World War 1 & The Roaring 20s
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
flappers
Young woman from the 1920s who rebelled against tradition; had short hair, wore short dresses and make up

19th amendment
Amendment to the U.S. Constitution (1920) extended the right to vote to women in federal or state elections.
(States cannot deny the right to vote based on gender).

“Blind pig”(Speakeasy)
The term “blind pig” originated in the United States in the 19th century; it was applied to lower-class establishments that sold alcohol during prohibition. The operator of an establishment (such as a saloon or bar) would charge customers to see an attraction (such as an animal) and then serve a “complimentary” alcoholic beverage, thus circumventing the law.
“Sociology Department”
Henry Ford’s intelligence gathering agency designed to spy on his employees to determine if they were model employees (did they smoke/drink?)
“Service Department”
What Ford’s “sociology department” evolved into that provided information to the police about who was breaking prohibition.
“Syndicates”
Gangsters and other “organized crime” families who supplied illegal liquor to those willing to break the law (they would soon enough work alongside of Ford’s “service department” to make sure they were never prosecuted for breaking the law.
WCTU
Women's Christian Temperance Union: organization that worked for women's suffrage and prohibition
Florence Kelley
The reformer who started the National Consumer League which worked to prohibit child labor and to improve conditions for female workers
Emma Goldman
Outspoken radical (anarchist) most notable for her support of birth control and who was deported during the Palmer raids on limited evidence.
Margaret Sanger
United States nurse who campaigned for birth control and planned parenthood.
Jane Addams
Founder of the Hull House in Chicago--a housing and job training facility for poor immigrants.
NAWSA
National American Woman Suffrage Association; founded in 1890 to help women win the right to vote
Alice Paul
Leader of the National Woman's party, campaigned for an Equal Rights Amendment to the Constitution
Red Scare
An outbreak of national alarm which began in 1919. The success of communists in Russia (Bolsheviks), was believed to inspire American radicals to embrace communism. Fears were followed by a series of mail bombings which frightened Americans.

Bolsheviks
Led by Vladimir Lenin, it was the Russian communist party that took over the Russian government during WWI

Palmer Raids
Prompted by a series of unexplained bombings, these raids were conducted by the Justice department to root out communists, socialists, and anarchists, who they believed were trying to overthrow the government. Led by Mitchell A Palmer 6,000 people were arrested, most of them foreign born; 500 including Emma Goldman were deported. They ended when the predicted riots on "May Day" (a pro-labor holiday) did not take place and people became concerned with abuse of civil liberties by the Government.

nativists
People that sought to limit immigration and preserve the country for native-born white Protestants in the late 1800's.

American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU)
an organization founded in 1920 to defend Americans' rights and freedoms as given in the Constitution

Xenophobia
a fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers

Sacco and Vanzetti
Italian radicals who became symbols of the Red Scare of the 1920s; arrested (1920), tried and executed (1927) for a robbery/murder, they were believed by many to have been innocent but convicted because of their immigrant status and radical political beliefs.
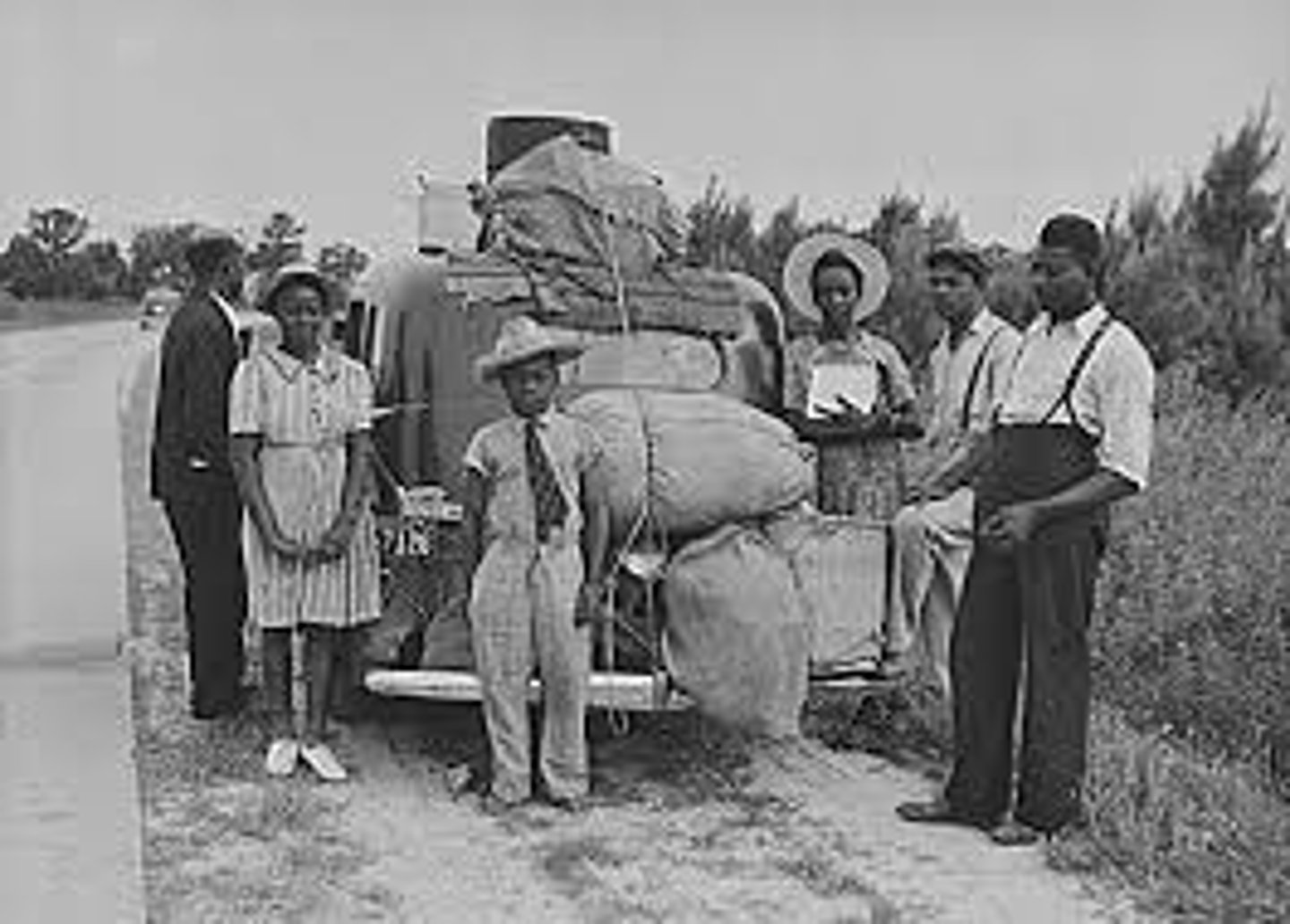
Great Migration
An early 20th century mass movement of African Americans from the Deep South to the Industrial North, particularly Chicago.

