(A) Unit 1: European Exploration and Conquest (1450-1650)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Departure of Columbus
August 3rd 1492
Reason for departure of the Europeans.
They wished to spread Christianity (approved by Rome), gain direct access to valued goods such as spices and silk’s, and wished to spread the recent crusader spirit.
Conquistadors
Spanish for “Conquerors”; armed Spaniards such as Hernan Cortes and Francisco Pizarro who sought to conquer people and territories in the New World for the Spanish crown. In exchange for there loyalty towards the crown, they would receive titles and land deeds.
Renaissance
The change of European Ideals marked by the ability to interact with classical texts, such as those of Pythagoras. It was greatly shaped by Humanism. The belief that the end of all humans is within themselves. Covering the 15th and 16th centuries, as the Renaissance gave the Europeans the wish to expand and learn new knowledge, it helped thrive the wish to explore for a new trade route to Asia, and to explore the new north American people.
Humanism
The idea that human beings are the end to themselves.
The Travels of Sir John Mandeville
A first-hand account of a travelers journey into ancient middle east, as well as India and China. Documents such as these impacted the Europeans to have a desire to set voyage.
Caravel
A small, maneuverable, two- or three-masted sailing ship developed by the Portuguese in the fifteenth century that gave them a distinct advantage in exploration or trade.
Ptolemy’s Geography
A second century-A.D. work that synthesized the classical knowledge of geography and introduced the concepts of longitude and latitude. Reintroduced to the Europeans about 1410 by Arab Scholars, its ideas allowed cartographers to create more accurate maps. It also mis-represented the size of the earth and depicted the length from europe to asia as far smaller then it actually is.
“dead reckoning.”
A method of travel by using a compass, and estimated length of time to travel over a distance, to help set voyages and determine courses.
Astrolabe
A special tool which was invented by the ancient Greeks to determine the position of the stars and other celestial bodies. It helped those at sea by allowing them to understand their latitude, by understanding the latitude of a polestar or the sun, and then consulting a chart with positions of these celestial bodies to help understand where they were at.
1454 Papal Bull decree of Pope Nicholas V
This decree stated that the Portuguese Empire had the right to conquer and enslave non-Christians and recognizing Portuguese possession of the territories in Africa.
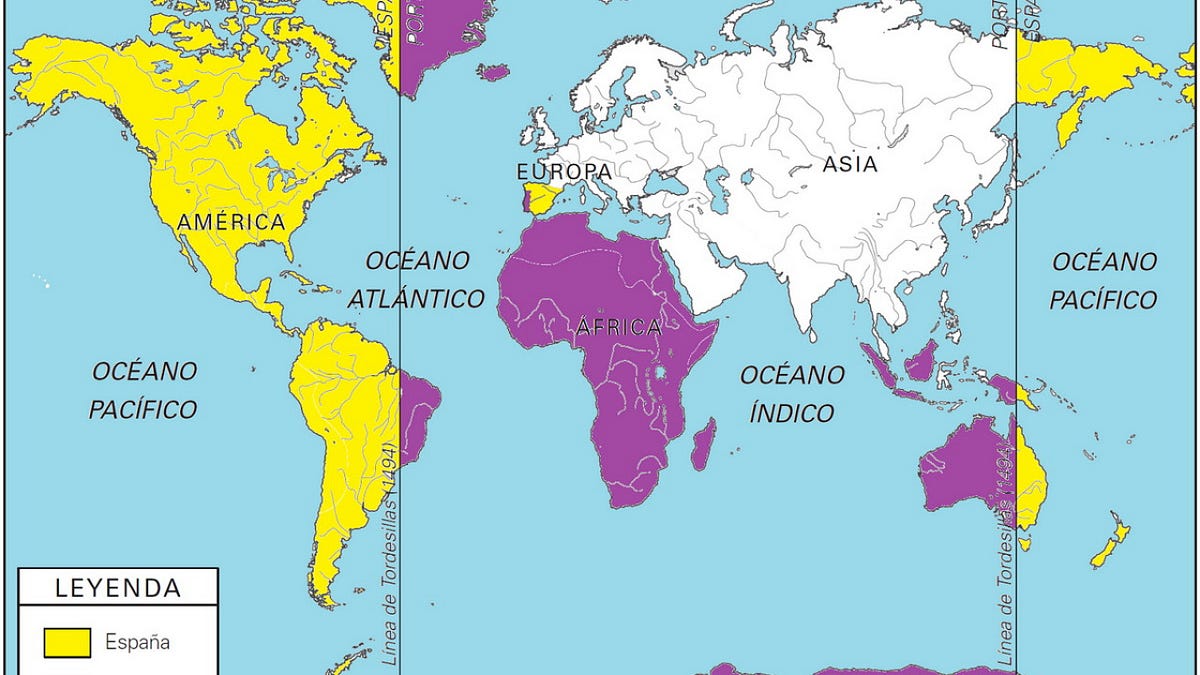
Treaty of Tordesillas
A treaty created in 1494 used to help settle disputes between Spain and Portugal about the new world, by giving Spain everything west of the imaginary line and Portugal everything east.
