cell bio exam 4
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
cytoskeleton functions
cell shape — especially in cells w/o cell wall
internal organization — organelle position, shape of nucleus
cell movement
3 types of filaments
microtubules, actin, intermediate filaments
assign actin vs microtubules to the following statements:
moves chromosomes in mitosis
phagocytosis
microvilli (intestines)
cleavage furrow (animal cytokinesis)
flagella
amoeboid movement (white blood cells, fibroblasts)
[TEXTBOOK]
intermediate filaments
most diverse
only found in some animals
provide mechanical strength
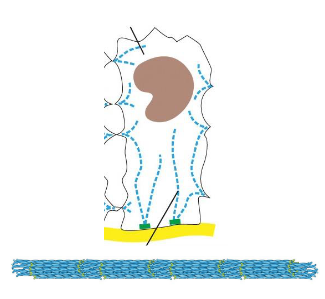
intermediate filaments structure
bundles of fibers — like a rope
bend + stretch w/o breaking
very stable
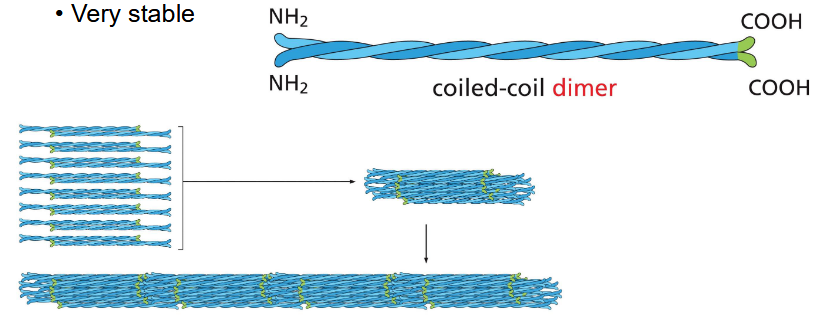
types of int filament: keratins
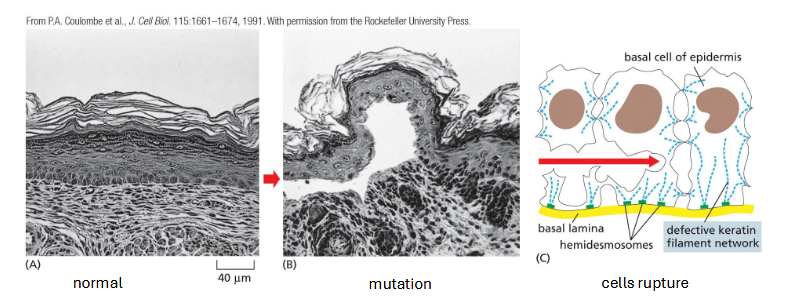
skin, hair, nails, claws, scales, horns
found in epithelial cells
provide mechanical strength
many different types
mutation: rare genetic disease (epidermolysis bullosa simplex) disrupts keratin filament formation
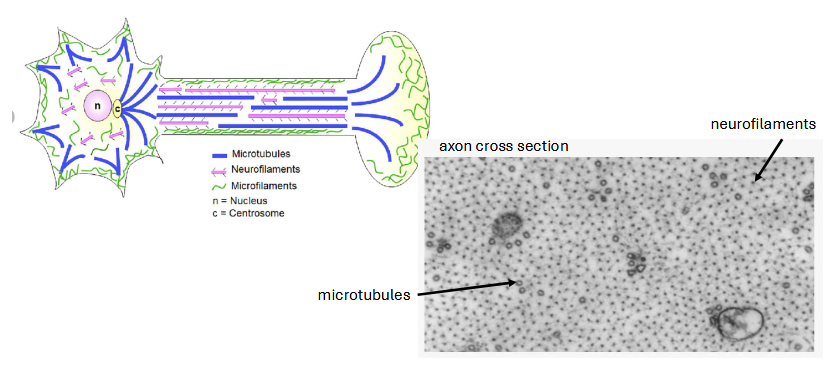
types of int filaments: neurofilaments
strength and stability along axon
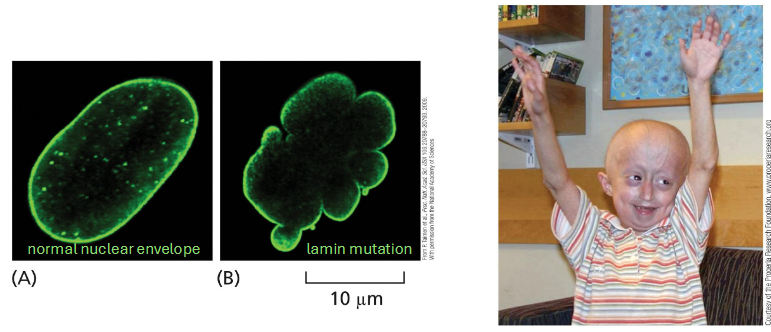
types of int filament: nuclear lamina
lines inside of nuclear envelope
lamin protein
provides mechanical stability and may be involved in chromosome positioning
lamin mutation — rare genetic disorder (type of progeria). signs of aging begin in childhood; mechanism unclear
