bio h genetics (mendelian and non mendelian)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/18
Last updated 8:07 PM on 3/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
1
New cards
Human body cells have ….
44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes
2
New cards
males sex chromosome
XY
3
New cards
female sex chromosome
XX
4
New cards
GAMETES
* are sex cells (22 auto 1 sex chromosome)
* Female gamete- egg cell
* Male gamete- sperm cell
* Female gamete- egg cell
* Male gamete- sperm cell
5
New cards
Pedigree (family tree of disease)
* A pedigree chart shows relationships within a family and shows how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
* Genetic counselors can use a pedigree to infer the genotype of family members.
* Genetic counselors can use a pedigree to infer the genotype of family members.
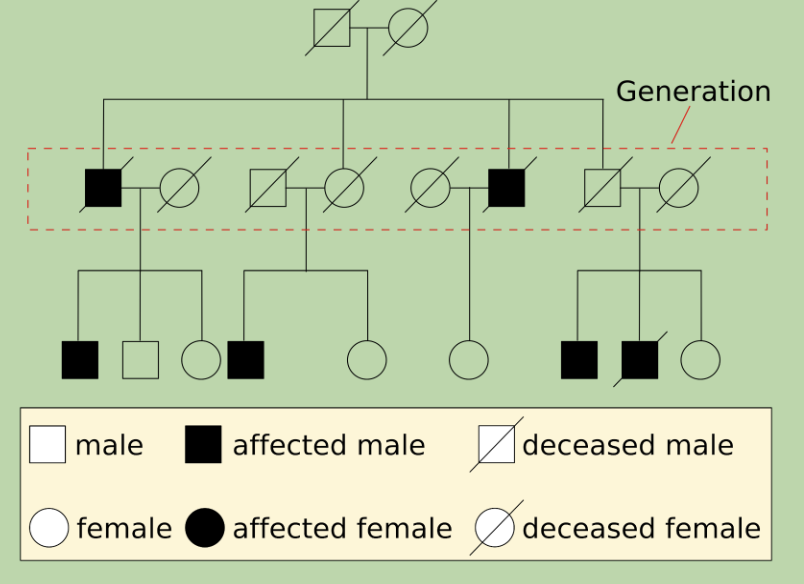
6
New cards
Genetics
The study of how hereditary info is passed from parents to offspring
7
New cards
Genes
* DNA code for trait
* Ex. eye color
Your genes come in pairs (one from mom and one from dad)
That pair is an **allele**
* Ex. eye color
Your genes come in pairs (one from mom and one from dad)
That pair is an **allele**
8
New cards
Alleles
* Variation of traits
* Ex. Blue eyes, green eyes, brown eyes
* Ex. Blue eyes, green eyes, brown eyes
9
New cards
Probability
Chances of inheriting a particular allele
10
New cards
**Genotype**
* **Genes**
* **Homozygous, heterozygous, dominant recessive**
* **Homozygous, heterozygous, dominant recessive**
11
New cards
**Phenotypes**
* **Physical traits**
* **Tall, short, green seeds, yellow seeds**
* **Tall, short, green seeds, yellow seeds**
12
New cards
**Law of Dominance**
* **Organsism have 2 copies of every gene**
* **1 from mom and 1 from dad**
* **Sometimes those genes are for different alleles**
* **Moms allele from blue eyes and Dads allele for brown eyes**
* dominant will override recessive (unless dominant isn’t present, like in homozygous recessive)
* **1 from mom and 1 from dad**
* **Sometimes those genes are for different alleles**
* **Moms allele from blue eyes and Dads allele for brown eyes**
* dominant will override recessive (unless dominant isn’t present, like in homozygous recessive)
13
New cards
**Law of segregation**
* **As the parent cell (p generation) prepares to make gametes (egg or sperM), it undergoes meiosis**
* **During meiosis, the 2 alleles segregate so that each gamete cell will have only 1 copy of each gene**
* **The law of segregation states that the movement of alleles into daughter cells is RANDOM**
* **During meiosis, the 2 alleles segregate so that each gamete cell will have only 1 copy of each gene**
* **The law of segregation states that the movement of alleles into daughter cells is RANDOM**
14
New cards
**Incomplete Dominance**
* **every genotype has its own phenotype (one allele is not completely dominant over the other) the resulting phenotype is a blending of the parental traits. (two alleles produce 3 phenotypes.)**
* **Heterozygous phenotype is somewhere in between homozygous phenotype (ex. red plus white is PINK not RED AND WHITE)**
* **Heterozygous phenotype is somewhere in between homozygous phenotype (ex. red plus white is PINK not RED AND WHITE)**
15
New cards
**Codominance**
* **both alleles are independently and equally expressed in the heterozygote. Examples include**
* Roan (stippled red and white) coat color in cattle. A cross between a red bull and a white cow produces all roan offspring
* ABO human blood groups
* __**Blood types are codominant**__
* In a cross between two heterozygous (roan) shorthorn cattle, red, roan, and white offspring are produced in a 1:2:1 ratio
* __**red + white= red and white not PINK**__
