Basic Bacteriology
1/333
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
334 Terms
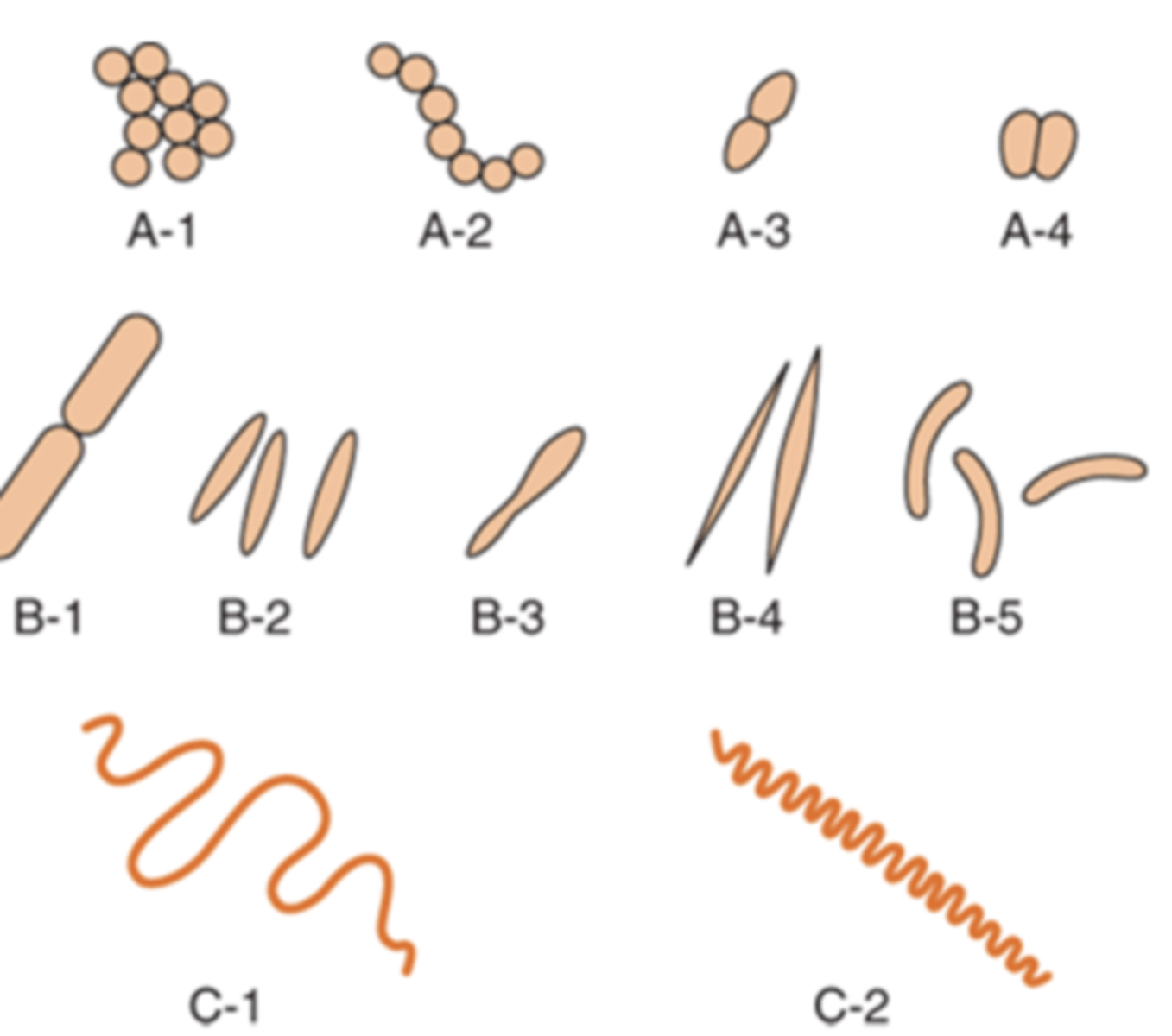
3 basic shapes of bacteria
1. cocci (round)
2. bacilli (rods)
3. spirochetes (spiral shaped)
what determines shape of bacteria
rigid cell wall
what is one of the most important criteria used in bacteria identification
microscopic appearance of bacterium
what are the 3 arrangements of cocci
1. diplococci
2. streptococci
3. staphylococci
diplococci occur in
pairs
streptococci occur in
chains
staphylococci occur in
clusters
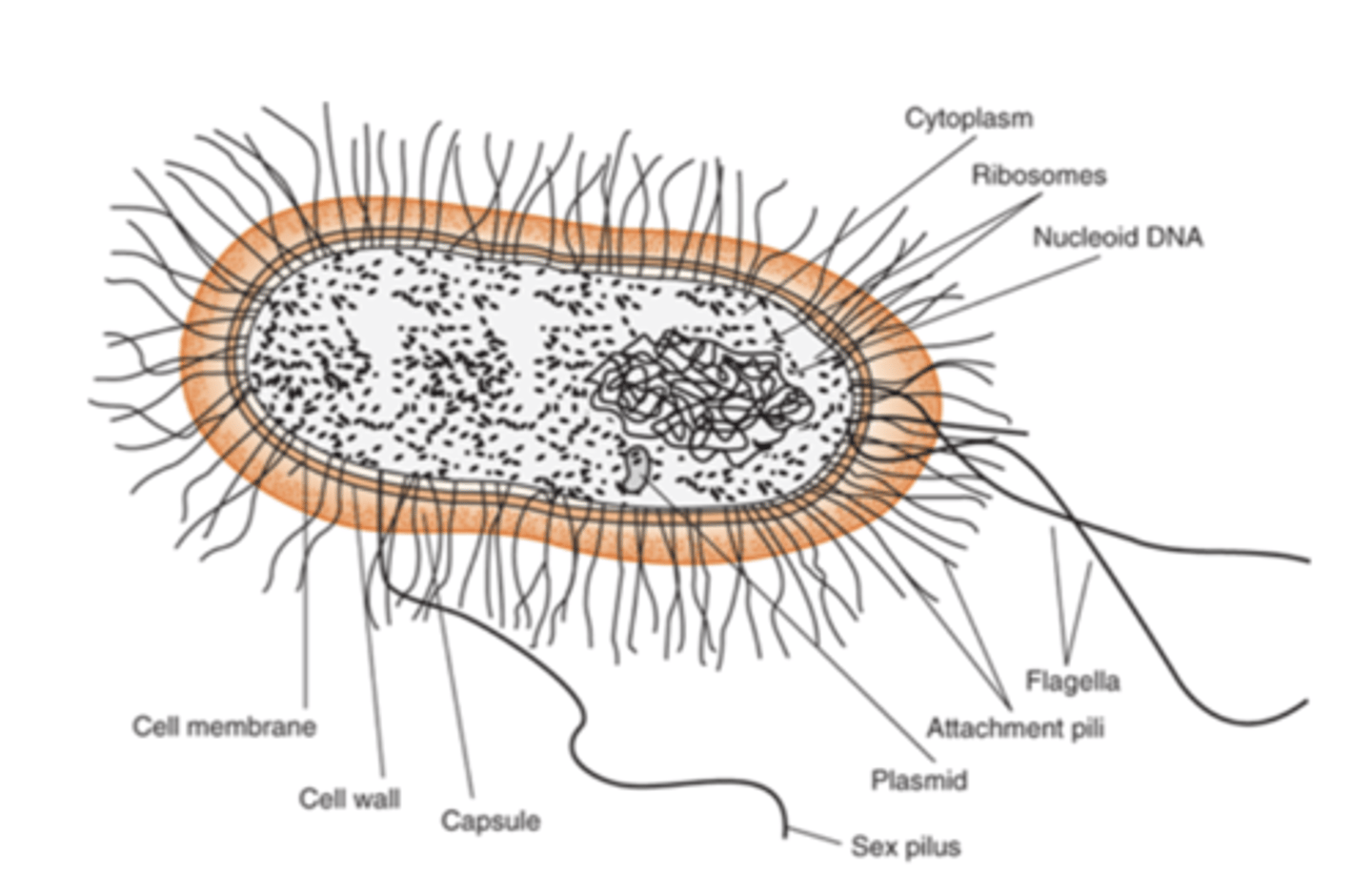