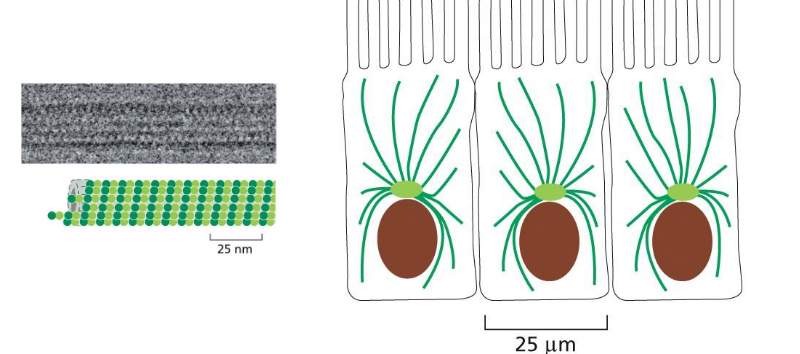
microtubules image
intermediate filaments image
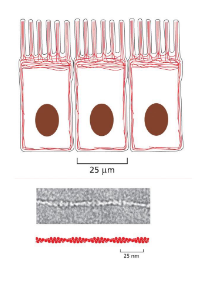
actin image
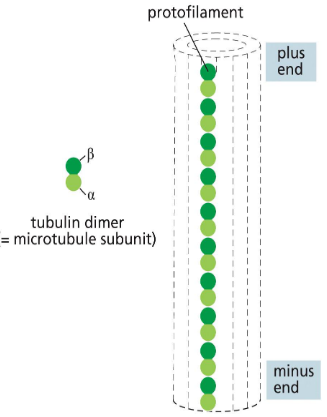
microtubule assembly and structure
made of repeating subunits of alpha and beta tubuliin proteins — always oriented in same direction and polar: (+) vs (-) end
repeating alpha beta subunits create protofilament
lateral association of 13 parallel protofilaments creates hollow tube -- can spontaneously assemble in vitro. filament has a consistent structure — always assembles this way
physical properties — compare/contrast microtubules and int fil
microtubules: small globular proteins. multiple contacts. very stiff
int filaments: elongated proteins. fewer contacts. very flexible
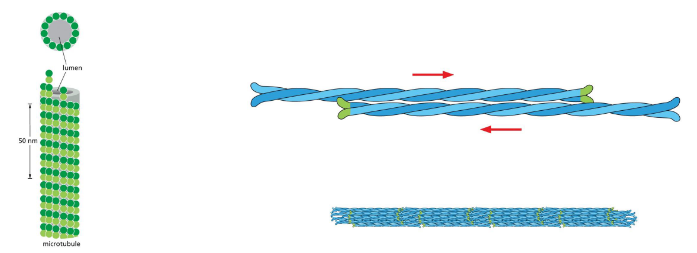
microtubule organization
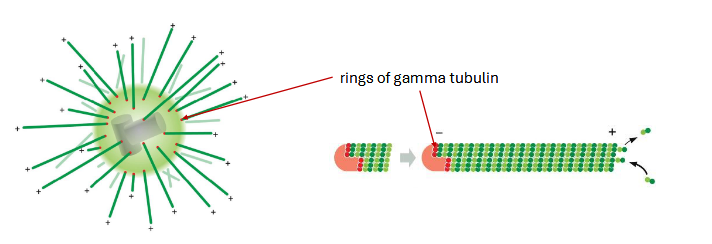
cellular arrangement is controlled by an organizing center. centrosome — common in animal cells near nucleus
concentration of alpha and beta tubulin is too low in cells to spontaneously assemble. gamma tubulin nucleates microtubule assembly. filaments grow from gamma tubulin rings towards the (+) end
organization of microtubules can vary depending on species and cell type
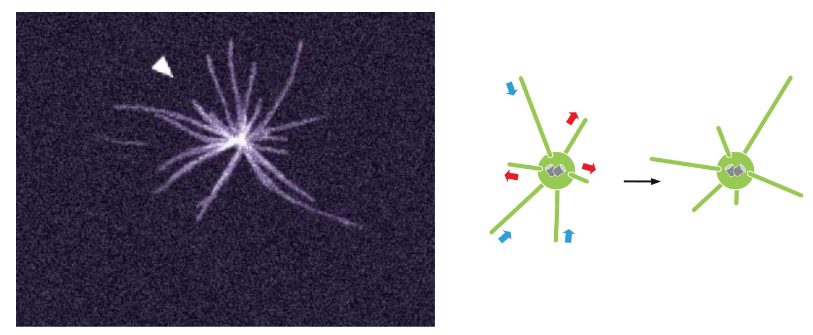
microtubule dynamic instability
each filament can grow/shrink
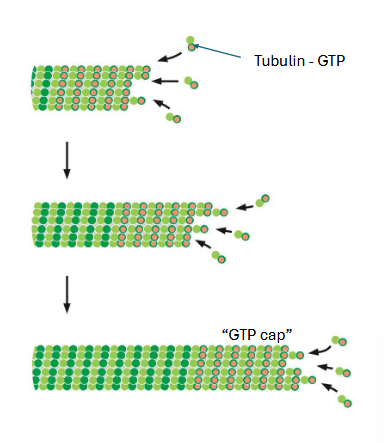
microtubule growth
tubulin is a GTPase. free subunits are GTP bound.
