chemical changes- topic 4 - EOY10
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nov-feb
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
reactivity
how easily electrons are lost/gained
(nothing to do with melting/boiling)
oxidation
process of gaining oxygen
e.g 2mg + O(2) → 2MgO
in electrolosys- loss of electrons
reduction
the loss of oxygen
e.g 2MgO →2Mg+O(2)
in electrolosys- gaining electrons
displacement reaction
where a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its compound
what do the roman numerals show on the transition metals
eg. Iron (II) chloride
to show the charge of transition metals
FeCl(2)
why is potassium more reactive than lithium (3)
-atoms get bigger down the group
-less attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron
-easier to loose an electron so more reactive (opposite for group7)
how do we explain the different reactivity’s of metals
-for a metal atom to react it must loose electrons to become a postitive ion.
-the easier an atom can do this,the more reactive the more reactive the metal will be
reactivity series
potassium (k)
sodium (Na)
Lithium (Li)
Calcium (Ca)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminium (Al)
Carbon (C)
Zinc (Zn)
Iron (Fe)
Hydrogen (H)
Copper (Cu)
Silver (Ag)
Gold (Au)
Please Stop Lazily Calling Me A Careless Zebra I Hatehow Copper Saves Gold
ore
a rock containing an ionic metal,compound,usually a metal oxide
how is iron extracted
-reduction with carbon
-carbon and iron ore (iron oxide) are heated to a very high temp in a blast furnace →iron is reduced- iron oxide + carbon →iron +carbon dioxide
-very wasteful
-bioleaching + phytomining produce solutions containing copper
-so you have to do electrolisis or displacement with scrapirion
how does pytomining work (4)
copper ions in soil are abdorbed by plants roots
copper ions become part of the plant
plant is burned-copper ions join with oxide ions in the air (forms copper oxide, CuO)
ash containing copper oxide reacts with sulfuric acid then filtered-makes copper sulfate solution- ash is dissolved -electrolysis of cop sul solution copper metal collects at neg electrode
advantages(6) and disadvantages(6) of phytomining
advantages
-uses low grade copper ore
-less energy than smelting
-less air polution produced
-less waste rock
-decontaminates polluted ground
-produces less greenhouse gases then smelting
disadvantages
-can produce toxic chrmicals
-a lot slower
-electrolysis requiress lots of energy (and money)
-plants need good growing conditions
-don’t get much-lower yield
-dependent on weather
how does bioleaching work (3)
-bacteria are used to extract copper ions from low grade copper ores
-bacteria converts copper compounds within ores into solution
-these copper compound solutions can be separated with electrolysis or displacement reactions to form copper metal
advantages and disadvantages of bioleaching
advantages
-economical→simpler,cheaper
-environmental→less landscape damage- bacteria grows naturally
-ore conservation→can eextract metals from ores that are too poor for other technologies
-low grade ores
-produces less air pollution than smelting
disadvantages
-economical-even slower compared to smelting-less profit
-environmental-toxic chemicals are produced →heavy metal ions leak during acid mine drainage
pros/cons of smlelting (1,2)
pro
-have equiptment already/know how it works
cons
-lots of equiptment is used
-produces lots of CO(2)
Pros/cons of mining (2,3)
pros
-creates jobs
-we know how it works/have equiptmwnt already
cons
-lots of waste
-very noisy
-can destroy habitats
acids
aqueous solutions that can obtain hydrogen ions (H+)
bases
chemicals that neutralise acids
alkalines
bases that form hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solution
when are salts formed
when the hydrogen ion (H+) in an acid is replaced by a positive ion from a base
making salts
(general equations to learn,how to work out name of salt)
-most involve the neutralisation of an acid
acid +metal →salt + hydrogen
acid + alkali/base → salt + water
acid + carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
acid +metal oxide → salt + water
how to work out name of salt
first part→from the base and is a metal
second part→ from the acid
e.g hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium chloride
why can’t we use all of these methods for making a salt using the required practical
matals, metal oxides and metal carbonates are insoluble bases so we can “see“ when they are in excess (all acid is neutraalisied) we can filter the excess to remove it
metal hydroxides are alkalis (soluble bases) so we can’t “see” when acid is fully neutralised or could we use filtration to remove excess alkali
how to make a pure dry salt
Mix-
measure acid using a measuring cylinder and pour into a beaker
add the base (metal oxide/carbonate) into the acid until no more reacts (all acid has reacted so we say the base is in excess)
filter-
filter using filter paper and funnel to remove the unreacted solids (excess base) leaving only the salt solution
crystalise-
pour into an evaportating dish
heat gently (safely) using a water bath (dont say budsen burner)
evaporate MOST of the water then leave to cool to form crystals
purify-
remove all crystials and rinse them
pat dry crystals
why wouldnt i use a metal hydroxide when making salt
beacsue its soluble|!!- can only use if insoluble
need to get rid of excess
ionic equation for neutralisation
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
dont forget state symbols!!
