Electricity
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Voltage
Energy per unit charge
Emf
the electrical work done by a source in moving a unit charge around a complete circuit
Pd
the work done by a unit charge passing through a component
Electric current
the charge passing a point per unit time
(rate of flow of charge)
Current formula
I = Q/t
Conventional current
From positive to negative
Flow of free electrons
From negative to positive
Ohm’s law
Voltage is proportional to current when resistance is constant (when temp is constant)
Power equations [4]
P=IV
P=I²R
P=V²/R
P=E/t
Energy equation
E = VIt
Voltage equations [2]
V = E / Q
V = W / Q [W: work done]
Ohm’s Law equation
V = IR
Thermistor
When temperature increases, resistance decreases
Filament Lamp
When temperature increases, resistance increases
Light Dependent resistor
When light intensity increases, resistance decreases
Diode
Allows current to flow in only one direction
A.C. current
Current flows both directions alternately
D.C. current
Current flows in only one direction
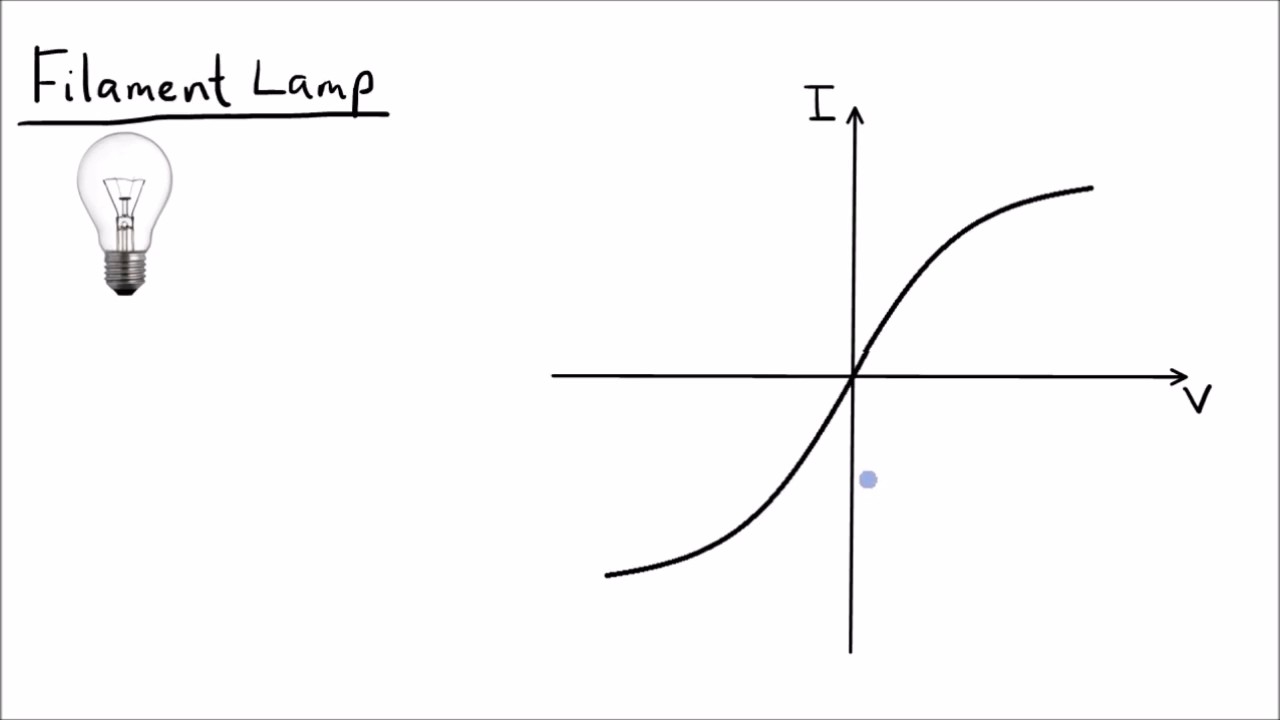
Filament lamp IV graph
V increases more rapidly than current
Voltage increases, increasing brightness and therefore temperature and resistance.
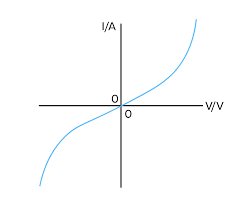
Thermistor IV graph
Current increases more rapidly than voltage
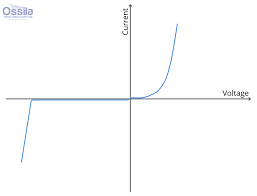
Diode IV graph
Forward bias: same as thermistor
Reverse bias: very high resistance (I=0)
Series circuit
same current
shares p.d./voltage
Parallel circuit
same p.d./voltage
shares current
Advantage of parallel circuit
when one equipment breaks, the rest still works
maximum voltage/p.d. for all equipment
a switch can be used to control each equipment separately
Advantage of series circuit
uses less wires
can be switched on/off all at once
easy to set up
Live, Neutral and Earth wire
Live: Brown
Neutral: Blue
Earth: yellow-green
Earth wire
Connects to the metal case of the appliance
provides a low resistance path to earth
causes a surge of current in earth wire and live wire to melt the fuse —> cuts of supply of electricity to appliance
KiloWatt Hours
The electrical energy consumed by 1000W of power in 1 hour
Potential divider
R1 / R2 = V1 / V2
Hazards of damaged insulation
If someone touches an exposed piece of wire, they could be subject to lethal shock
Hazards of overheating of cables
Too much current can overheat a wire which could cause a fire or melt insulations
Hazards of damp conditions
If moisture comes in contact with live wires, it could conduct electricity which can cause a short circuit (could cause fire) or an electrocution risk
Hazard of excess current from overloading plugs, extension leads, single and multiple sockets when using a mains supply
Overload can cause fires from the heat created
Main circuit components
live wire
neutral wire
earth wire