GTP tubulin interactions are more stable. tubulin eventually hydrolyzes to GDP
rapid growth — GTP cap — stabilizes microtubule
shrinking microtubule
if end hydrolyzes to GDP, cap is lost
tubulin GDP interactions are less stable
rapid disassembly occurs
cap is dynamic — maintained by the rate of growth
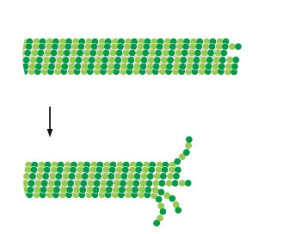
microtubule dynamic instability is regulated by ___
other proteins
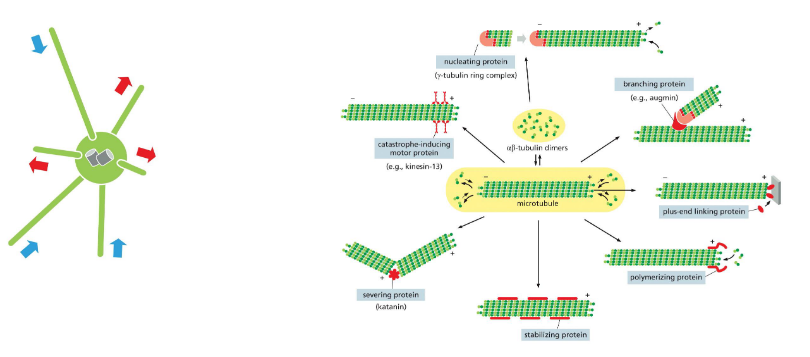
microtubule function (4)
intracellular transport, organelle positioning, mitosis, flagella and cilia
spindle microtubules in mitosis
move chromosomes to metaphase plate
move chromosomes to opposite poles in anaphase
taxol (paclitaxel) is a chemotherapy drug. it stabilizes microtubules. its primary effect is thought to be during mitosis. why would stable microtubules prevent mitosis? how might taxol affect tumors vs how it might affect other body tissues?
**add more if you can
tumors are defined by uncontrolled mitosis; by preventing them from dividing/replicating/etc the cancer does not grow
intracellular transport
motor proteins move along microtubules and carry cargoes
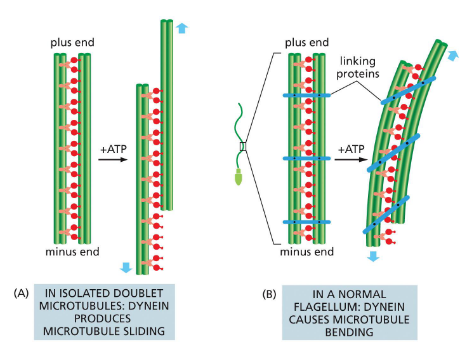
kinesins move towards plus end (outward); dyneins move towards minus end (inward)
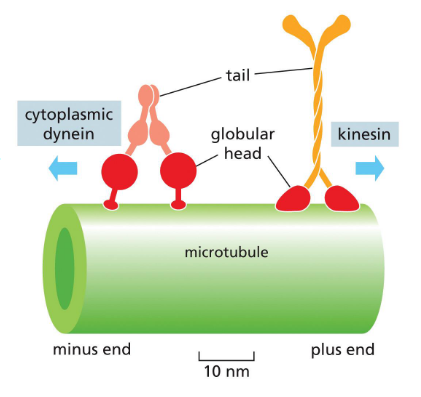
microtubule gliding assay
used to study motor proteins
which direction does kinesin go? where could a vesicle be going?
kinesin goes from (-) to (+)
a vesicle could go from the ER to the golgi, the golgi to PM, etc
microtubules also help position organelles
ER attaches to microtubules — tubes extend to periphery
kinesin is the motor protein (remember — moves out to periphery)
golgi attaches to microtubules — keeps it “collapsed”/pulled in so it remains near nucleus
dynein is the motor protein (remember — pulls inward)
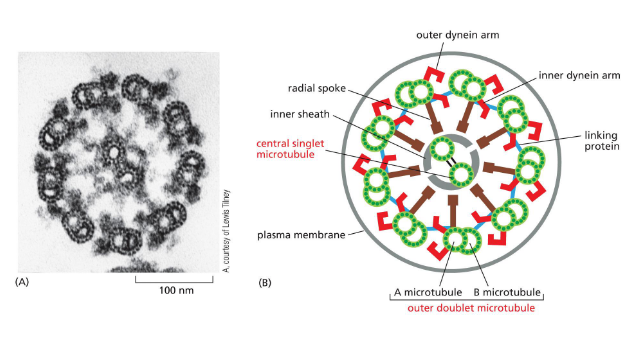
flagella and cilia
same structure.
lung cells, sperm cells, single-celled organisms like paramecium, etc
one long flagella vs many tiny cilia
same organization — arrangement of microtubules.
