OPT 246: Midterm 2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Does HSV elevate IOP?
Can cause these that raise IOP:
1) Uveitis
2) Stromal disease
**Not in first episode
**Not diagnostic
HSV Treatment
1) Topical antiviral (HZ and HSV dose same):
- Trifluridine 1% q2h (until ulcer heals), then QID x 7d, do not excess 9 drops/day
- Ganciclovir 0.15% 5x/day (until ulcer heals), then TID x 7d
2) Oral Antiviral:
- (400mg Acyclovir 5x/day x 10d)
- 800mg Acyclovir 5x/day x 10d
Other Antivirals
1) Famciclovir (Famvir)
- 500mg TID x 10d
2) Valacyclovir (Valtrex)
- 1000mg TID x 10d
3) Acyclovir
- 800mg 5x/day x 10d
Contraindications of using Zoster dose for HSV?
Zoster dose = 2x Simplex dose
- Pregnancy risk category B
- Drug interactions
- Side effects
- Metabolized and excreted in kidneys
Antivirals Contraindications
- Increased risk of CNS adverse effects elderly:
- Acyclovir and Valacyclovir
--> Agitation, hallucination, confusion at higher doses
- Consider Famciclovir instead
- Lactose intolerant --> avoid Acyclovir
- Kidney function
- Acyclovir major side effect: GI upset
How do antivirals work?
- Antivirals work on the virus, NOT the host
- Interfere with viral DNA replication
Treatment for Recurrent cases of HSV
Maintenance dose of antiviral medications:
- Acyclovir 400mg BID
- Valacyclovir 500mg QD
Resistance
- Acyclovir and Trifluridine use the same mechanism , therefore NOT additive
Fluoroquinolones in Bacteria
HSV uses Topoisomerase II, so fluoroquinolones effective against HSV
When to use topical fluoroquinolones for HSV?
--> Adjunctive therapy only (never alone)
When primary antiviral is:
- Slowly to work
- Persistent lesion
- Pt knows they don't get better without it
- Immune-compromised patients
Take Home Points: HSV
- Diagnostic Pearls: upper lid edema, corneal edema disproportionate to lesion
- Rose Bengal staining
- Zirgan less toxic, but more expensive
- 800 mg Acyclovir 5x/day for keratitis far more effective than 400mg
- Consider adding Fluroquinolones if slower response to treatment that suggests resistance
Tx example for HSV Keratitis
- 800mg Acyclovir 5x/day x 10d
- Zirgan 5x/day until ulcer heals, then TID x 7d
