Exam 3 EENT (cornea/ant chamber/lens)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Keratitis (corneal ulcer)- Etiology/Pathophysiology
Interruption of corneal epithelium and/or abnormal tear film permits entrance of microorganisms, proliferate, and cause ulceration
Commonly due to infectious agents, but noninfectious causes include neurotropic keratitis (loss of sensation), severe dryness, etc
Bacterial keratitis is an EYE EMERGENCY (sight-threatening)
Bacterial keratitis rapidly progresses; corneal destruction in 24-48 hrs
Keratitis (corneal ulcer)- Bacterial responsible for bacterial keratitis are
Streptococcus
Pseudomonas
Enterobacteriaceae (including Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Proteus)
Staphylococcus
Viral: HSZ, HZO
Fungal: common after eye trauma
Keratitis- Risk factors for bacterial keratitis
Contact lens use
Contaminated ocular medications or contact lens solution
Decreased immunologic defenses secondary to malnutrition, alcoholism, and diabetes
Tear film abnormalities
Recent corneal disease (including herpetic keratitis, neurotrophic keratopathy)
Structural alteration or malposition of the eyelids
Use of topical corticosteroids-risk
What is the main risk factor for the development of bacterial keratitis?
Extended contact lens usage
Keratitis Hx
RAPID onset of PAIN, photophobia, and decreased vision
Document:
-contact lens wear (type, wearing time, type of disinfection system)
-Trauma (including corneal surgery)
-use of ocular meds
Decreased immunologic defenses (immunocompromised)
Tear film abnormalities
Recent corneal disease
Structural alteration or malposition of they eyelids
Use of topical steroids
Keratitis- Physical
Ulceration of cornea; infiltrates, surrounding edema
Anterior chamber reaction with or without hypopyon
Eyelid edema
Corneal haze
Conjunctiva hyperemia
Mucopurulent exudate
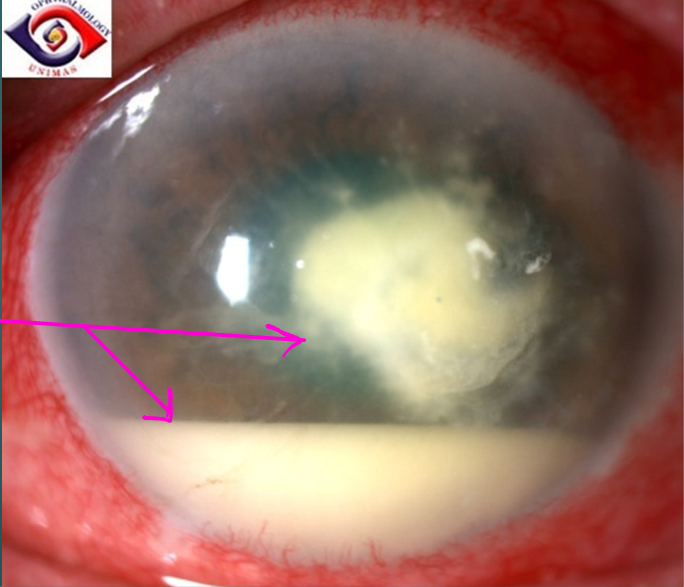
What is a hypopyon?
Inflammatory cells layered in the anterior chamber
Which of the following symptoms is most suggestive of corneal involvement?
Red eye
Tearing
Decreased vision
Keratitis- Diagnostic assessment
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment to reduce possibility of permanent visual loss
Diagnosis by H&P (fluorescein stain and slit lamp)
Cultures of they eyelids/conjunctiva, topical ocular meds, contact lens cases, and solutions
Referral to ophthalmology for corneal scrapings or biopsy in cases of deep infiltrates, particularly if cultures are negative and eye not improving
Complete corneal destruction from bacterial keratitis can occur in?