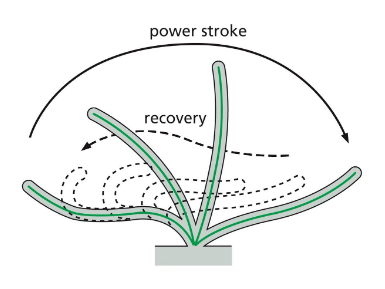
flagella and cilia movement
dynein movement produces bending. bending on alternate sides of flagella creates whip-like, back and forth motion
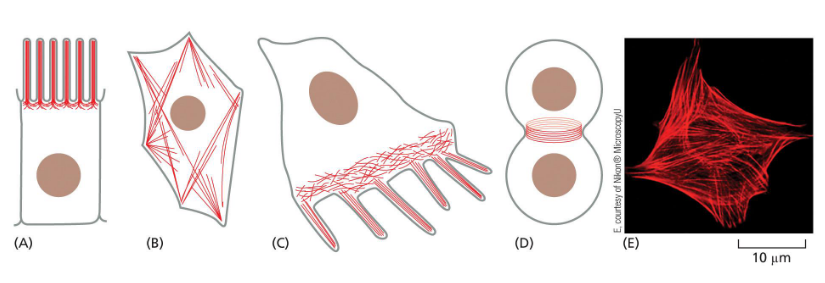
actin organization
typically most dense at cell cortex
creates cell shape
bundles — parallel fibers
webs — branching fibers
arrangements vary depending on cell and function
actin assembly/structure
made of repeating subunits of actin monomer. pointed in same direction = polarized
forms helix
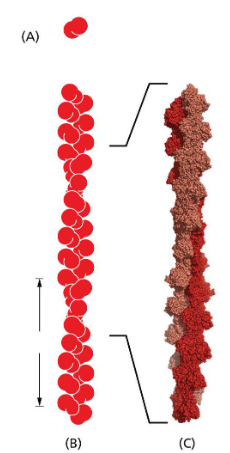
actin physical properties
more flexible than microtubules (which are very stiff)
strength+flexibility incr with bundling and branching
actin filament assembly
actin monomer-ATP binds to + end
soon hydrolyzes to ADP
actin ADP dissociates from - end
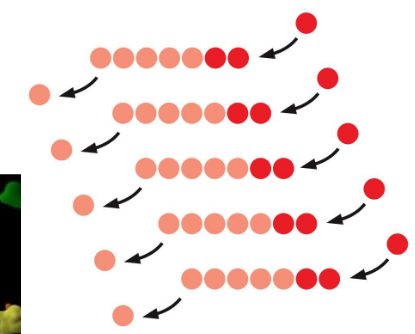
regulation of actin network
regulated by other proteins
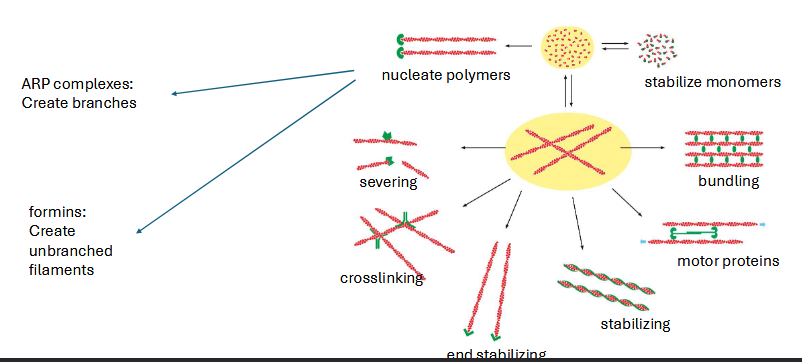
myosin
motor protein
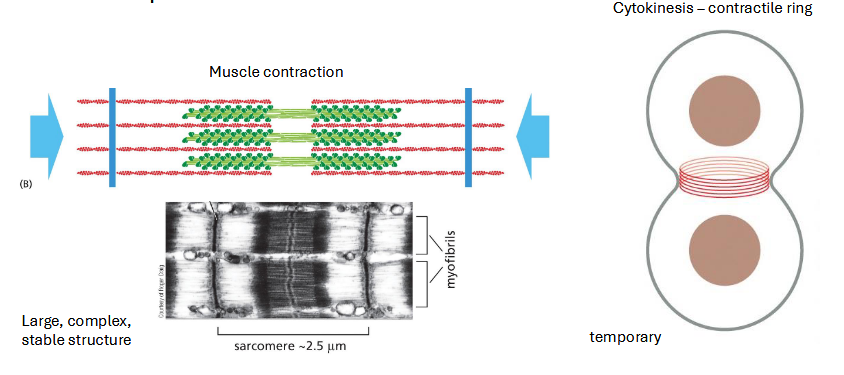
muscle contraction
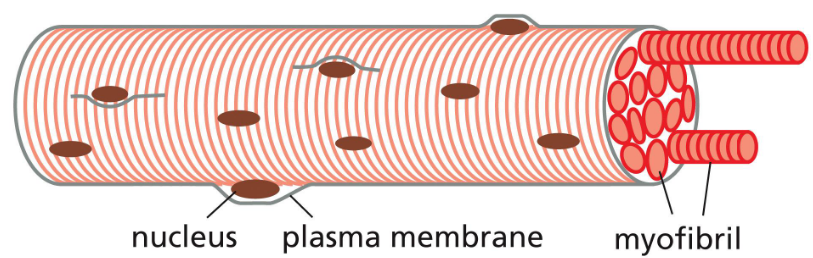
myofibrils fill most of cytoplasm of muscle cell
cells merge (syncytia) to create large continuous bundles
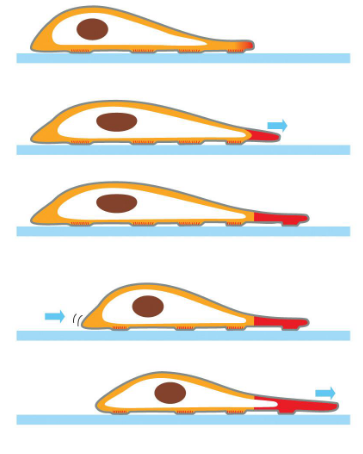
cell migration — actin function
cell migration = crawling along surface
continuous reshaping of the front and back of the cell
fish scale keratocyte is a model for actin based movement. fluid continuous movement
3 processes that req actin: protusion (cell extends @ front end), attachment to surface, contraction of rear end
migration — protusion (relevant structures)
lamellipodium — flat sheet
filopodium — strands sticking out from cell
lamellipodia
sheets. continuous polymerization at + end pushes plasma membrane
actin branching creates flat sheet — ARP complexes
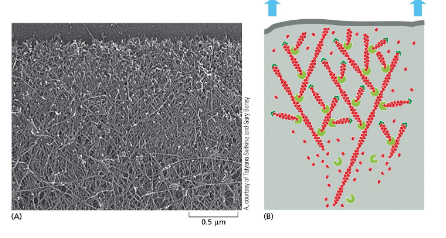
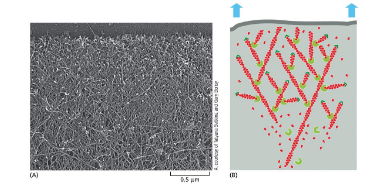
suppose that actin molecules in a cultured cell have been labeled so that 1 in every 10k actin molecules has a fluorescent label
how would a fluorescent molecule appear @ leading edge? a dot or a line?
what would the fluorescent look like as the cell moves? would it move with the cell?