* Roan (stippled red and white) coat color in cattle. A cross between a red bull and a white cow produces all roan offspring
* ABO human blood groups
* __**Blood types are codominant**__
* In a cross between two heterozygous (roan) shorthorn cattle, red, roan, and white offspring are produced in a 1:2:1 ratio
* __**red + white= red and white not PINK**__
16
New cards
**Multiple alleles in blood**
* **The 4 common blood groups of the human ABO blood group system are determined by three alleles Ia, Ib, and i (also represented in some texts as A, B, and O)**
* **ABO antigens consist of sugars attached to the red blood cell surface. These sugars provide individual antigenic properties. The alleles code for enzymes that join these sugars together.**
* **Allele i produces a non-functional enzyme that is unable to make changes to the basic antigen (sugar) molecule**
* **The other two alleles (IA, IB) each produce a different enzyme that adds a different specific sugar to the basic antigen.**
* **Any one individual possesses only two alleles and they are expressed equally.**
* **ABO antigens consist of sugars attached to the red blood cell surface. These sugars provide individual antigenic properties. The alleles code for enzymes that join these sugars together.**
* **Allele i produces a non-functional enzyme that is unable to make changes to the basic antigen (sugar) molecule**
* **The other two alleles (IA, IB) each produce a different enzyme that adds a different specific sugar to the basic antigen.**
* **Any one individual possesses only two alleles and they are expressed equally.**
17
New cards
**Sex Linkage**
* **phenotypic expression of an allele that is dependent on the sex of the individual and is directly tied to the sex chromosomes**
* **Most sex-linked genes are present on the X chromosome (x linkage) and have no corresponding allele on the smaller male chromosome**
* **In some cases, a phenotypic trait is determined by an allele on the Y- chromosome. Because the Y chromosome is small and does not contain many genes, few traits are - y-linked, and Y- linked diseases are rare.**
* **Most sex-linked genes are present on the X chromosome (x linkage) and have no corresponding allele on the smaller male chromosome**
* **In some cases, a phenotypic trait is determined by an allele on the Y- chromosome. Because the Y chromosome is small and does not contain many genes, few traits are - y-linked, and Y- linked diseases are rare.**
18
New cards
**Sex Linkage (pt. 2)**
* **Sex-linked traits show a distinct pattern of inheritance**
* **Fathers pass sex-linked alleles to all their daughters but not to their sons**
* **Mothers can pass sex inked alleles to both sons and daughters**
* **In females, sex-liked recessive traits will be expressed only in the homozygous condition**
* **In contrast, any male receiving the recessive allele from his mother will express the trait.**
* **Fathers pass sex-linked alleles to all their daughters but not to their sons**
* **Mothers can pass sex inked alleles to both sons and daughters**
* **In females, sex-liked recessive traits will be expressed only in the homozygous condition**
* **In contrast, any male receiving the recessive allele from his mother will express the trait.**
19
New cards
**Sex-linked Dom Inheritance**
* **Sex-linked dom inheritance is rarer because all daughters of affected males will be affected (the heterozygous condition is not a carrier)**
* **Sex-linked dominant traits are never passed from father to son**
* **Affective females produce 50% normal 50% affected offspring**
* **Sex-linked dominant traits are never passed from father to son**
* **Affective females produce 50% normal 50% affected offspring**