Fundamentalism
Literal interpretation and strict adherence to basic principles of a religion (or a religious branch, denomination, or sect). Led to Scopes Monkey Trial and Prohibition.

Scopes trial
1925 - Prosecution of Dayton, Tennessee school teacher, John Scopes, for violation of the Butler Act, a Tennessee law forbidding public schools from teaching about evolution. Former Democratic presidential candidate, William Jennings Bryan, prosecuted the case, and the famous criminal attorney, Clarence Darrow, defended Scopes. Scopes was convicted and fined $100, but the trial started a shift of public opinion away from Fundamentalism.

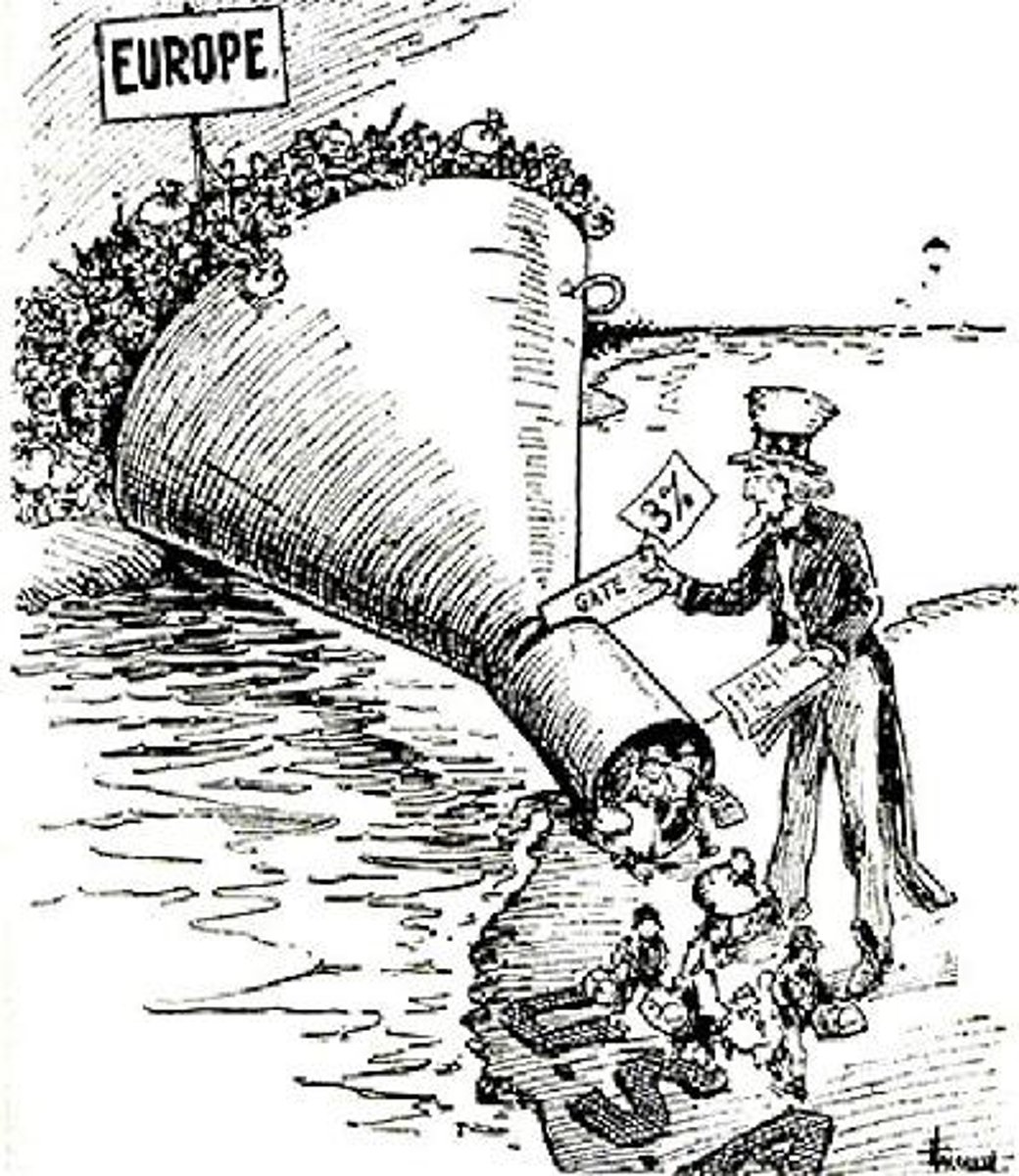
Emergency Quota Act
A government legislation that limited the number of immigrants from Europe which was set at 3% of the nationality currently in the U.S. Immigration numbers decreased considerably compare to previous years.

National Origins Act
Act which restricted immigration from any one nation to two percent of the number of people already in the U.S. of that national origin in 1890. Severely restricted immigration from Southern and Eastern Europe, and excluded Asians entirely

