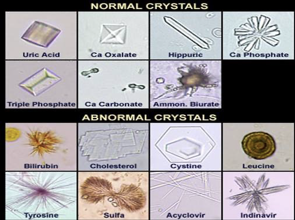
Microscopic Examination of CRYSTALS
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Crystals in Sediment
precipitation of solutes
are not normally present in freshly voided urine
can precipitate on storage
most are not clinically significant
pH critical to differentiating some important crystals
Acidic Urine Includes…
All clinically significant crystals are found in acid urine
Include: cystine, tyrosine, leucine & iatrogenic crystals: sulfonamide & ampicillin
Amorphous Urates
Amorphous Urates
Non crystalline urate salts of Na, K, Mg, & Ca
small & yellow-brown granules and can be in acidic or neutral urine
Will dissolve in alkaline or when heated
If add acetic acid, uric acid crystals will precipitate out

Amorphous Urates vs Amorphous Phosphates
Amorphous urates are non-crystalline urate salts, small yellow-brown granules found in acidic or neutral urine, whereas amorphous phosphates are non-crystalline forms of calcium and magnesium phosphates that typically occur in alkaline urine.
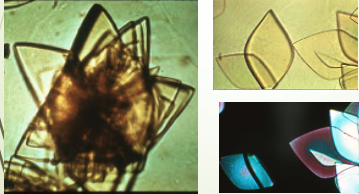
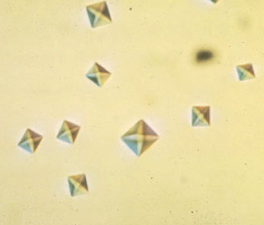
Uric Acid Crystals
Urine pH = 5.0 to 5.5
Common form = diamond shape but may be cube shaped or cluster in rosettes
Usually yellow to orange-brown
Are birefringent under polarizing light
When do Uric Acid Crystals appear?
Can appear normally BUT can see large #s in gout & increased purine metabolism such as cytotoxic drugs
What are the two forms that Oxalate Crystals appear as?
Both colorless
Dihydrate Form:
2 pyramids / squares w/ intersecting lines
Monohydrate Form:
small ovoid or dumb bell
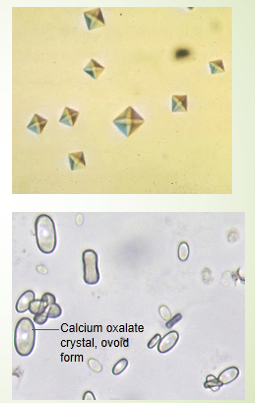
Calcium oxalate Dihydrate Form
Usually octahedral or look like envelope, less common than monohydrate form although both are seen in kidney stones
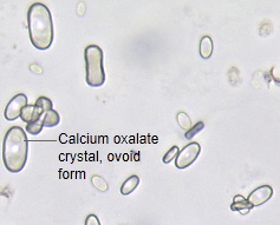
Calcium oxalate Monohydrate Form
A birefringent, colorless crystal that varies in size, often seen in neutral or acidic urine. It can appear due to normal dietary intake (e.g., ascorbic acid, tomatoes, spinach) and also indicates ethylene glycol.
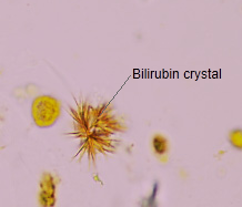
Bilirubin Crystals: Abnormal State
Appear as fine needles, granules, or plates
urine is acidic
always yellow-brown
the bile stains the other components of the sediment
presence of the crystals indicate high concentrations of bilirubin in the urine
What is the next step when bilirubin crystals are suspected in urine?
Confirm the presence of bilirubin with a strip reaction; positive results indicate a pathological process and abnormal crystals, often associated with liver disease.
Amino Acid Crystals and Pathology
Amino acid crystals are ALL ABNORMAL & seen in overflow aminoaciduria
can be seen in rare cases of liver disease, more likely to reflect inherited metabolic disorder
Include: TYROSINE, LEUCINE, AND CYSTINE
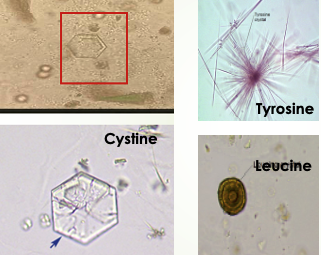
Tyrosine Crystals
fine, delicate needles, colorless or yellow
frequently in clusters or sheaves [as in stacks of wheat]
in acidic urine
less soluble than leucine, so found more often
![<ul><li><p>fine, delicate needles, colorless or yellow</p></li><li><p>frequently in clusters or sheaves [as in stacks of wheat]</p></li><li><p><strong>in acidic urine</strong></p></li><li><p>less soluble than leucine, so found more often</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6fb8d3bb-783e-4528-b0d4-20a2dd427eec.png)
Leucine Crystals
Highly refractile yellow to brown spheres in acid urine.
Have concentric/radial striations on their surface
Can be mistaken for fat globules [or vice versa]
will not stain with fat stains or appear as maltese cross under polarization
![<ul><li><p>Highly refractile yellow to brown spheres in acid urine.</p></li><li><p>Have concentric/radial striations on their surface</p></li><li><p>Can be mistaken for fat globules [or vice versa]</p><ul><li><p><u> will not stain with fat stains or appear as maltese cross under polarization </u></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a3e6f00b-030a-4353-bae9-be8c353c24e0.png)
Cystine Crystals
Colorless hexagonal plates
sides may be uneven
primarily seen in acidic urine
Clincally significant, seen in congenital cystinosis or cystinuria
Deposit out in tubules as calculi/stone causing damage