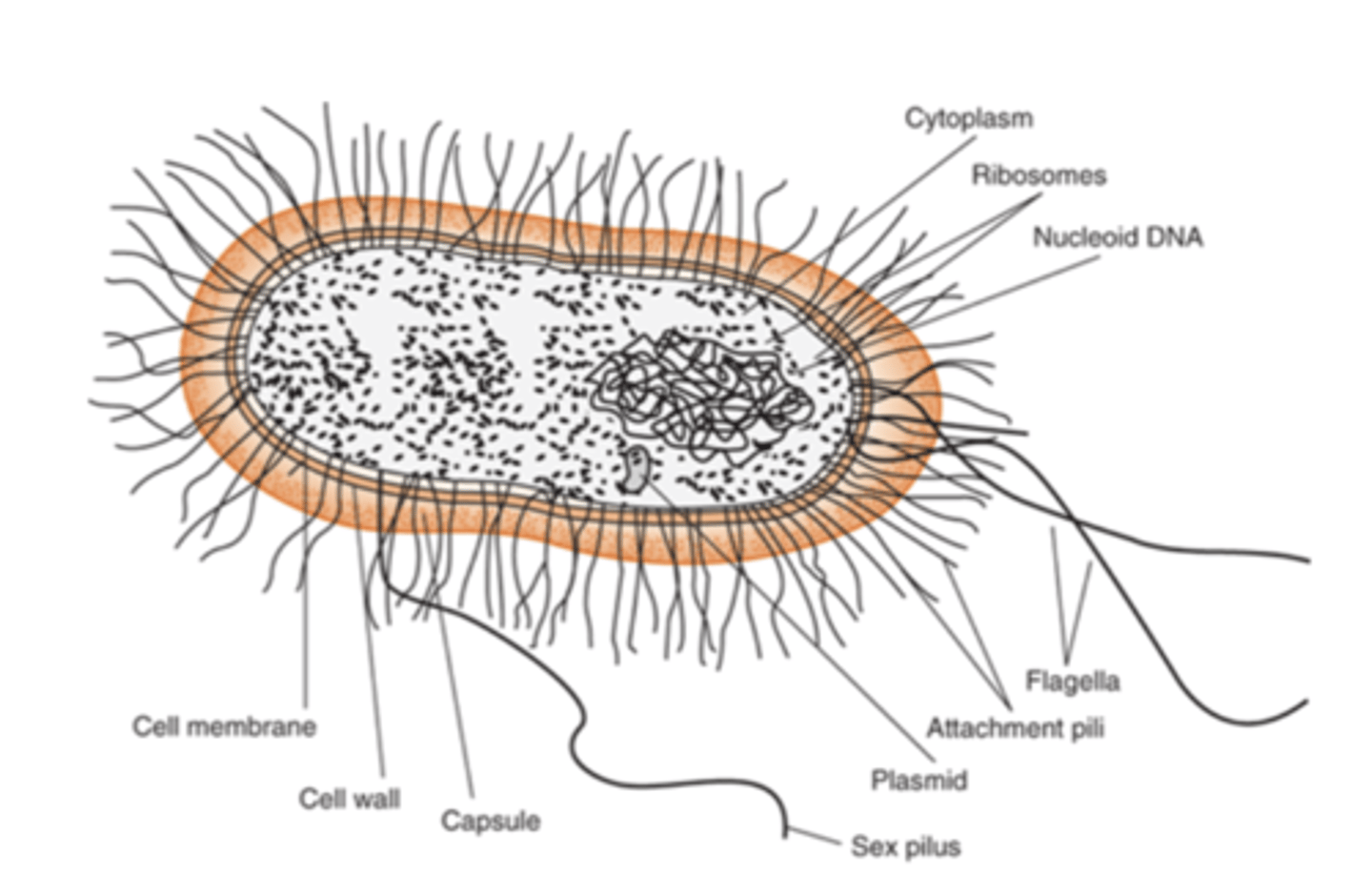
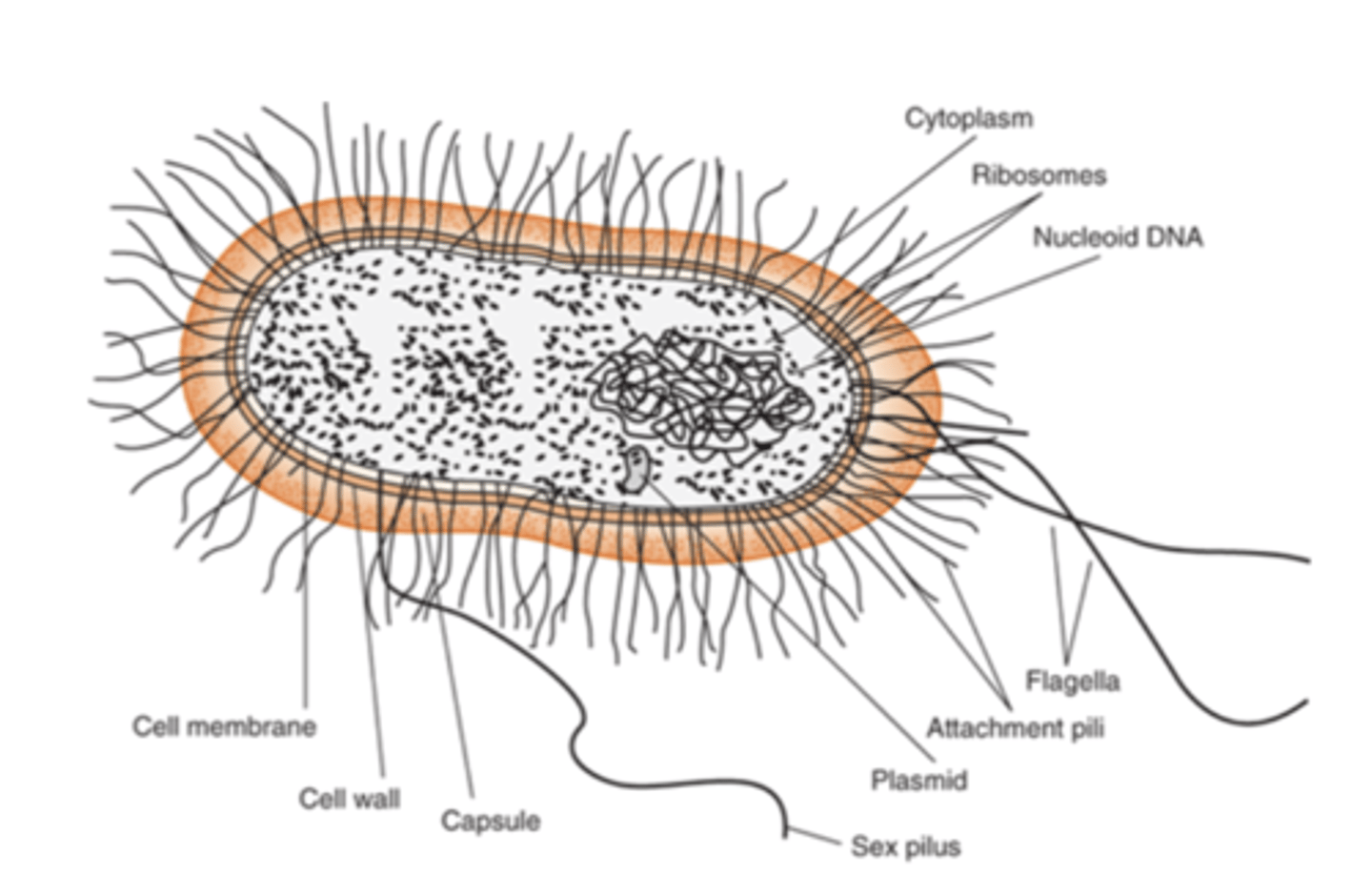
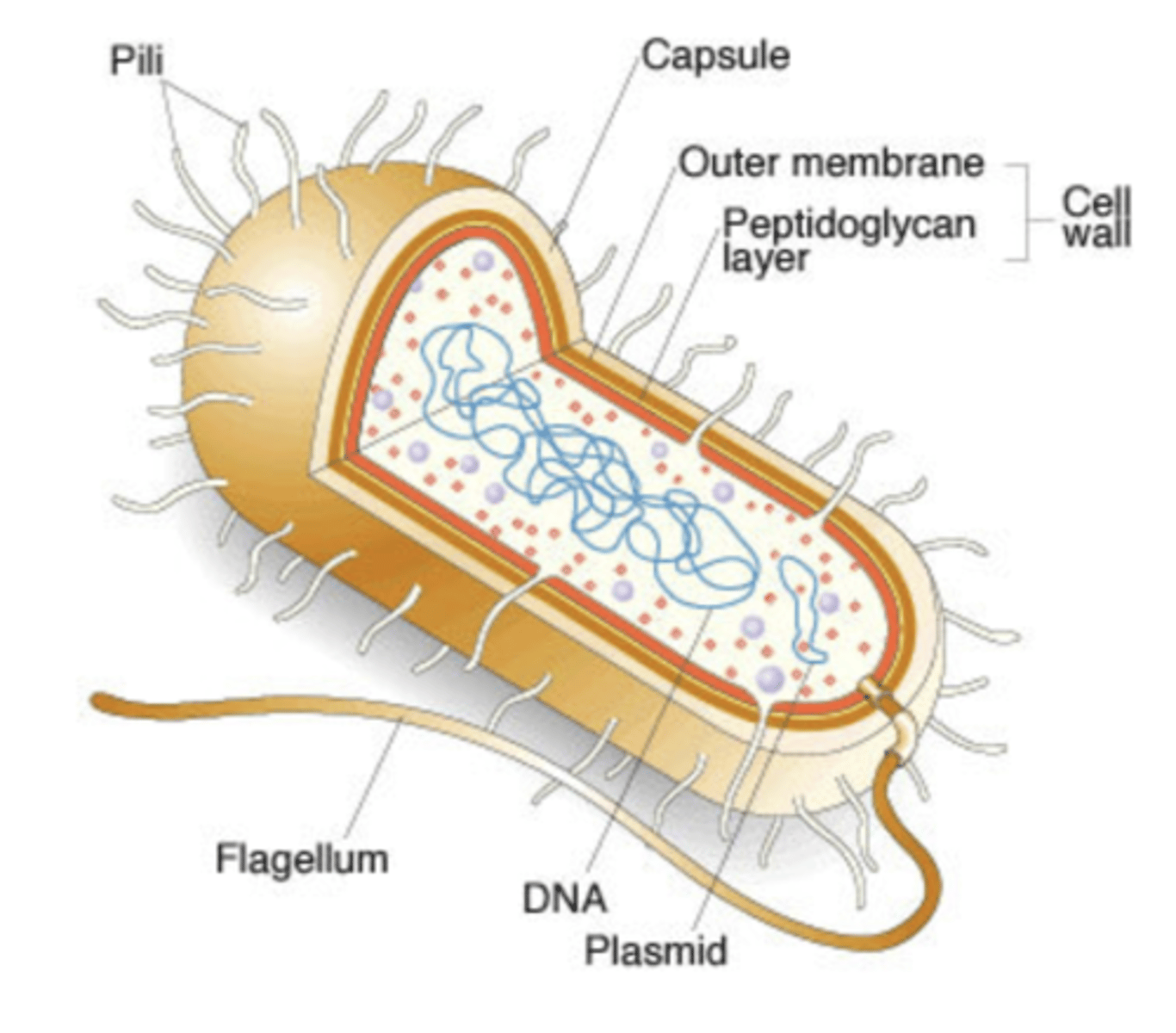
what is the outermost component common to all bacteria
cell wall
what is the exception of bacteria that does not have a cell wall
mycoplasma species
how is the cell wall located in comparison to the cell membrane
located externally
what is the cell wall composed of
peptidoglycan
what is the role of peptidoglycan
1. structural support
2. maintains characteristic shape of cell wall
what are some features that are external to the cell wall (some bacteria have these things)
1. LPS (endotoxin)