neutralisation
the neutralisation of an acid can bee “seen“ if we use an indicator
indicator-changes colour with a change in pH
-universal indicator is a mixture of indicators so cant be used for this practicle
end point
point when neutralisation occurs
how do indicators work
-indicators cgange colours- from acid to alkali
the acid and alkali are neutralised
what colour is the indicator thymol blue when its an acid, alkali and at its end point
acid→ yellow
alkali→ blue
end point→ green
what colour is the indicator phenolphthalein when its an acid, alkali and at its end point
acid→colourless
alkali→pink
end point→ pale pink
what colour is the indicator methyl orange when its an acid, alkali and at its end point
acid→red
alkali→yellow
end point→peach/orange
titrations
-the volumes of acid and alkali solutions that react with each other can be measured by titration using a suitable indicator
titration method (9)
use a funell to fill up a burette with the solution of known concentration- take funnel out after so no extra liquid is added
use a pipette and bulb to transfer the solution with thw unknown concentration into a conical flask
add indicatir to flask
stir. place flask on a white tile (so you cvan see the colour change later) under the burette
gradually add solution from the burette into the conical flask
swirl after each addition-stop as soon as misture in flask changes colour
recored how much solution was added
repeat until 2 measurements within 0.1³ are obtained
calculate mean volume of solution added for nuetralisation to occur
what is the pH scale
a logarithmic scale
a measure of concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, H(aq)
acids are small covalent molecules until they are dissolved in water (aq) and form ions
pros and cons of ph probe (3) (1)
pros
more accurate
objective
measures continually
cons
expensive- needs calibration/trainig
pros/cons of univeral indicator (2)(2)
pros
cheaper
easy to use
cons
less accurate
subjective
concentration
(+how to calculate)
the mass of solute in a given volume of solution- measured in g/dm³
to calculate concengtration → mass divided by volume
weak acids
partially ionise in a solution
strong acids
fully ionise in aqueous solution
what type of acid are these?
qijfw
when does electrolysis happen
when an electrical current is passed through an ionic compound
whats an electrolyte
the ionic compound being broken down during electrolysis
what are the electrodes
the rods the current flows into the electrolyte
what are the ions turned into during electrolysis
the ions are turned back into elemants
whats a positive electrode called
whats a negative electrode called
anode
cathode
where do the + metal ions go to
where do the - metal ions go to
-cathode
+anode
what are the parts of the electrolysis equiptment
be able to lable electrolosis equiptment
power supply, ammeter/bulb, beaker, cathode (-electrode), anode (+electrode), electrolyte
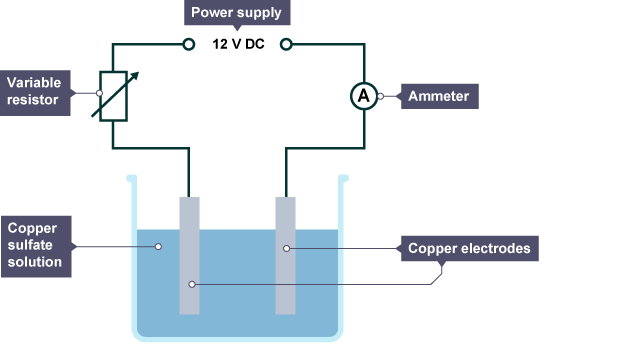
why do you need an ammeter/bulb in the electrolysis apparatus
so you know that the current is flowing through the circuit
why does the ionic compound have to be molten (melted) OR dissolved in water (solution,aq) in the electrolysis equiptment
becasue the ions need to be free to move
solution
a mixture where a substance is dissolved in a solvent
solute
the substance being dissolved
solvent
the liquid part of a solution
soluble
describing a solid that is able to dissolve
dissolving
a process where a substance mixes with a liquid to form a clear solution
what happens at electrodes (2)
