Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Class 12 Revision
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Molecular Basis
Fundamental molecular mechanisms of genetic inheritance.
Inheritance
Transmission of genetic information across generations.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, carrier of genetic information.
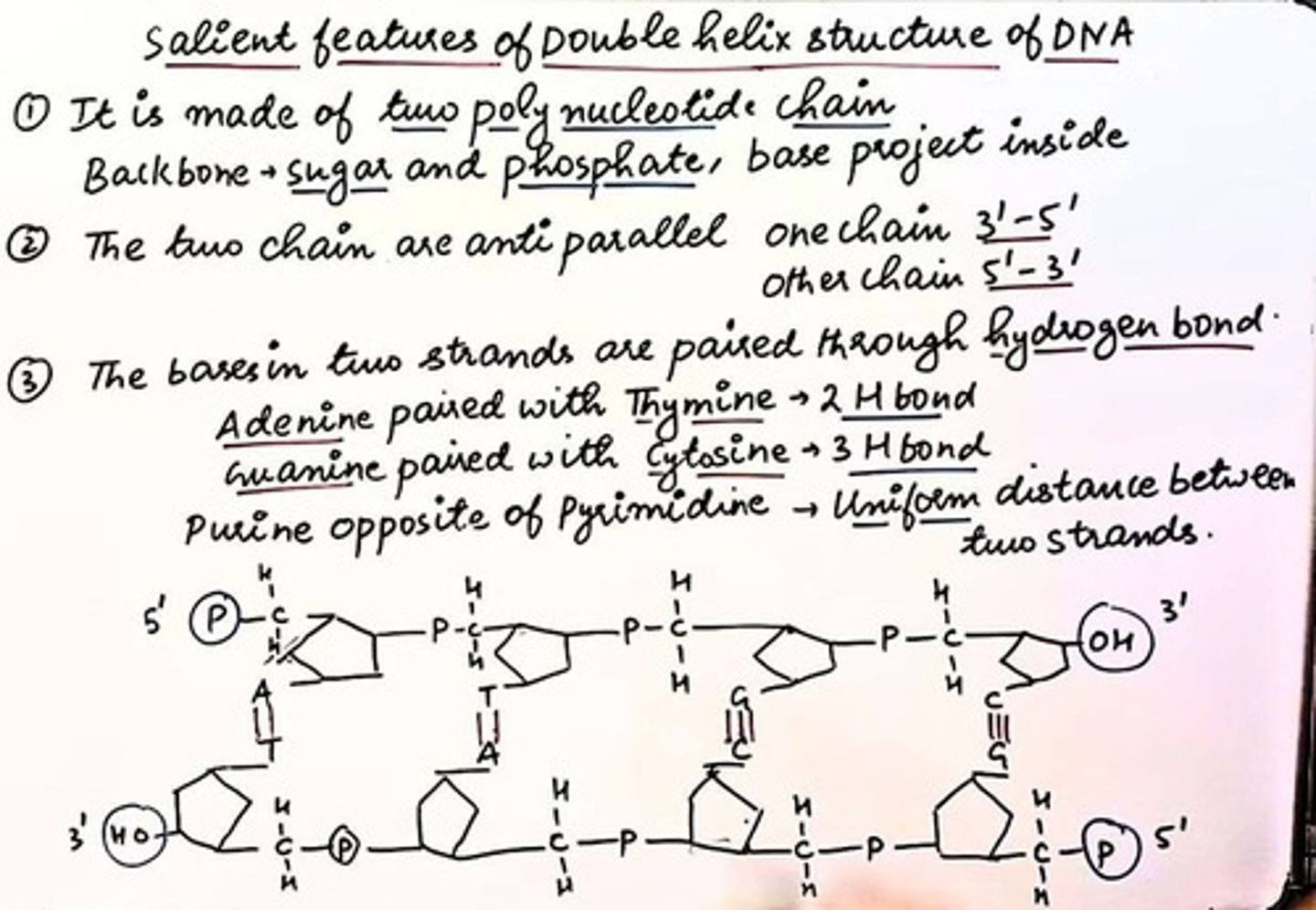
Gene
Segment of DNA coding for a trait.
Chromosome
Structure containing DNA and associated proteins.
Allele
Different forms of a gene at a locus.
Genotype
Genetic constitution of an organism.
Phenotype
Observable characteristics resulting from genotype.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait.
Dominant allele
Allele that expresses its trait in phenotype.