2. capsule
3. flagella
4. pilli
describe the difference in peptidoglycan in the cell wall of gram-positive vs gram-negative
gram-positive have thick peptidoglycan while gram-negative have thin peptidoglycan
what do gram-positive bacteria have in their cell wall that protrude outside the peptidoglycan (gram-negative bacteria do not have this)
teichoic acid
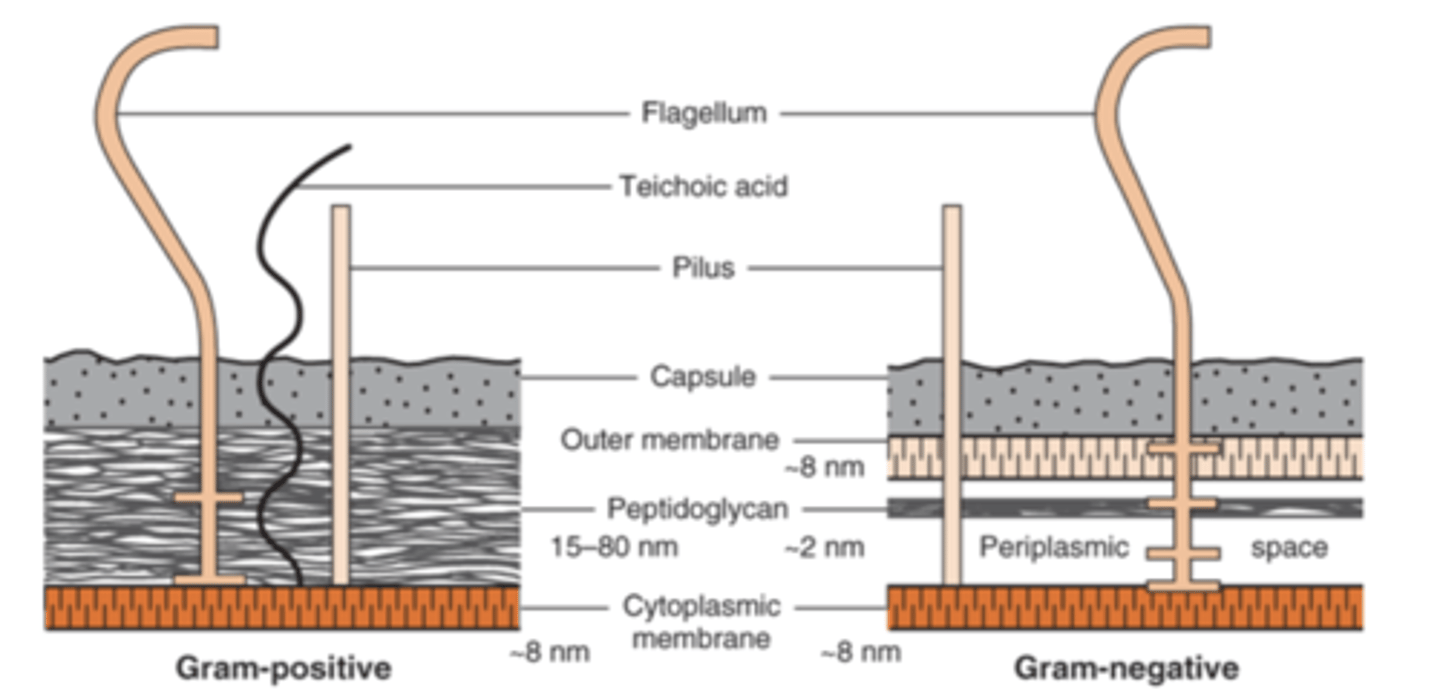
what makes up the complex outer layer of gram-negative bacteria outside of their cell wall
lipopolysaccharide (LPS, endotoxin), lipoprotein, and phospholipid

