Science - Fossils yr 10
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
So far it includes lesson 1.1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is a fossil
preserved evidence in rocks or soil of organisms that once existed on earth
How common is fossilisation?
very rare
What are the conditions for fossilisation
Quick burial in sediment - mud, sand, tar, amber
usually in/near water (though not always)
ONLY viable in sedimentary rock
Organisms with hard parts like bones or shells are more likely to fossilise successfully (as soft tissue decays quickly)
Why does soft tissue decay quickly
Its mostly made of proteins + other complex organic molecules which are easily broken down by bacteria + other decomposers, especially in warm/moist environments
Why fossils usually form in/near water
because water promotes rapid burial which allows the organism to be preserved and protects from scavengers/oxygen/bacteria (aka fulfils appropriate conditions for fossilisation).
What is a scientific model
A visual/physical representation of a concept/object that is too complex or small/large to create a real version of.
index fossils
used to compare the ages of strata in different locations
conditions for a species to be used as an index fossil
Must be widespread, have been abundant, have lived in a narrow period of time, and be easily identified
law of superposition
rock layers form parallel to the earth, deeper rock layers are older than superficial ones
the law of cross-cutting relationships
any rock layer that cuts across another is younger than those layers
the law of correlation
rock layers with the same index fossils in them are the same age
radioactive decay
absolute dating method
Definition of evolution
The process by which different kinds of living organism are believed to have developed from earlier forms during the history of the earth
How an original fossil forms
part of the organism is preserved, the chemical composition same as when it was alive, proteins within the orgs 'living’ bone decay, leaving behind minerals as hard but brittle bones
How carbon film fossils form
organism is buried, sediment piles up subjecting the organism to pressure and heat, gas + liquids are forced from it + a film of carbon forming a silhouette is left
What is an indirect fossil
No parts of fossil but evidence that it existed, e.g preserved footprints, burrow
What is relative dating
compares the age of one fossil/rock to another to determine which is older. Uses index fossils
What is absolute dating
Gives the actual age of rock (in yrs). Two types are radioactive dating and tree ring dating.
what is carbon-14 dating
uses half lives to date fossils that are less than 50,000 years old
what did lamarck think about evolution
‘evolution by inheritance of acquired characteristics’ (organisms are able to pass acquired features onto their offspring, offering them an advantage over others)
What did Darwin+Wallace think about evolution
‘evolution by natural selection’ (acquired features arent passed on, those BORN with features giving them survival advantages pass them onto their offspring)
what drives evolution
natural selection
Necessary conditions for natural selection
variation between members of the population (must have better features for survival)
selection pressure in the environment (feature of environment that gives some a competitive advantage)
competition for fixed resources (food, water, shelter, mates)
best suited reproduce more offspring + greater number of organisms in the next gen have this feature
population slowly changes over many generations (repeats other steps)
How the fossil record (e.g horse fossils) provide evidence for evolution
Because they provide evidence for the existence of organisms that dont exist today, allows to see the sequence of evolution (orgs become more complex over time)
How transitional fossils provide evidence for evolution
show the ‘transitional stage’ as an animal transitions from one type of animal to another and has characteristics from both (archeopteryx is a mix between reptile and bird) through evolution, showing how organisms change over time
How comparative anatomy provides evidence for evolution
similar structures common to many animals (e.g pentadactyl limb, or five fingers) that have been inherited from a common ancestor
How DNA sequences provide evidence for evolution
shows how we all inherited some DNA from a common ancestor, so the more DNA you share with a species the more recent your common ancestor (eg humans and chips share 96-99% DNA, meaning our common ancestor was very recent
Similarities in present day organisms
there are common shapes and features that have developed through evolution and are shared across species due to needing to solve a common problem (analogous structures), e.g dolphins and sharks
common features inherited from a common ancestor in the ancient past like similar chemistry across all organisms (DNA and proteins), are all cellular (have cell/s)
Example of evolution in action via natural selection
Peppered moths, black ones were very rare until industrial revolution. Factories were built and a dark smoke covered nearby countryside (so trees that were previously light + covered in lichens became dark). So the white moths stopped blending in and were spotted by birds. The black moths now blended in and survived + passed the black moth genes down
bacteria exposed to antibiotics
example of human impact on natural selection
use of anitbiotics in human/veterinary medicine, peppered moths
What is the carbon cycle
theres carbon in the atmosphere and the air → plants take in the carbon → animals eat the plants → animals breath the carbon out → plants and humans die and the carbon goes back into the soil → plants grow from the dirt
What is the greenhouse effect
natural process that warms the earths surface. Some of the suns energy is absorbed, warming the planet. Earth then emits heat as infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases (CO2, methane) in atmosphere trap some of this heat, which keeps the planet warm enough to support life.