"nickelodeons"
Five-cent movies from the 1920s.
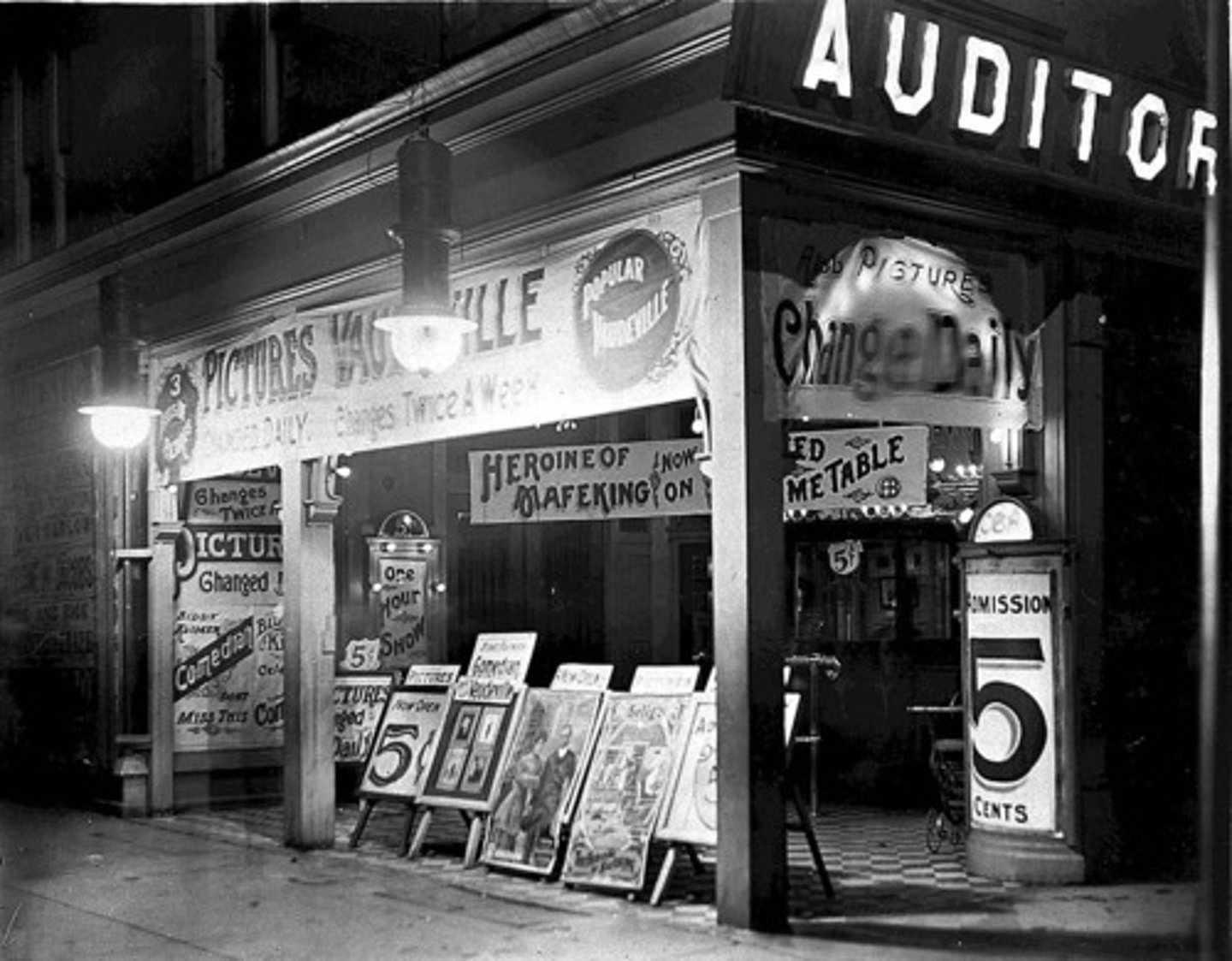

"talkies"
the first motion picture with sound

Jazz Age
Name for the 1920s, because of the popularity of jazz-a new type of American music that combined African rhythms, blues, and ragtime.
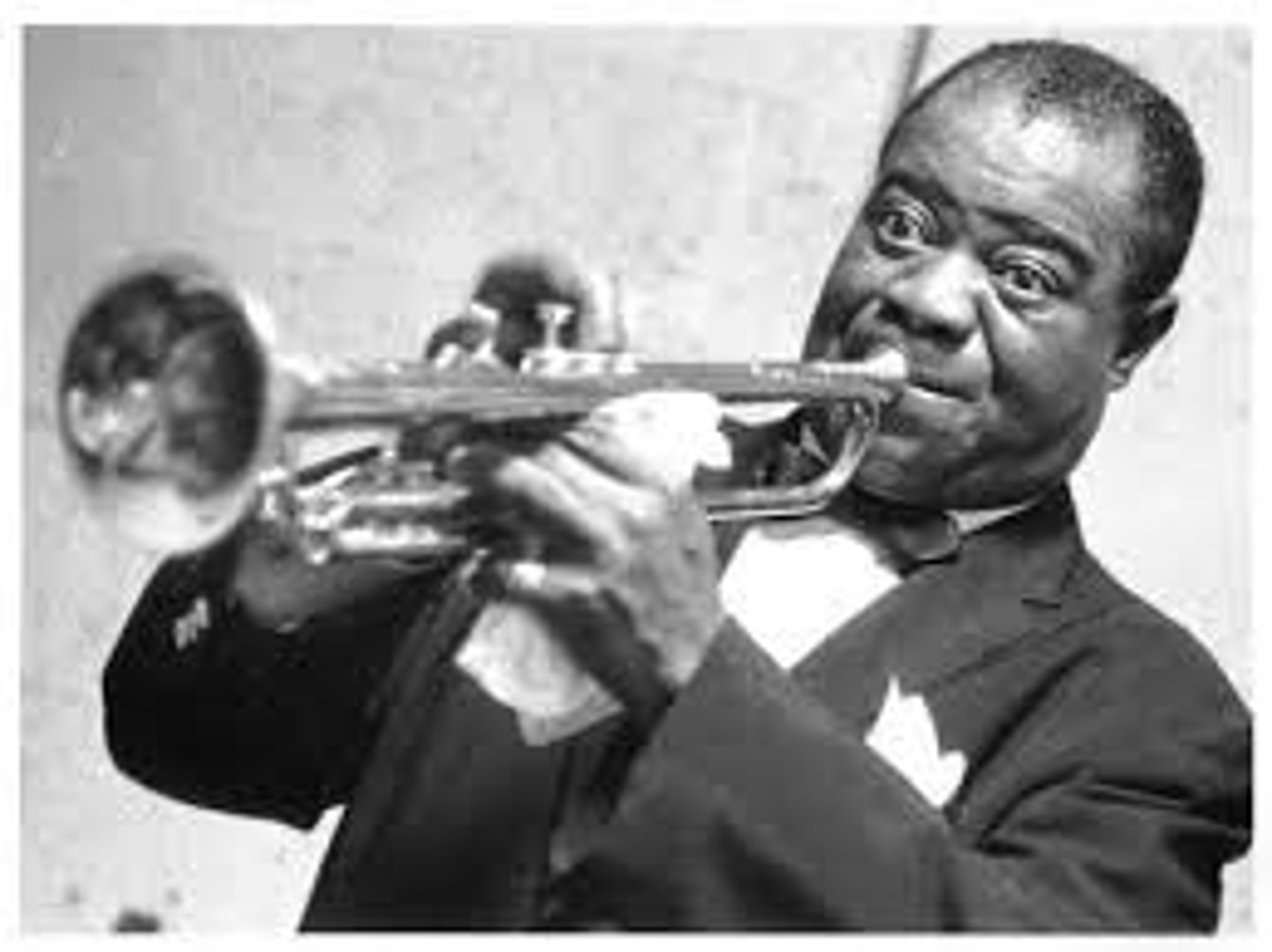