what is the name of the combined gram-negative bacteria outer layer and cell wall
envelope
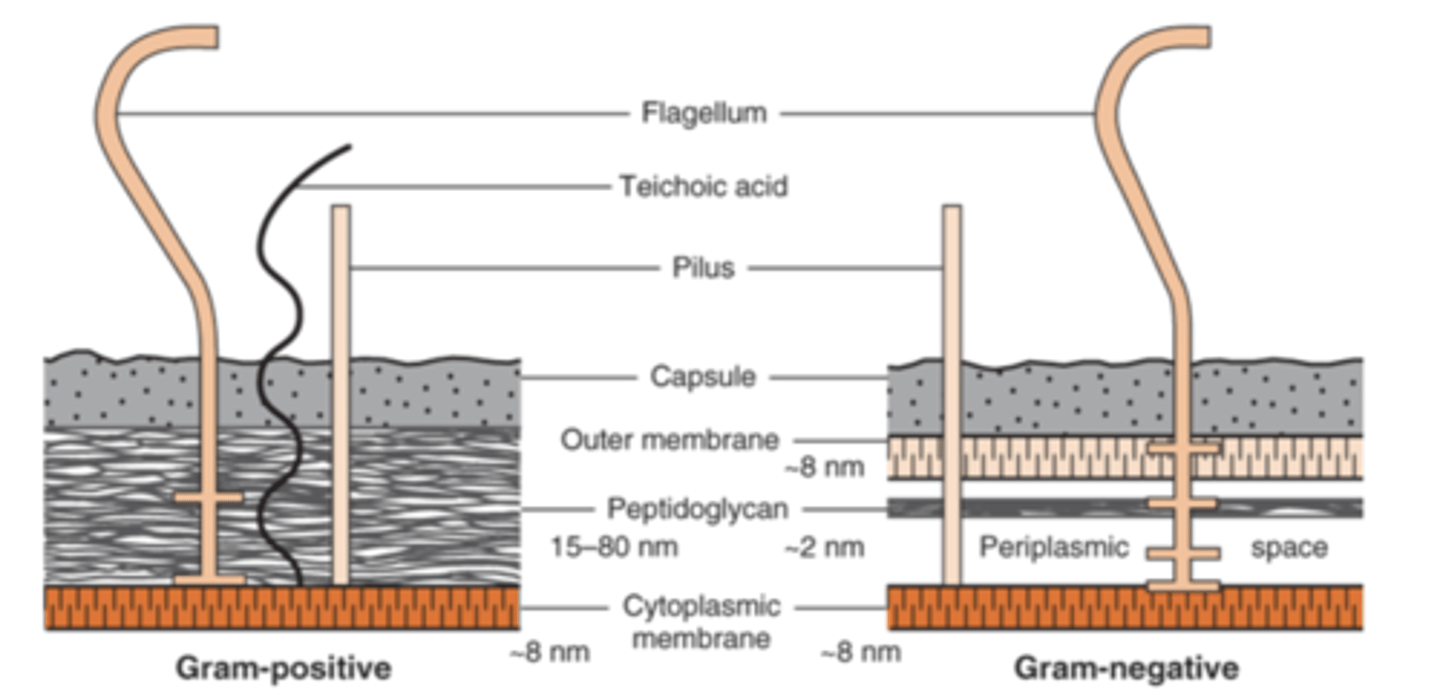
what is laying between the outer-membrane layer and the cytoplasmic membrane in gram-negative bacteria
periplasmic space
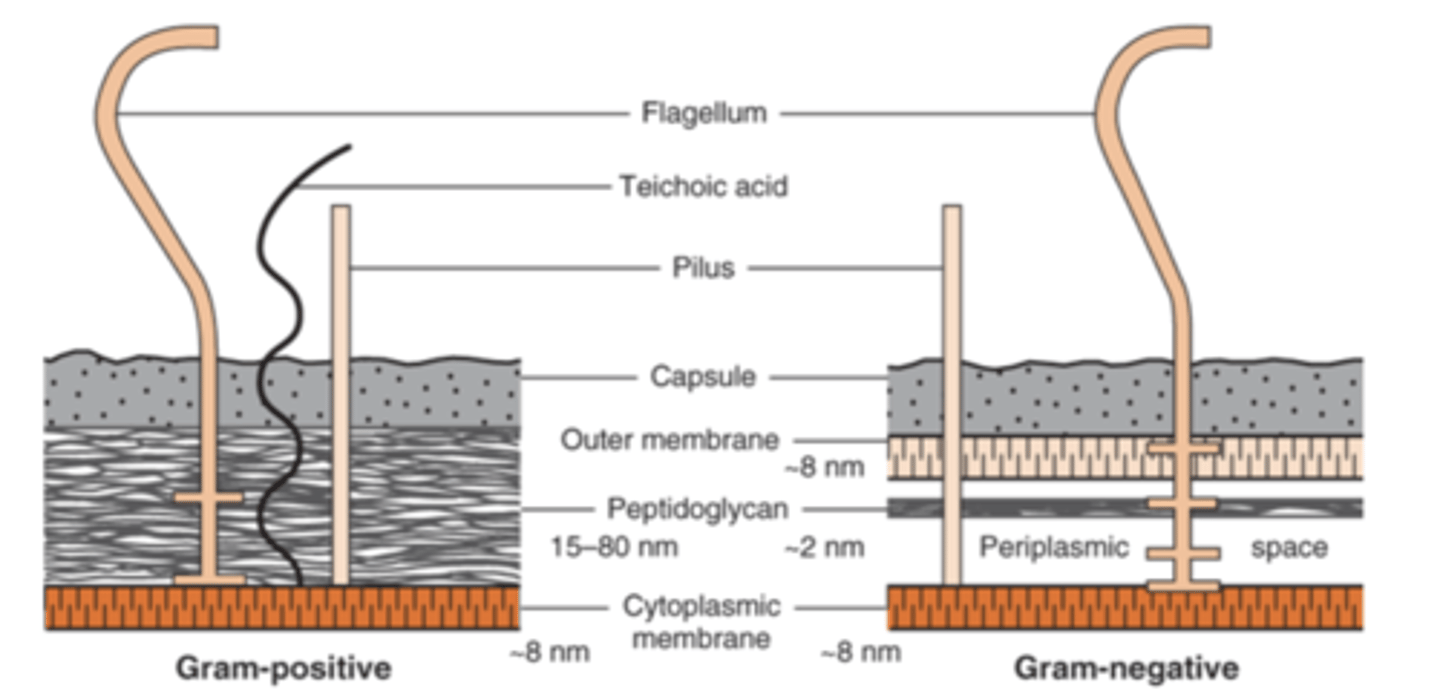
what enzymes are within the periplasmic space in gram-negative bacteria
B-lactamases
role of B-lactamases
degrade penicillin and other B-lactam drugs
B-lactamases make gram-negative bacteria what in terms of sensitivity to antibiotics
less sensitive
photo showing comparison of cell walls between gram-negative and gram-positive