[textbook]
filopodia
bundles of actin — formins
thought to function in sensing, attachment and guidance during movement

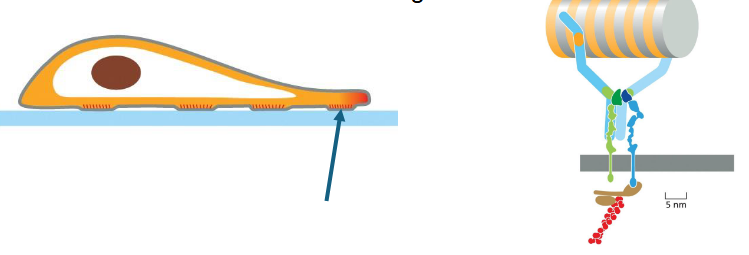
migration — attachment
actin attaches to integrin proteins which span the plasma membrane and attach to smth extracellular
adhesion matters
why is this necessary for movement?
migration — contraction of rear end
actin forms bundles @ rear end
myosin motor proteins create contraction of cytoplasm
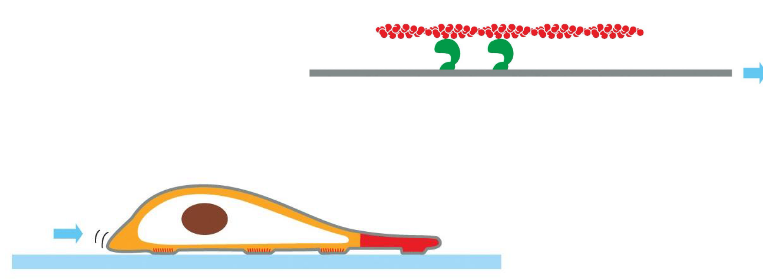
cell migration summary
actin networks assemble and disassemble continuously
structure and proteins involved depends on region of cell
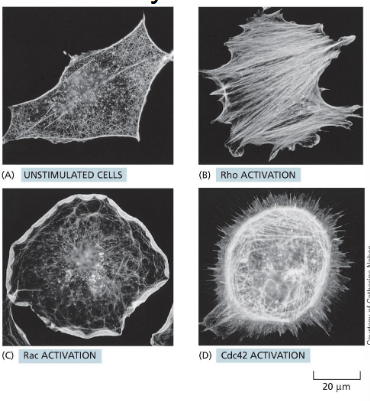
rho family proteins regulation of actin dynamics
related GTPases are regulators of actin shapes
these proteins can be active in different parts of the cell to create directional movement
these are effectors of various signaling cascades
many of these GTPases are upregulated in cancer. how might this contribute to cancer progression?
the only way to get new cells is by ___
division of existing cells
functions of cell division
development, reproduction, wound healing, continual cell division of skin, etc
phases of euk cell cycle — control system
processes happen in the correct order
each phase is finished before the next begins
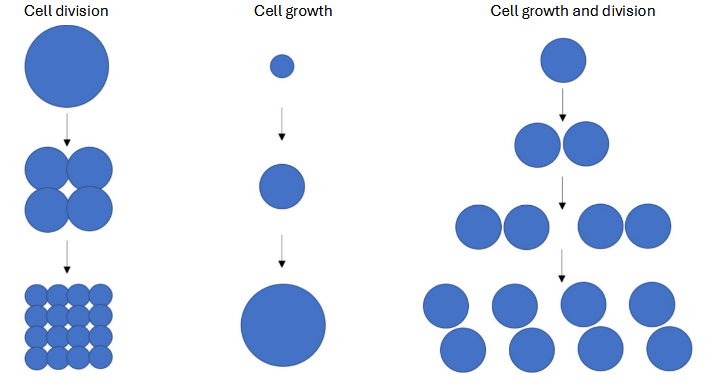
diagram cell division vs cell growth vs cell growth+divison
how long is the cell cycle? what proportion of time will a cell spend in each phase?
during early development?
a skin cell?
[textbook]
cell cycle control — asks 2 questions
how do cells control coordinated progression thru cell cycle
how do cells ensure each daughter cell gets a complete genome + necessary cytoplasm
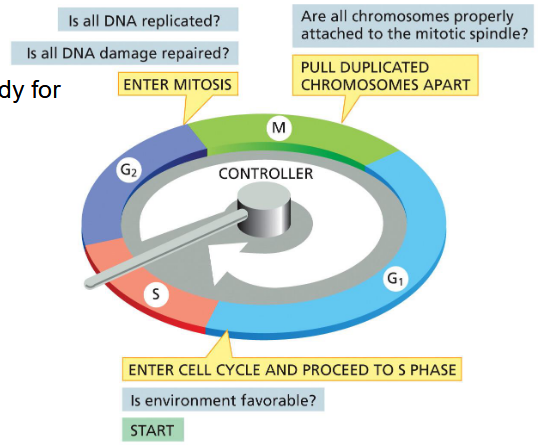
cell cycle checkpoints
cells pause until ready for next phase
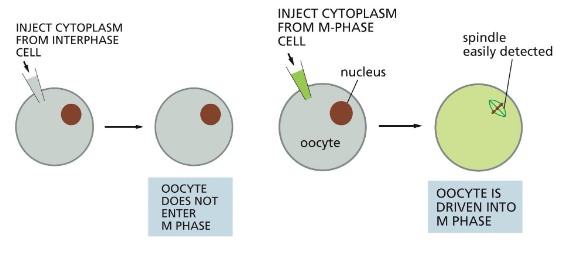
how is cell cycle control coordinated?