What is global warming/enhanced greenhouse effect
long term increase in earths average surface temp due to human activities.
What causes the enhanced greenhouse effect
human activities, primarily greenhouse gas emissions from industrial processes, so more heat is trapped and earths temp rises (global warming)
Impacts + evidence for enhanced greenhouse effect
global temp increase (global warming) leading to melting ice caps, rising sea levels and extreme weather events
how does global warming create extreme weather events
increased air + ocean temp affects water cycle, shifts weather patters and melts land ice, which are all things that make extreme weather worse
example of method of generating electricity using renewable source, pros and cons
Wind turbines
Pros:
completely renewable and doesnt emit greenhouse gases
simple repairs
no fossil fuels used
low cost (wind is free)
Cons:
heavily relies on weather conditions which are unpredictable (if there is no wind, no energy will be generated during that period)
Common forces
gravity
friction (static, which prevents motion, and kinetic, which resists ongoing motion)
applied force (like pushing a box, force applied to something by another person/object)
air resistance
electromagnetic force (opposite charges attract, like charges repel)
Common forms of energy + when their highest (kinetic, gravitational, elastic)
Kinetic (energy of motion, greatest when object is moving fastest)
gravitational potential energy (stored energy, highest when an objects at the top of a hill)
elastic potential energy (energy stored in stretched/compressed elastics and springs)
Newtons 1st law
Inertia - an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
What is inertia (newtons 1st law)
the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity, whether in motion or motionless
Newtons 2nd law
An object will accelerate in the direction of an unbalanced force acting upon it. The magnitude of its acceleration is proportionate to the mass of the object and the size of the force acting on it.
Net force of an object = mass x acceleration
Newtons 3rd law
for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
How does an airbag (in car) reduce injury (inc. newtons laws)
1st law: object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force (airbag acts as a ‘safe’ unbalanced force to stop the motion, rather than something hard like window or steering wheel)
2nd law: airbag increases passengers ‘stopping time’ (aka acceleration), therefore reducing the force exerted on the passenger (an object’s acceleration is proportionate to the force exerted on them)
Why do cars crumple
crumple zone is meant to absorb the force of the crash and extend the stopping time (time over which deceleration takes place, therefore reducing the amount of force the occupants are subject to (newtons second law, the force on an object is proportional to their acceleration)
Why are bull bars on cars dangerous for pedestrians
Dont crumple, all forces from the collision are transmitted to the pedestrian
how do seatbelts increase safety for passengers (in a crash)
extend the passengers stopping time, therefore reducing the passengers inertia/force on them (exerts a safe ‘unbalanced force’ to stop their motion, reduces acceleration which reduces force on them bc force is proportionate to acceleration)
how to calculate distance with a speed/time graph
find the area under the lines
average speed formula
Average speed (km/h) = total distance / total time
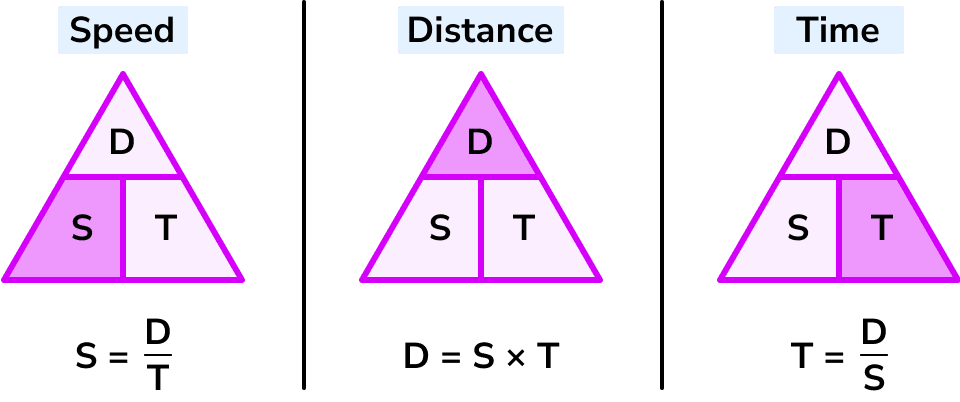
Acceleration formula
average acceleration (m/s²)= final velocity - initial velocity / time
average velocity formula
average velocity (m/s) = displacement / time
speed vs velocity
speed is a measure of how fast something moves (scalar) whilst velocity is the speed at which something travels in one direction (vector)
How replacement (petrified) fossils form
parts of the organism are chemically changed into another over a long period of time (shells/skeletons are often replaced by silica)