- Pain management?
- Ex: Ibuprofen 600mg q4-6h PRN for pain, do not exceed 3200mg/day
- RTC 7 days or sooner PRN
**Do not write "until ulcer heals" on sig
Tx example for Adenovirus with infiltrates
- If acuity still good, no steroid treatment indicated
- Consider Betadine treatment
- Artificial tears
- Council pt on hygiene
- RTC 1 week
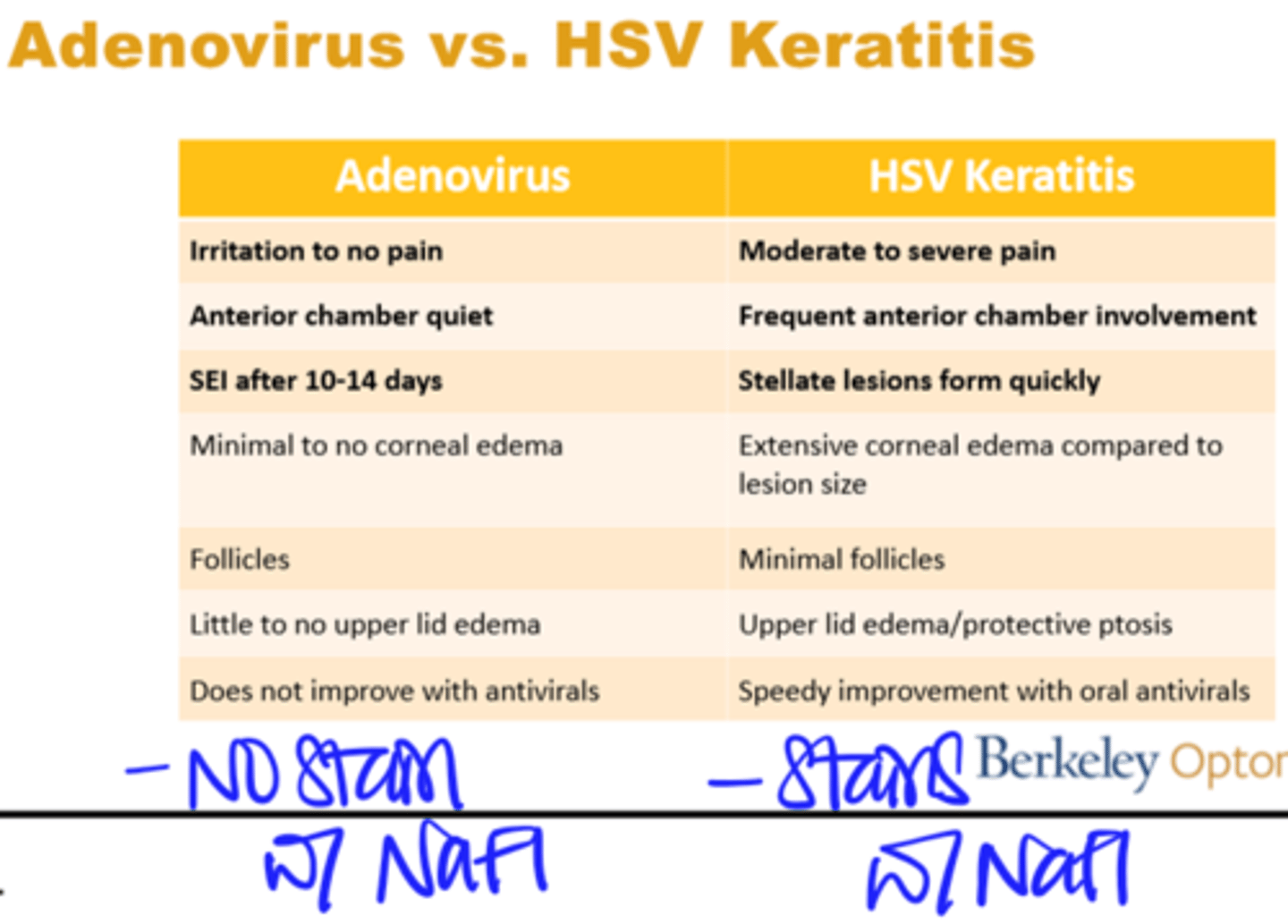
Adenovirus vs. HSV Keratitis
HSV Keratitis patient education example
- HSV Keratitis is when you have a virus attacking the clear surface of your eye so that's why it hurts.
- Infection on front surface of eye
- Everyone has this virus in them but this became active
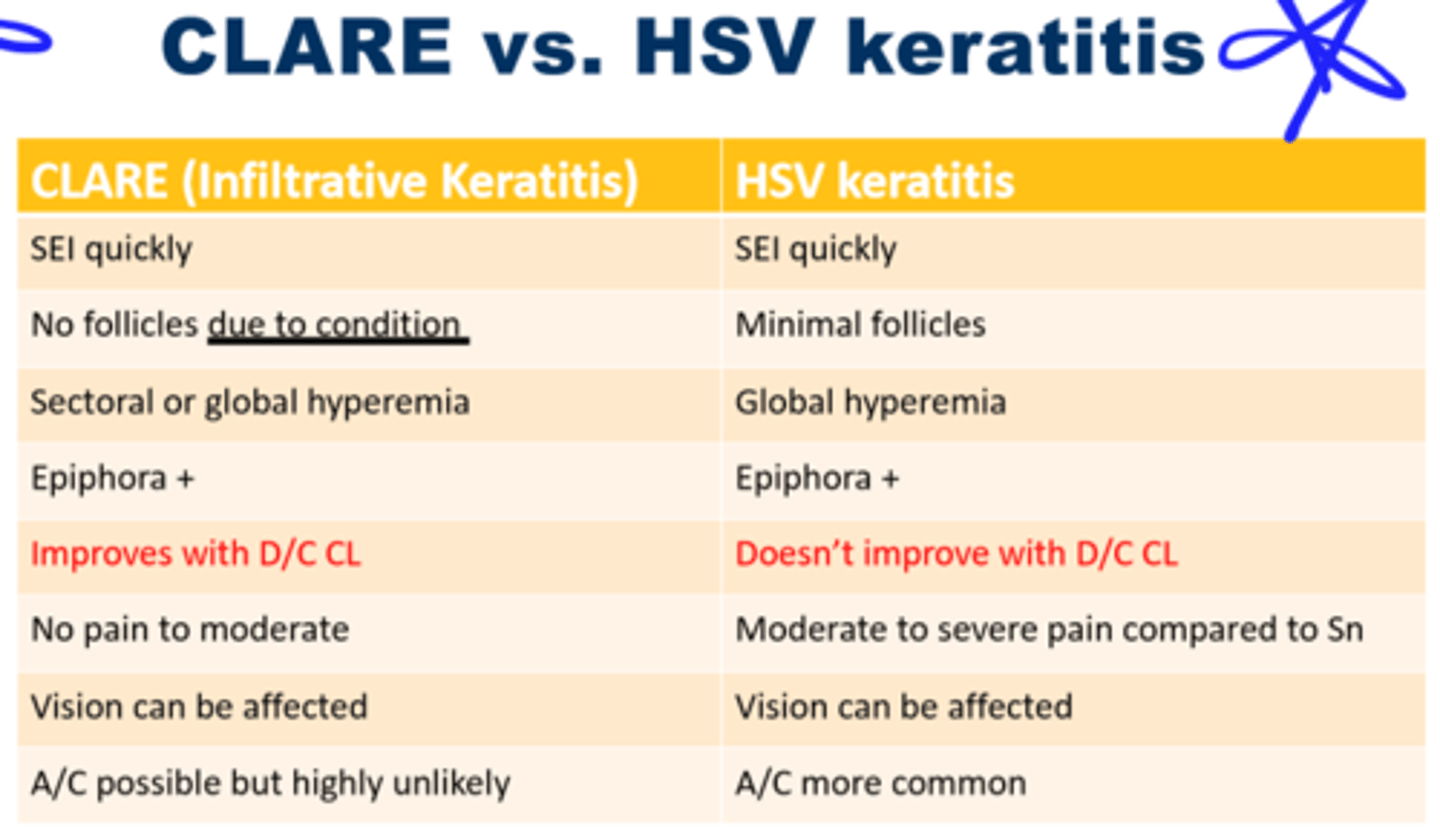
CLARE vs. HSV Keratitis
Tx example for Corneal abrasion
- Tobramycin QID
- No BCL
- Ibuprofen for PRN as needed
- RTC 24h
RCE vs. HSV Keratitis
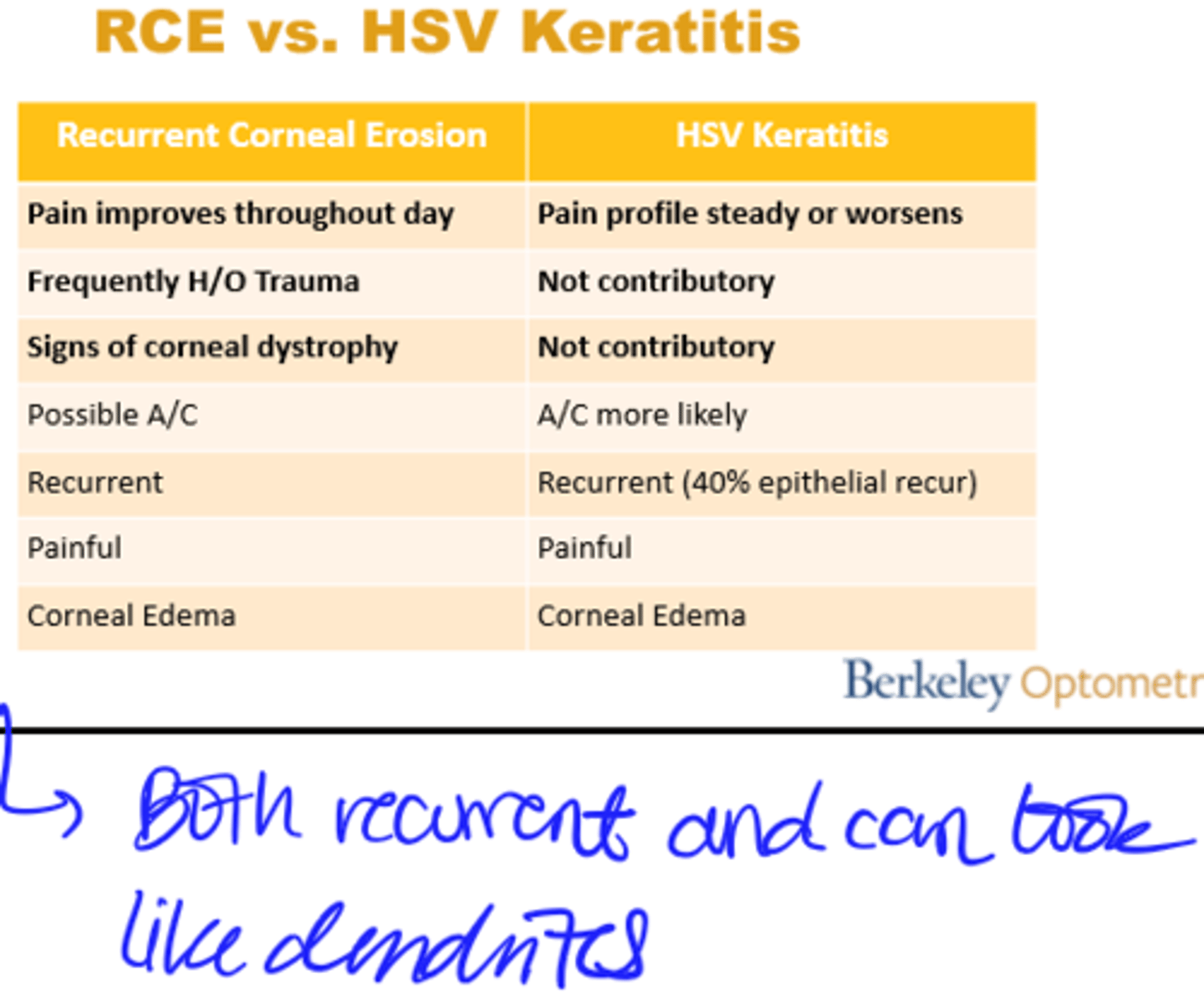
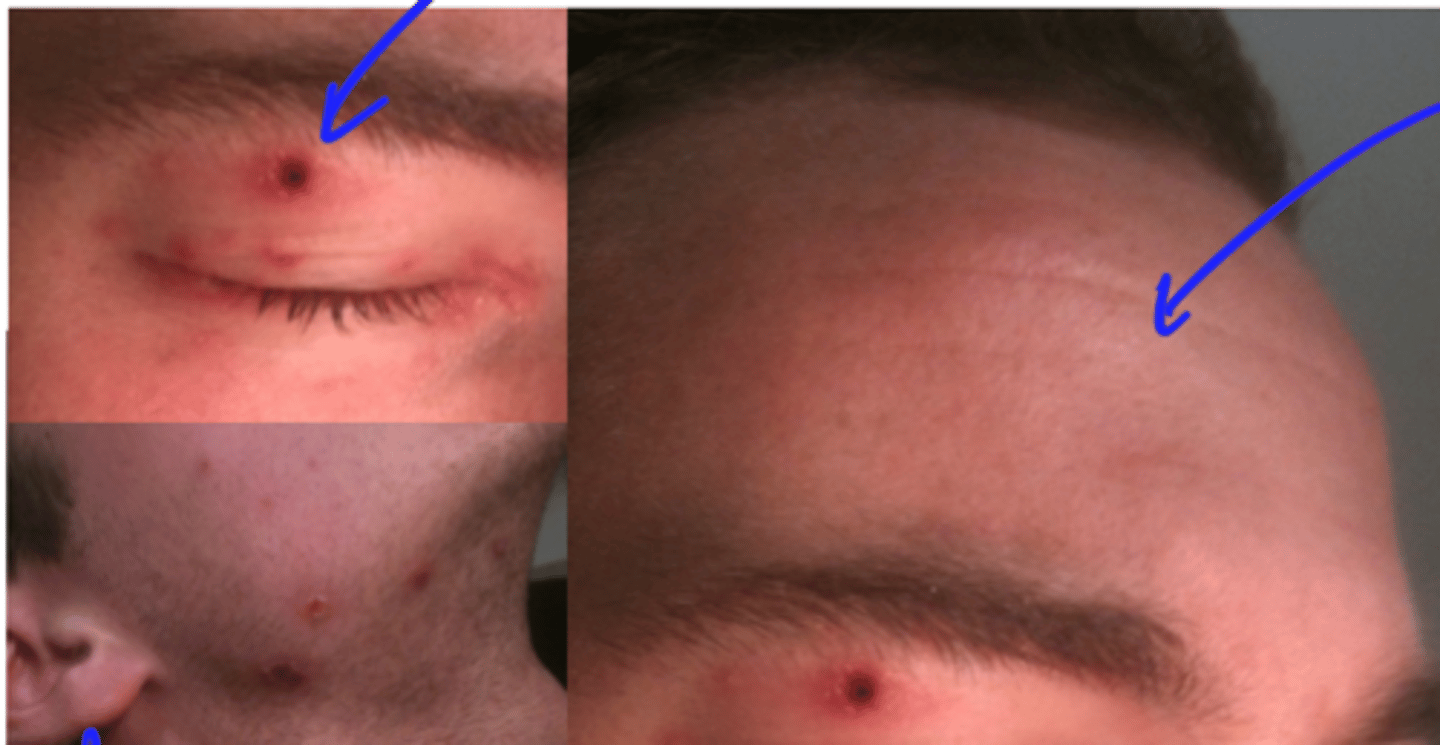
Image: Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
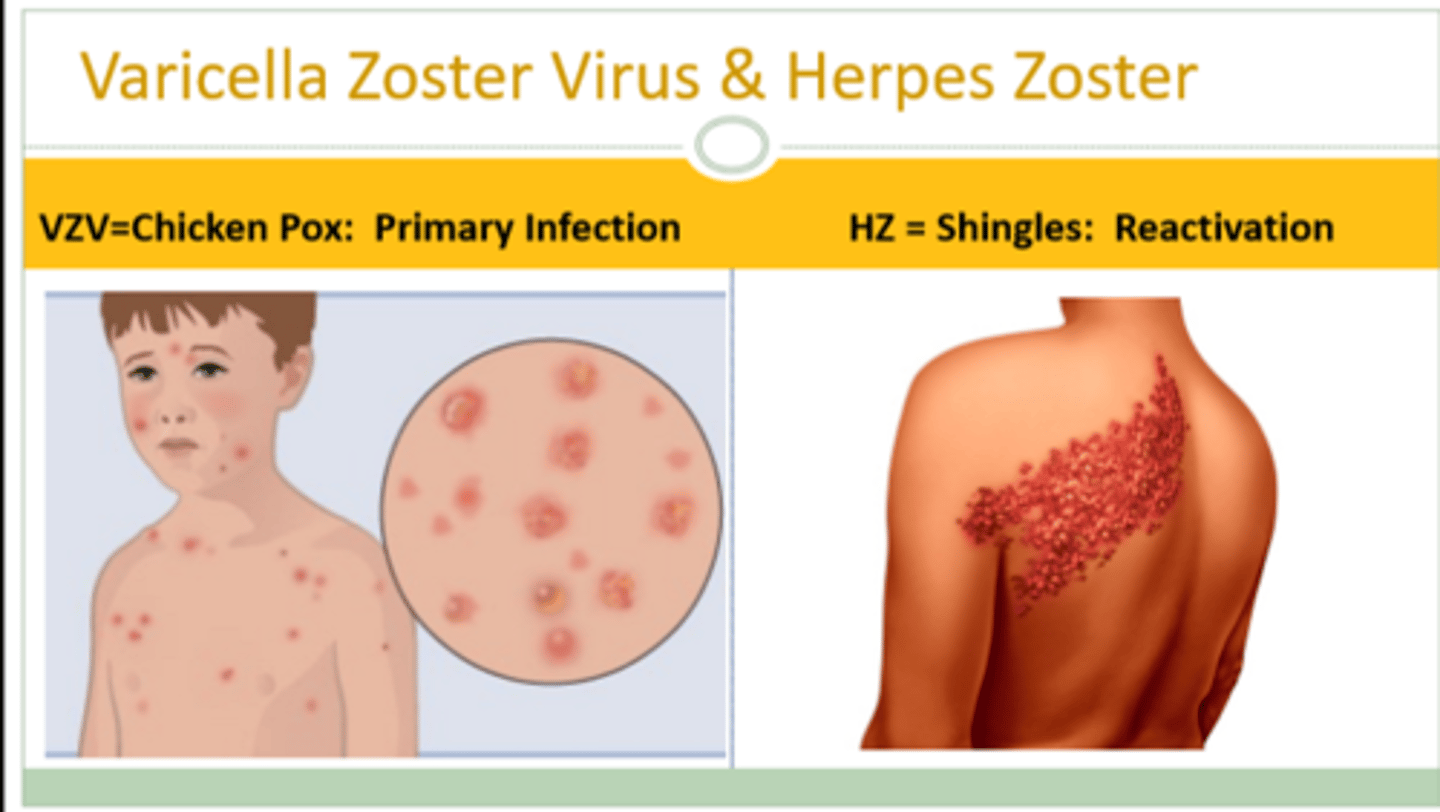
VZV vs. HZ
R0
R0 = Rho Naught or Rho Zero
- Expected number of cases directly generated by one case
Affected by:
- Duration of contagiousness
- Likelihood of transmission
- Contact rate
- Airborne vs. bodily fluid transmission
- Population density
- Cultural differences

Varivax Vaccine again VZV
- Live-attenuated virus, immunocompetent patients only
- 2 doses
- Subcutaneous
- Decrease in # of deaths
- Establishes latency in sensory ganglia
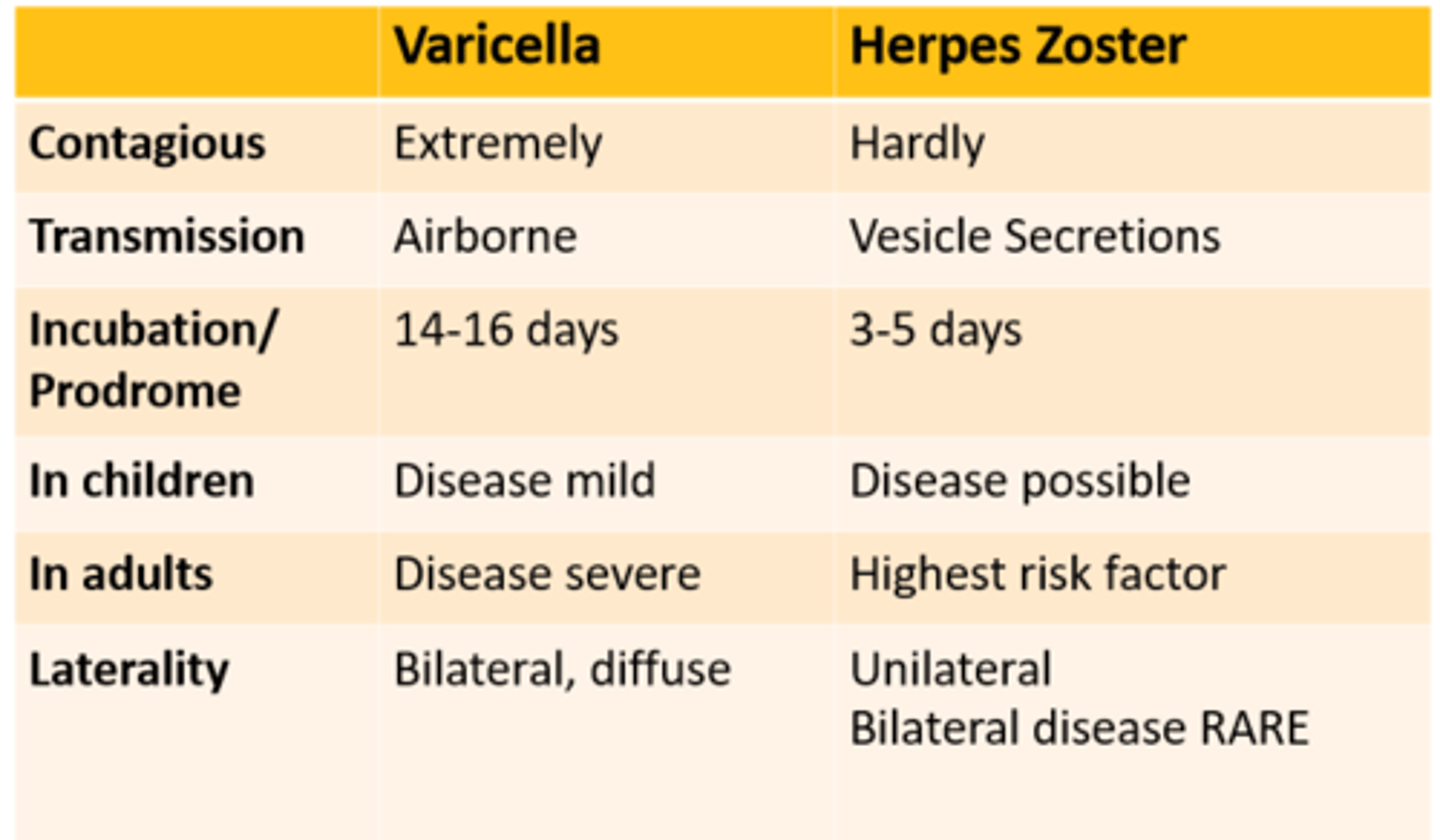
Varicella vs. Herpes Zoster
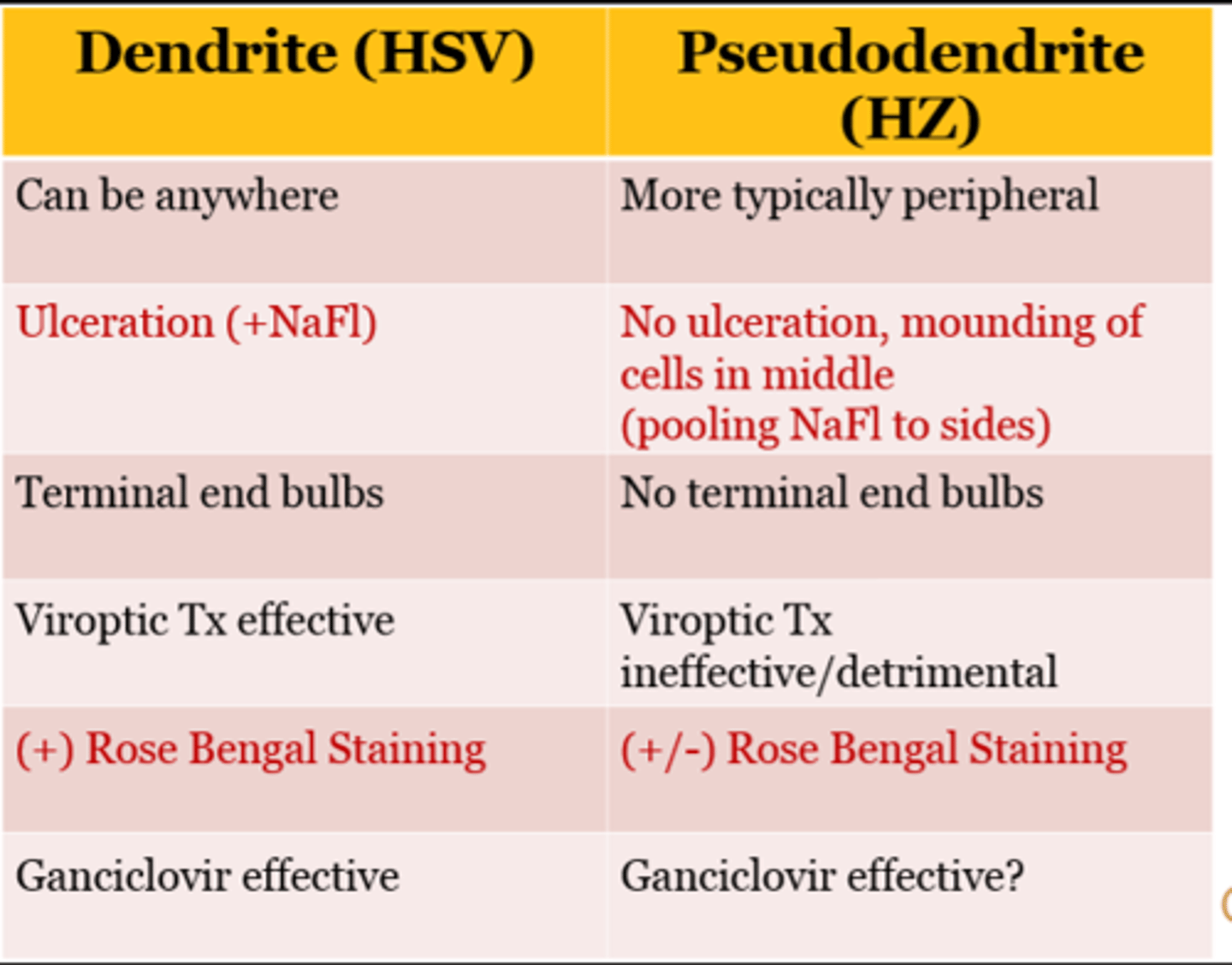
Dendrite (HSV) vs. Pseudodendrite (HZ)
Treatment of HZ
Treatment of HZ:
1) Pain management
- NSAID, Acetaminophen
2) Antiviral (pick one)
- Acylovir (400/800mg 5x/day)
--> Give Zoster dose even for Simplex cases (800mg Acyclovir)
- Valacyclovir 1000mg TID
- Famicyclovir 500mg TID
**Better if start antiviral medication within 3 days of rash (not prodrome)
3) Cimetidine? (OTC)
- H2 blocker for gastric ulcers
Herpes Zoster Take-Home Points
- Older age still the primary risk factor for HZ
- No therapeutic benefits of other antivirals over Acyclovir
- Patient's risk for HZ is dependent on their vaccine status