early studies used frog eggs — easy to see/manipulate
suggests a maturation-promoting factor (cyclin): can trigger mitosis, activity is cyclical
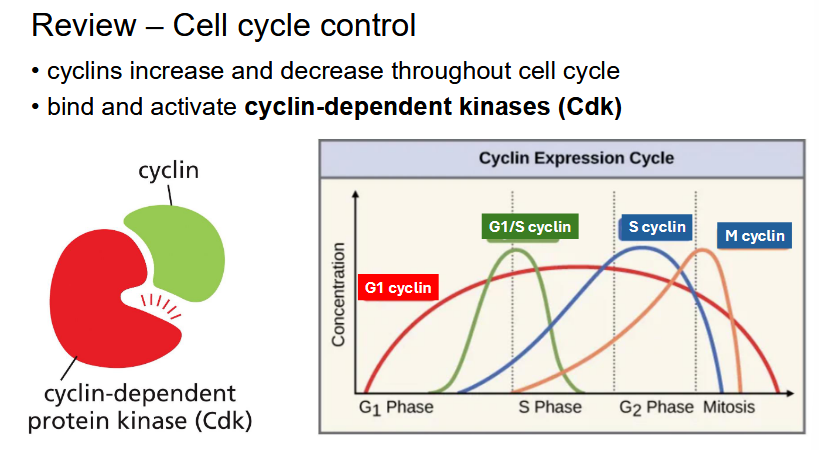
cyclins
proteins that increase and decrease throughout cell cycle
bind and activate cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk)
Cdk regulate cell cycle activites. phosphorylate effector proteins, levels stay constant, only active when bound to cyclin partner
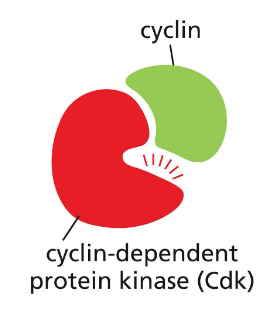
Cdk inactive vs active
inactive: not bound to cyclin. always present
active: bound to cyclin. adds phosphates to target protein → activate cell cycle functions
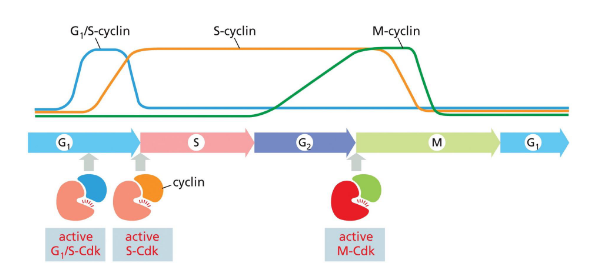
cyclin-cdk complexes
specific pairs function in phases of cell cycle
G1-cdk complex: early G1
G1/S-cdk complex: late G1
S-cdk complex: DNA synthesis
M-cdk complex: mitosis
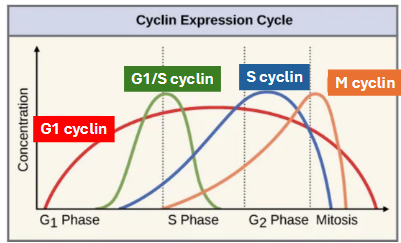
cyclin vs cdk: what cell processes might affect cyclin levels vs cdks?
cyclin level fluctuates (goes up during transcription/translation, then down during degradation) while cdk is always around
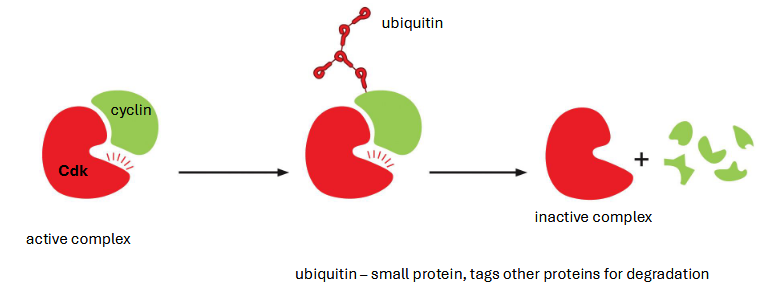
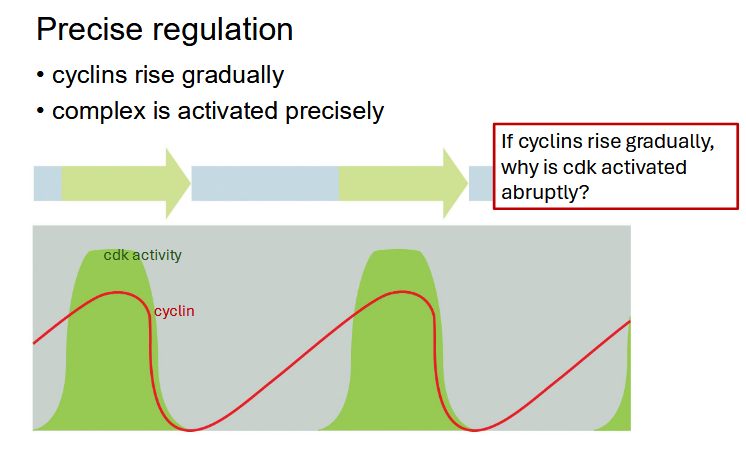
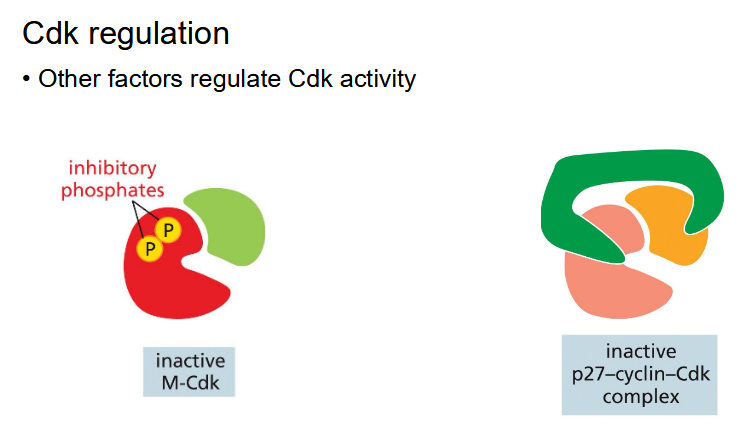
skipped these slides in class i think but i wasnt paying that much attention so maybe
cell cycle control review
where does cell cycle begin + why does it matter?
