Unit 3 college bio
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/79
Last updated 9:58 PM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
Explain why Mendel chose pea plants and how he became the “father of genetics”
he chose pea plants because they carry both male and female parts and are able to self pollinate. Mendel is the one who figured out how traits are passed on but no one listened until after he died
2
New cards
Describe how Mendel’s law of segregation and the law of independent assortment are related to the movements of chromosomes during gamete formation and fertilization.
The law of segregation means that the allele pairs separate or (segregate) and then come back and pair up randomly at fertilization. Law of independence means that the allele from one gene does not influence the allele from another gene.
3
New cards
Alelle
one of two or more DNA sequences occurring at a particular gene locus
4
New cards
Dominant gene
Capital letter represents this, refers to the allele that will mask the expression of the recessive gene when both are present
5
New cards
Recessive gene
lower case letter, has to have two lower case letters to be present, is masked by a dominant gene
6
New cards
Genotype
complete set of genetic material. Can also be referred to as alleles. Represented by letters
7
New cards
Phenotype
he observable characteristics of an individual. Such as brown fur, blue eyes etc…
8
New cards
Heterozygous
Aa or a mixture of the two. Or it means that the dominant one still carries the recessive. Also known as a carrier
9
New cards
Homozygous
AA or aa which also means “purebred” it means that its either completely dominant or completely recessive
10
New cards
Predict outcome ratios and probabilities for problems based on Mendelian patterns of inheritance.
Multuply the individual probabilities together. Say you have 2/4 things be white and ¾ things be male than your ratio is 6/16 things are white males
11
New cards
Autosomal dominant
one parent must have the trait. Dominant traits will not skip a generation
12
New cards
Autosomal recessive
neither parent has to have to trait but the kids can still have the trait. Meaning that the parents have to be heterozygous
13
New cards
Incomplete dominace
blend together like a white flower and a red flower make a pink flower
14
New cards
Codominance
phenotypes are both shown. So a white flower and a red flower mix and make a white and red flower
15
New cards
Explain how ABO blood types are examples of multiple allele inheritance and which blood type shows codominance.
ABO blood types are all examples of multiple alleles because they all are the same gyne “blood type” but they are all different alleles of that blood type. The AB blood type shows codominance because they both show up in the allele.
16
New cards
Polygeneic inheritence
Occurs when a trait is governed by two or more genes (each with their own set of alleles) such as skin color
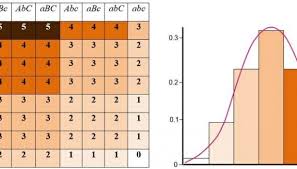
17
New cards
Describe ways in which the environment can influence genetic traits
Sometimes the environment changes a gene due to things like nutrition and temperature. If someone doesn’t eat enough than even though they have the gene to be tall they won’t be able to grow as tall as they can because they arent getting the right nutrients. Or if plants have to have above 32 degree weather to grow white ones but it can grow red ones at that temp then there will be far more red ones than white ones.
18
New cards
Describe what is meant by the term *linkage group*
all the genes on one chromosome that tend to be inherited together
19
New cards
Autosomes
Chromosomes #1-22 that everything from eye color, to hair lenght, to height
20
New cards
Sex-linked
Chromosome #23 that determines whether someone is male or female
21
New cards
Explain X-linked genetic inheritance - why males get more x-linked genetic disorders than females.
Only found on the X chromosome. Males get their x chromosome only from their mother. They have one X and one Y. So if the mom has a genetic disorder there is a 50-100% chance that the male will get the disorder because his mom had it.
22
New cards
Solve crosses involving sex-linked traits
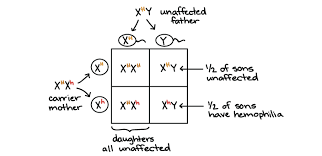
23
New cards
Describe how chromosomes number disorders arise
these occur at random during the fermentation of the sperm or egg.
24
New cards
Karyotype
chromosomes arranged by pairs according to their size and general appearance
25
New cards
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate during meiosis
26
New cards
Trisomy
a chromosome is present in three copies
27
New cards
Monosomy
a chromosome is present in one copy
28
New cards
Barr Body
an inactive X chromosome
29
New cards
Types of mutations
chromosomal and gene mutations
30
New cards
Types of chromosomal mutations
Duplication, Deletion, Inversion, Translocation
31
New cards
Deletion
occurs when a single break causes a chromosome to lose an end piece or when two simultaneous breaks lead to the loss of an internal chromosomal segment
32
New cards
Duplication
chromosomal segment is repeated in the same chromosome or in a nonhomologous chromosome
33
New cards
Translocation
involves the exchange of chromosomal segments between two nonhomologous chromosomes
34
New cards
Inversion
a segment of a chromosome is turned 180 degrees, reverse sequence of alleles can lead to altered gene activity
35
New cards
Types of gene mutations
Frame shift and point
36
New cards
Frame shift mutation
insertion or deletion, the worse kind of gene mutations because it moves every allele up or down one
37
New cards
Point mutation
has 3 different types; nonsense meaning it creates a stop codon, silent meaning that the codon doesnt change, and a missense meaning that it creates a different codon
38
New cards
Describe the structure of DNA
DNA is a chain of nucleotides and each nucleotide is a complex of three subunits that include a phosphate, deoxyribose, a nitrogen base. The two strands make up a DNA double helix. The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between base pairing. **Complementary base pairing**: A goes to T and C goes to G
39
New cards
Explain why DNA replication is semiconservative
Each daughter DNA double helix consists of one new strand but then also still has one of the old strands. Meaning that it semi conserves the first strand
40
New cards
Helicase
opens or “unzips” the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds apart
41
New cards
RNA primer
lays down the rna for the first couple nucleotides so that the polymerase knows where to start
42
New cards
DNA polymerase
adds the new nucleotide strand by adding complementary base pairs and then joins these two together. Builds from the 5’ end to the 3’ end. This all happens normally with the leading strand, but with the lagging strand it works backwards and then goes back to the beginning. Making sure that it always follows the helicase
43
New cards
DNA ligase
connects okazaki fragments and seals breaks in the sugar-phosphate backbone
44
New cards
mRNA
the messenger, it carries the protein information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
45
New cards
tRNA
transfer, serves as a link between the messenger RNA and the growing chain of amino acids
46
New cards
rRNA
ribosomal, direct the catalytic steps of protein synthesis
47
New cards
Transcription
takes place in the nucleus, a portion of the DNA serves as a template for mRNA formation. Takes the original DNA structure and turns it into mRNA. Begins when RNA polymerase binds to the promoter site. Then the DNA helix is opened so base pairing can occur. RNA polymerase adds the complementary base pairs but uses U instead of T.