- Vaccine strain HZ will probably be much less common and less severe
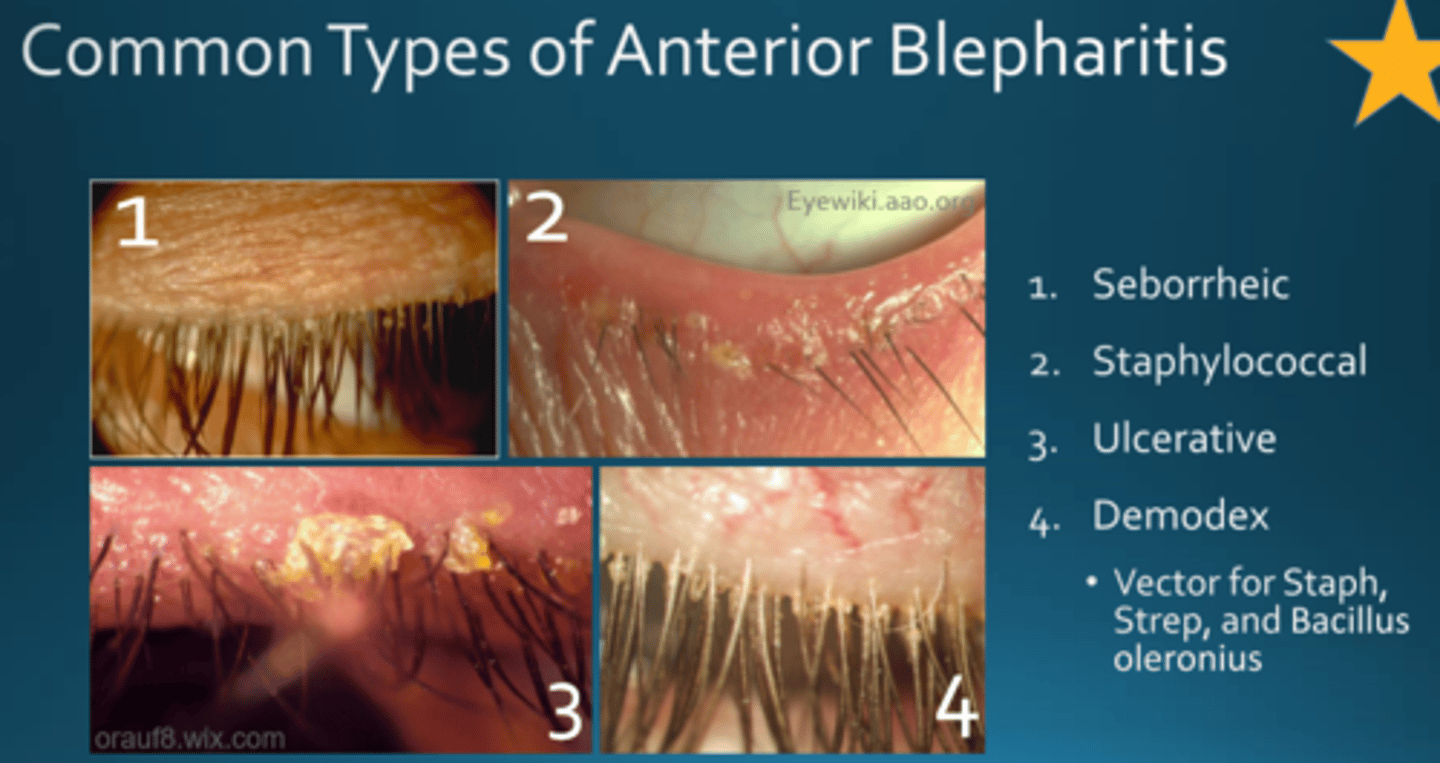
Types of Anterior Blepharitis
1) Seborrheic
2) Staphylococcal
3) Ulcerative
4) Demodex
- Vector for staph, strep, and Bacillus oleronius
Demodex
- 100% on body by age 70
- Considered normal skin fauna
- Presence ≠ Sn/Sx
- Demodicosis = exacerbation to pathology (+) Sn/Sx
Demodex mite
- Most common ecto-parasite in humans
- Two species live on the human body:
- Demodex folliculorum
- Demodex brevis
- Life cycle: egg to adult ~14-18 days
- Mobile during dark of the night
- Invisible to naked eye
Demodex diet
- Epithelial cells (secrete digestive enzymes to break down cells)
- Hormones
- Oils
Diet = oil, skin cells, hormones
Cylindrical dandruff
Composition under debate:
- Termite mound
- Excrement
- Keratin
- Lipids
- Decaying mites
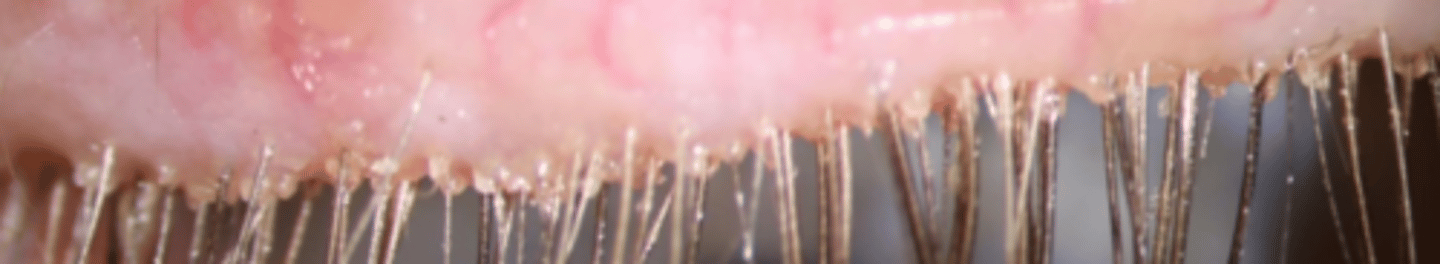
Where Demodex call home
1) Pilosebaceous glands
- All over our body
- Not on our palms or soles
- Lots on face
- Zeis in eyelash follicles (folliculorum)
2) Sebaceous glands
- Often located near mucous membranes
- Meibomian glands
Demodex Transmission
1) Direct contact
- Hair, eyebrows, sebaceous glands on nose
- Lifespan limited outside living body --> die
- Young pediatric cases rare
- Low sebum production <5yo
Grading Demodex Blepharitis
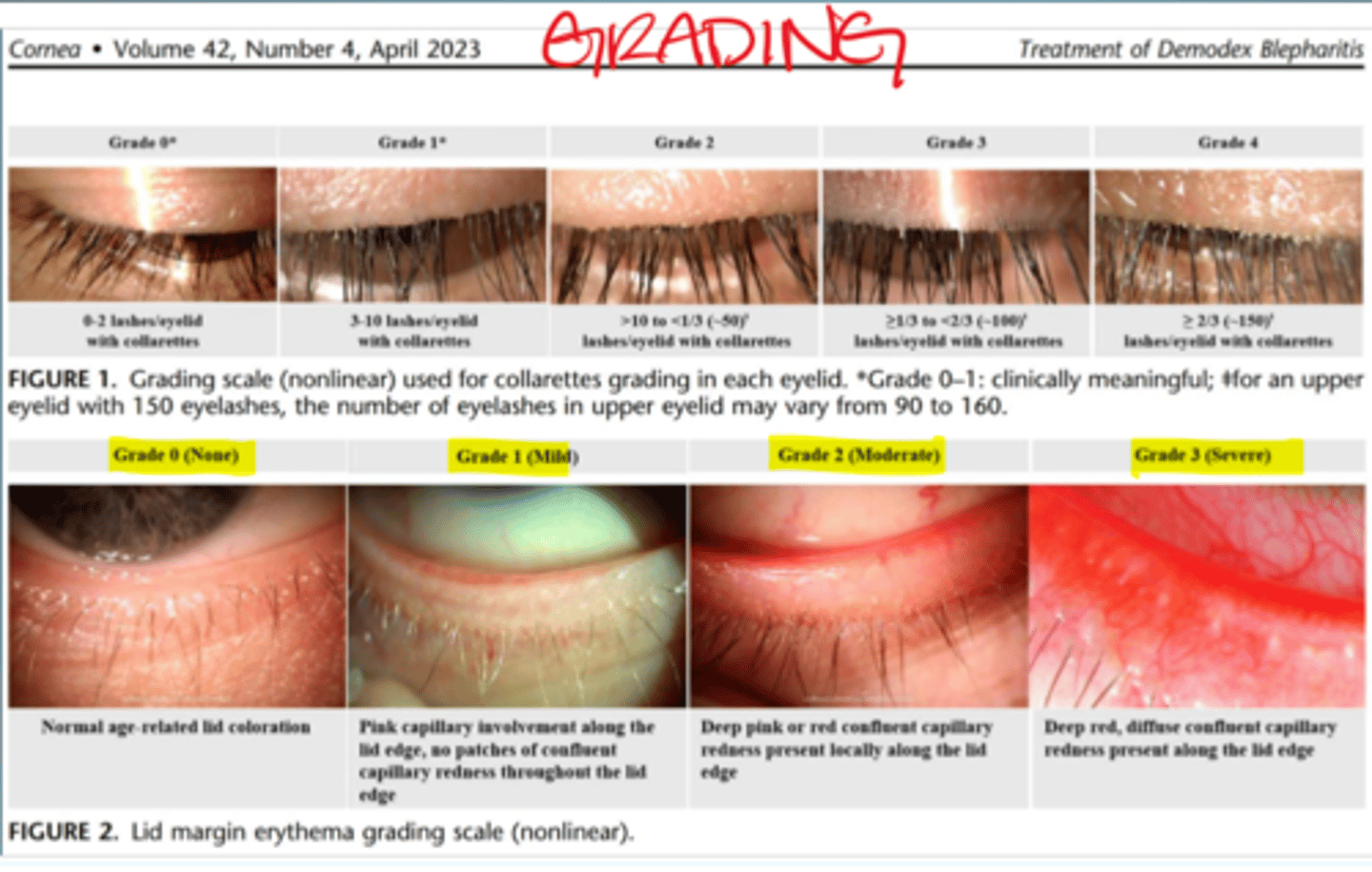
Demodex Treatment
1) Patient Consultation
2) Pre-Tx Grading/Photos
3) Kill Demodex
4) Maintenance
Demodex Tx (killing demodex)
- Tx needs to penetrate follicle (In-office debridement, demo at-home lid hygiene)
- Tea tree oil adjunct therapy (wipes, cleansers)
--> Kills demodex with minimal SEs
--> High concentrations TTO = ocular surface toxicity
- Lotilaner (XDEMXY) - new treatment
- Avoid oil-based products (moisturizers, sunscreen, makeup removers)
- TTO face wash BID and after sweating
Exfoliate skin q2-3 days
- TTO shampoo if cannot shave beard
Demodex Blepharitis Clinical Pearls
Consider Demodicosis if:
- Any irritation
- CL discomfort or dropout
- Cylindrical dandruff/collarettes
(+) CD --> Demodex present
(-) CD with Sx --> Demodex still possible