Harlem Renaissance
Celebration of African American culture. A period in the 1920s when African-American achievements in art and music and literature flourished. Ex: Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, and Louis Armstrong
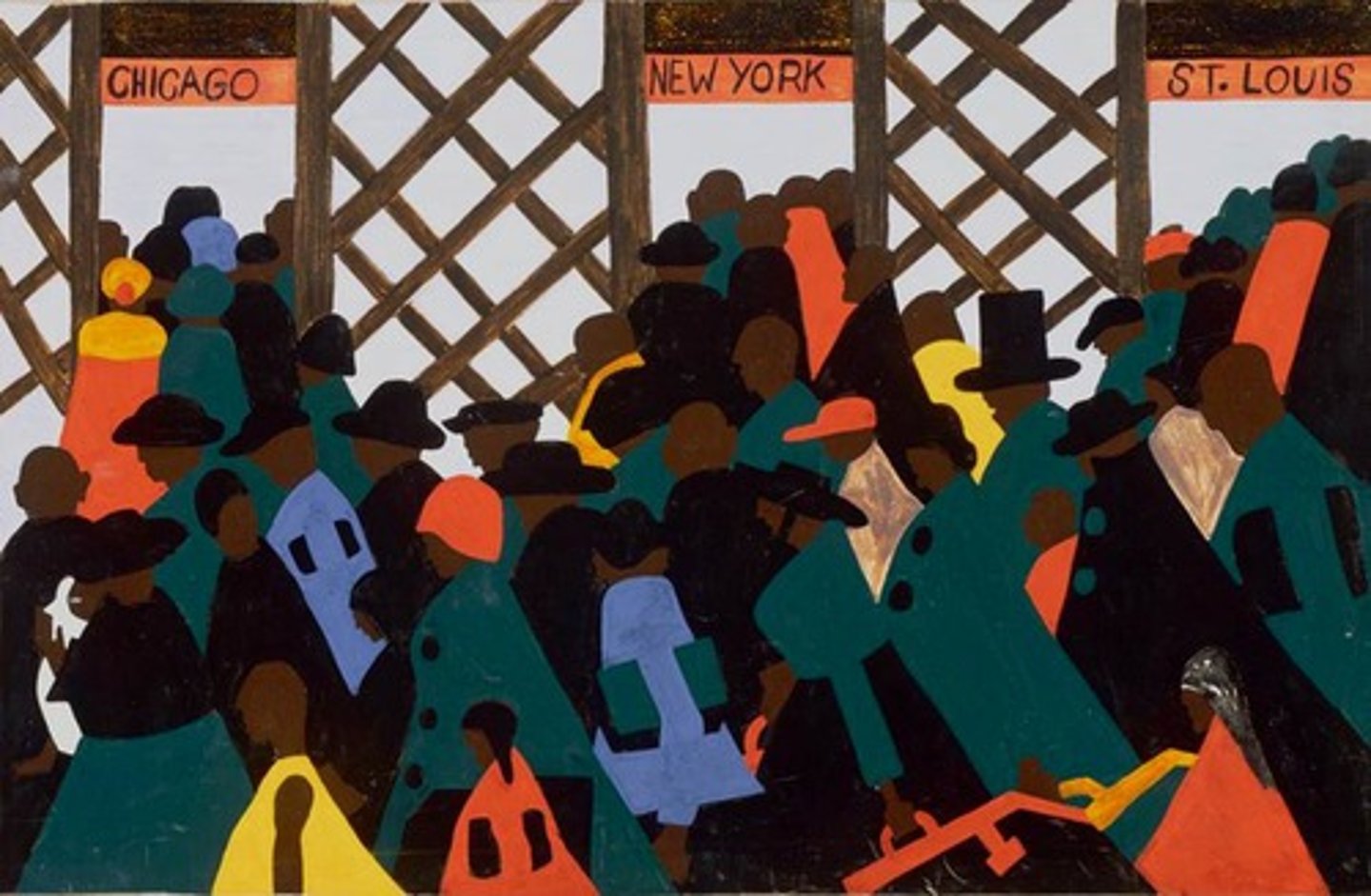

Lost Generation
Group of writers in 1920s who shared the belief that they were lost in a greedy, materialistic world that lacked moral values and often choose to flee to Europe
Prominent writers included T.S. Eliot, Ezra Pound, and Ernest Hemingway among others.

Red Summer
A series of 1919 race riots in 25 cities, with several Americans, both black and white, killed and numerous others injured. While they occurred across the country, the worst was in Chicago, where, when one white killed a black who strayed into a "white-only" swimming area, and riots developed between both groups.
Espionage Act
This law, passed after the United States entered WWI, imposed sentences of up to twenty years on anyone found guilty of aiding the enemy, obstructing recruitment of soldiers, or encouraging disloyalty. It allowed the postmaster general to remove from the mail any materials that incited treason or insurrection.

Sedition Act
a law passed by Congress in 1918 to make it illegal to say anything disloyal, profane, or abusive about the government or the war effort

Ku Klux Klan
This organization was a group of Americans that often engaged in acts of violence and terror against African Americans. Other persecuted groups were Jews, Catholics, and many other groups that were not native-born white Protestants.
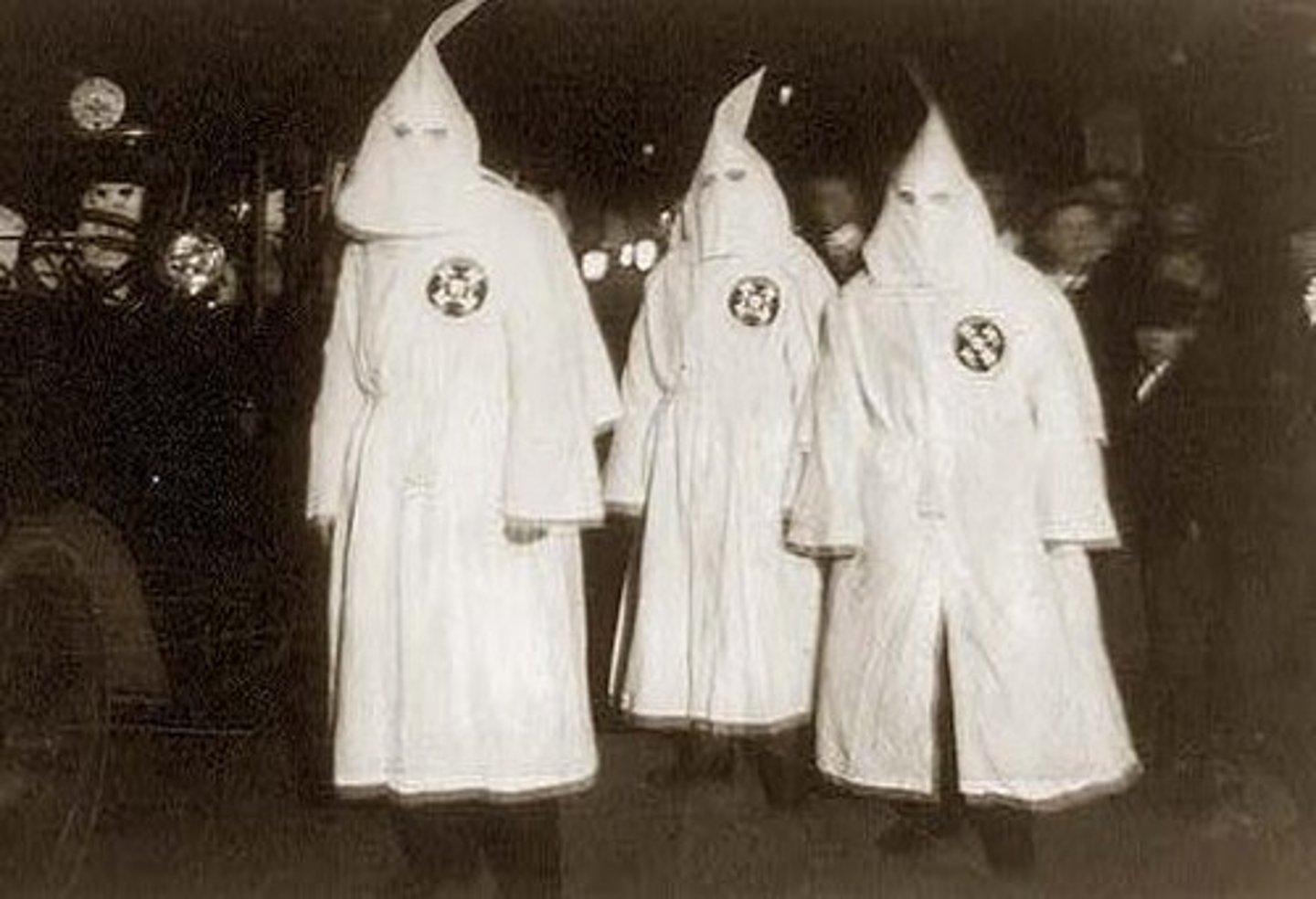