Recessive allele
Allele that expresses its trait only in homozygotes.
Punnett Square
Diagram predicting genetic variation in offspring.
Mendelian inheritance
Patterns of inheritance established by Gregor Mendel.
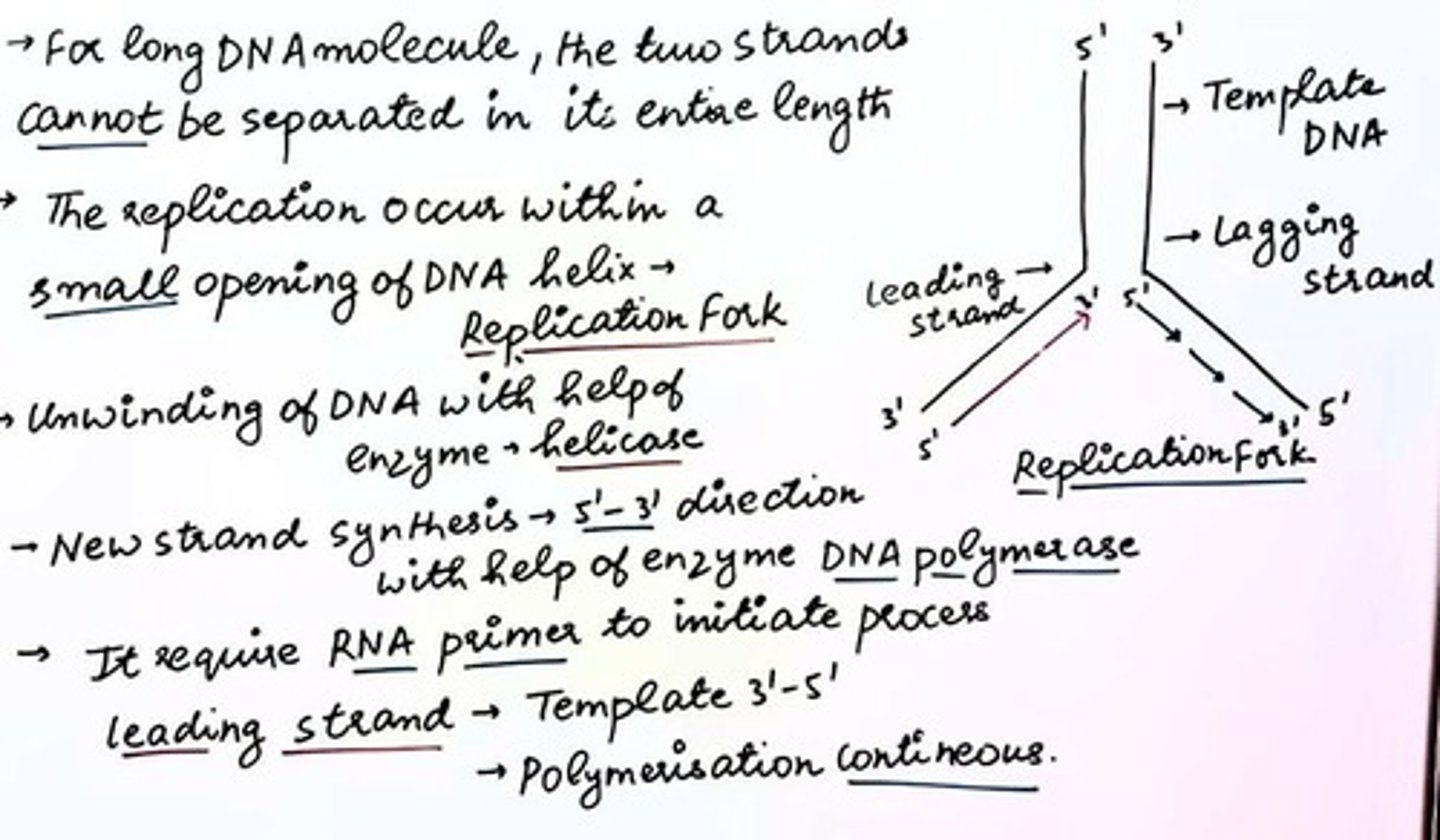
DNA replication
Process of copying DNA before cell division.