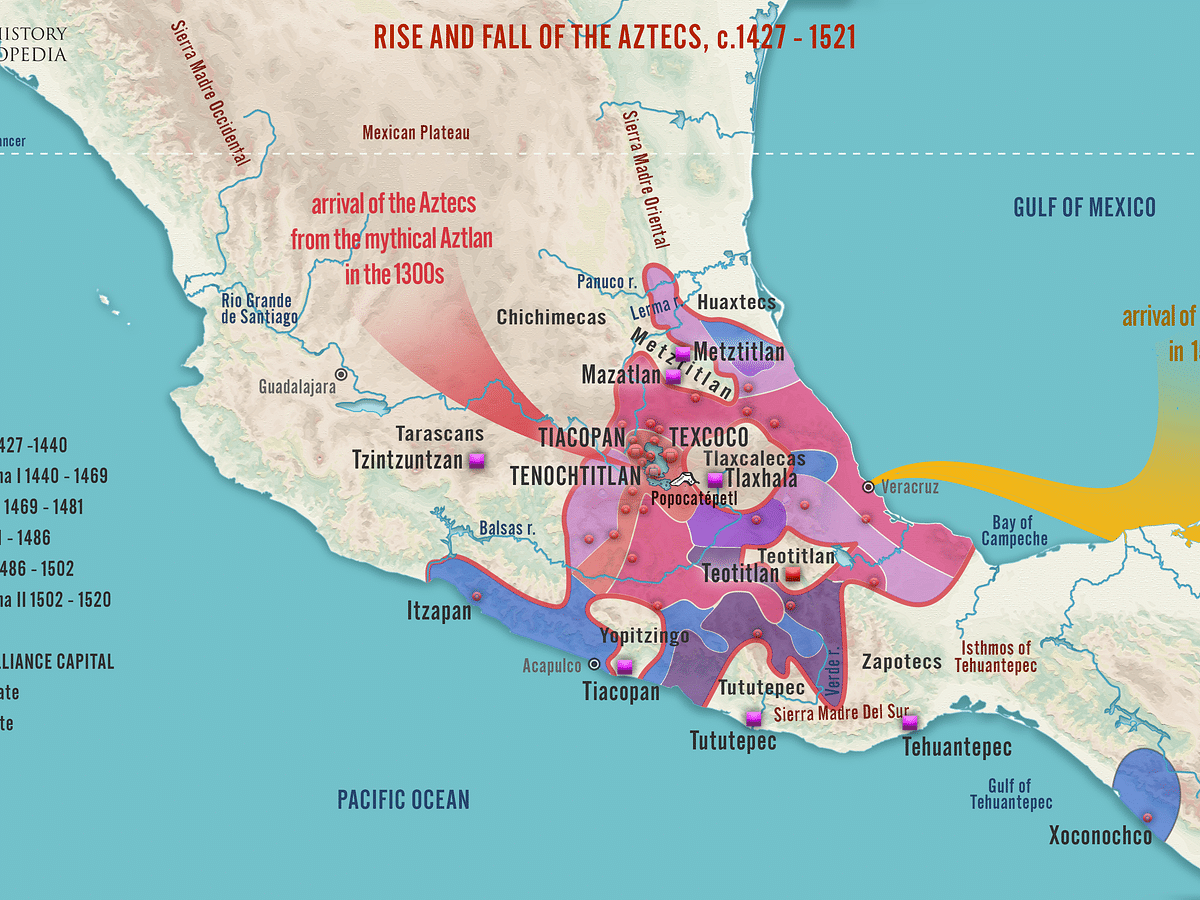
Aztec Empire
A large and complex Native American civilization in modern Mexico and central America which possessed advanced mathematical, astronomical, and engineering technology.