most important staining procedure in microbiology
gram stain
what does gram stain separate bacteria into
2 groups:
1. gram-positive stain purple
2. gram-negative stain pink/red
4 step procedure of gram stain
1. crystal violet dye stains all cells purple
2. iodine solution is added to form a crystal violet-iodine complex; all cells continue to appear purple
3. organic solvent extracts the purple dye/iodine complex from the lipid-rich, thin-walled, gram-negative bacteria to a greater degree than from the lipid-poor, thick-walled, gram positive bacteria
4. red dye (safranin) stains the decolorized gram-negative cells red/pink; the gram-positive cells remain purple
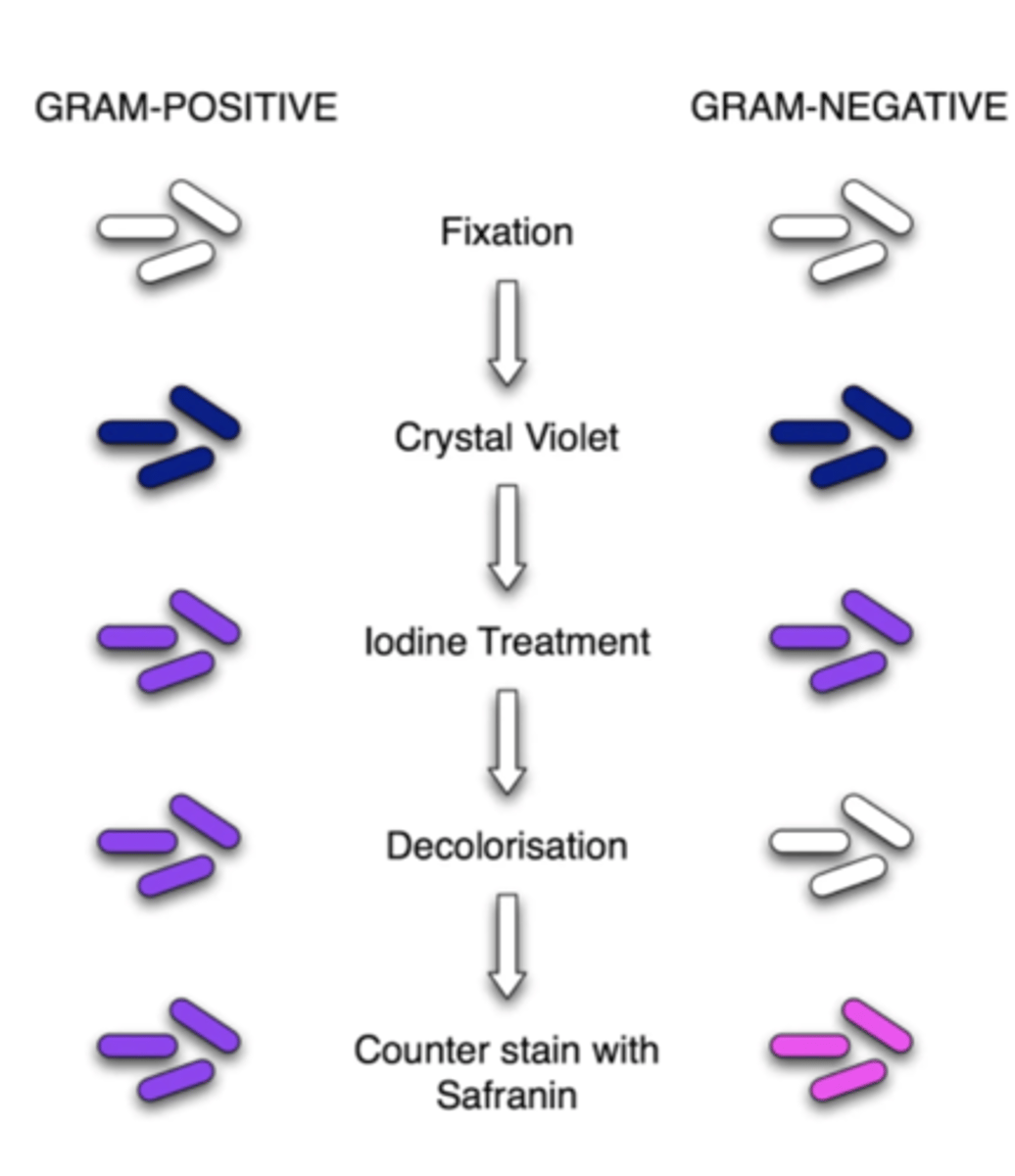
gram stain is useful in which 2 ways
1. identification
2. influencing choice of abx - gram-positive bacteria are more susceptible to penicillin (lack periplasmic space)
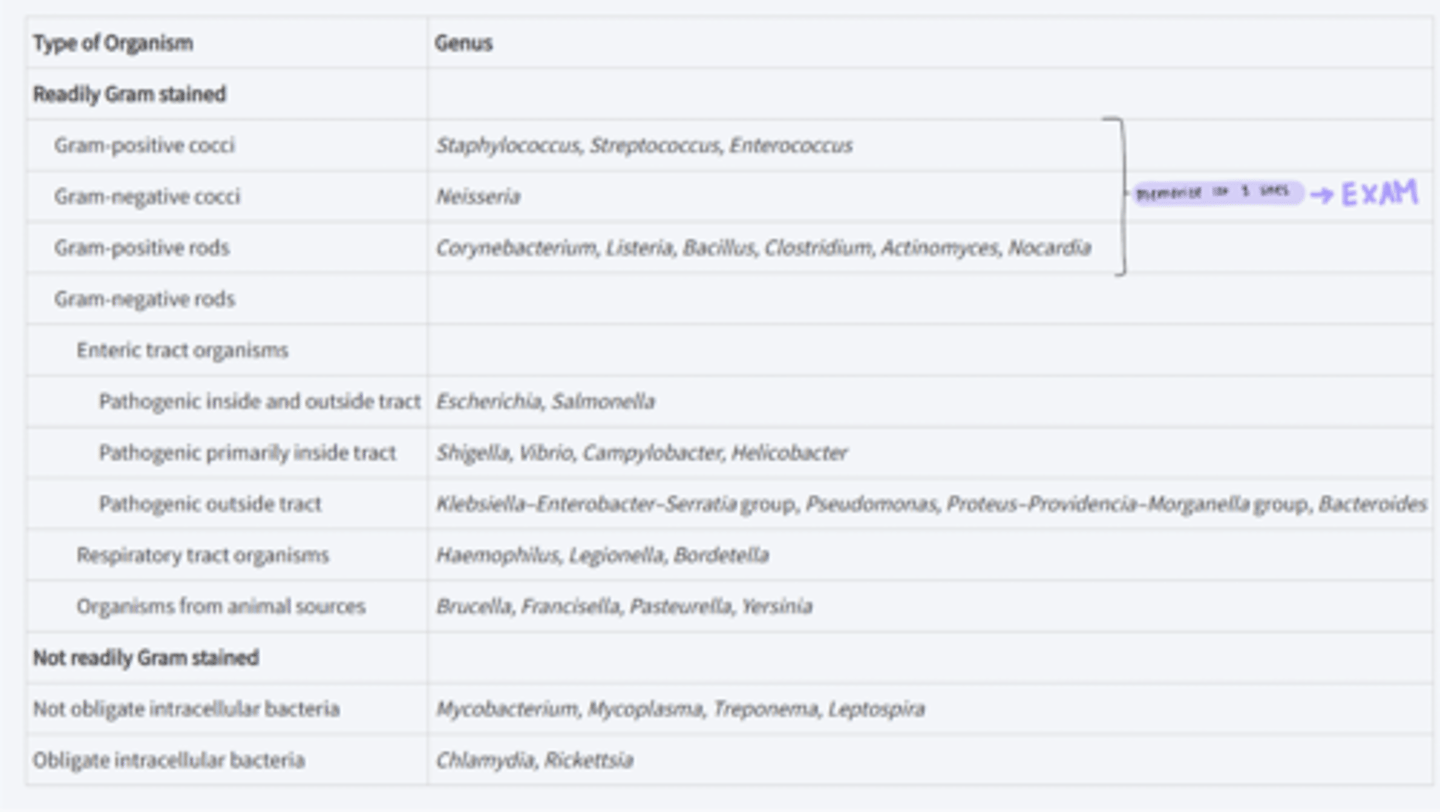
photo showing which bacteria you need to know (first 3 lines)
does mycobacteria cell wall stain with gram stain
no
mycobacteria are ___-fast
acid
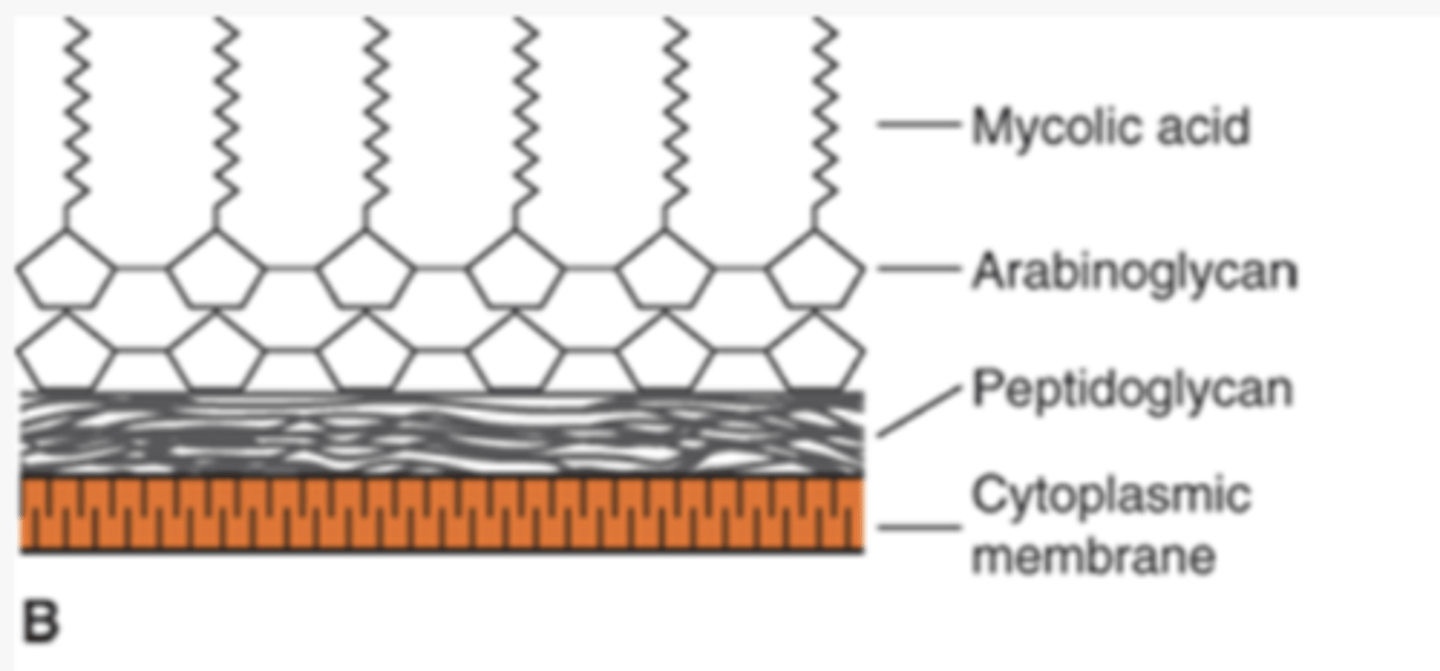
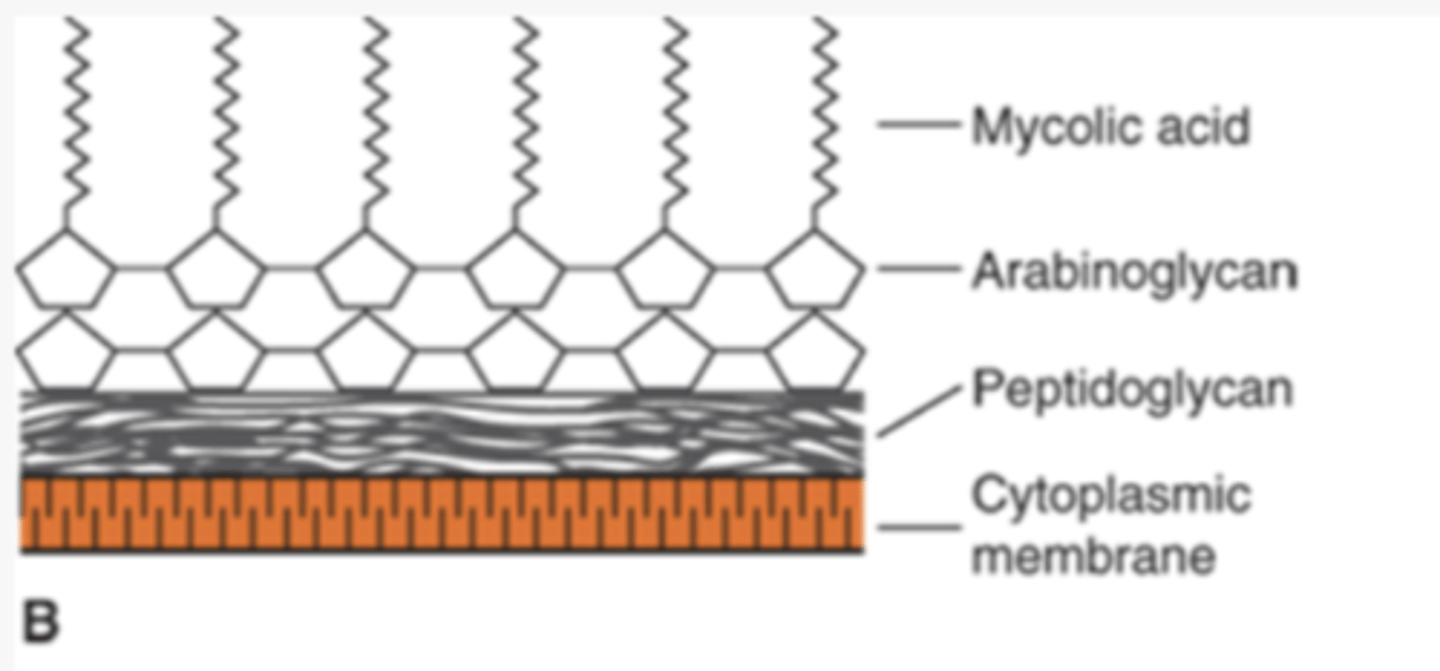
what does mycobacteria being acid fast mean