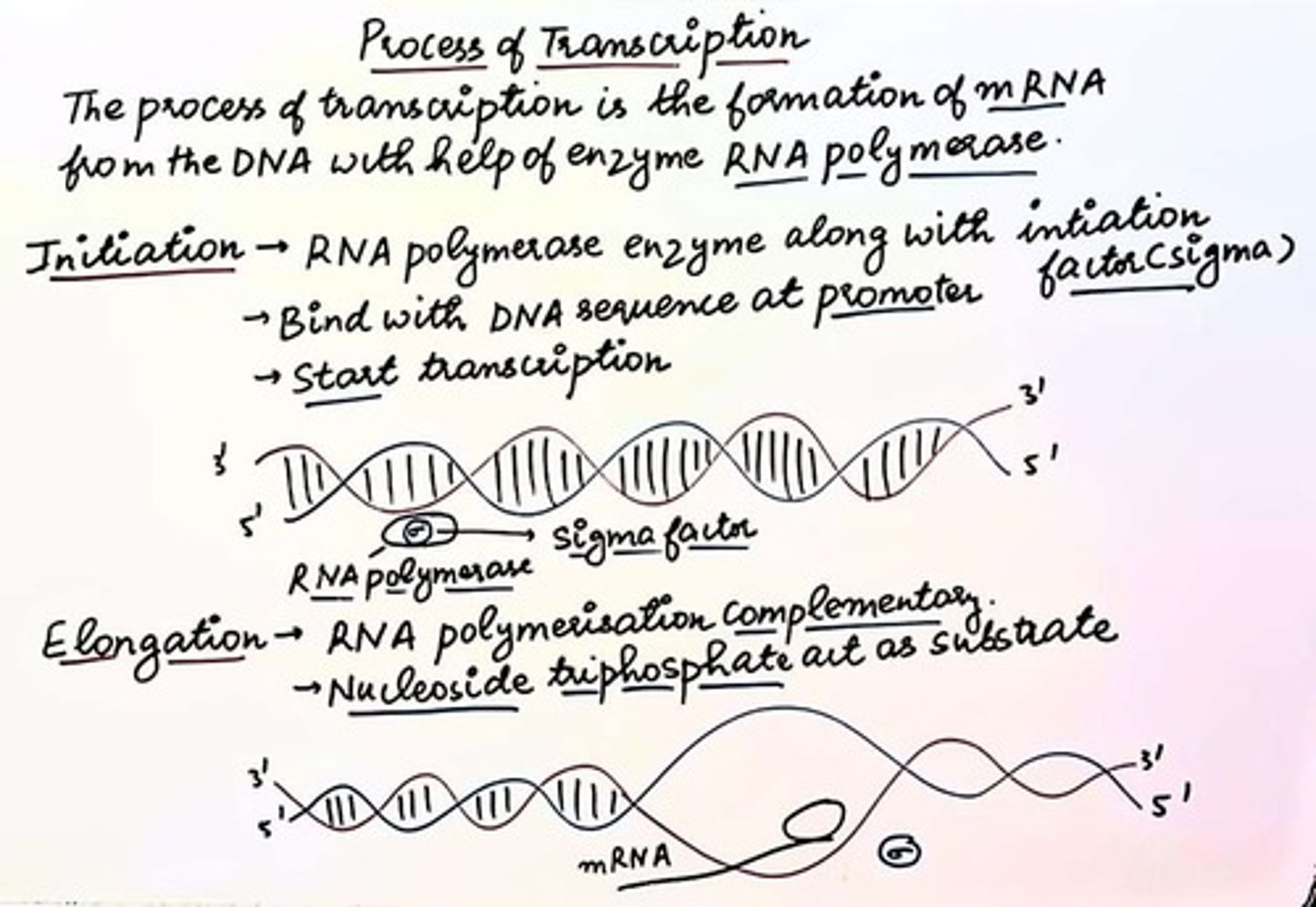
Transcription
Synthesis of RNA from a DNA template.