Presence of Demodex ≠ Demodicosis
- Tx PRN
- Easier with Lotilaner
- Consider family members
- Encourage your patient to get through 1st week of TTO cleanser
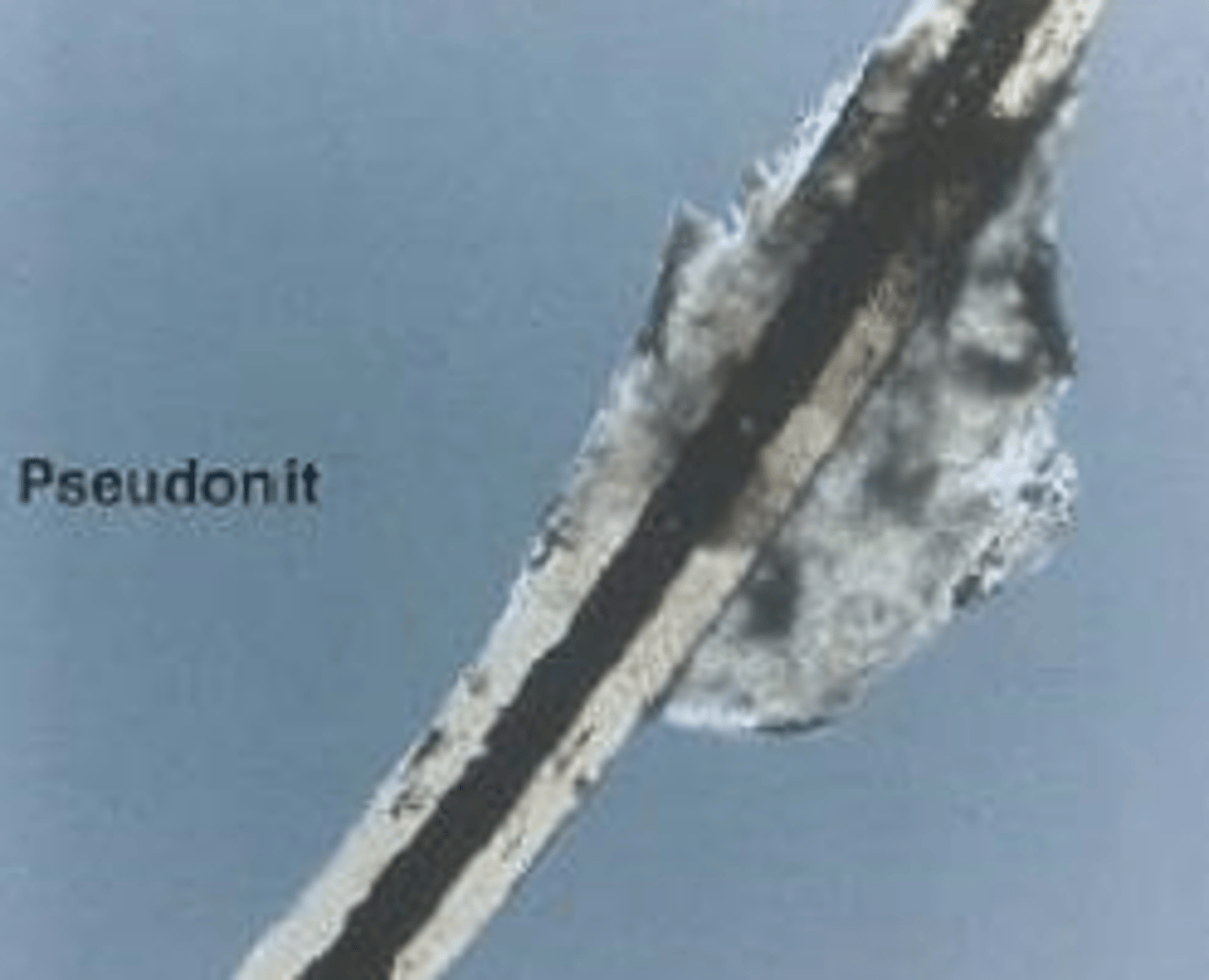
Nit vs. Pseudonit
Nit:
- Egg of Phthiriasis Pubis
- Cemented 1-2mm from lash base
- Cap with air holes
- Mimics blepharitis debris
Pseudonit:
- Blepharitis debris
- Makeup debris
- Hair casts
- Pseudonits will move when manipulated! (vs. a nit will be cemented and not move)

P. pubis Take Home Points
- Not always itchy
- Burrow and semitransparent
- No movement when shine bright light on it
- Lids and lashes can appear clean
- Look for waste products on the lids
- Examine eyebrows and facial hair
- Eggs (nits) will not move if you manipulate them
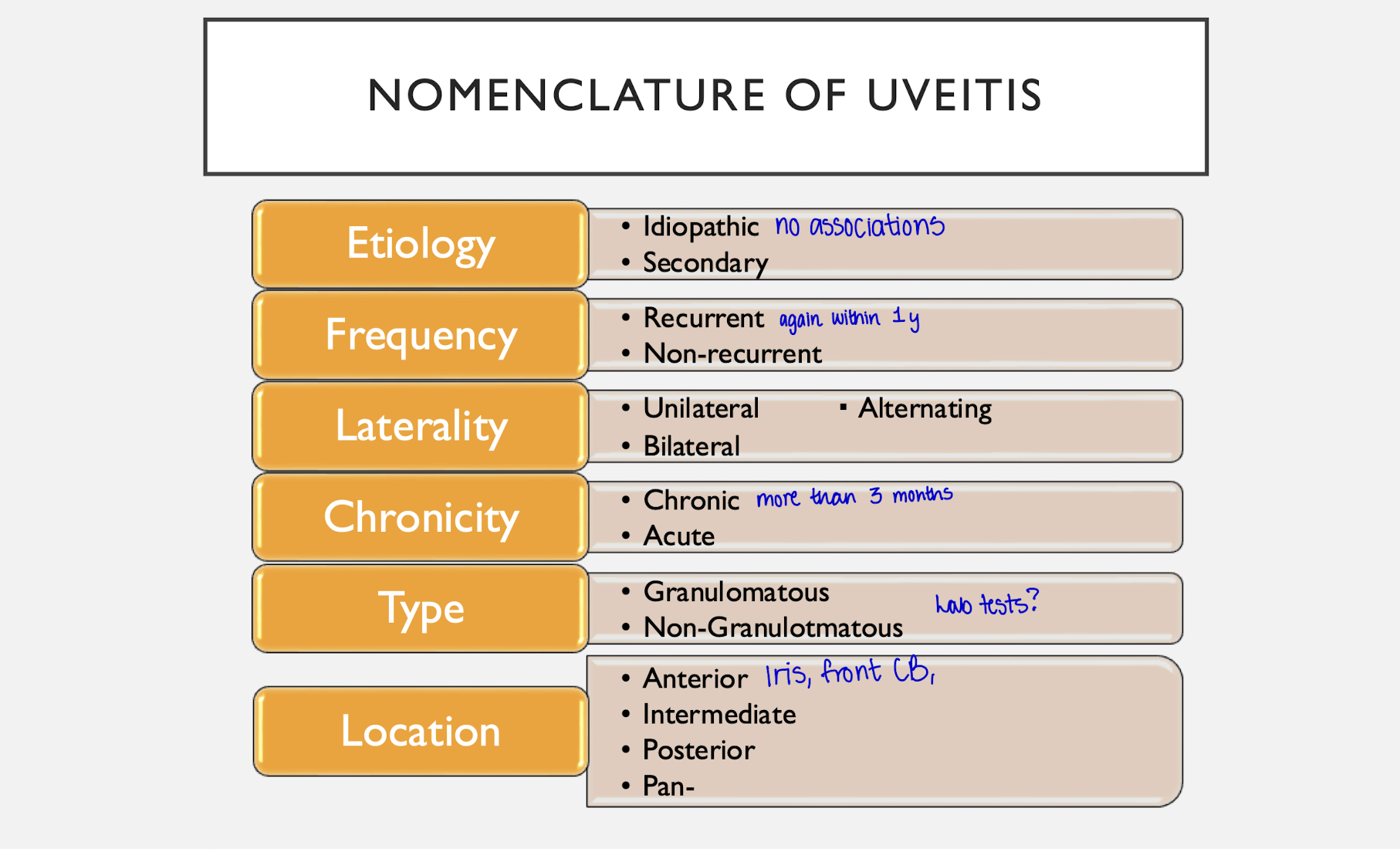
Nomenclature of Uveitis
1) Etiology
- Idiopathic vs. Secondary
2) Frequency
- Recurrent (more than 1x/year)
- Non-recurrent
3) Laterality
- Unilateral vs. Bilateral vs. Alternating
4) Chronicity
- Acute vs. Chronic
5) Type
- Granulomatous vs. Non-Granulomatous
6) Location
- Anterior
- Intermediate
- Posterior
- Pan-
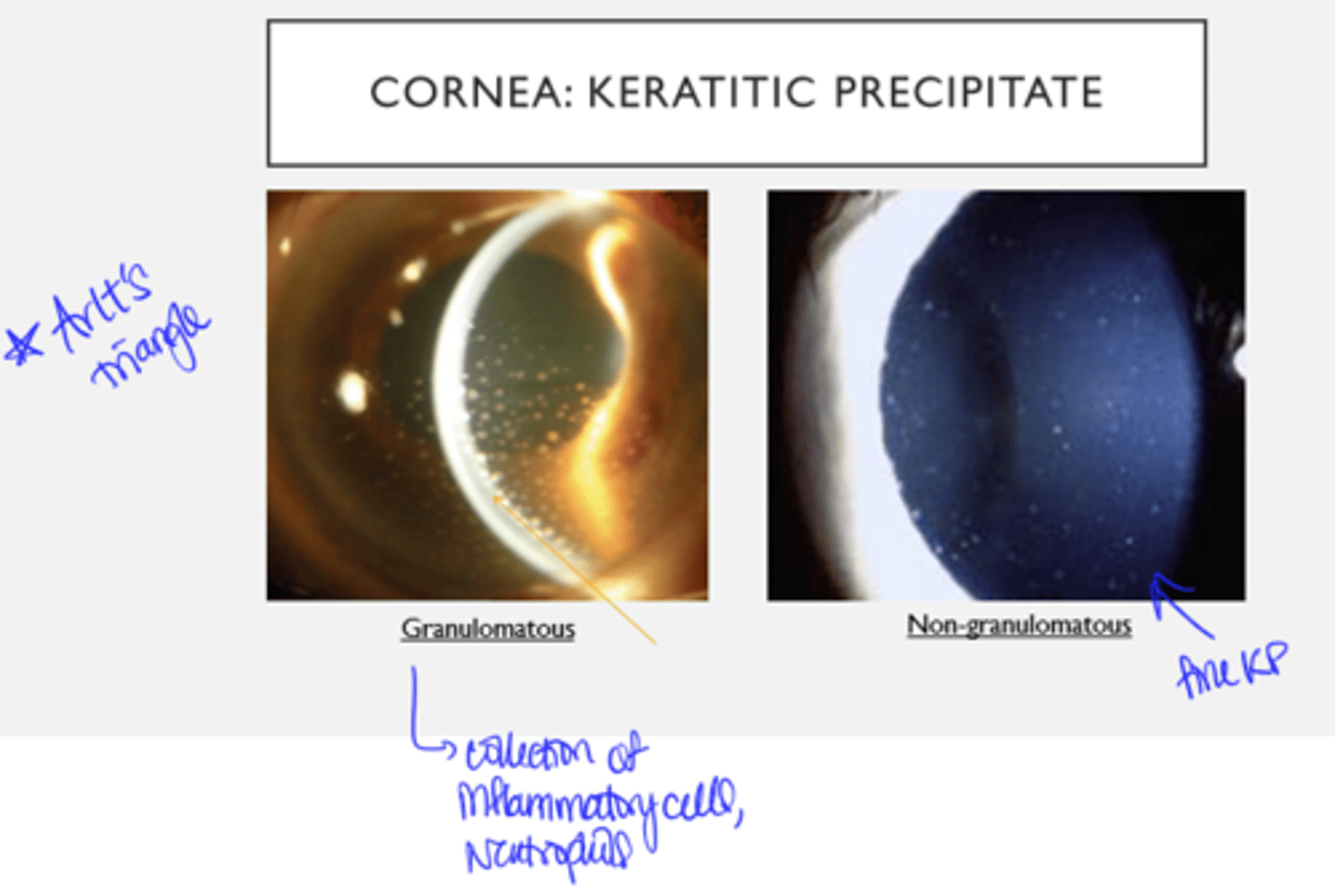
Anterior Uveitis: Keratitic Precipitates - Granulomatous vs. Non-Granulomatous
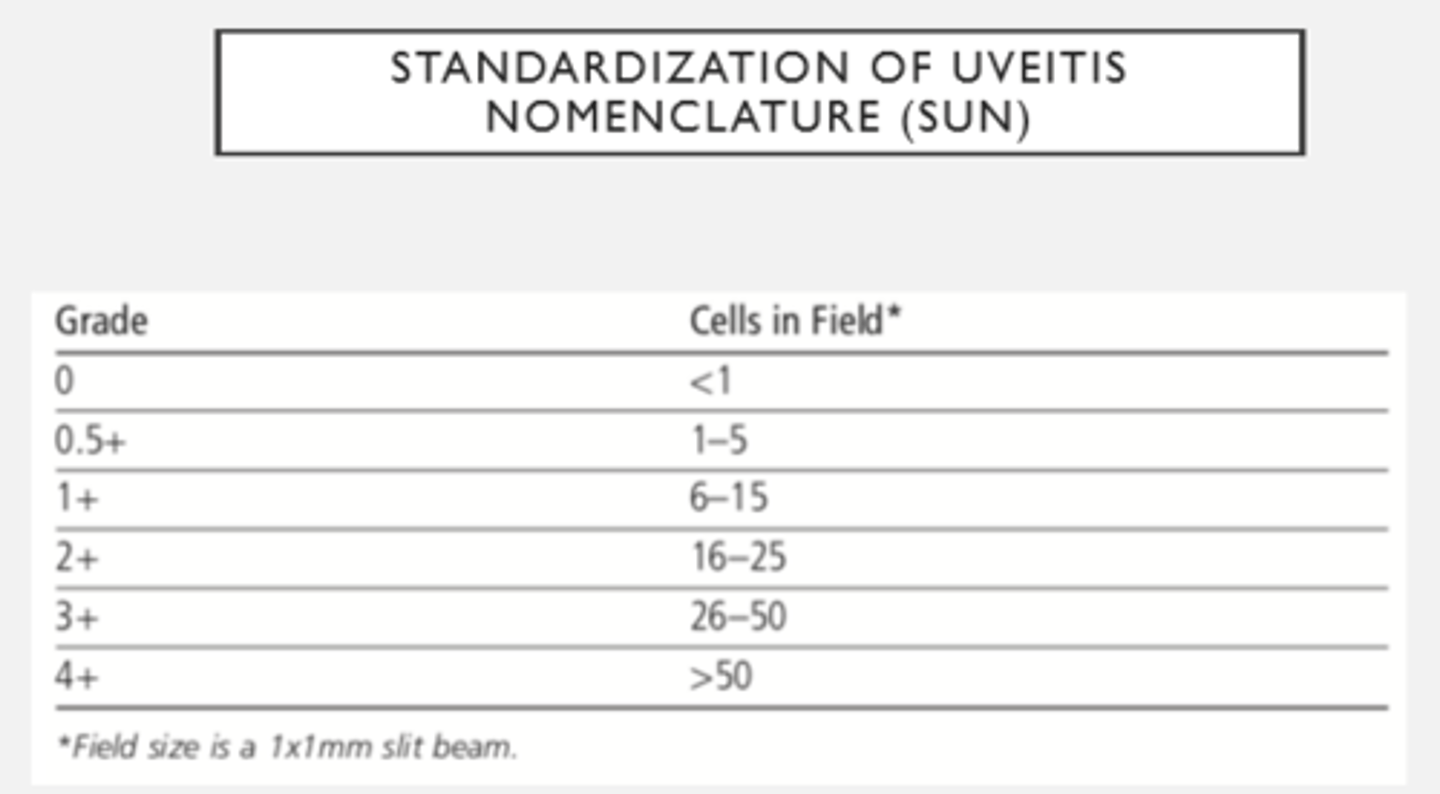
Anterior Uveitis: Anterior chamber reaction (grading cells)
- Flare = protein release --> cloudy
- Uveitis inflammation makes a lot of things leaky
- Ciliary body has blood aqueous barrier that prevents stuff from getting into AC
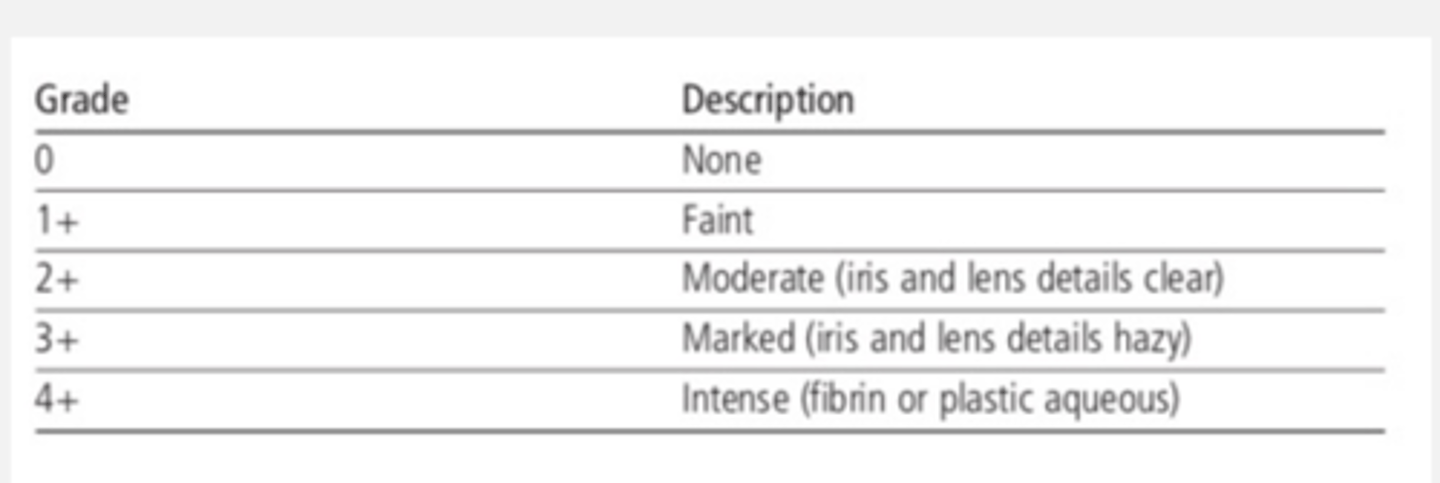
Anterior Uveitis: Anterior chamber reaction (grading flare)
stickiness in angle --> posterior iris synechiae --> angle closure
how much cells move can determine the amount of flare
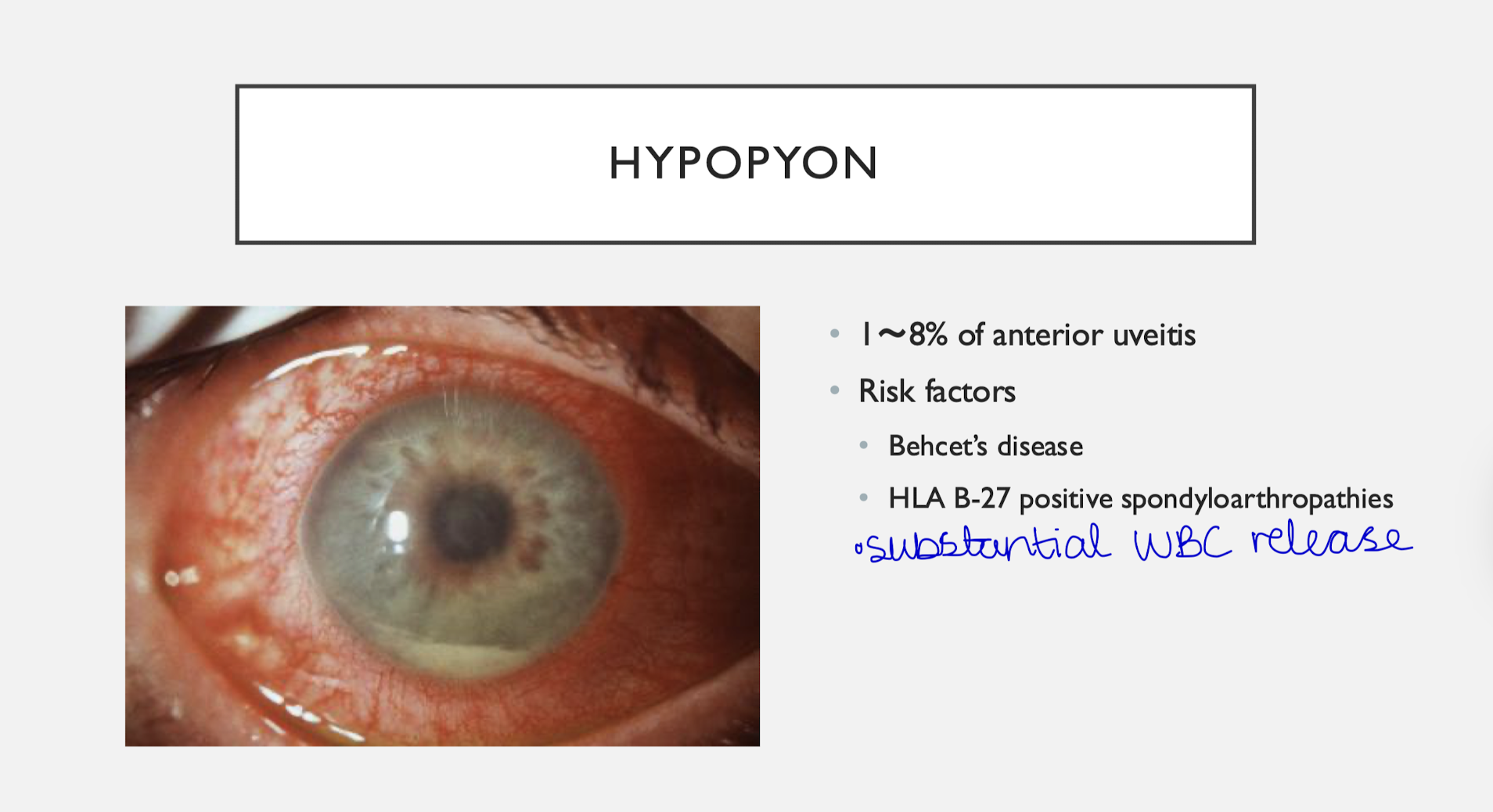
Hypoyon & Uveitis
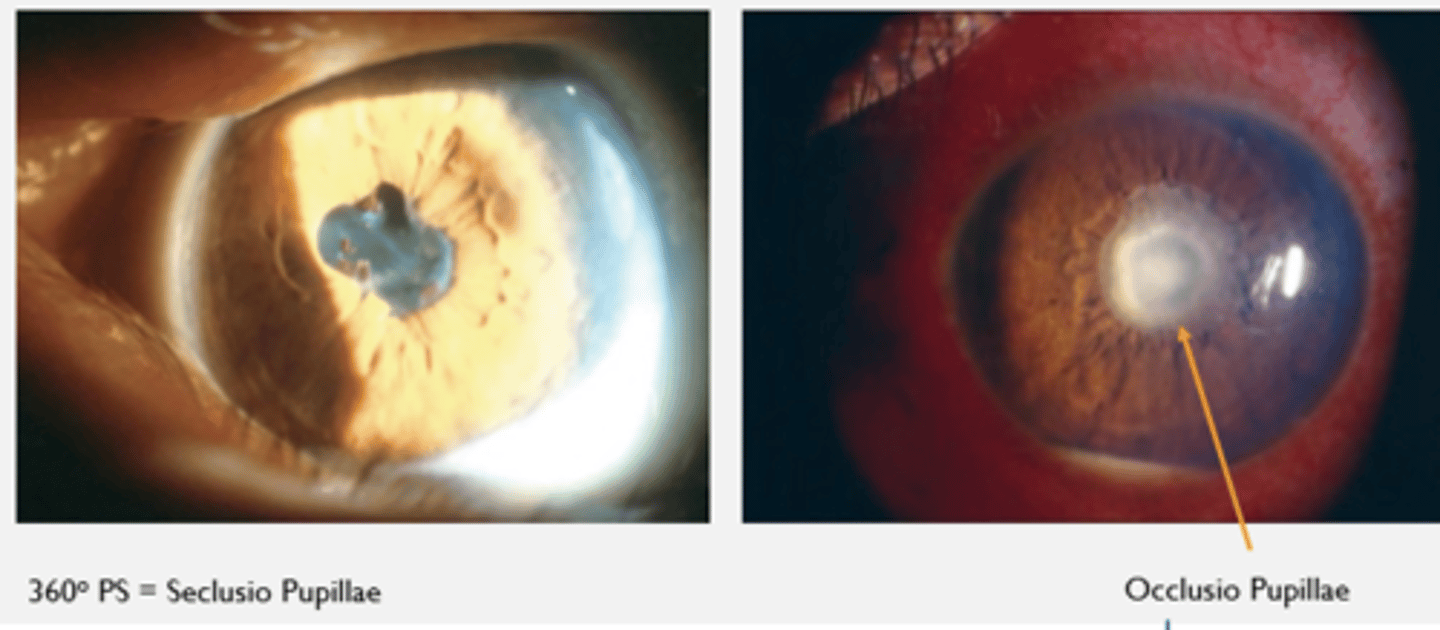
Anterior Uveitis: Posterior Synechiae
--> Too sticky, can interfere with aqueous flow
Seclusio pupillae = 360 posterior synechiae
Occlusio pupillae = collection of fibrous proteins that will melt away with Tx
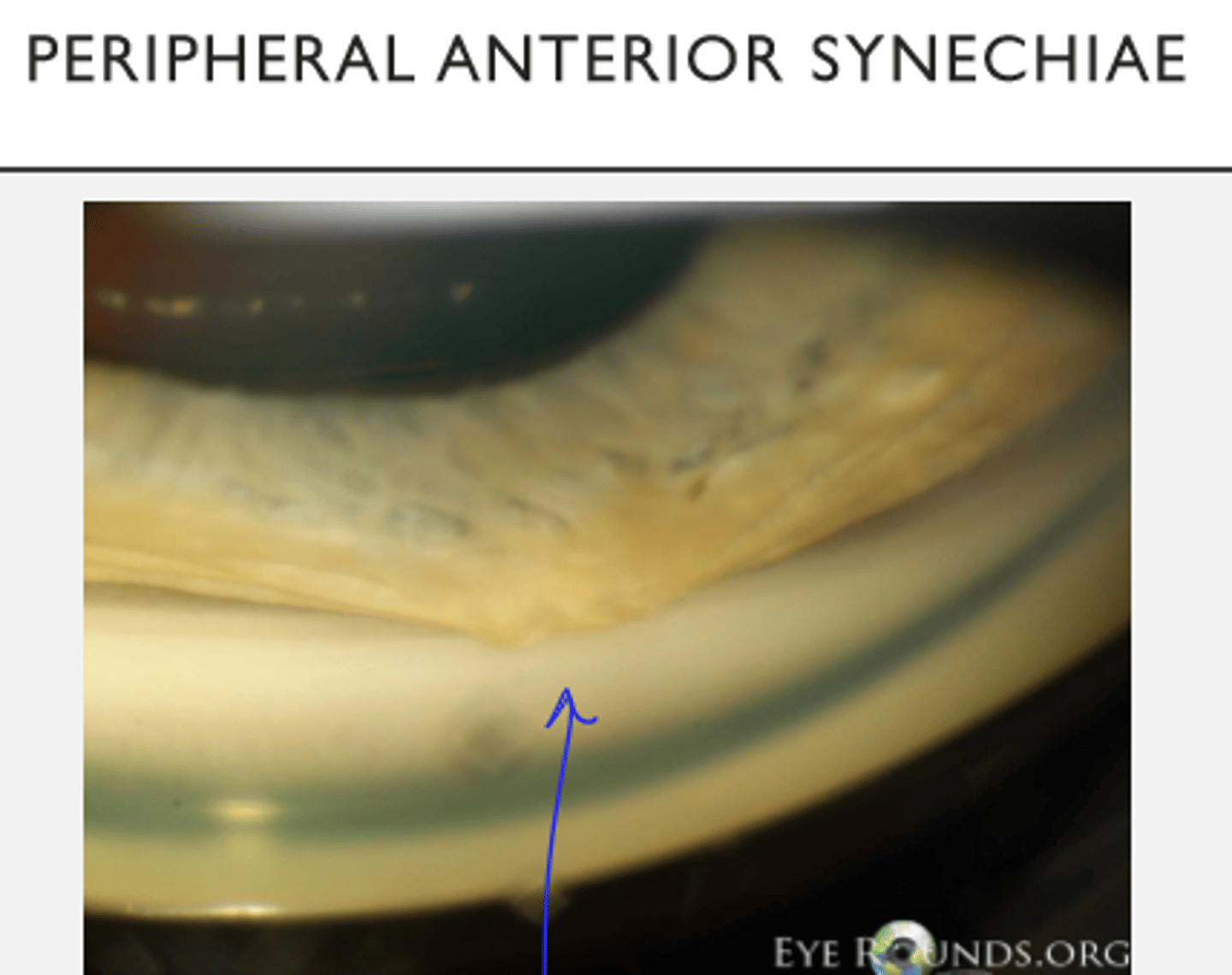
Anterior Uveitis: Peripheral Anterior Synechiae
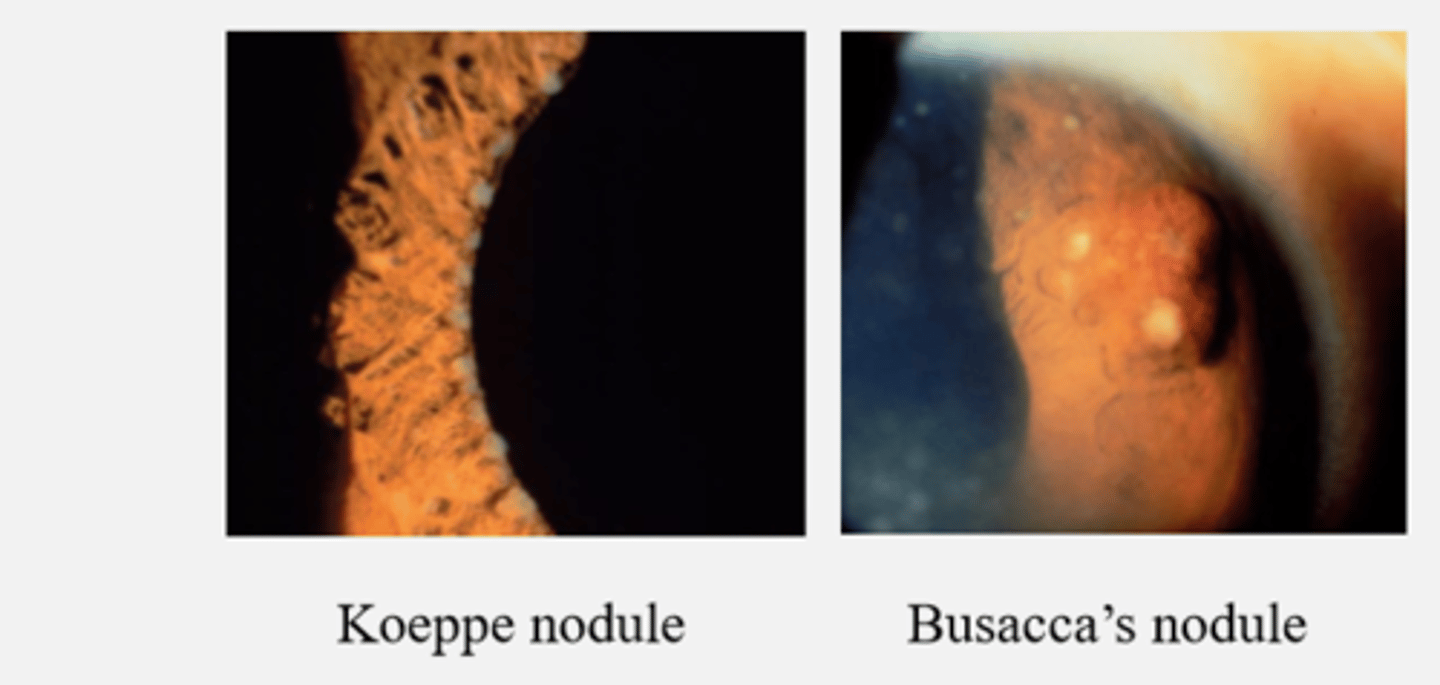