1-2 days
Keratitis Tx
Refer suspected cases to ophthalmology immediately
Topical antibiotics - mainstay of treatment
If no organisms are identified on slide or smears not obtained, initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics (Cipro drop)
Depends on size, contact lens use, anterior chamber rxn
Cycloplegic drops, Tylenol
Monitored closely and follow-up in 24hrs to make certain infection responding
Admission and systemic antibiotics for perforation, refractory or slow to respond to tx, visual loss or specific organisms (N gonorrheae)
In perforation, clear plastic shield
Viral: oral/topical antiviral
Fungal: antifungal eye drop
Keratitis complications
Thinning of the cornea and eventual perforation of cornea may result in endophthalmitis and loss of eye
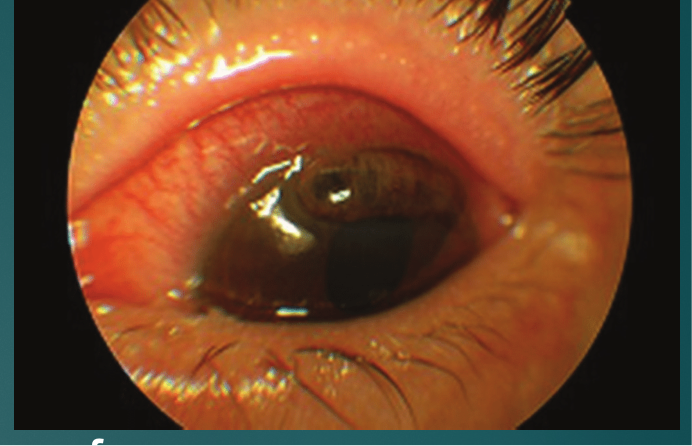
Keratitis Patient Ed
Pts who are contact lens wearers are instructed not to use lenses with hyperemia, irritation, or FB sensation, and to use sterile contact lens solutions to avoid contamination
Topical antibiotics given routinely after any traumatic injury to the cornea (including surgery)
Keratitis Prognosis
The visual prognosis depends on:
-Virulence of the organism
-Extent and location of corneal ulcer
-Resulting vascularization and/or collagen deposition
Ultraviolet (Actinic) Keratitis
UV light is the most common cause of radiation injury to eye
Cornea epithelium absorbs UV radiation- cumulative
Prolonged exposure can lead to chronic toxicity, which is associated with pinguecula, pterygium, squamous metaplasia and carcinoma
Inflammation- edema, superficial puctate keratits (SPK, pictured) to total desquamation
Reepithelialization- can occur in 36-72 hrs
Sunburn to cornea
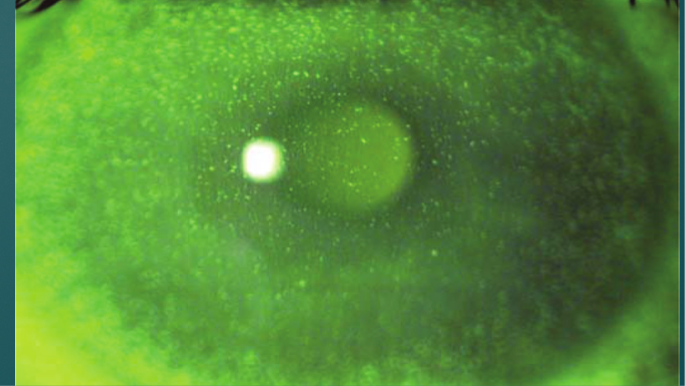
Ultraviolet (Actinic) Keratitis eitology
Unprotected or long exposure to sun, particularly high altitudes
UV radiation reflected off snow, ice, or water
Viewing solar eclipses
Welder’s arcs
Carbon arcs
Sun tanning beds
Photgraphic flood lamps
Lightning
Electric sparks
Halogen desk lamps
Ultraviolet (actinic) keratitis Hx
FB sensation, irritation, pain, photophobia, tearing, blepharospasm, and decreased visual acuity 6-12 hours after exposure
Contact lens use, past ocular trauma or surgery, current meds, and allergies to meds
Document info regarding nature and duration of exposure
Was protective eye wear used?
