Basal Nuclei/Cerebellum Poll Everywhere
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The corpus striatum consists of:
Caudate and putamen
Caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus
Putamen, globus pallidus and substantia nigra
Caudate, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra
Substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus
Caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus
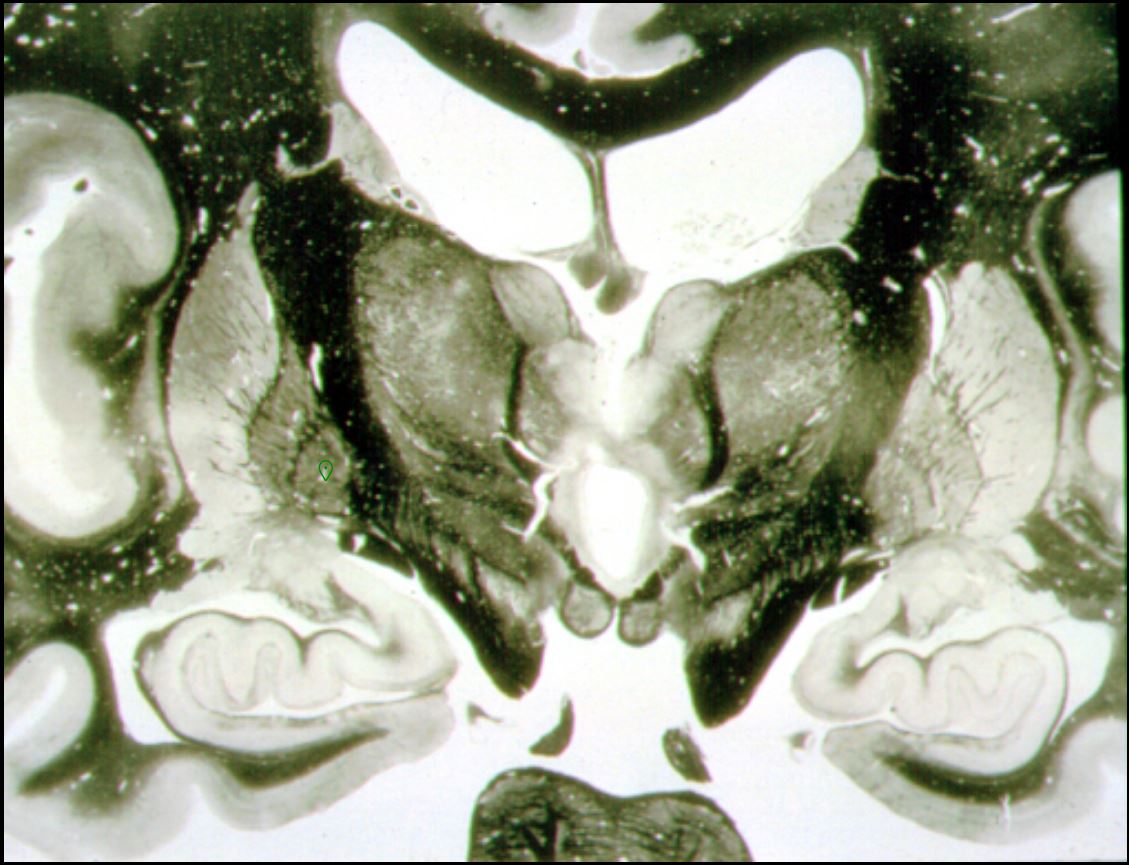
What is marked?
