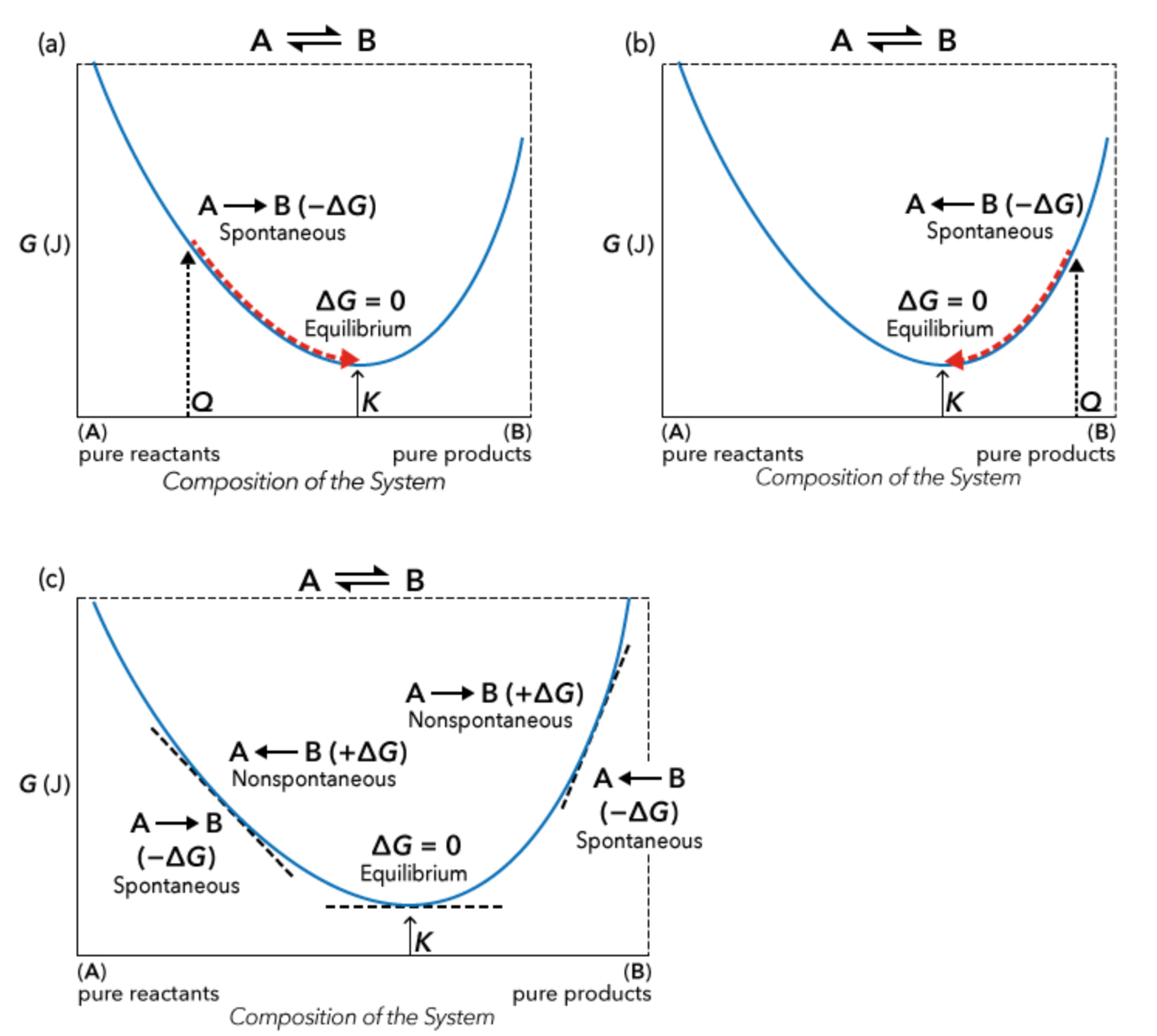
Problem-solving: relating Gibbs free energy, the equilibrium constant (K), and the reaction quotient (Q)
• Use the sign on ΔG to determine spontaneity and the relative value of Q vs K
• Use the value of Q to calculate ΔG (or vice versa)
• Use the sign on ΔG° to determine the relative magnitude of K
• Use the value of K to calculate ΔG° (or vice versa)