Always look and document exam/presence of FB
Ultraviolet (actinic) keratitis Physical
Visual acuity
Lids and conjunctiva-lid edema, conjunctival hyperemia, and chemosis. Diffuse corneal haze, severe cases
Fluorescein staining- superficial punctate epithelial surface irregularities, covers entire surface of cornea
Dx: Slit lamp exam with fluorescein
Eye pain from UV radiation occurs in?
6-12 hours
Ultraviolet (actinic) keratitis Tx
Resolves in 24-72 hours if we do nothing
Short-acting cycloplegic drop- relieve pain or reflex ciliary spasm. Administer pain meds- topical ophthalmic NSAID or oral NSAID
Oxycodone (oxytocin) and acetaminophen- breakthrough pain
Topical antibiotic ointment or drops
Topical anesthetic only in office, frequent use retards healing and may lead to corneal ulcer formation
Follow-up with ophthalmologist not necessary except with extensive corneal damage, persistent pain or vision deficits 48 hrs after injury or preexisting eye conditions
Should not wear contact lenses until symptoms resolve
Ultraviolet (actinic) keratitis Patient Ed
Educate pts about proper eye precautions, such as the use of UV-filtering lenses or limiting exposure to the sun
Complications
-Superinfection- rarely
-Vision loss-rarely
Prognosis
-excellent for full recovery in 24-76 hrs
Reepithelization from UV radiation keratitis generally occurs in?
A few days
An old snowplow operator complains of pain and photophobia in both eyes. Which of the following are TRUE regarding his condition?
Onset of symptoms are delayed 6-12 hours after exposure
What is SPK characterized by?
Small pinpoint defects in the cornea
How should a pt with suspected bacterial keratitis be treated?
Topical antibiotics and follow-up in one week
Corneal abrasions
Very common!
Scraping away of corneal surface from external forces
Cornea and bulbar conjunctiva are affected