Anterior Uveitis & Iris nodules
- Koeppe nodule
- Busacca’s nodule
Granulomatous/nodules = granulomatous uveitis
Anterior Uveitis features
- Most common form of uveitis
- Most are acute
Associations:
- Idiopathic
- HLA-B27 associated
- Infectious
- Other
- Masquerade syndromes
Anterior Uveitis and Systemic Association features
Likely Systemic Association if:
- Chronic
- Bilateral
- Recurrent
- Granulomatous
- Systemic signs and symptoms
Anterior Uveitis: Systemic Association Granulomatous vs. Non-Granulomatous
Granulomatous:
- KP: mutton fat
- Iris nodule
Non-Granulomatous:
- KP: fine
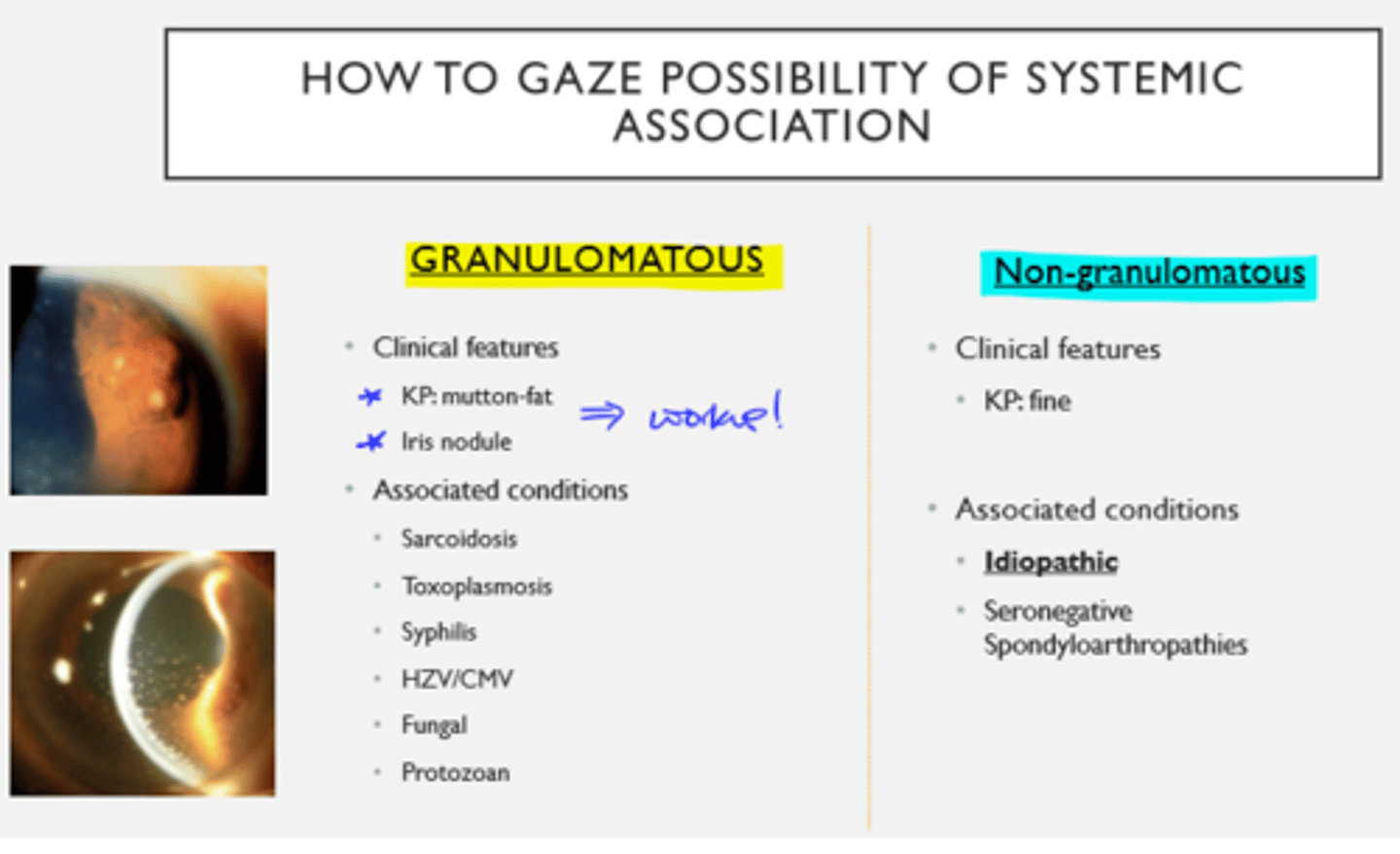
Granulomatous Anterior Uveitis assoc conditions

Conditions that increase IOP
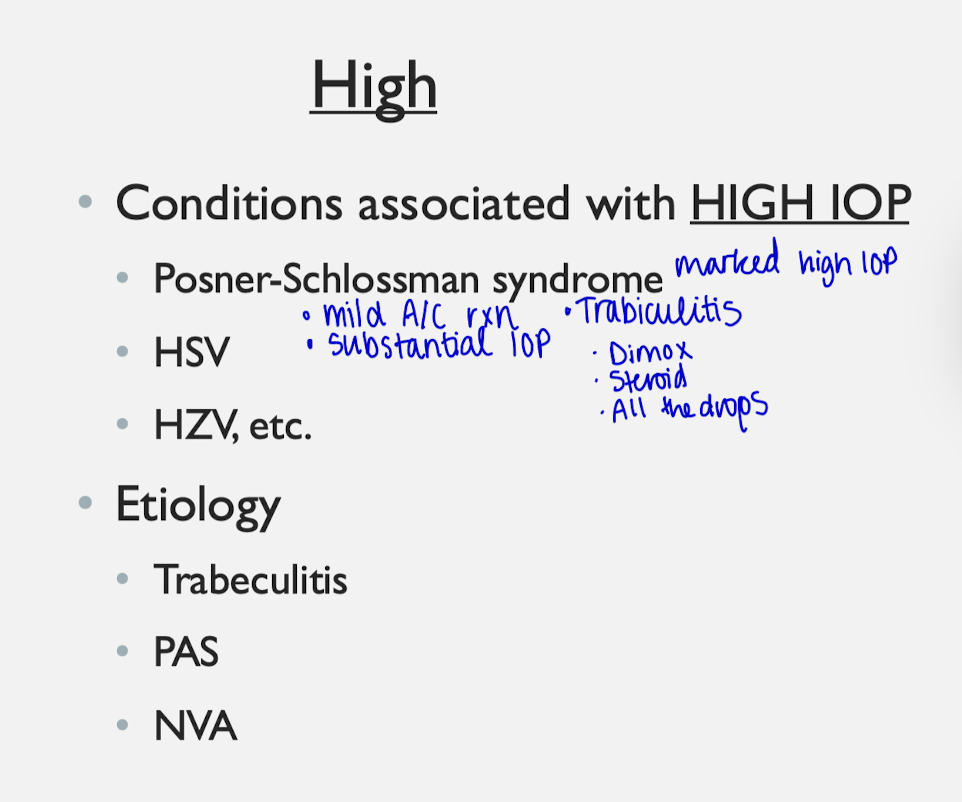
Questions for ppl with uveitis (try for 6)

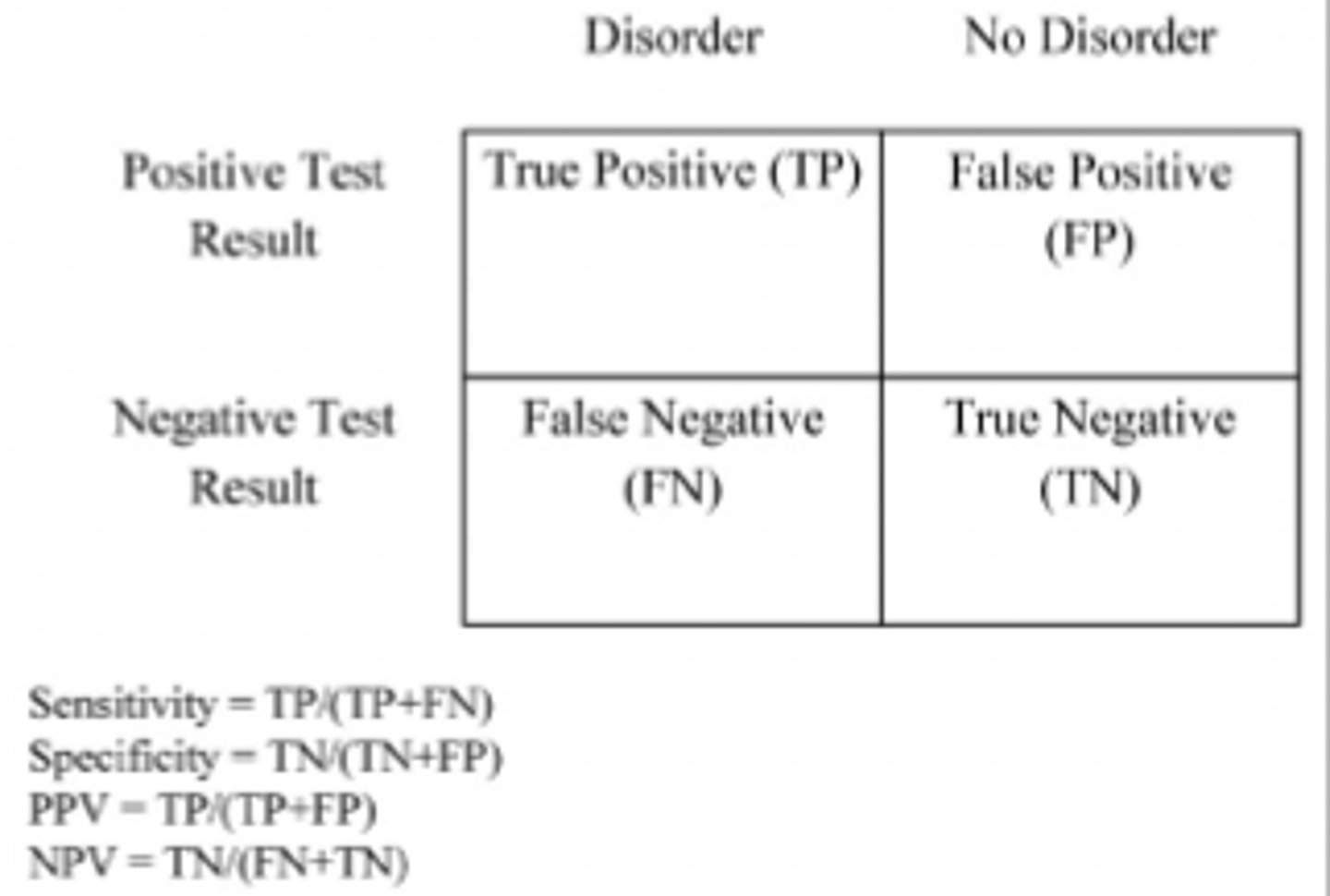
Last Test: Specificity vs. Sensitivity
Specificity = correctly identifies patients without disease
--> If test result is positive, the likeliness you have the disease
Sensitivity = correctly identifies patients with disease
--> If you have the disease, the likeliness the test will come out positive
HLA-B27 assoc Uveitis
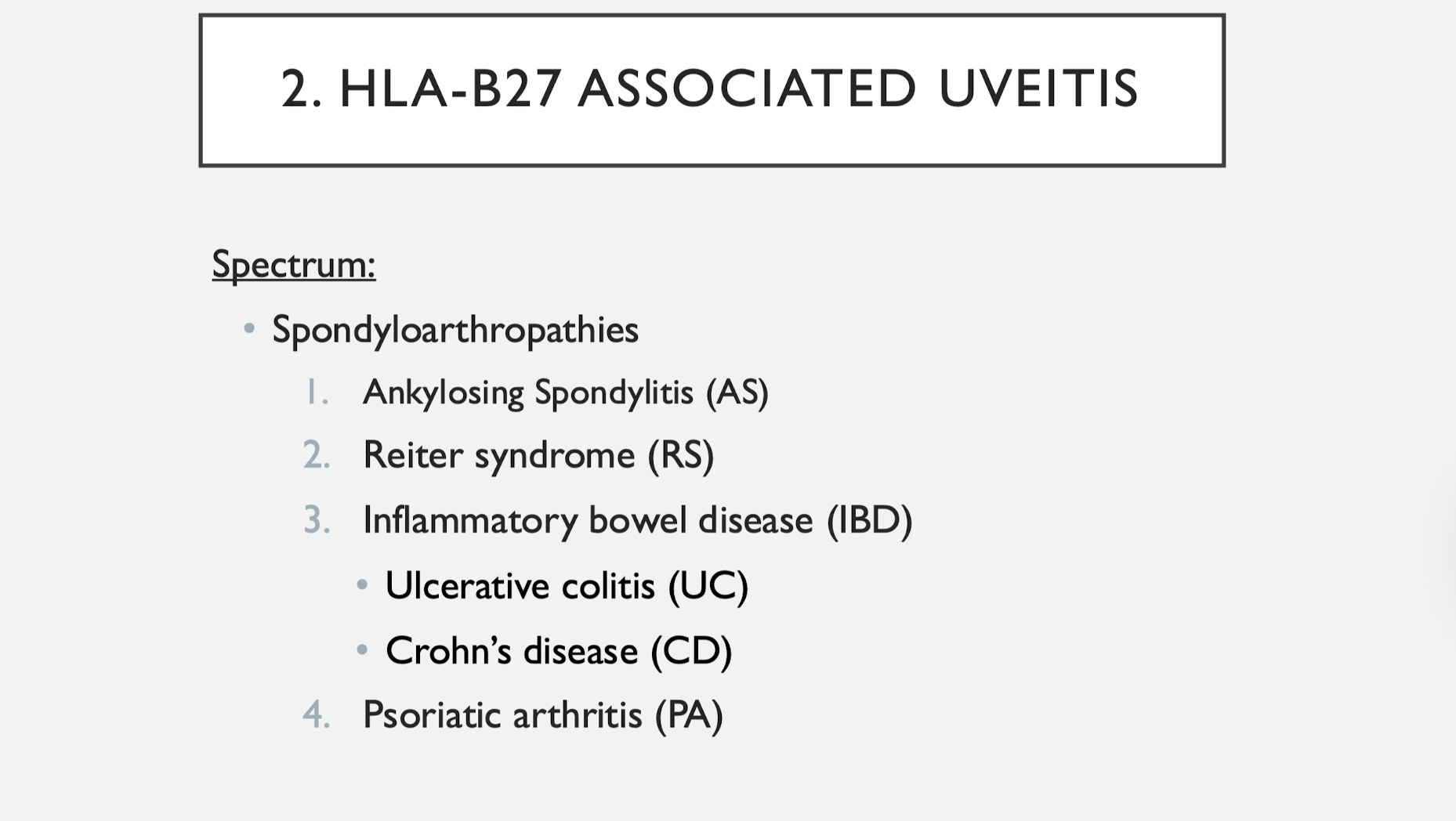
and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Infectious causes of Uveitis

other common causes of anterior uveitis

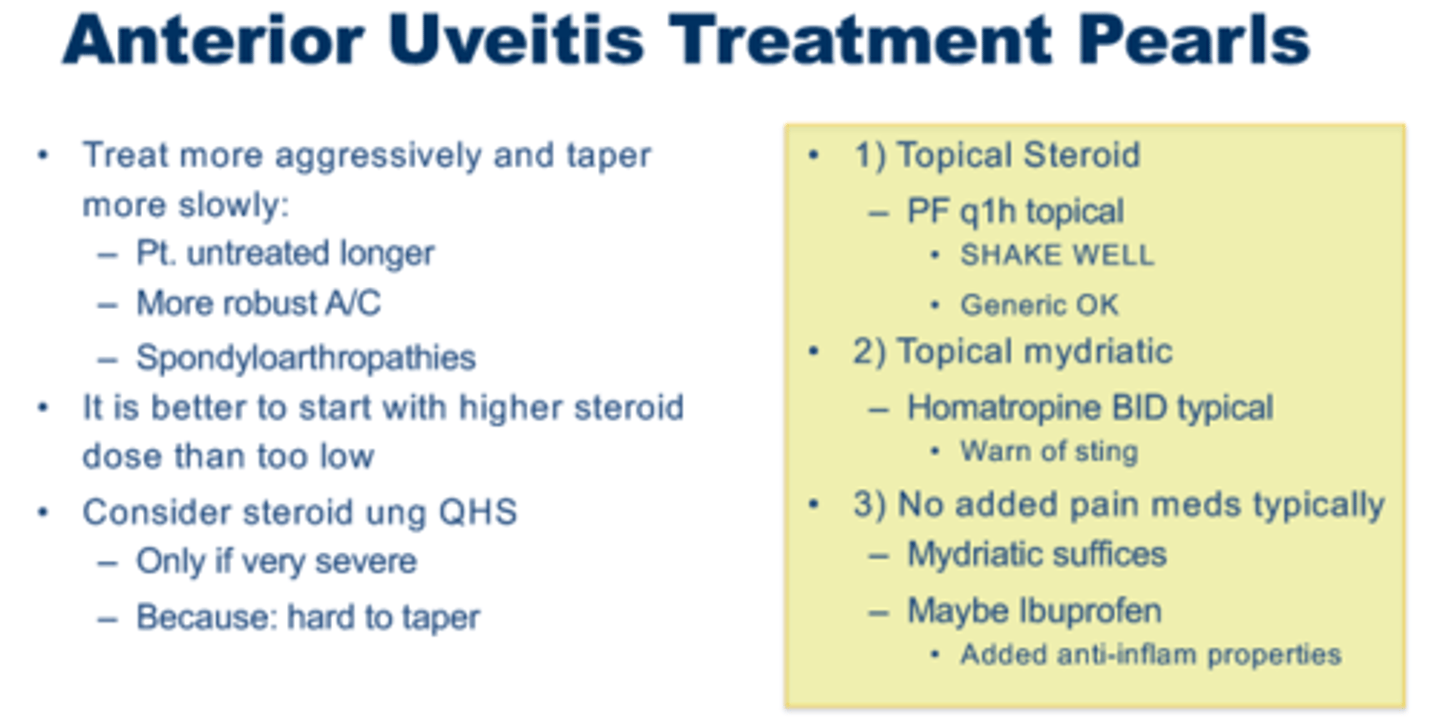
Anterior Uveitis Treatment
1) Corticosteroids
- Pred Forte, Durezol, Lotemax
- Dose: Typically every 1-6h
- Concerns with steroid response: typically takes weeks to occur
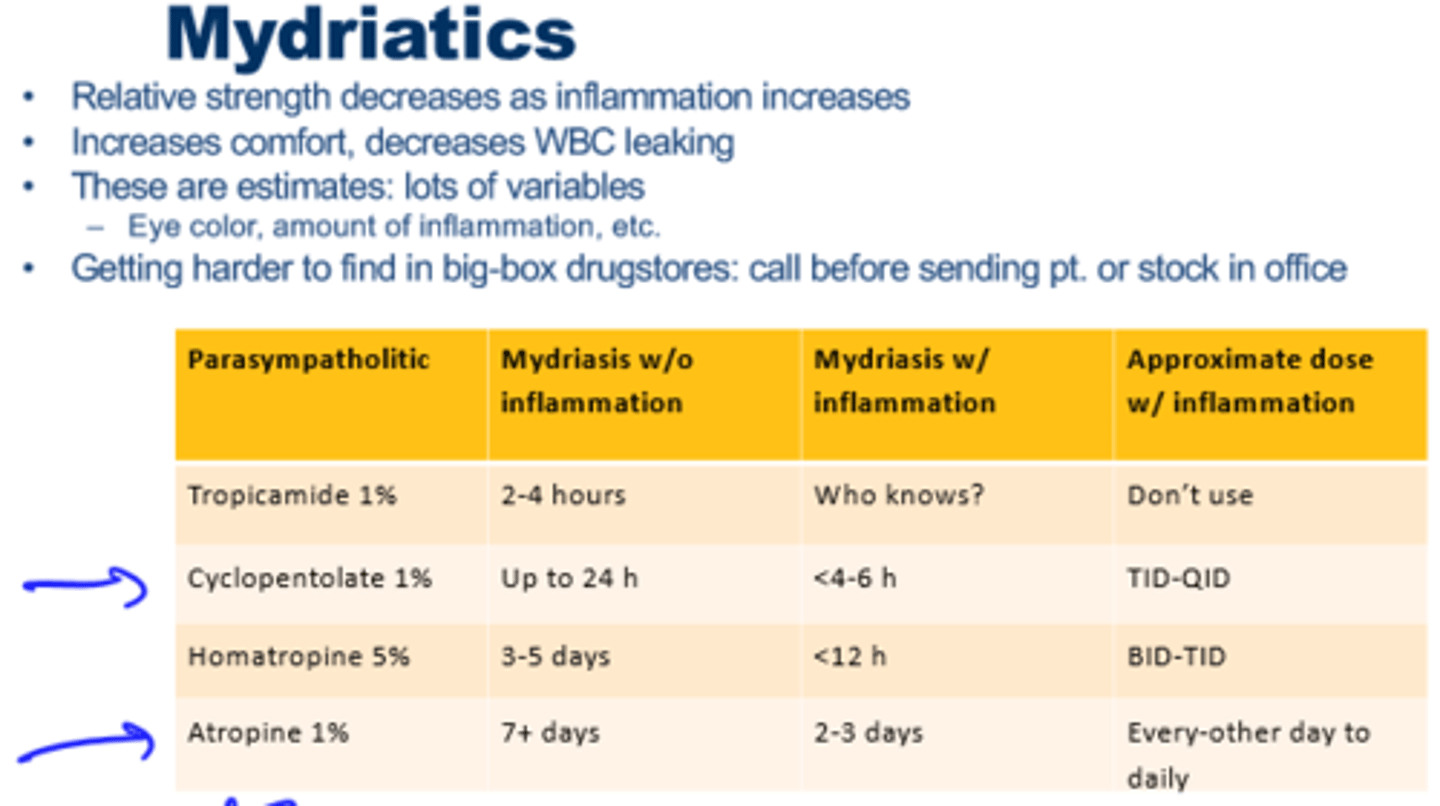
2) Cycloplegic mydriatics
- Cyclopentolate, Homeatropine, Atropine
- To prevent posterior synechiae
- Relieve ciliary muscle spasm
- Stabilize blood-aqueous barrier and reduce flare
3) Other Treatment
- Oral NSAIDs (GI issues with chronic use of Ibuprofen)
- Peri-ocular steroid injection
- Subconjunctival injection
- Refer out to do this, not a replacement for eye drops, synergistic to do both
- Good for patients who may not respond well to meds
- Oral steroid
- Immunosuppressant
Sjogren's Syndrome
Autoimmune disease, aqueous deficiency dry eye
Steroid Rebound and Taper
Durazol = 2x stronger than Pred Forte