anarchist
A person who opposes all forms of government
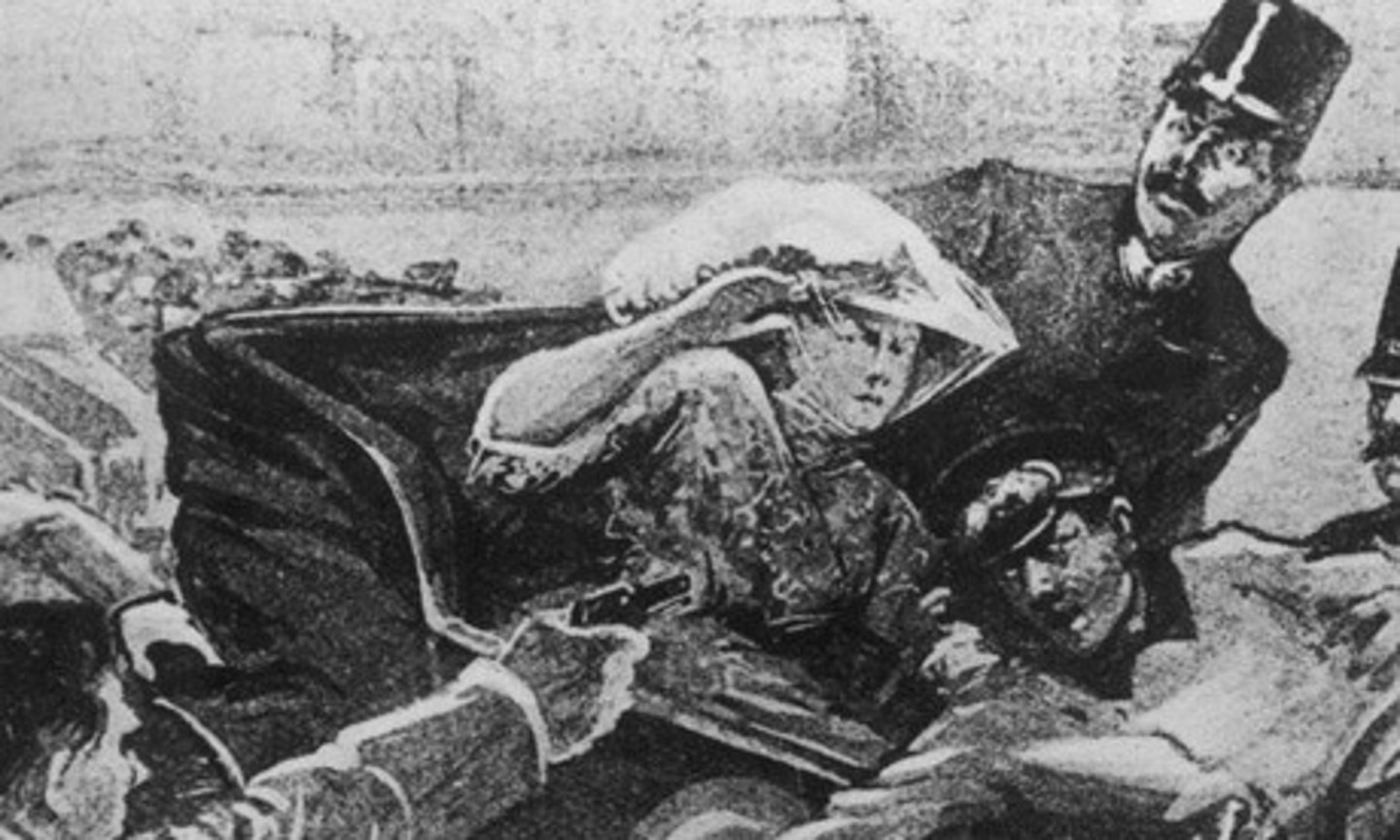
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
This was the spark that started World War I. Archduke Ferdinand, the Austrian crown prince, was murdered on June 28, 1914, by a Serbian nationalist while visiting Sarajevo, Bosnia. Germany urged Austria-Hungary to fight and they went to war against Serbia; all of this due to Serbia wanting to expand.
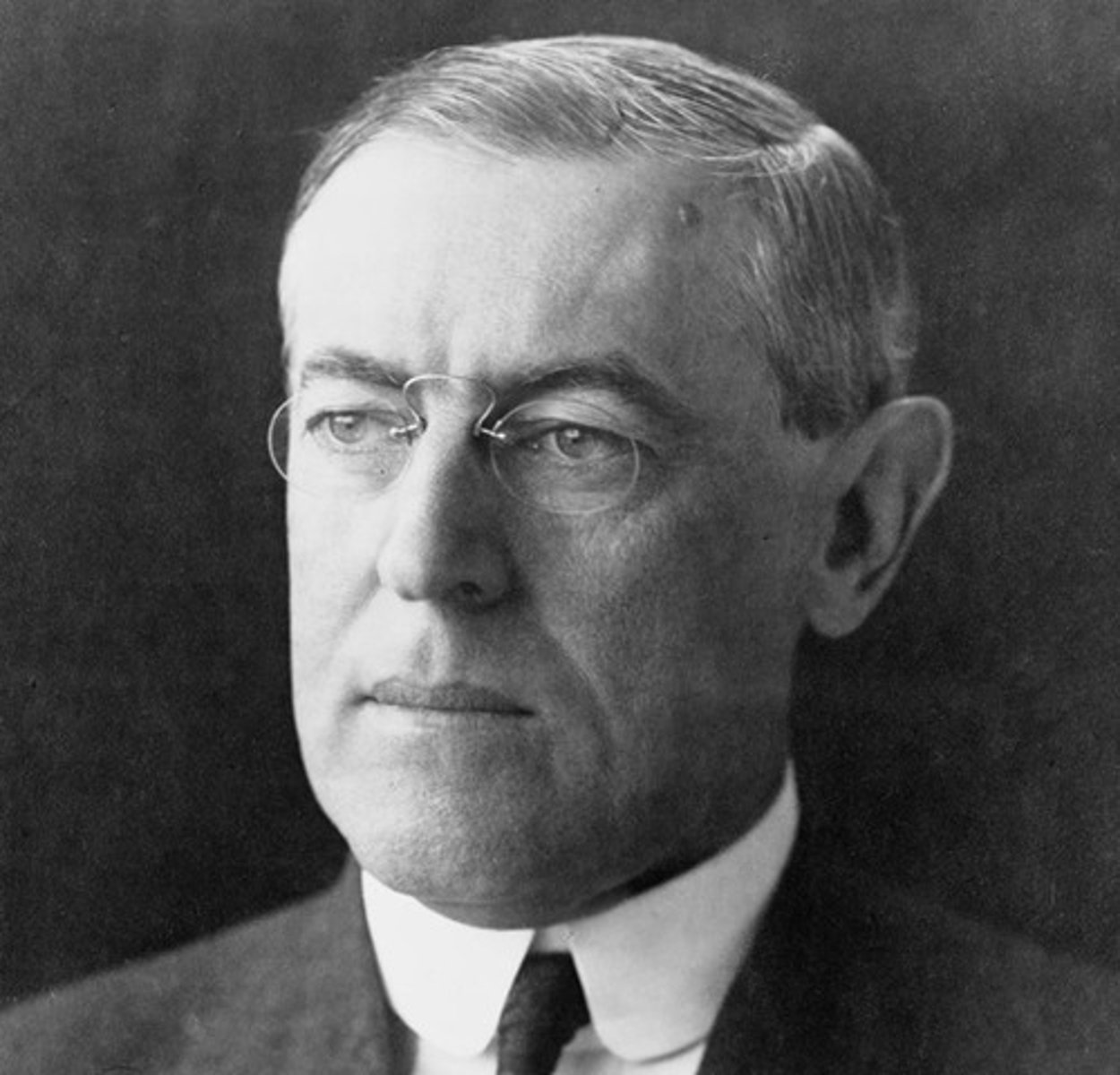
Woodrow Wilson
The US president who was elected in 1912 on the campaign "he kept us out of war" but later asked for Congress to declare war on the Central Powers.

