M1: LEC 2: Phylogenetics
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
define systematics.
a science for classifying organisms and determining their evo. relationships
define phylogeny.
evo history of species, pop.s, or genes (visualized as a tree)
define taxonomy.
naming and grouping of organisms as a nested hierarchy
What is the format for the binomial nomenclature (for naming species)?
Genus species
1) genus is capitalized
2) species comes after genus
3) the nomeclature is italized
What are the (9) parts of the phylogenetics tree?
1) root of tree — lineage leading to the MRCA of all taxa (organisms) in the tree
2) nodes — common ancestors
3) branching — lineage
4) clade — ancestor + its descendants
5) sister taxa — 2 clades share a common ancestor
6) MRCA (most common recent ancestor) — 1st ancestor encountered when tracing back from a group of species
7) anagenesis — evo change within a lineage
8) cladogenesis — branching of lineage into 2 or more lineages
9) topology — branching pattern (or order) of the tree
What is internal vs terminal nodes on the phylogenetic tree?
internal node: hypothetical last common ancestor
terminal node: tips
What is extant vs extinct on the phylogenetic tree?
extant means still in existence
extinct means no longer in existence
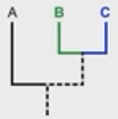
What is the difference btwn common ancestors vs MRCA?
1) ABC share a common ancestor
2) BC share the MRCA
T/F - rotating the nodes will affect the topology (evo history).
false - the evo history stays the same despite the rotation of the nodes
T/F - collapsing some clade will effect the topology (evo history).
false
define clade (monophyletic group).
all descendants are from a single MRCA
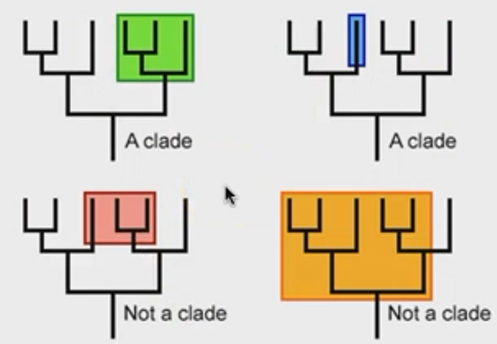
define polyphyletic group.
descendants from the MRCA + other species
poly- means extra or more
define paraphyletic group.
descendants from a single MRCA, but some species are missing
para- means besides
T/F - paraphyletic and polyphyletic groups are clades.
false
T/F - some taxonomic groups are not monophyletic groups.
true
What are the types of the trees?
1) cladograms — branch length gives no info (only topology)
2) phylogram — branch length = # of character changes (amount of evo change)
3) chronogram — branch length = time
With a chronogram, how do we determine the age of a speciation event at the node?
fossils found after an internal node, but before the desired node
define homologous traits.
traits that have been inherited from a common ancestor
define morphological traits.
anything physical that we can see
What is used to create trees now?
genetic sequences used for inferring phylogenies
Why do we use DNA sequence?
1) get lots of data easily
2) easy to compare across species
3) traits are easy to categorize (A,C,T,G)
What are the disadvantages of using DNA sequences?
1) convergence (homoplasies) is common
2) get a diff. picture depending on the sequence
define homoplasy.
1) some traits are the same, but independently evolved
2) characters are shared, but not b/c of shared ancestry
3) result from convergent evo. and evo. reversals
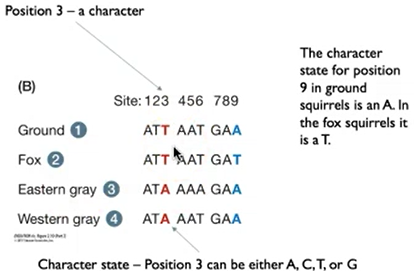
define characters.
each trait of an organism
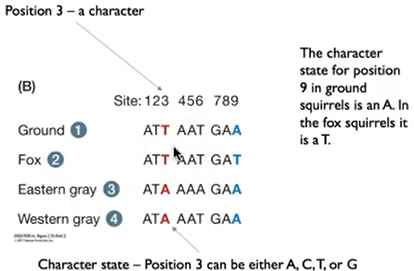
define character state.
the form that character takes in an individual lineage
T/F - each phylogenetic tree is a hypothesis about the evo relationship of the species.
true
define unrooted tree.
shows possible evo relationship, but not what ancestor they came from
What are the methods used to choose the right tree?
parisomy, max likelihood, and baysian
define parisomy.
the tree w the fewest # of changes is the REAL tree
What is a limitation with parisomy?
assumes all evo change is equally likely
What does the max likelihood and baysian allow us to do? What is an issue of it?
uses the probability of all changes occurring —> to select a tree, but it is a lot of work bc we have to calculate the probability for all trees
Why is all homology not informative?
1) shared ancestral character - not useful
2) shared derived character (synapomorphy) - useful
How do we know what the ancestral state is vs the derived state?
outgroup(s)
define polytomy. what causes it?
unresolved node due to limited info. such as slow evo. (not much change btwn splitting events) and rapid diversification (not much time for traits to change)
note: polytomy represents uncertainty, so we do not know the true branching order
how can we resolve polytomy?
1) collecting more data
2) using millions of bases of DNA sequences
how do we use phylogenies?
1) date evo. events (timeline of divergences)
2) constructing the appearance of our ancestors
3) constructing character changes
4) comparative analysis: map multiple traits and determine a connection btwn the traits