G1 — a reset of the control system
reset necessary bc during mitosis: cyclins are degraded, synthesis of new cyclins is blocked, cdk inhibitors are active
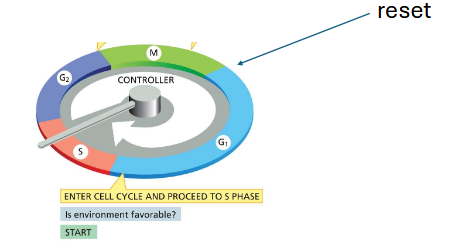
in mammalian cells, arrest is the default
mammalian cells require mitogens (growth factors) to progress thru G1
mitogen signaling activates synthesis of G1 cyclins (RTK - MAP kinase cascade)
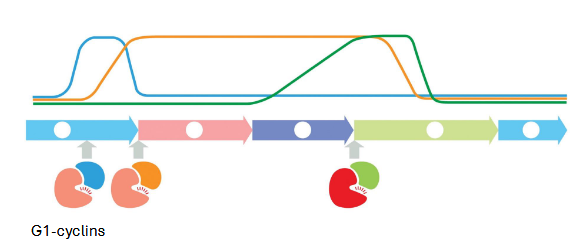
G1-cdk: activates sequential production of cyclins
sequential cdk activity leads to DNA replication
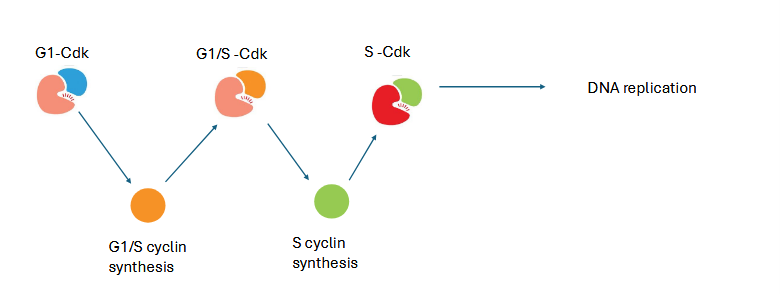
how is dna synthesis activated?
replication machinery pre-loaded @ origins of replication
S-cdk triggers DNA replication by recruiting remaining machinery
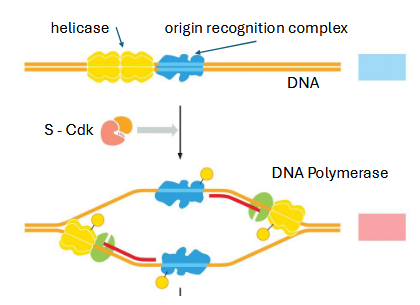
checkpoints
cells pause until ready for next phase
G1 checkpoint: is environment favorable? → enter cell cycle and proceed to S phase
G2 checkpoint: is all DNA replicated? is all DNA damage repaired? → enter mitosis
M checkpoint: are all chromosomes properly attached to the mitotic spindle? → pull duplicated chromosomes apart
what if DNA is damaged?
G1/S and S cdks are inhibited
DNA damage activates p53 (“guardian of the genome) → production of G1/S and S cdk inhibitor
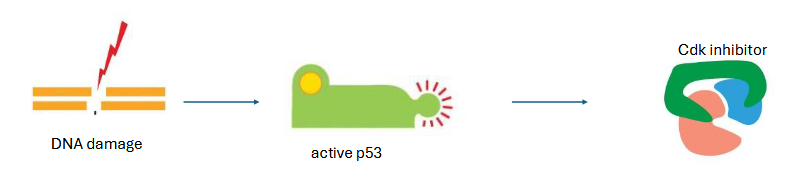
[___] and [___] are key regulators of control system
cyclins and cdks
cell cycle overview
coordinated progression thru stages
cyclin-cdk complexes regulate timing
activation and inhibition can provide gas and brakes
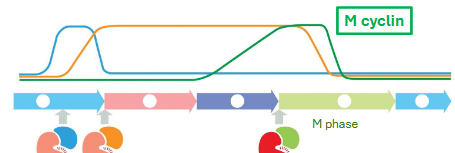
m-phase: mitosis and cytokinesis — goals?
equal segregation of chromosomes and equal distribution of cytoplasm (usually)
M phase usually takes how long in mammalian cells?