-the negative electrodes (cathode) attracts the zinc ions as zinc is positive and opposites attract
-the positive electrode (anode) attracts the chloride ion as chloride is negative and opposites attract
is oxidation the loss or gain of electrons
is reduction the loss or gain of electrons
loss
gain
O-oxidation
I-is
L-loss of electrons
R-reduction
I-is
G-gain of electrons
at the cathode
are the metal ions gained or lose electrons to form metals
gained
so its reduced
because the cathode is negative so the pos ions are attracted
at the anode
non metal ions lose or gain electrons to form elements (gas molecules)
lose
it is oxidised
because the anode is positive so the neg ions are attracted
where do positive ions become elements
where do negative ions become elements
cathode
anode
what do half equations and ionic equations come in
pairs-they made an ionic equation when added together
the electron in each pair must cancel out to make the ionic equation
when is electrolysis used to extract a metal from its ore
if the metal is too reactive to be displaced by carbon (smelting) e.g aluminium
extraction of aluminium by elelectrolysis
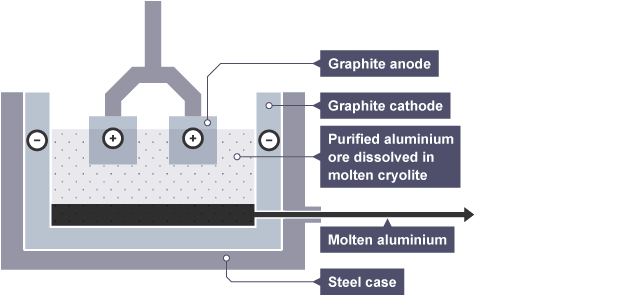
electrolysis of aluminium oxide Al(2)O(3)
has a V high melting point - mixed with cryolite (lowers mp - lowers energy needed + money)
add an electric current to the molten aluminium oxide (electrodes arw made of graphite (carbon) -V high melting point)
Al3+ is attracted to cathode (neg electrode) where each ion gains yhere electrons (reduced) and forms and aluminium atom Al3+ + 3e- → Al
O2- ions attracted to positive electrode (anode) and looses 2 electrons (oxidised) to form oxygen atom O2- → O + 2e- (but oxygen atoms pair up to form oxygen molecule O2 so half equation gets doubled to) 2O2- → O(2)+ 4e- (write this one above)
~ anode must be replaced regularly - as oxygen molecules produced at the anode react with the graphite carbon - forming CO2 gas
rules for cathode (+ ions)
the least reactive element will be discharged
If the metal is more reactive than hydrogen water will form hydrogen gas (observe bubbles)
otherwise metal ions will form that metal
so
if the metal is more reactive than hydrogen- then hydrogen formed
if not- metal formed
Rules for anode
a solution containing a metal halide (g7) will produce that halogen gas
any other solution- the water will produce oxygen gas
are there halide ions
yes-halogen formed
no-oxygen formed
what do you observe and what gas is present when a glowing splint held in a test tube
observation-splint relights
oxygen is present
what do you observe and what gas is present when a lighted splint held in a test tube
pop sound heard
hydrogen is present
what do you observe and what gas is present when gas bubbles through lime water
lime water turns milky/cloudy white
carbon dioxide is present
what do you observe and what gas is present when damp litmus paper held in a test tube
pper bleached white
chlorine is present
formular for hydrochloric acid
HCL
formukar for sulfuric acid
H2SO4
formular for nitric acid
HNO3
formular for sodium hydroxide base
NaOH
formular for calcium carbonate
CaCO3
why do you swirl the conical flask when doing titration
you add the acid from the burette in order to evenly distribute it, and ensure that the colour change occurs as soon as neutralisation takes place.
why do you place the coniical flask on a white tile on the titration practical
so you can more easily see when the colour change takes place.
what iondoes acid form in water
H+
what ion does alkali form in water
OH-
how do you make a soluble compound into an electrolyte
dssolve in water
produces H+ and OH- as well