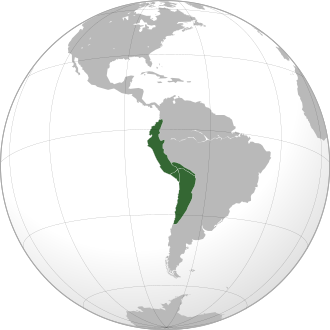
Inca Empire
The vast and sophisticated Peruvian empire centered at the capital city of Cuzco that was at its peak from 1438 till 1533.
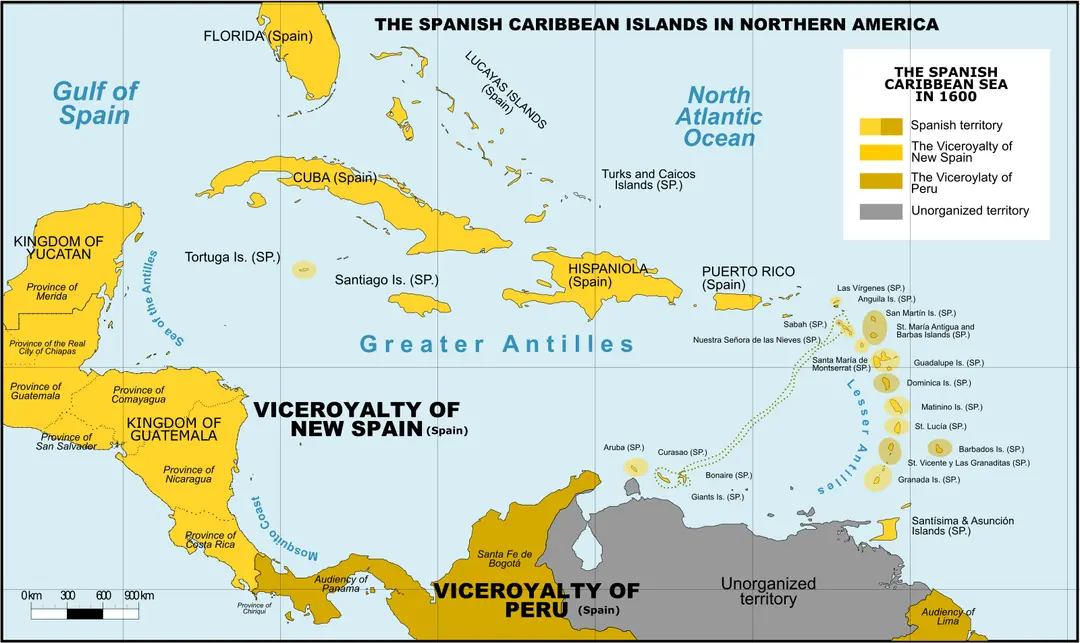
Viceroyalties
The name for the four administrative units of Spanish possessions in the Americas: New Spain, Peru, New Granda, La Plata
Encomienda system
A system whereby the Spanish Crown granted the conquerors the right to forcibly employ groups of Native Americans in exchange for providing food, shelter, and Christian Teaching.
Columbian Exchanged
The exchange of diseases, animals,a nd plants between the Old and New worlds, named after Christopher COlumbus who initated this contact.