globus pallidus
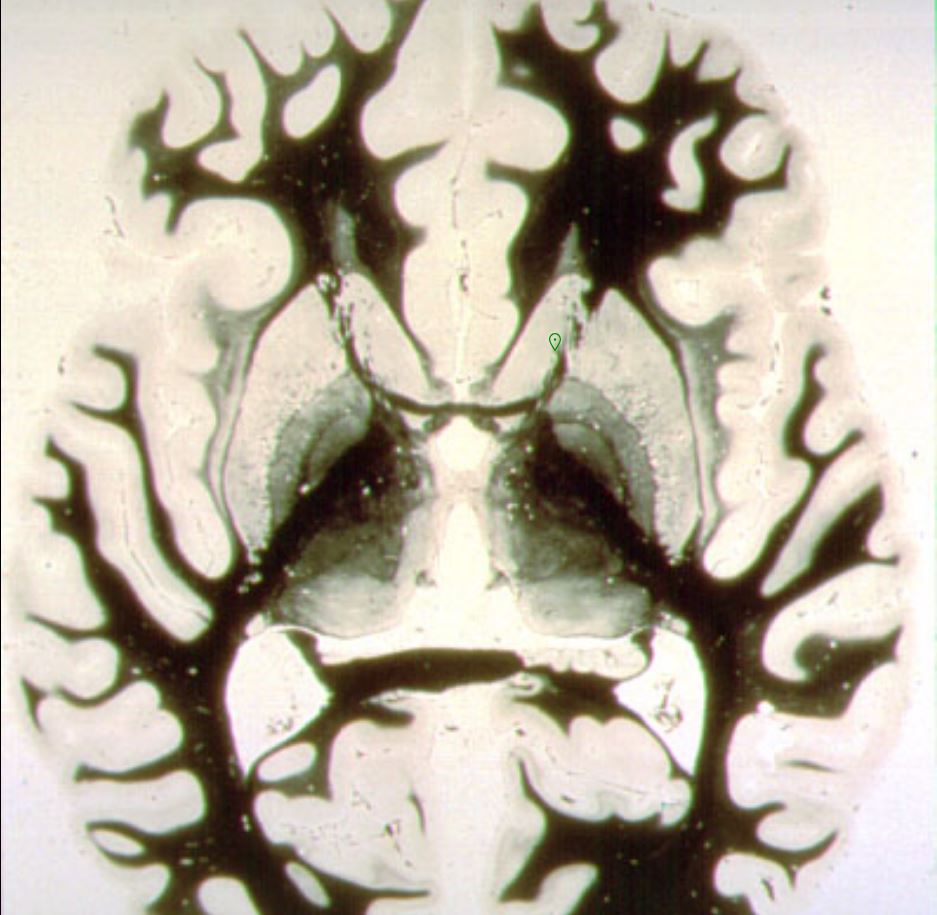
What is marked?
Head of the Caudate nucleus
Activation of the basal nuclei direct pathway caused increased motor cortex activity and increased movement (1True/1False)
1True
A hyperkinetic movement disorder which has slow, writhing, snake-like movements is called:
Athetoid movements
Choreiform movements
Contralateral hemiballism
Hypotonia
None of the above
Athetoid movements
A lesion to the subthalamic nucleus will result in:
Athetoid movements
Choreiform movements
Contralateral hemiballism
Contralateral hemiballism
Which CNS structure(s) is initially affected in Huntington's disease?
Globus pallidus
Substantia nigra
Subthalamic nucleus
Striatum
Lentiform nucleus
Striatum
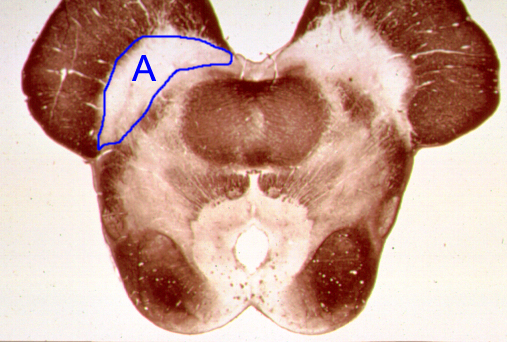
Name the clinical condition when structure "A" is lesioned.