- Durazol faster resolution of uveitis so it is good for patients with poor compliance, but IOP increase faster
- Can cut dosage up to half
- Insurance may not cover it or not available readily on shelf
- Durazol or Pred Forte vs. Homatropine taper schedule
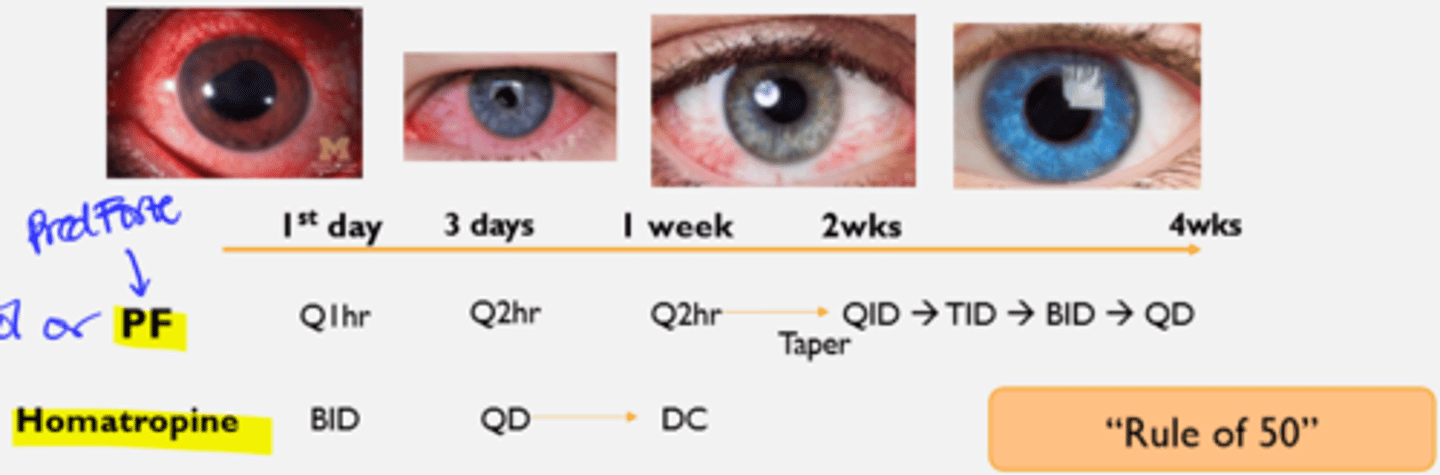
Anterior Uveitis Tx Pearls
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD)
Evaporative dry eye
Prevalance of Dry Eye
- Higher incidence due to increase screen time and contact lens use
- The common cause of CL intolerance, leading to discontinuation of wearing
- NOT all contact lens intolerance or dropout is CL-induced
- NPATs not a way to manage dry eye, overuse disrupts the ocular surface homeostasis
- CL discomfort likely due to pre-existing ocular surface conditions
- Most common are Evaporative dry eye
Dry Eye Definition
Dry eye = multifactorial disease of the ocular surface characterized by a loss of homeostasis of the tear film, and accompanied by ocular symptoms, in which tear film instability and hyperosmolarity, ocular surface inflammation and damage, and neurosensory abnormalities play etiological roles
DED Considerations
- Hybrid forms of evaporative and aqueous-deficient DED exist
- Role of increased friction in DED --> shear force when blink --> unhealthy tear film is not enough cushion between lid wipers
- Consider neuropathic pain in DED (When Sn/Sx don't match)
- Ocular-surface inflammation can cause decreased lacrimal secretion --> decrease oil production --> loss of epithelial barrier function at ocular surface
--> Goal: Restoration of tear film homeostasis
--> Reduce inflammation, re-establish baseline, re-evaluate your management
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
MGD = chronic, diffuse abnormality of the meibomian glands. Characterized by terminal duct obstruction and/or quantitative/qualitative changes in the glandular secretion
- Secreting bad oils
- Not all MGD have bad tear film
Dry Eye Workup
- Symptoms
- External and SLE of ocular surface:
- Eyelids
- Tear glands
- Corneal and conjunctival epithelium
- Tear film (quality and quantity assessment)
Ocular surface includes...