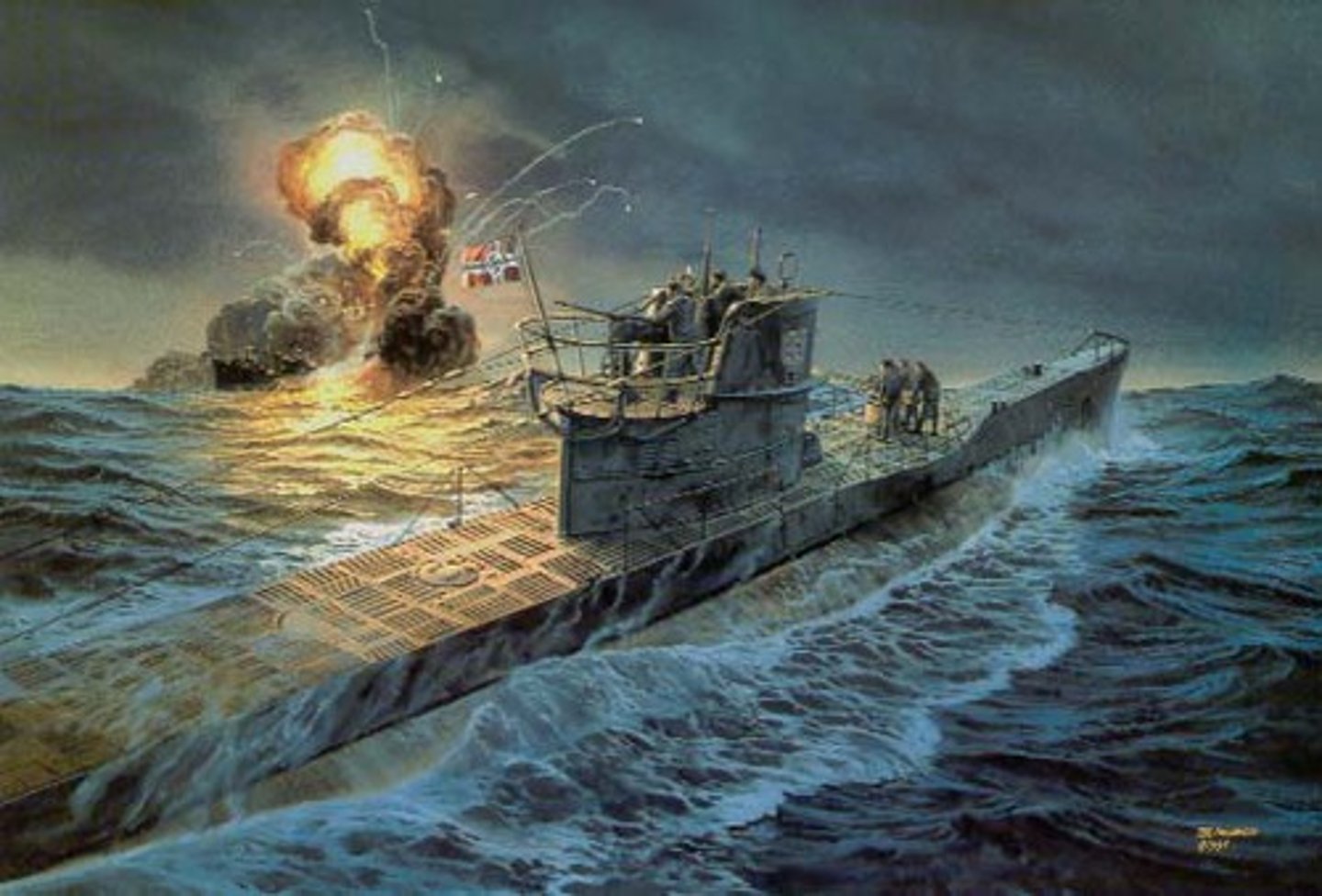
U-boats
This new military arsenal used by the Germans in sea warfare, to attack British and American supply ships in the North Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.