Minor or superficial abrasions involve only corneal epithelium
Severe injuries involve deeper, thicker stromal layer
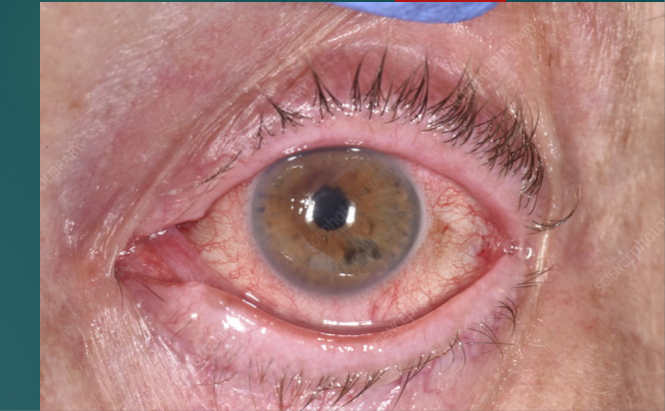
Main causes of corneal abrasion
Trauma (finger nails, tree branches, makeup brushes)
Foreign body (dust, sand, metal, wood)
Contacts (themselves can cause, poor fit)
Iatrogenic (we cause the harm- eye exam, eye surgery)
Corneal abrasions Hx
“something is in my eye”, sudden onset pain, irritation, photophobia, blepharospasm, tearing, redness, and/or visual disturbance
Extended contact wear
Occupational Hx (trades, FB)
Recreation Hx (hunters, beach)
Last tetanus shot (trauma- want to have updated tetanus)
Corneal abrasion Physical
Sudden onset
FB may or may not be seen
Every eyelid for FB
Bulbar conjunctival injection
Visual acuity usually normal, unless abrasion within central visual axis or large
Superinfection- rarely
Vision loss- rarely
Corneal abrasion Dx
Topical anesthetic for severe pain
Severe photophobia causing blepharospasm- (have someone hold eye open so you don’t have to use drops and wait) instillation of cycloplegic 20-30 minutes prior to exam
Fluorescein instillation and exam with blue light
Slit lamp- anterior chamber for evidence of iritis (cells and flare)
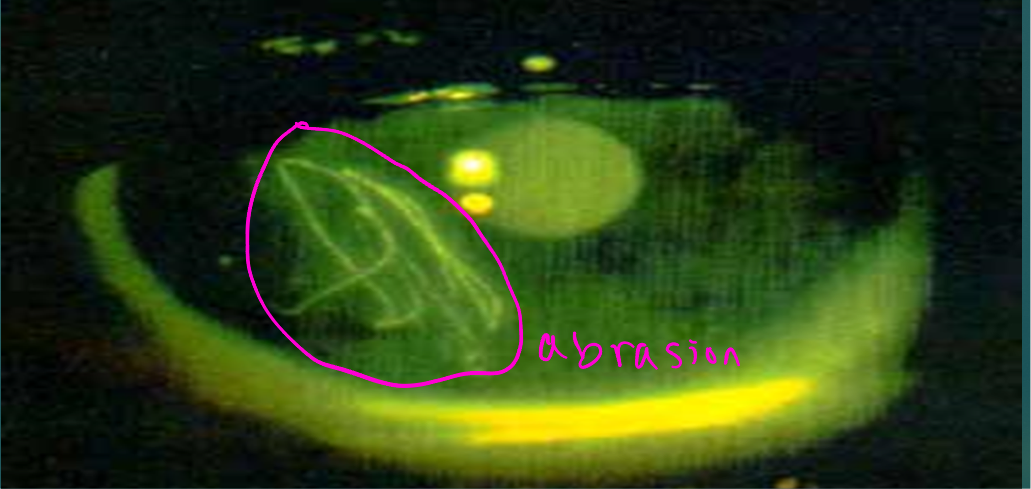
Corneal abrasions Dx cont
Fluorescein can permanently stain soft contact lenses; remove
Corneal ulcer suspected, consider bacterial cultures before instilling antibiotics
Ocular penetration with retained FB suspected, ocular CT scan indicated
Corneal abrasions Tx
Update tetanus
Topical anesthetic and or cycloplegic- comfort and exam (not usually necessary)
Topical anti-inflammatory eye drops- relieve pain, oral if not effective
FB remove with sterile cotton tipped applicator or tuberculin needle
“rust ring” after removal metal - remove rust ring
Once violated, cornea becomes susceptible to infection and prophylactic antibiotic drops used