1) Eyelids
2) Tear glands
3) Corneal and conjunctival epithelium
4) Tear film (quality and quantity assessment)
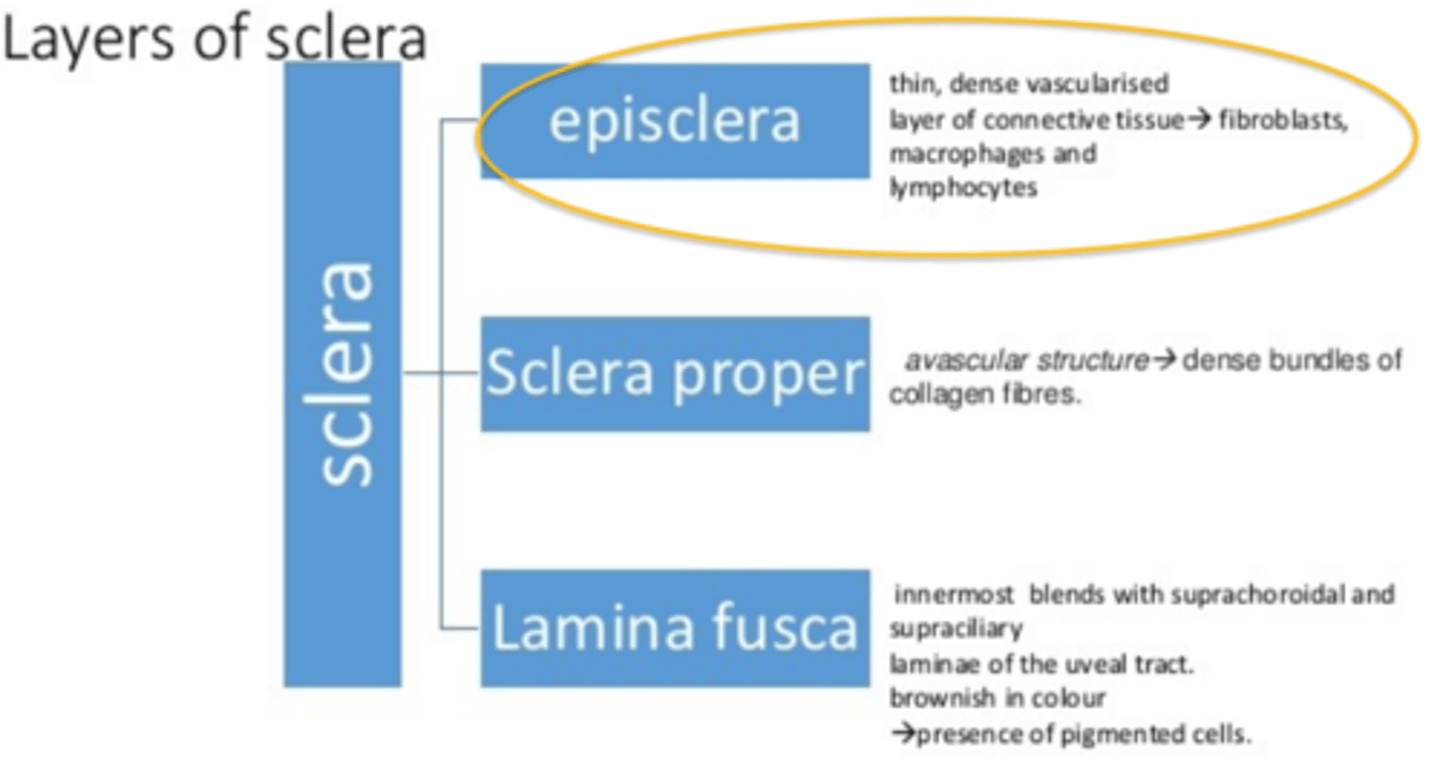
Layers of the Sclera
1) Episclera
Thin, dense vascularized layer of CT → fibroblasts, macrophages, lymphocytes
2) Sclera proper
Avascular structure → dense bundles of collagen fibers
Sclera has very little vasculature b/c inactive metabolically
3) Lamina fusca
Innermost blends with suprachoroidal and supraciliary laminae in the uveal tract
Brownish in color
Presence of pigmented cells
Episclera's function
- Similar to synovial membrane, allows smooth movement of joints
- Connective tissue: scleral stroma, Tenon's capsule
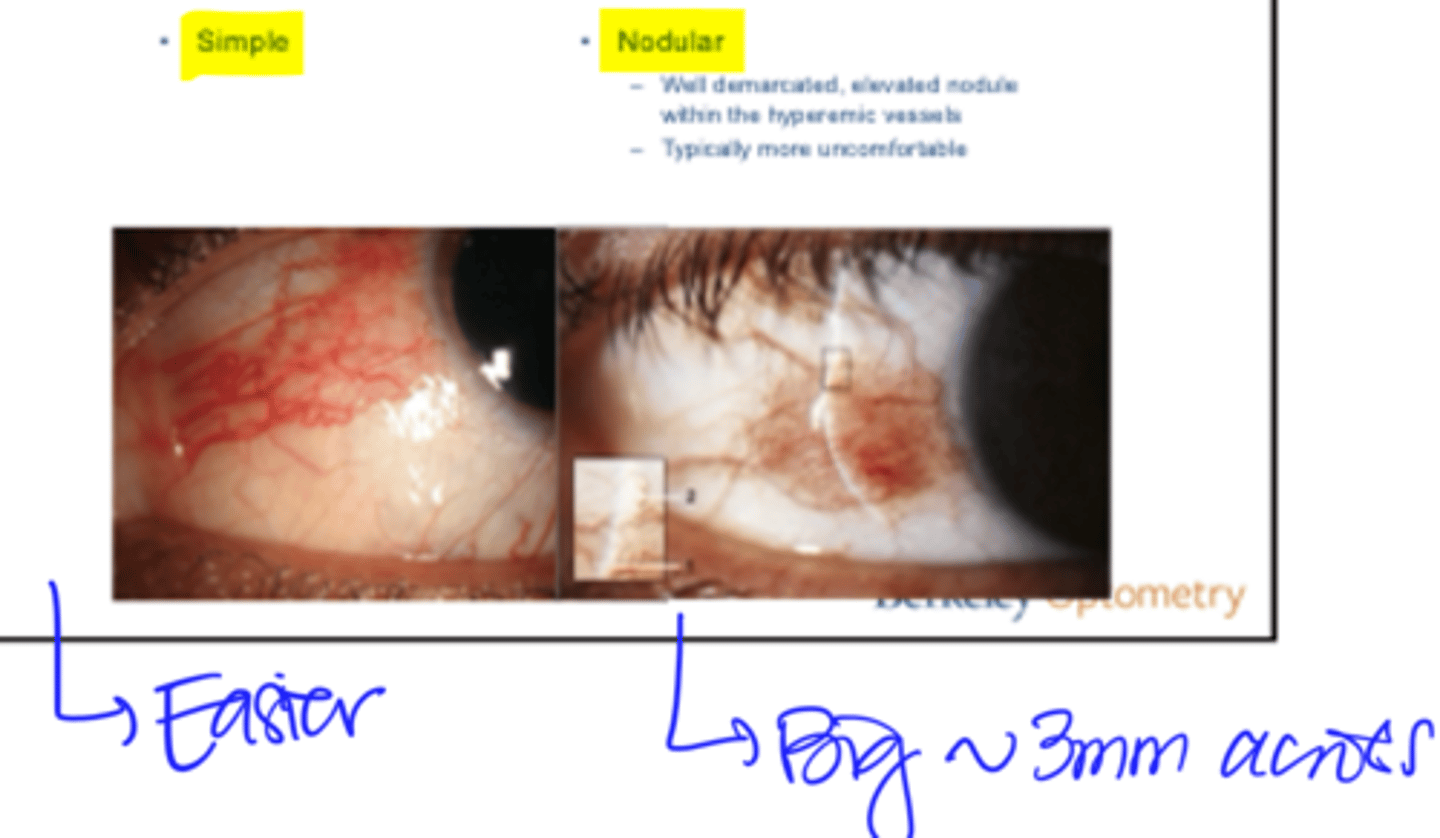
2 Types of Episcleritis
1) Simple
- Easier to treat
2) Nodular
- Well demarcated, elevated module within the hyperemic vessels
- Typically more uncomfortable
- Big, ~3mm across
DDx for painless to mild pain SECTORAL redness of ONE eye
- Pingueculitis
- Pterygium
- SLK
- Phlycten
- FB
- Sterile ulcer/CLPU
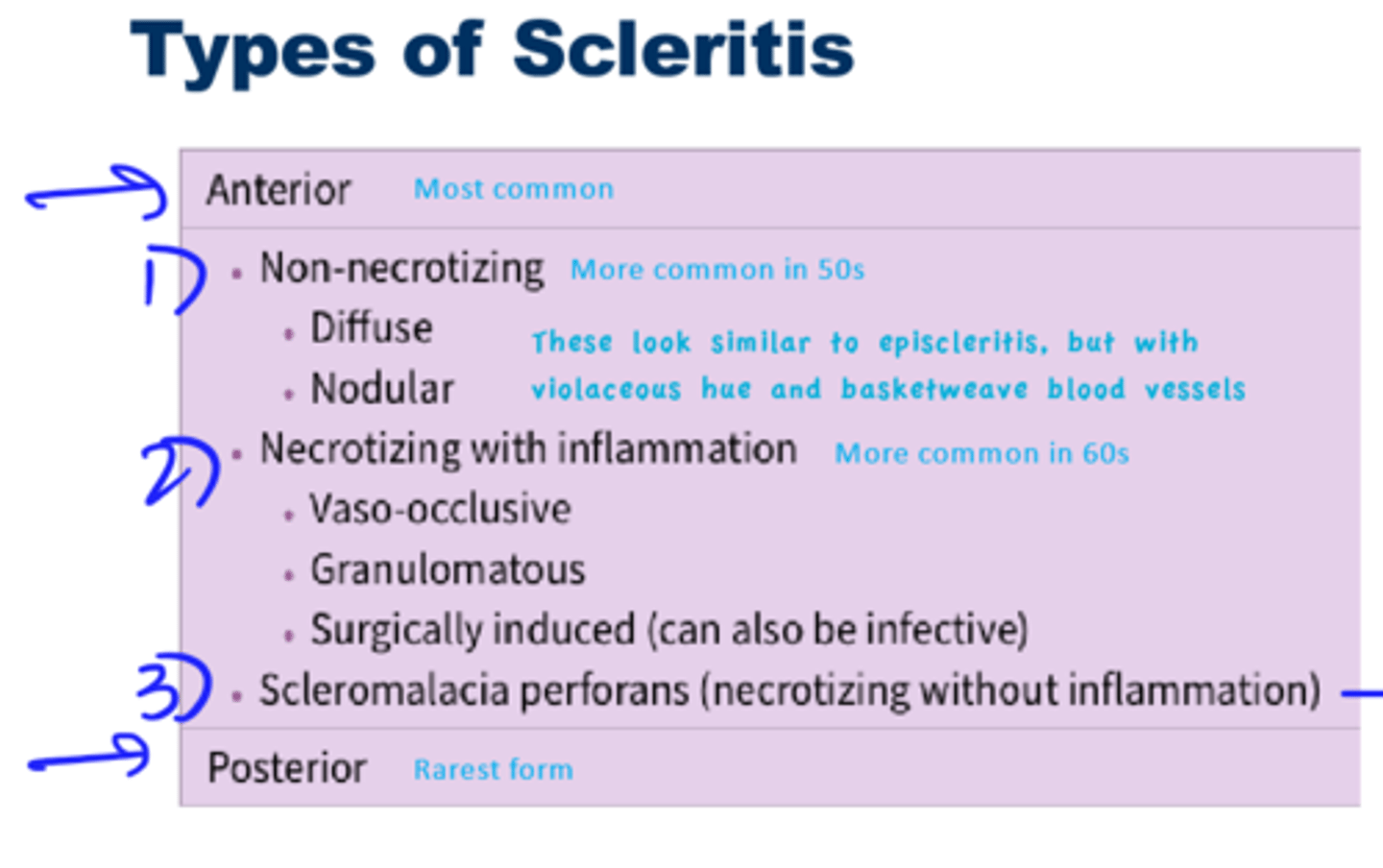
Types of Scleritis
Corneal sensitivity
First episode of HSV:
- Not decreased, not helpful, not diagnostic
IF want to decide whether the pt has ever had HSV keratitis or HZO:
- Corneal sensitivity can be very helpful
- Iris TID
- Corneal scarring
--> Use dental floss with no mint
--> Test all 4 quadrants, only do central if fail all 4 quadrants
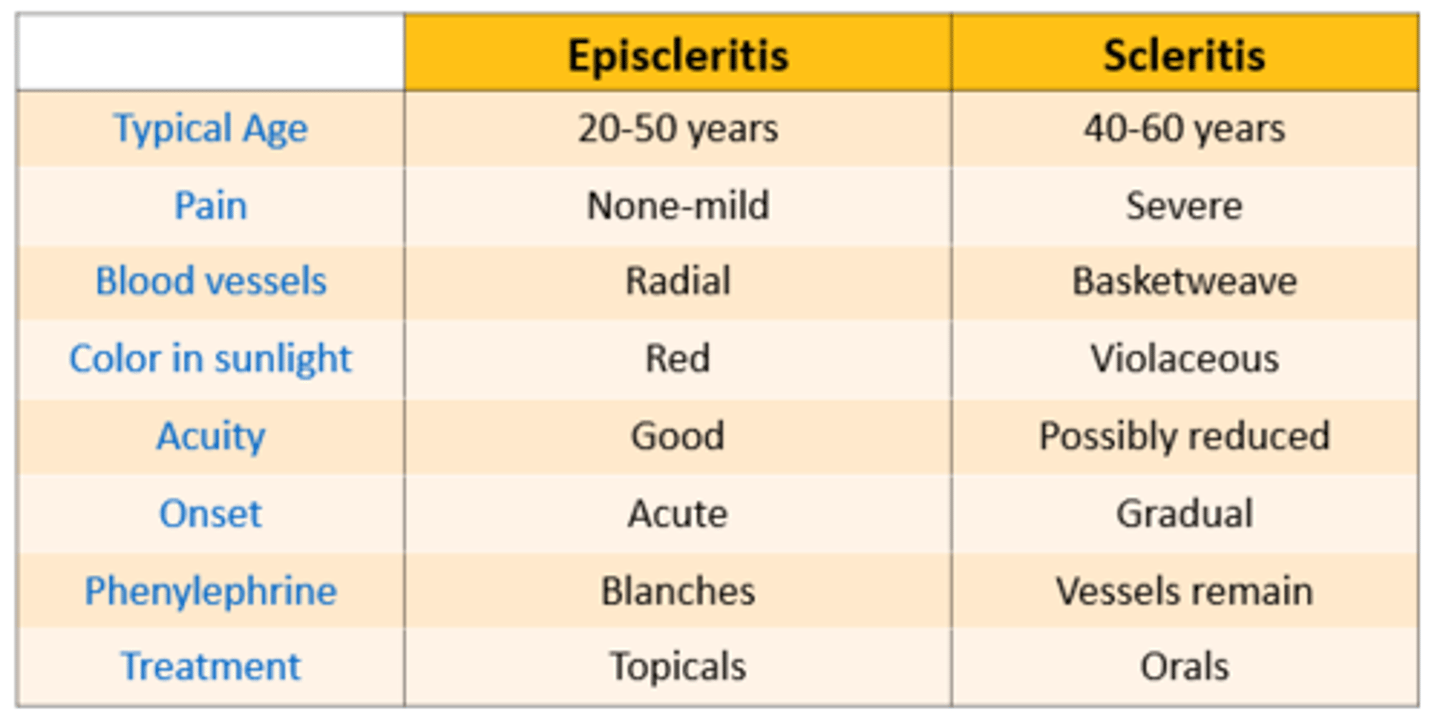
Episcleritis vs. Scleritis
Mydriatics
Signs to keep looking for cells in AC
- If patient eyes dilates more slowly
- If the eye's pupil reacts differently to pupil testing
- Light shone in opposite eye causes pain in affected eye
- If you see flare
Ex: Iritis
- Cover the red eye, blast light into the good eye, the red eye should hurt or be photophobic
- Affected eye will dilate slower, helpful Dx sign if unilateral
Cells grading
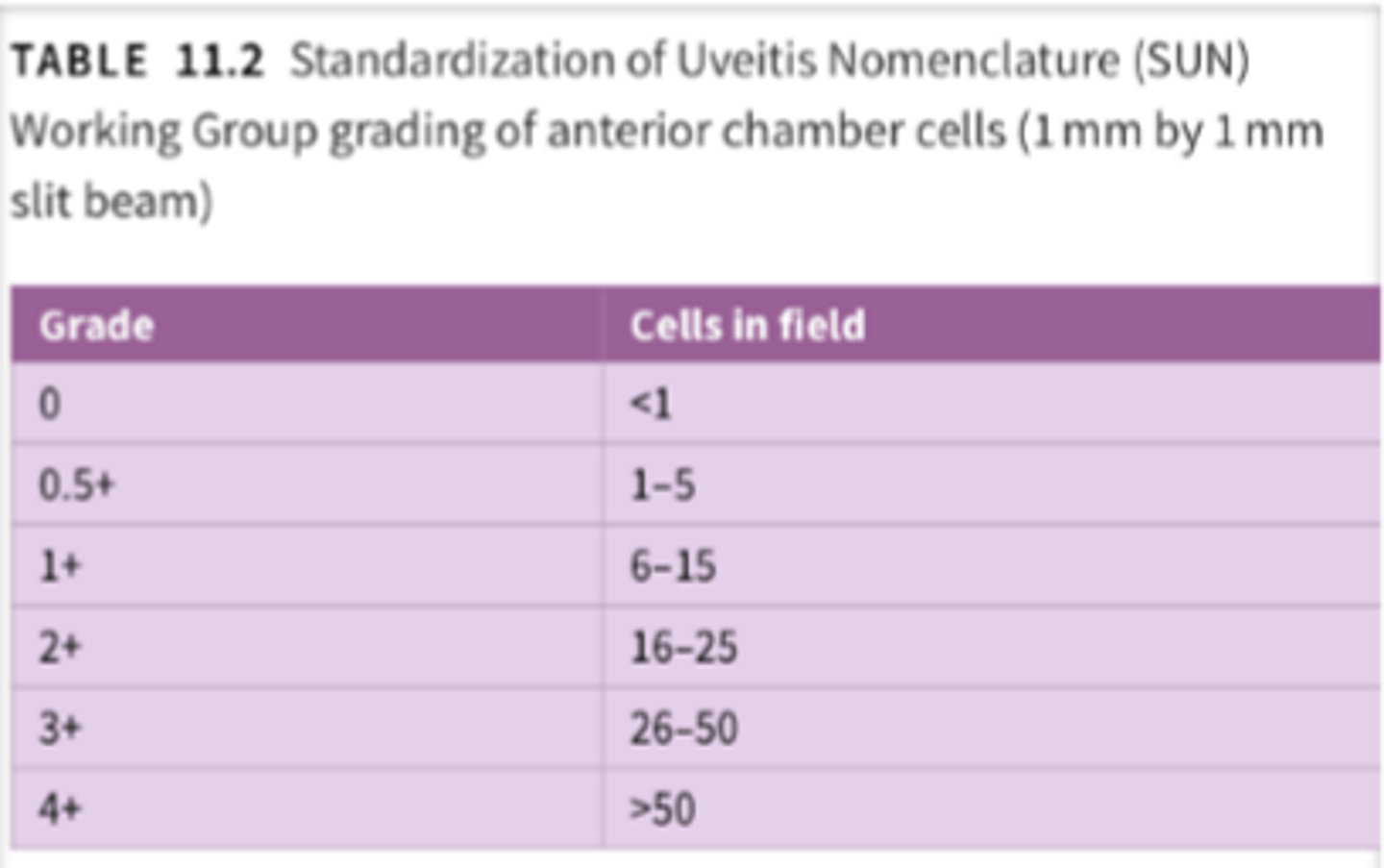
Flare grading

What conditions causes an INITIAL IOP spike?
- HSV
- HZV
Acute Anterior Uveitis A&P

Do not order labs for first episode of Anterior Uveitis EXCEPT:
Exceptions:
- Severe
- Bilateral
- Resistant to Tx
- Granulomatous
- Pan uveitis
- Compelling secondary symptoms
**DO NOT order every lab
Acute Anterior Uveitis likely due to Ankylosing Spondylitis A&P

Tapering Schedules
- Don't put tapering schedule into the chart
- No 3-2-1 out taper for acute anterior uveitis
- 1 month taper = done with meds in a month

When MUST you have to taper a steroid?