Why are Cystine Crystals confused with Uric Acid Crystals? How do we confirm Cystine Crystal presence?
both may present as hexagonal shapes. To confirm cystine crystal presence, perform cyanide-nitroprusside test using SODIUM CYANIDE which will yield a positive result for cystine (purple color)
Cholesterol Crystals
Clear flat rectangular plates with notched corners
in acidic urine
Rarely seen
Presence indicates both ideal conditions for precipitation & supersaturation
When are Cholesterol Crystals commonly seen?
Always see with positive protein + fat droplets, fatty casts or oval fat bodies
Seen in nephrotic syndrome & other renal damage

Ampicillin Crystals
Appear in acidic urine
Require large dosage for formation, so rarely seen
Calcium Phosphate Crystals
Colorless, thin, star-shaped prisms with one tapered end; they often appear as irregular granular sheets resembling degenerating squamous epithelial cells.

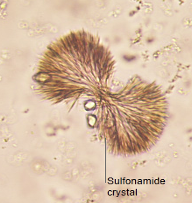
Sulfonamides Crystals
Highly refractile & birefringent
In acidic urine
Closely resemble ammonium biurate but differentiated on
pH & solubility
chemical confirmatory test
Type varies with form of drug prescribed
rarely seen due to recent solubility of sulfa drugs
Alkaline Urine Crystals
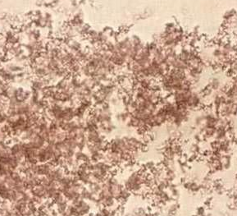
Amorphous Phosphate
precipitate white rather than pink-orange of amorphous urate
presence enhanced by refrigeration
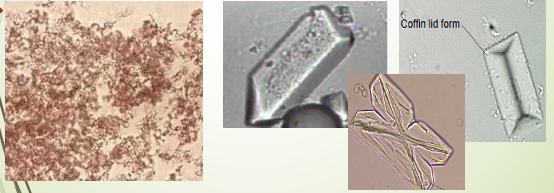
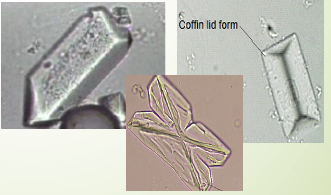
Triple Phosphate
most common are 3 & 6 sided ‘coffin lids’, vary in size
Amorphous Phosphate
alkaline or neutral urine
microscopically not distinguishable from amorphous urates
distinguishable on urine pH & solubility
precipitate white rather than pink-orange of amorphous urates
are soluble in acid & will not dissolve when heated to 60C
presence enhanced by refrigeration
Triple Phosphate Crystals
Colorless & in different forms
most common are 3 & 6 sided ‘coffin lids’
vary greatly in size
may also see a ‘fern leaf’ form, feathery
See in normal healthy individuals but are often present in formation of calculi
are associated with UTI
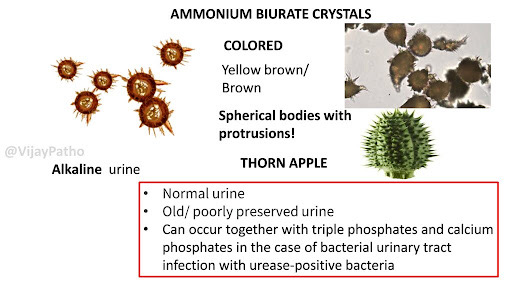
Ammonium Biurate
Yellow brown spheres with striations
Can have irregular spicules ‘thorny apple’
In alkaline or neutral urine
Not significant unless seen in fresh urine
Usually seen in old specimens
Dissolve in acetic acid or heating to 60C
Calcium Carbonate
Very small granular crystals
Can be misidentified as bacteria
Usually found in pairs ‘dumbbell shape’
Acidic Urine (pH < 7) Crystals
Amorphous Urates
Uric Acid
Calcium Oxalate
Bilirubin
Tyrosine
Leucine
Cystine
Cholesterol
Sulfonamides
Ampicillin
Alkaline Urine (pH > 7) Crystals
Amorphous Phosphates
Triple Phosphate
Ammonium Biurate Crystals
Calcium Phosphate Crystals
Calcium Carbonate Crystals
What crystal can appear in acidic AND neutral pH?
Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Clinical Significance of Crystals
kidney stone formation: Calcium oxalate, Uric acid, Cystine, Triple phosphate
metabolic disorders: Cystine, Tyrosine, Leucine
liver disease: Bilirubin, Tyrosine, Leucine, Cholesterol
UTI: Triple phosphate
drug therapies: Sulfonamides, Ampicillin
benign: Amorphous urates, Amorphous phosphates
Shapes of Crystals
Envelope-shaped = Calcium oxalate dihydrate
Needle-shaped = Uric acid, Bilirubin, Tyrosine, Sulfonamides, Ampicillin
Hexagonal = Cystine
"Coffin lid" = Triple phosphate
"Thorny apple" = Ammonium biurate
Rhombic = Uric acid
Spherical = Leucine