48
New cards
Translation
takes place in the cytoplase, sequence of mRNA bases (complementary to those in the template DNA) determines the sequence of amino acids, tRNA assist by bringing amino acids to the ribosome.
49
New cards
3 stages of translation
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
50
New cards
Initation
mRNA comes in and gets a small ribosome, tRNA and a large ribosme added to it
51
New cards
Elongation
mRNA codes for an amino acid and it gets attached to the tRNA, moving down the mRNA each time making the polypeptide chain longer
52
New cards
Termination
mRNA codes for a stop codon and it releases the polypeptide chain
53
New cards
Promoter
a region of DNA where RNA polymerase begins to transcribe a gene
54
New cards
Exons
nucleic acid coding sequences, found in mRNA
55
New cards
Introns
non-coding sequences that ger removed before translation
56
New cards
Gene
sections of DNA that contain a set of instructions to produce one specific molecule in your body
57
New cards
Codon
a sequence of three nucleotides that forms a unit of genetic information. The codon then codes into an amino acid. Such as AUG codes for MET
58
New cards
Anticodon
a sequence of three nucleotides located at one end of a tRNA molecule which is complementary to the corresponding codons in mRNA. Allow the mRNA to connect to the tRNA
59
New cards
Determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein, given the messenger RNA sequence
* Example: TACCCTAGATTTATC ----> AUGGGAUCUAAAUAG -----> MET-GLY-SER-LYS
* Takes it from DNA changes it to mRNA and changes that into amino acids
* Use the star chart to figure out the amino acid
* Takes it from DNA changes it to mRNA and changes that into amino acids
* Use the star chart to figure out the amino acid
60
New cards
Describe the relationship between gene regulation and gene activity in a cell
**Gene regulation** is how a cell controls which genes are “turned on” or expressed. And because of this each cell has a different set of active genes or “turned on” genes.
61
New cards
Operator
a sequence of DNA where RNA polymerase attaches and transcription begins
62
New cards
Active Repressor
binds to the promoter and stopping transcription
63
New cards
Pretranscriptional Control
eukaryotes use DNA methylation and chromatin packing as a way to keep genes turned off.
64
New cards
Transcriptional Control
eukaryotic transcriptional control is dependent on the interaction of protiens with particular DNA sequences
65
New cards
Posttransprictional Control
following transcription, mRNA is processed before it leaves the nucleus and passes into the cytoplasm
66
New cards
Spontaneous mutations
due to abnormalities in normal biological processes
67
New cards
Induced mutations
enviromental influences
68
New cards
gene mutations
a permanent change in the sequence of bases in the DNA
69
New cards
Mutagens
enviromental influences called mutagens cause mutations in humans. Such as radiation or X'-rays
70
New cards
Transpoons
specific DNA sequences that have the remarkable ability to move within and between chromosomes
71
New cards
Describe why cancer is a failure in genetic control
If a person has an error in DNA repair that means that mistakes remain uncorrected and they become mutations such as cancer
72
New cards
Characteristics of a cancer cell
Genetically unstable, do not regulate the cell cycle, escape the signals for cell death, can survive elsewhere in the body
73
New cards
Explain what is meant by a DNA “fingerprint”
During a process called gel electrophoriesis, whereby an electrical current is used to force DNA through a porous gel material, these fragments are seperated according to their size. Smaller fragments move farther through the gel than larger fragments, and result in a pattern of distictive bands.
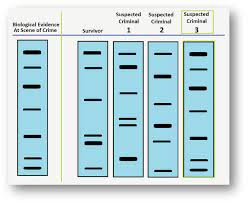
74
New cards
Explain why STRs may be used for identification
STRs are short tandem repeats that are the same short sequence of DNA bases that recur several times, such as GATAGATAGATA. these show in the gel electrofercies
75
New cards
What is a PCR
it is used to allow humans to duplicate DNA
76
New cards
What are the 3 stages of PCR
Denature, Annealing, Extension
77
New cards
Denature
heats up the DNA so it can seperate
78
New cards
Annealing
allows us to be able to lay down primer
79
New cards
Extension
builds the nucleotides like a polymerase
80
New cards
What is recombinate DNA
where a gene is cut out with the use of a restrictive enzyme and placed into a vector which was taken out of a bacteria. One the gene is placed into the vector it then goes back into the bacteria which then goes through mitosis and duplication making the creation of the specific gene protien to be amplified