Must taper if...
- All other uveitis (esp. if related to systemic illness)
- Episcleritis, Scleritis (maybe not infectious)
Screening Questions Differentials

Labs to Know

Cystoid Macular Edema (CME)
CME = leading cause of permanent vision loss in uveitis
- Production of inflammatory mediators:
- Prostaglandins
- Histamine
- Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
- Difficult to see clinically
Durezol
Advantages:
- Better penetration of epithelium
- 6x stronger than prednisolone
- Preserved with sorbic acid
- Administered in an emulsion
- Longer half life
- May be able to go all the way to the macula
Disadvantages:
- Higher # of adverse events compared to PF
Mydriatics in Uveitis
1) Pain management
2) Increase blood/aqueous barrier --> reduce cell
3) Prevent posterior synechiae
Differentials for Sectoral, Red, Unilateral
- Episcleritis
- Staph Marginal Keratitis
- Phlyctenule
- FB
- CLPU (peripheral ulcer)
- Pterygium
- Bacterial ulcer
- Pingueculitis
Differentials for Painless, Sectoral, Red, Unilateral
- Pingueculitis
- Pterygium
- SLK
- Phlycten
- CLPU
- FB
Differentials for Lid pain/swollen lid
- Dacryoadenitis
- Orbital cellulitis
- Hordeolum
TBUT and CL use
- Short TBUT --> Likely not CL-induced dry eye
- If do a CL vacay from the night before, TBUT should be normal if CL-induced only
Lid Wiper and Line of Marx
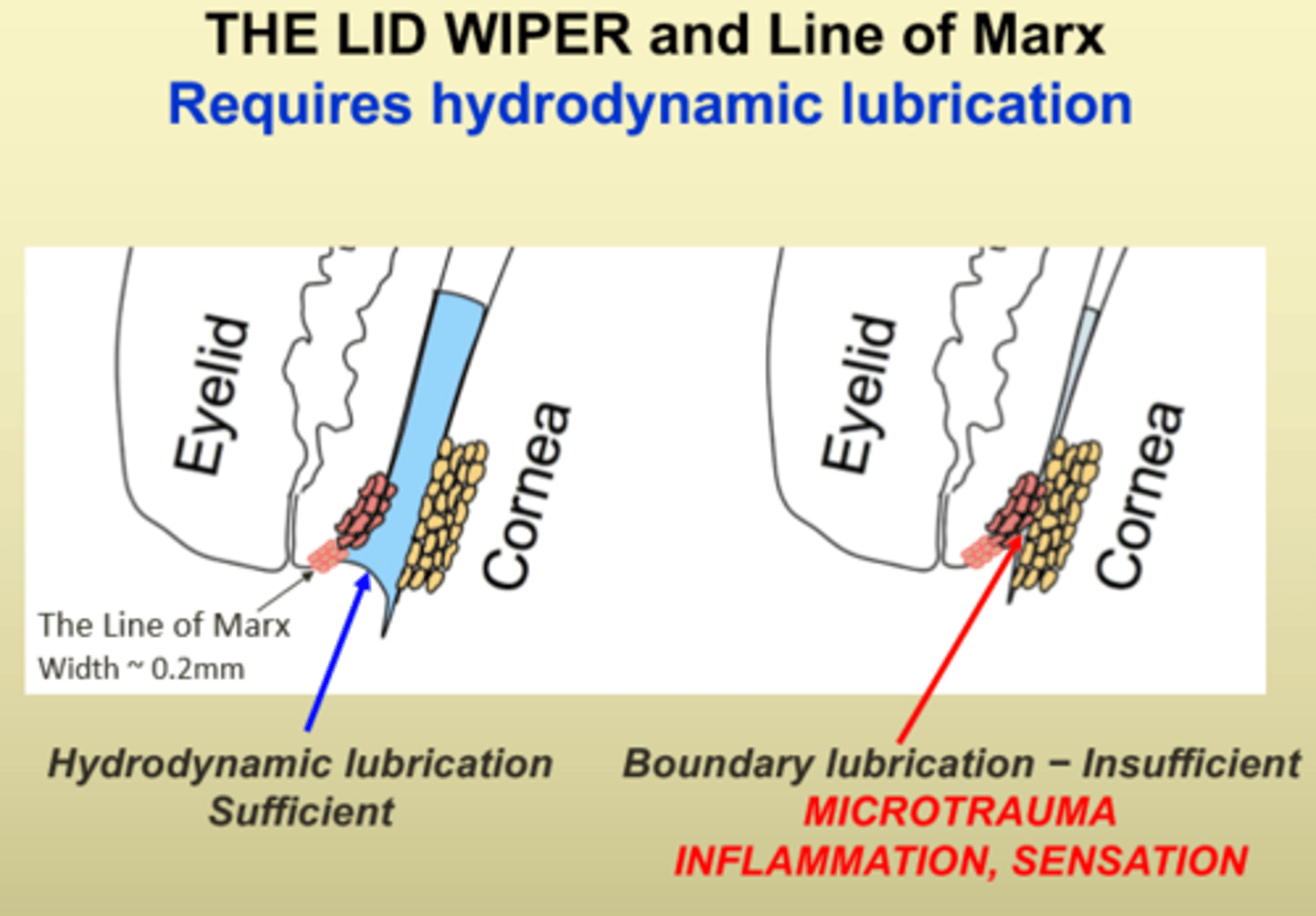
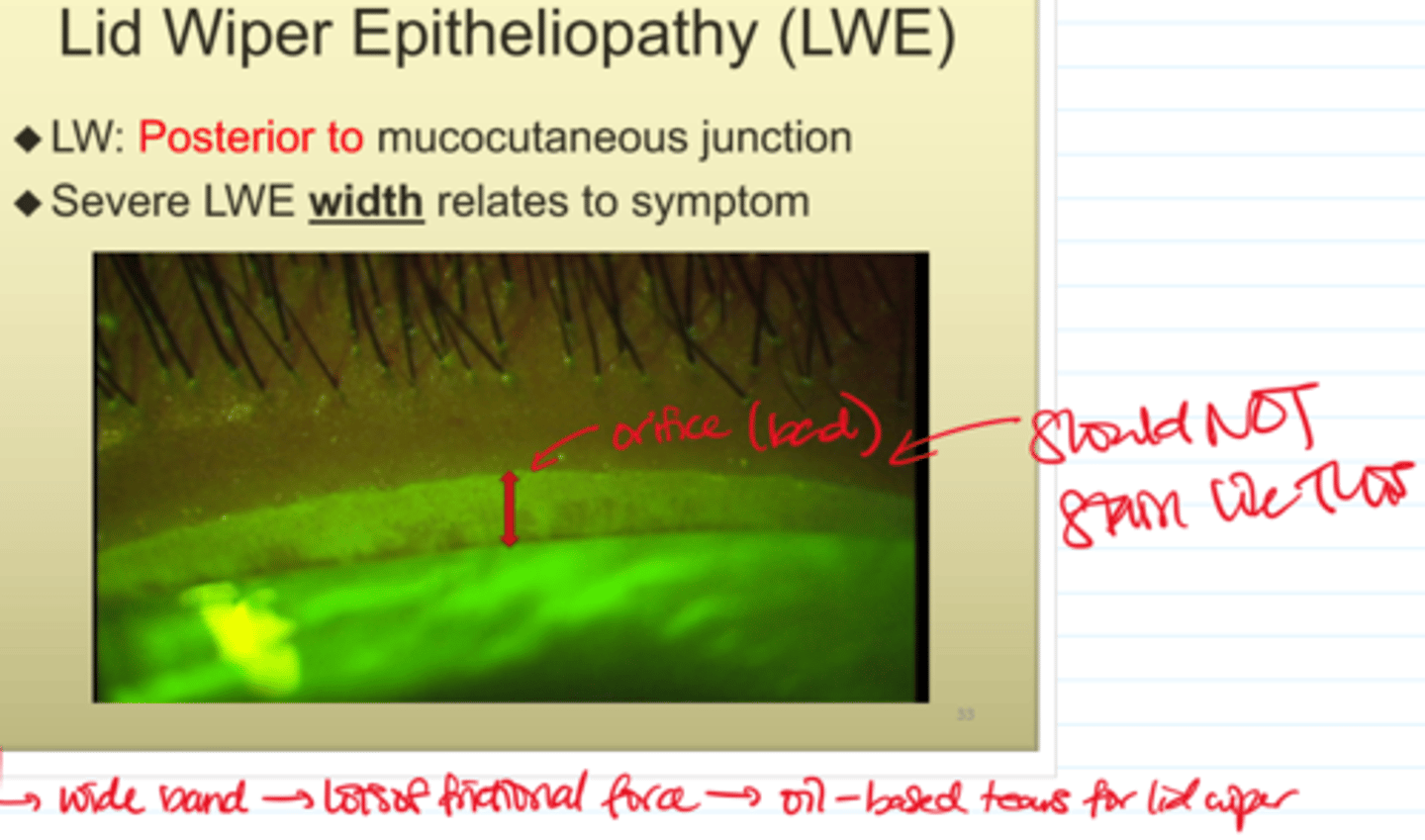
Lid Wiper Epitheliopathy
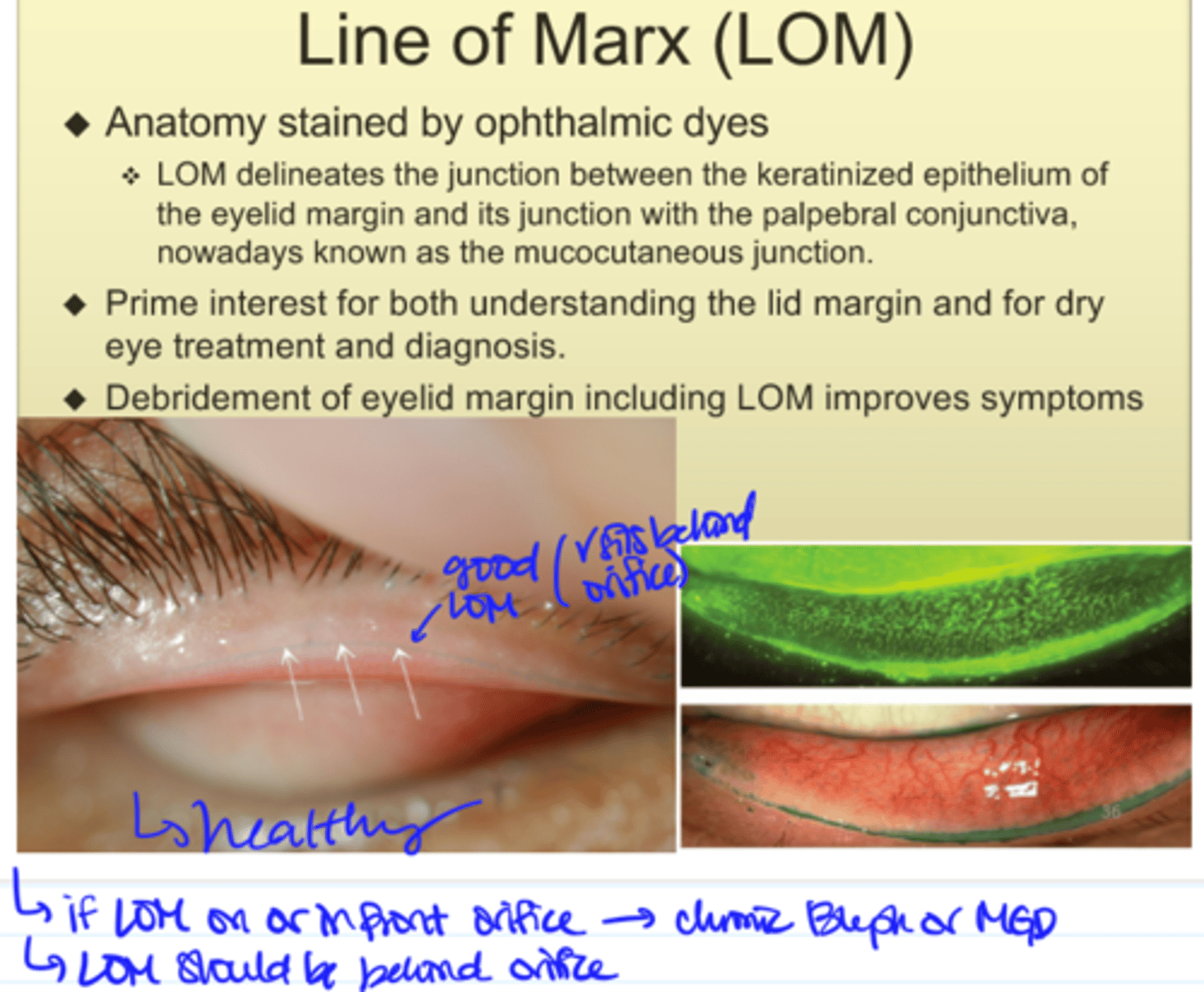
Line of Marx (LOM)
- Anterior displacement of LOM --> ocular surface problem, not CL-induced
- LOM should be behind the orifices NOT in front
Neurotrophic pain vs. Neuropathic pain
Neurotrophic pain:
- If poke eye and don't feel
- Lost of corneal staining
Neuropathic pain:
- Signs/symptoms don't match
- Make sure ocular surface is clear
- Hypersensitivity
- Tx is long, must be patient, educate pt
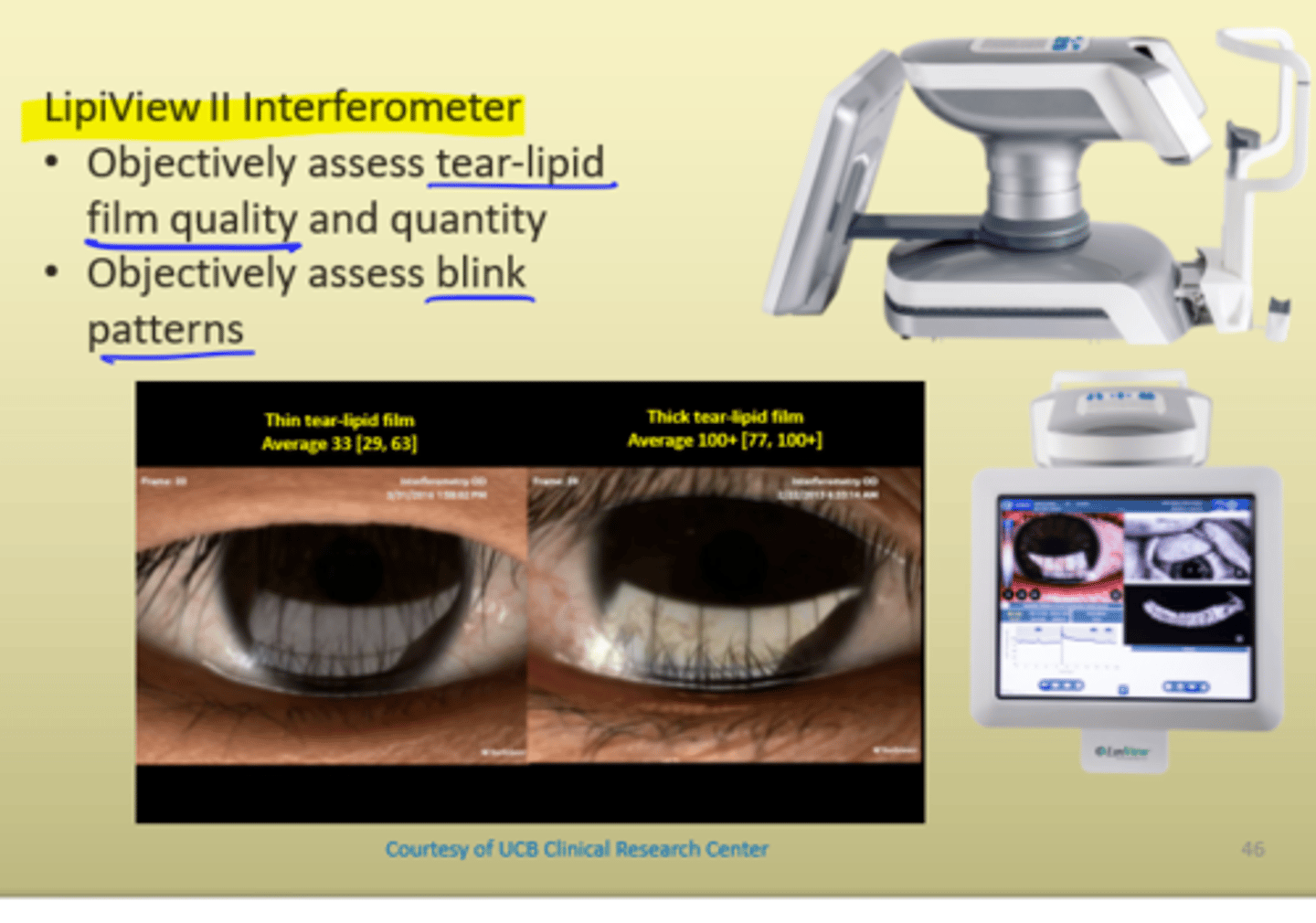
Lipiview
--> Look at tear lipids and blinking patterns
- Ocular surface interferometer
- Interferometric color unit (ICU)

Tear- Lipid Thickness
Lipiview II Interferometer
- Objectively assess tear-lipid film quality and quantity
- Objectively assess blink patterns
- Normal tear film: 40-80
- Combo of tear composition and thickness