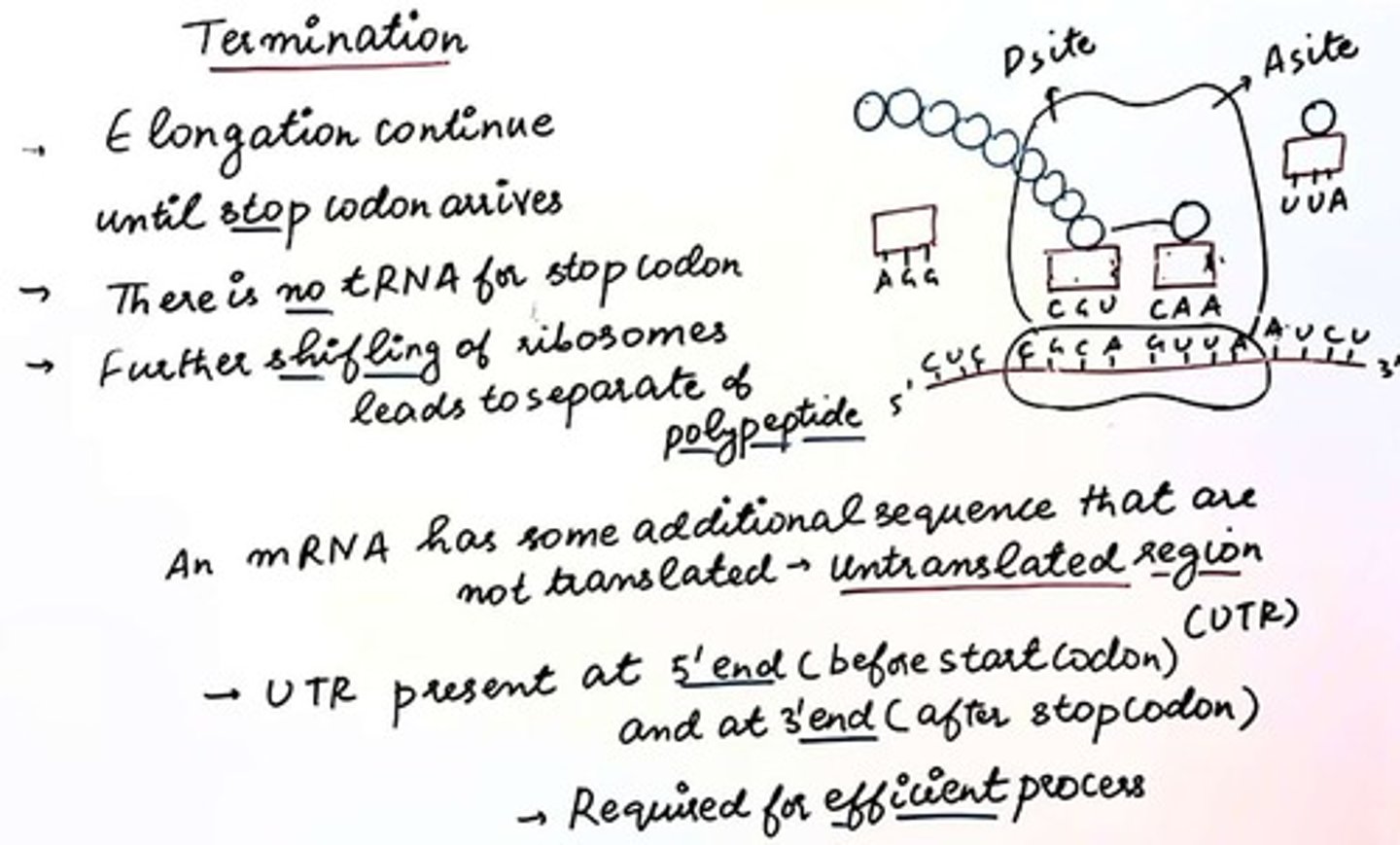
Translation
Synthesis of proteins from RNA.
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence affecting genetic information.
Chromatid
One of two identical halves of a duplicated chromosome.
Centromere
Region where two sister chromatids are joined.
Karyotype
Number and appearance of chromosomes in a cell.
Genetic variation
Diversity in gene frequencies within a population.
Sex-linked traits
Traits associated with genes on sex chromosomes.
Polygenic inheritance
Trait controlled by multiple genes.
Epigenetics
Study of heritable changes not involving DNA sequence.
Nucleotide
Basic building block of DNA and RNA.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, involved in protein synthesis.
Transposons
DNA sequences that can change positions within the genome.
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in small populations.
Natural selection
Process where organisms better adapted survive and reproduce.
Gene flow
Transfer of genetic material between populations.
Chromosomal aberration
Structural changes in chromosomes affecting genetic information.
Genetic engineering
Manipulation of an organism's DNA using biotechnology.
Cloning
Creating a genetically identical copy of an organism.
Biotechnology
Use of biological processes for industrial and other applications.
CRISPR
Gene-editing technology using targeted DNA modification.
Genetic counseling
Guidance for individuals regarding genetic disorders.