Will heal on its own
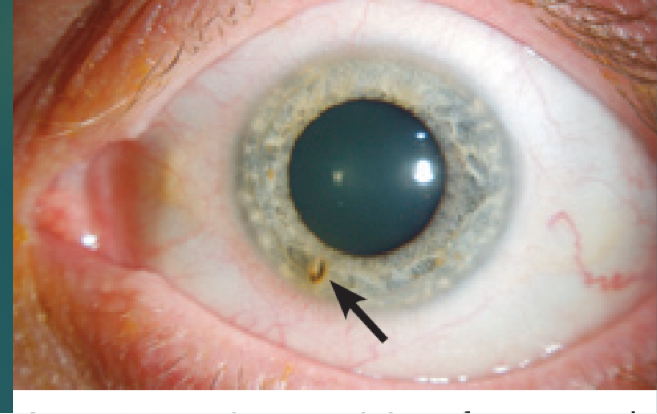
Corneal abrasions Therapeutics
Large or dirty abrasions, broad-spectrum antibiotic drops
Contact lens- infectious corneal ulcers likely, cover for gram-negative organisms/pseudomonas (don’t wear lenses until healed)
NO EYE PATCHING (increases bacteria risk, doesn’t improve healing)
Avoid neomycin- higher incidence of allergy
Antibiotic drops more comfortable than ointments, but administered every 2-3 hrs (Cipro drops or erythromycin ointment)
Ointments, retain antibacterial effect longer, used less often but blur vision temporarily
Corneal abrasions Consultations
Emergent ophthalmologic consultation warranted for suspected retained intraocular FBs
Urgent consultation is needed for suspected corneal ulcerations (white necrotic areas around abrasion with gray exudates)
Corneal ulcers are round, with upward edges, lumps or divots
Corneal abrasions Patient Ed
Return in 24 hrs for re-evaluation
Minor abrasions heal in 24-48 hrs (no driving)
Larger abrasions examine daily until healed and potential for infection no longer exists
Eye rest- movement interferes with re-epithelialization
Avoid light or wear sunglasses with photophobia
Antibiotics continue until asymptomatic
Protective eyewear at jobs with increased risk,
Corneal abrasions Complications
Recurrent epithelial erosion- days to weeks after healed abrasion
Corneal ulcerations common after contact lens abrasion
Tetanus (rare)
Allergic conjunctivitis, meds (neomycin)
Acute narrow-angle glaucoma precipitated by cycloplegics/mydriatics
Intraocular Foreign Body (IOFB)
Less acute eye damage compared to blunt trauma
Tissue reaction varies with composition. Inert substances such as glass, stone, and plastic better tolerated than metals that oxidize
Less inert, organic material pose significant tissue reaction. the risk of endophthalmitis increases