~1 hr
M-phase: [___] levels rise gradually but cells [___] rapidly
cyclin levels rise gradually but cells enter mitosis rapidly
m-cdk complexes
m-cyclin rises gradually in G2 but is kept inactive by an inhibitory kinase
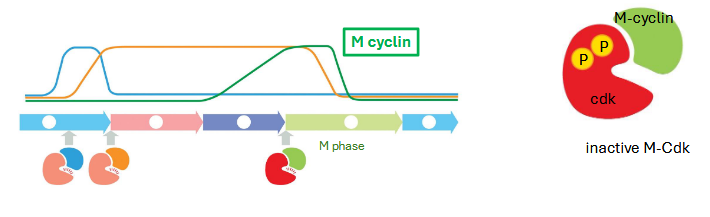
rapid activation of m-cdk
phosphatase removes phosphates — activating m-cdk (active after G2 complete)
positive feedback — active m-cdk activates more phosphatase
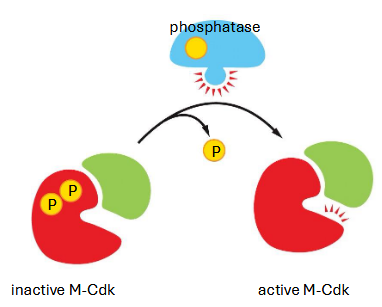
m-cdk — regulates what?
most actions of early mitosis
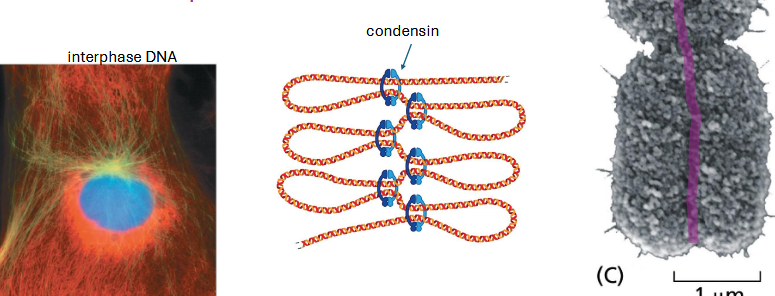
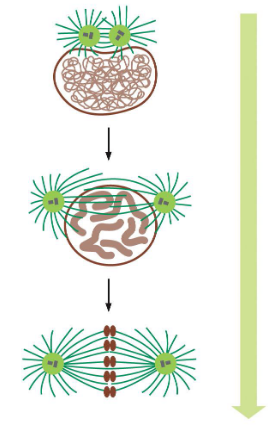
mitosis stages overview — chromosomes condense
condensin protein packs chromosomes
sister chromatids remain attached — cohesin protein
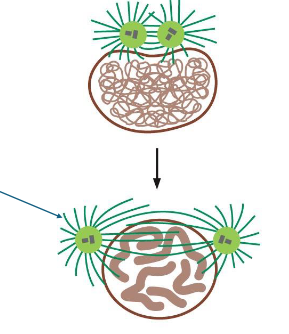
mitosis stages overview — mitotic spindle formation
microtubules grow and shrink
centrosomes move to opposite poles of cell
aster microtubules provide an anchor (green arrow)
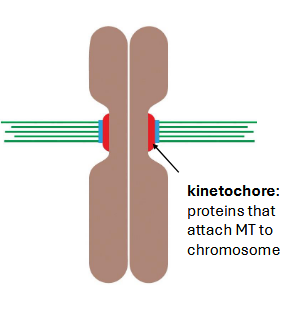
mitosis stages overview — microtubules attach to chromosomes
bi-polar attachment — what does this mean?
microtubules (MTs) grow and shrink until they attach (kinetochore)
how does the cell sense bi-polar attachment? — tension
mitosis recap — M-Cdk regulates what 3 things?
chromosomes condense
bi-polar spindle forms
bi-polar attachment to chromosomes (sister chromatids)
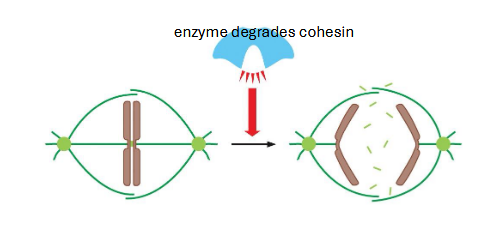
m-phase checkpoint
spindle moves chromosomes around until all are aligned
anaphase promoting complex (APC)
chromosome bi-polar attachment and metaphase alignment triggers anaphase
active APC complex leads to cohesin degradation
tension pulls chromosomes to opposite poles
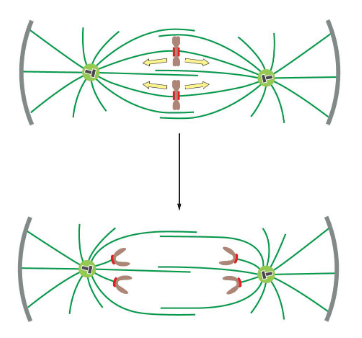
microtubules move chromosomes to opposite poles
kinetochore microtubules shrink; centrosomes move apart
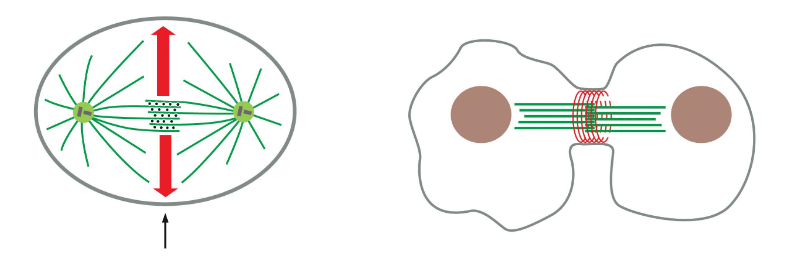
cytokinesis
contractile ring (actin) forms at mid-point
likely some signal from microtubules to actin
m-phase summary
m-cdk activates early stages of mitosis — chromosomes condense, spindle forms bi-polar attachment, metaphase checkpoint
APC triggers anaphase — breaks down cohesins
actin contractile ring forms during telophase