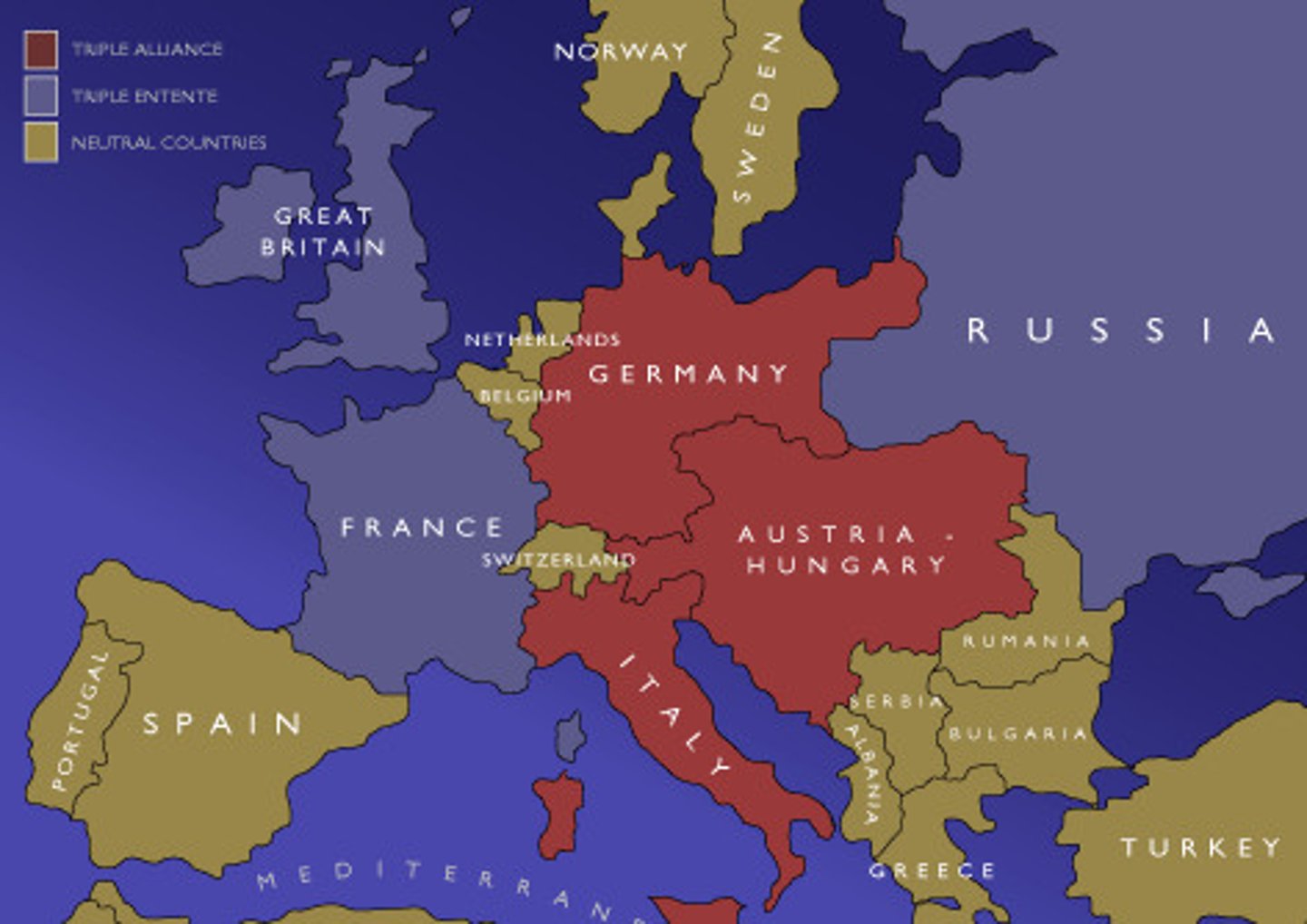
Allied Powers
This alliance during WWI included the United States, Great Britain, France, Russia and Italy (switched to the Allied Powers in 1915). (The blue countries of the East and West on map above)
Wilson's Fourteen Points
This is the plan for post-World War I outlined by President Wilson in 1918. This plan called for self-determination (countries in Africa and Asia govern themselves), freedom of the seas, free trade, end to secret agreements, reduction of arms and a league of nations.

Zimmerman Telegram
This intercepted note from the German foreign minister to the Mexican government offered, territories in Texas, Arizona and New Mexico for Mexico. The note also confirmed the new policy of unrestricted submarine warfare by Germany against the Allied Powers. This helped turn Americans against Germany in WWI.

Lusitania
This British passenger ship was sunk by German U-boats in 1915, carrying civilians and ammunition to Britain from the U.S. The event turned American opinion against Germany.

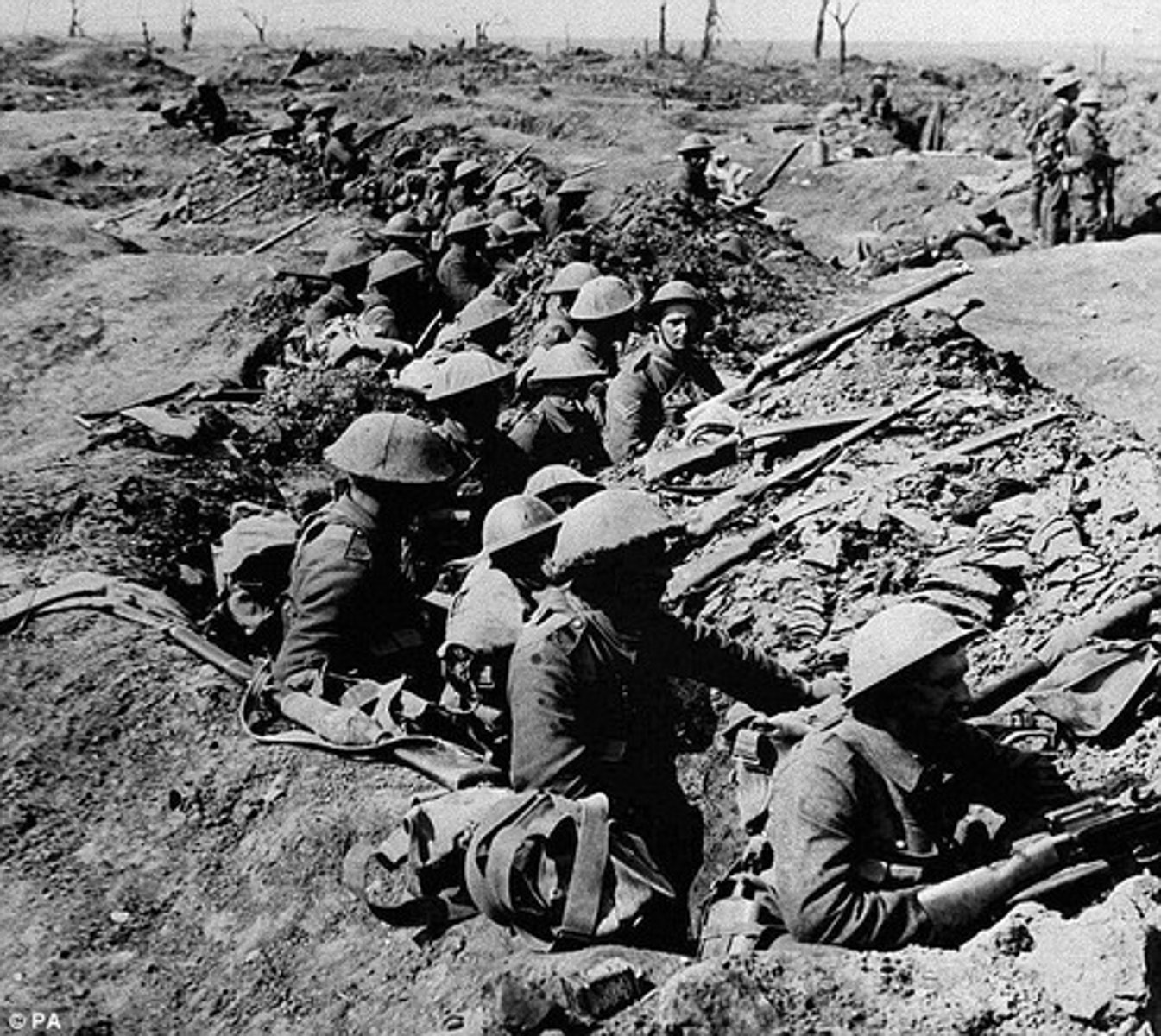
Trench Warfare
This style of warfare was common in WWI, due to the invention of the machine gun and heavy artillery. It included digging long trenches, separated by barbed wire and a no mans land.