Most injuries at work using various tools with metal striking metal- 80%; metallic or magnetic
Incidence higher in males
20-40 years with no protective eye gear
IOFB Hx
What happened-medical-legal and workman’s compensation
Suspect foreign object with projectile (hammering, grinding, etc.)
Feel something enter the eye, no obvious external changes; dismissed
Irritation or conjunctival injection
Decreased visual acuity if visual axis affected
Determining if IOFB is inert- important to the surgical management
Usually unilateral but need to examine both eyes closely
IOFB Physical
Examine both eyes
Document the vision bilaterally
Location (clock notation)
Slit-lamp exam- anterior segment, fluorescein streaming
Cornea- edema surrounding the perforation site, opacification, irregular shape
Scleral entry- conjunctival injection, darker pigmentation in sclera indicated choroid exposure
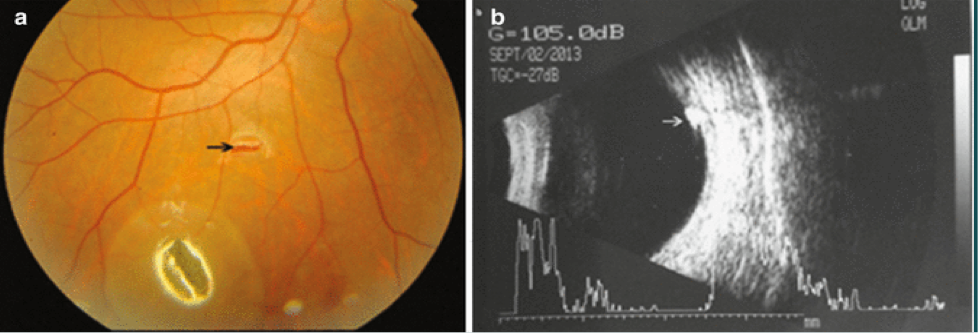
IOFB opacification and neovascularization
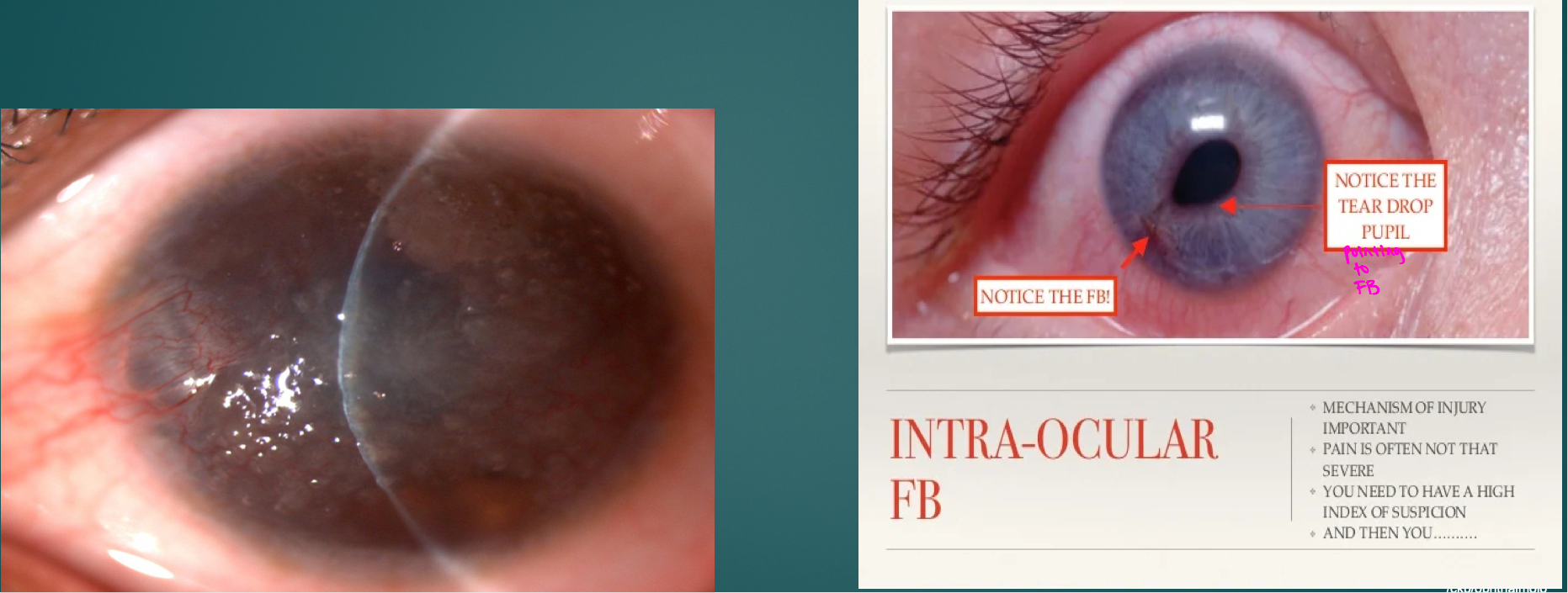
IOFB Dx
CT scan- test of choice for localization
X-ray plain films if metallic when CT scan not available
MRI avoided if metallic
U/S- adjunct tool in localizing and to determing if metallic
IOFB therapeutics
Get to ophthalmo right away
Minimize pressure on globe
Eye shield
Tetanus updated
24 hr delay in removal increases risk of endophthalmitis
reactive substances, copper and iron, removed urgently because oxidative process induced on retina
Vegetable matter- high risk for endophthalmitis- removed urgently
Inert possible to remove later
Antibiotic coverage for gram pos/neg organisms
Surgical approach for removal depends on if object is anterior or posterior to the iris
IOFB consultations
Radiologist help determine location and type of material
EMERGENCY and referred immediately to ophthalmology
IOFB Pt Ed