Parkinson’s disease
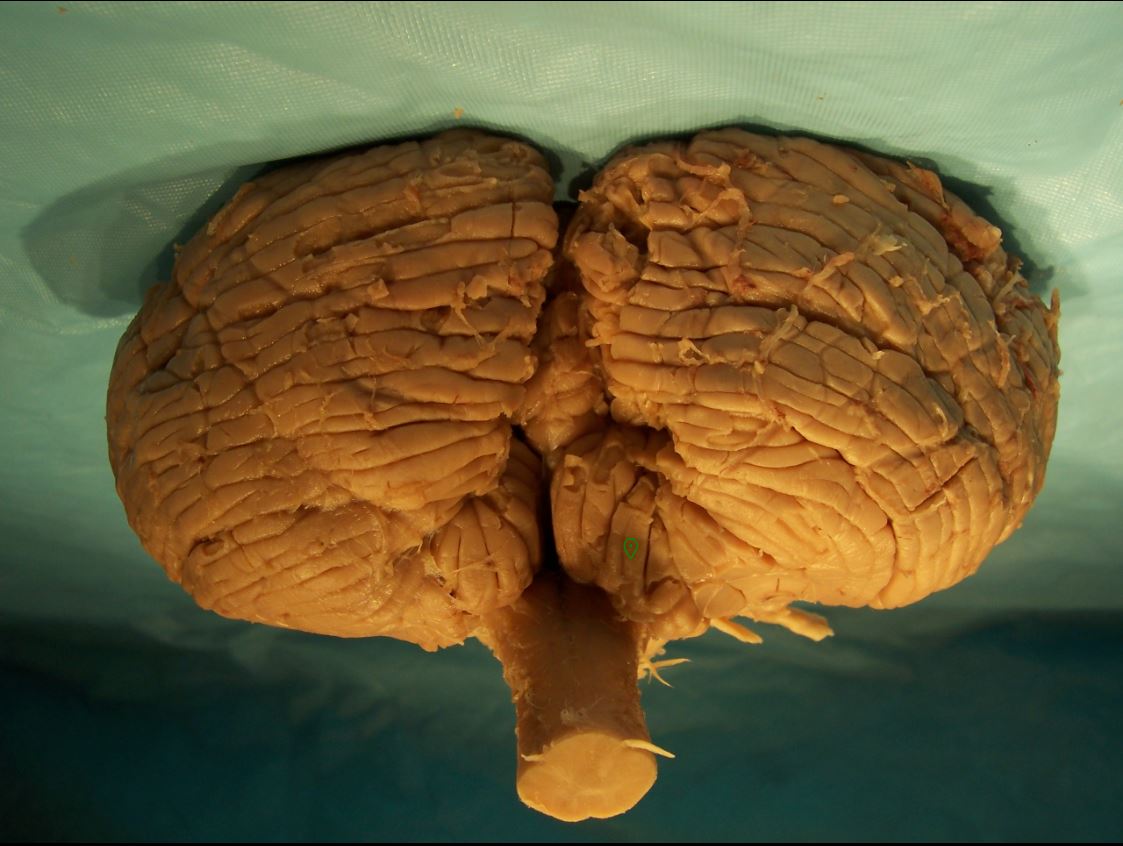
What is marked?
cerebellar tonsils
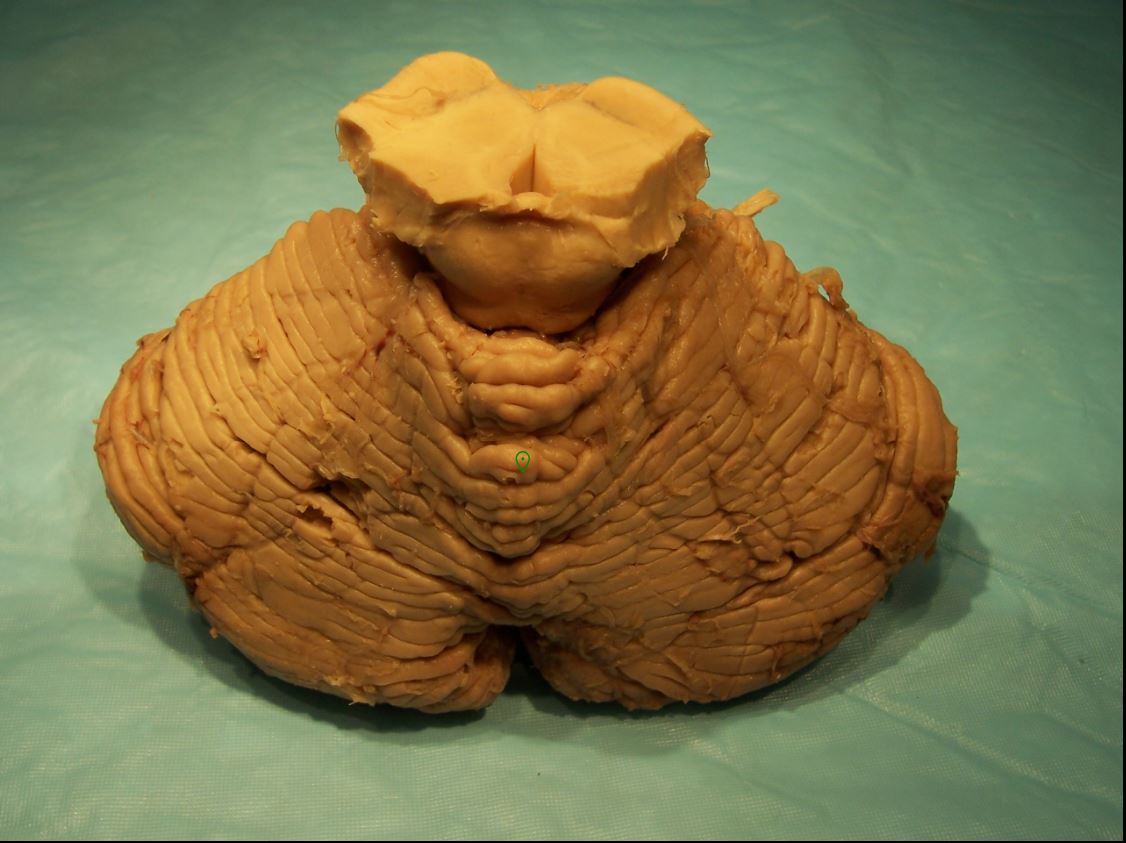
What is marked?
vermis
Which cerebellar neuron sends inhibitory output to the deep cerebellar nuclei?
Granule cells
Basket cells
Stellate cells
Purkinje cells
None of the above
Purkinje cells
A 59 year old patient presents with trunkal ataxia. Which cerebellar functional zone has been lesioned?
Pontocerebellum
Spinocerebellum
Vestibulocerebellum
None of the above
Ataxia
Jerky, inaccurate movements
Hypotonia
Decreased muscle tone and deep tendon reflexes
Dyssnergia
Deterioration and decomposition of coordinated movement
Dysmetria
Past pointing by over or under shooting the target
Dysdiadochokinesia
Awkward performance of rapidly alternating movements
An intention tremor is caused by a cerebellar lesion (2True/2False)
2True
The superior cerebellar artery supplies the superior surface of the cerebellum (3True/3False)
3True
Gamma motor neurons innervate intrafusal muscle fibers to maintain muscle tone (4True/4False)
4True
Which motor neuronal pathways excite the antigravity muscles
Reticulospinal tracts
Vestibulospinal tracts
Rubrospinal tracts
Tectospinal tracts
Reticulospinal tracts and Vestibulospinal tracts
Which motor pathway activates the flexors of the upper extremity?
Reticulospinal tracts
Rubrospinal tracts
Tectospinal tracts
Vestibulospinal tracts
None of the above
Rubrospinal tracts
The lateral premotor cortex is involved in:
Sensorimotor integration
Fine control of individual muscle movement
Initiating and coordinating internally generated movements
None of the above
Sensorimotor integration
A patient with decorticate rigidity has a lesion located:
Above the red nucleus
Below the red nucleus
Above the red nucleus
Your 65 year old patient is unable to close their mouth or smile on the left side of their face. They are able to raise their eyebrows and close their eyelids bilaterally. What structure has been lesioned?
Facial motor nucleus on the left side
CN VII on the left side
Corticobulbar tracts on the right side
Corticospinal tracts on the left side
None of the above
Corticobulbar tracts on the right side
Your 23 year old patient's tongue deviates to the right when protruded. You inspect the surface of the tongue and note that there is NO atrophy of the tongue muscles. What structure has been damaged?
Hypoglossal nucleus on the right
Hypoglossal nucleus on the left
Corticobulbar tracts on the left
Corticospinal tracts on the right
None of the above
Corticobulbar tracts on the left