Armistice [1918]
This was the agreement between the Allies and Central Powers that ended the fighting after WWI. It began at 11/11/1918 at 11:11 am. This marked a victory for the Allies and stated that the Central Powers lost. Germans would later look at this as "the stab in the back."

Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that ended WW I. It blamed Germany for WW I and handed down harsh punishment in the form of reparations. Although the armistice, signed on 11 November 1918, ended the actual fighting, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty.
Reparations
This term refers to the payments and transfers of property that Germany was required to make under the treaty of Versailles ($33B).

League of Nations
This intergovernmental organization lasted from 1919-1946, was founded after the Paris Peace Conference. It did not work effectively to prevent WWII.

"M.A.N.I.A."
These are the five main causes of World War I. Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, Nationalism, and Assassination.
Triple Alliance (Central Powers)
This alliance was made Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI. IN RED ABOVE
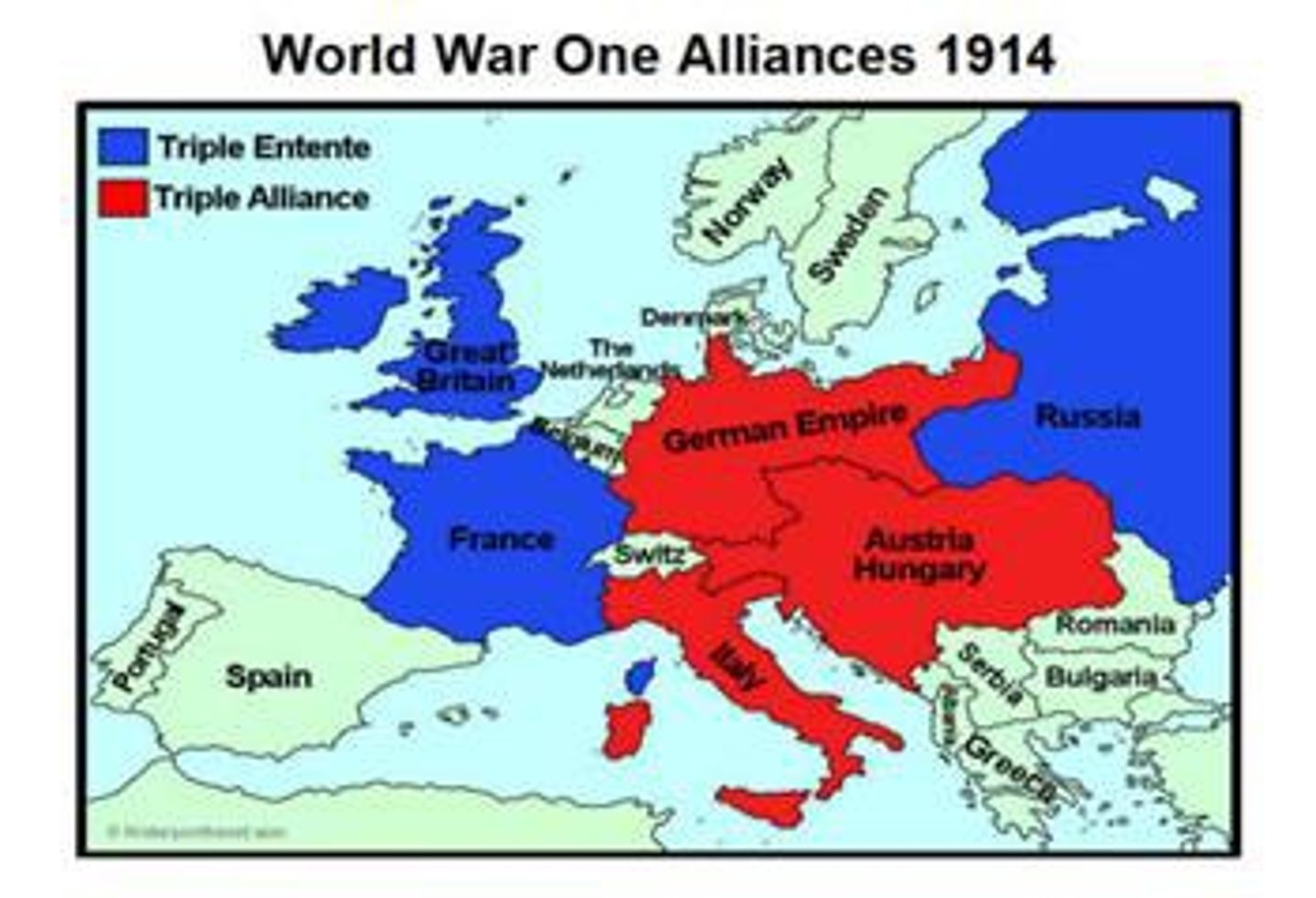
Triple Entente (Allied Powers)
This alliance between Great Britain, France and Russia in the years before WWI. IN BLUE ABOVE
Propaganda
These are ideas or information that usually designed by a government to influence public opinion, often times to persuade a people to go to war.
Ernest Hemingway
"Lost Generation" writer, spent much of his life in France, Spain, and Cuba during WWI, notable works include A Farewell to Arms