Reduce activity and Valsalva (bearing down) maneuvers prior to surgery- Incr. IOP
Daily follow-up exam to watch for complications
The use of polycarbonate safety glasses reduces risk
IOFB complications
Corneal opacity
Cataract
Endophthalmitis
Retinal detachment/vitreous hemorrhage
Optic neuropathy
Siderosis- ocular reaction from iron (cataract)
Hyphema
Trauma to the eye- bleeding in anterior chamber
Stretches limbal vessels and displaces the iris and lens
-may result in tear of iris or ciliary body causing bleeding
Blood exits anterior chamber via trabecular meshwork and Schlemm canal. Blood clots form blocking exit causing hyphema and increased IOP
Males are involved in ¾ of cases
Spontaneous hyphema are secondary to neovascularization (DM, ischemia), ocular neoplasms (retinoblastoma) and vascular anomalies
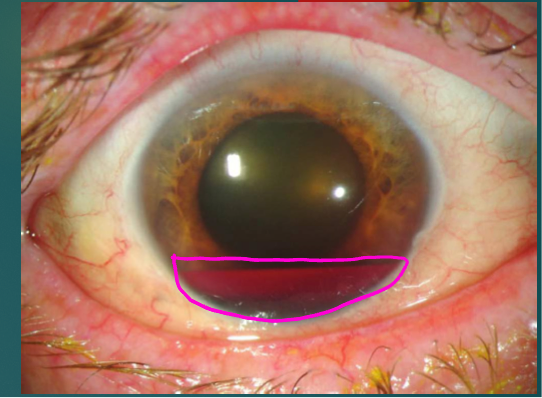
Hyphema Likelihood/grading system
African Americans & Mediterranean descent screened for sickle cell disease, -early surgery
Grading system:
Grade 1- layered blood occupying less than 1/3 of anterior chamber
Grade 2- blood filling 1/3 to ½ of anterior chamber
Grade 3- layered blood filling ½ to less than total of anterior chamber
Grade 4- Total clotted blood, blackball or 8-ball hyphema
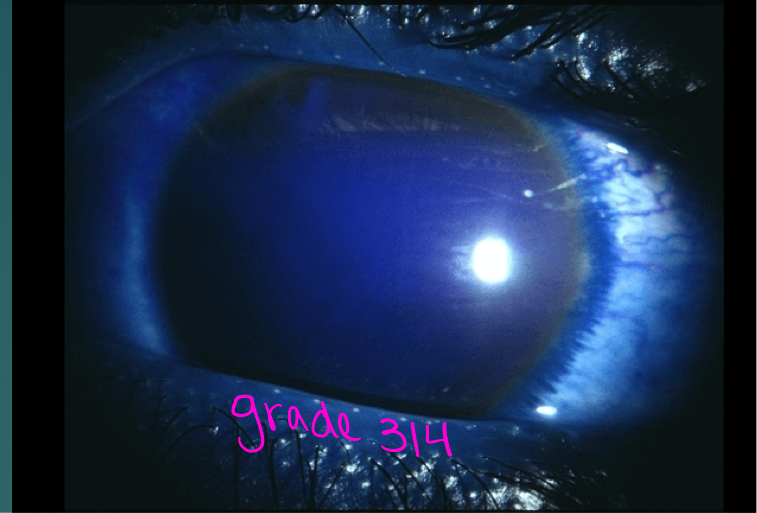
Hyphema
Most hyphemas fill less than 1/3 of anterior chamber
trauma initially may cause a small hyphema
More severe bleeding may follow in 3-5 days
Usual duration of an uncomplicated hyphema in 5-6 days
Mean duration of elevated IOP is 6 days
Hyphema H&P
Eye trauma- eye pain and blurred vision
Nausea and vomiting
Red eye
Layered blood in anterior chamber of eye
Corneal blood staining
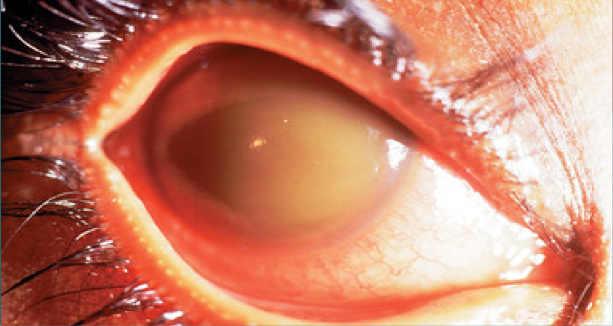
Hyphema Dx
Visual acuity test
IOP must be checked
Check for optic atrophy-pale optic disk (funduscopic exam)
Corneal blood staining
Watch for secondary hemorrhage