resist decolorization with acid-alcohol after being stained with carbolfuchsin
what do acid-fast bacteria (mycobacteria) have in their cell wall
high concentration of lipids - mycolic acids
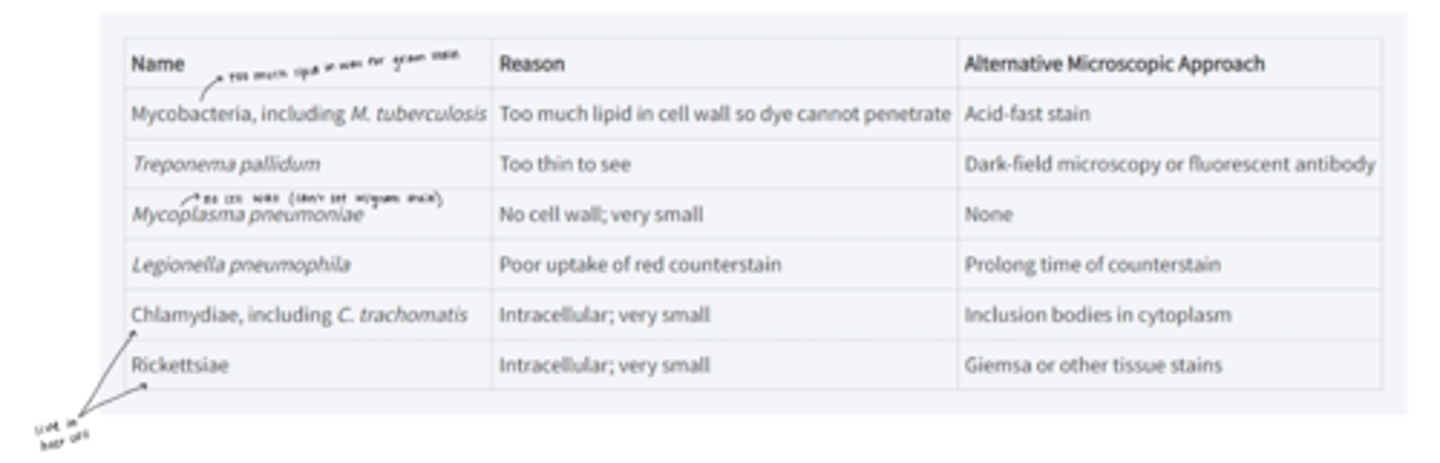
list of medically important bacteria that cannot be seen with gram stain
know mycobacteria, chlamydia, and rickettsiae
peptidoglycan is found only in ____ cell walls
bacterial
2 functions of peptidoglycan
1. important in maintaining shape of cell
2. allows cell to withstand low osmotic pressure
(complex, interwoven network that surrounds the entire cell)
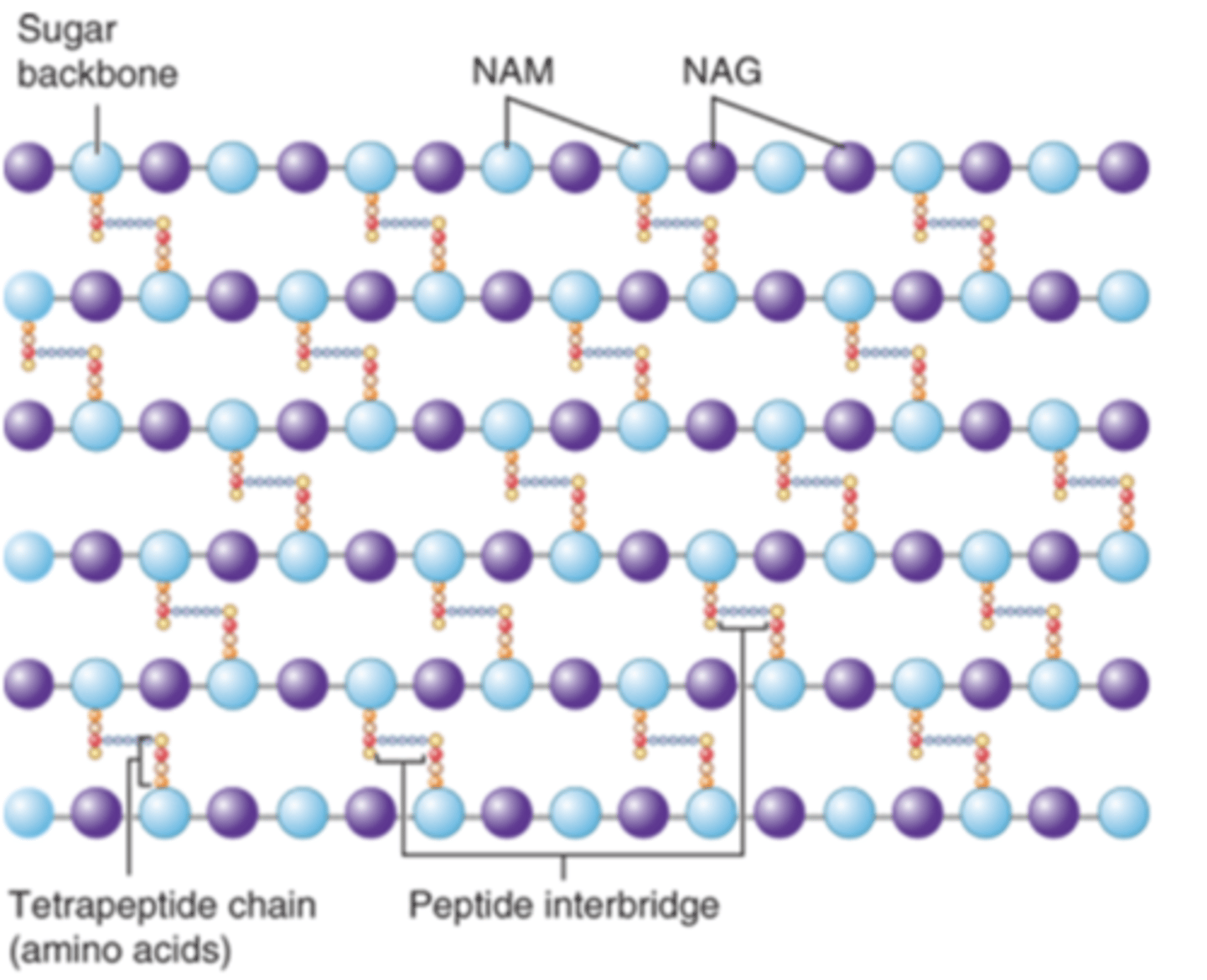
why is peptidoglycan a good target for antibiotics
antibiotics inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan
list 3 antibiotics in particular that inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan
1. penicillin
2. cephalosporins
3. vancomycin
name the enzyme that is present in tears, mucus and saliva
lysozyme
role of lysozyme
contributes to natural resistance of host to microbial infection
what specific action does the lysozyme carry out
cleaves the peptidoglycan backbone of bacteria
the LPS of the outer membrane of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria is ___
endotoxin
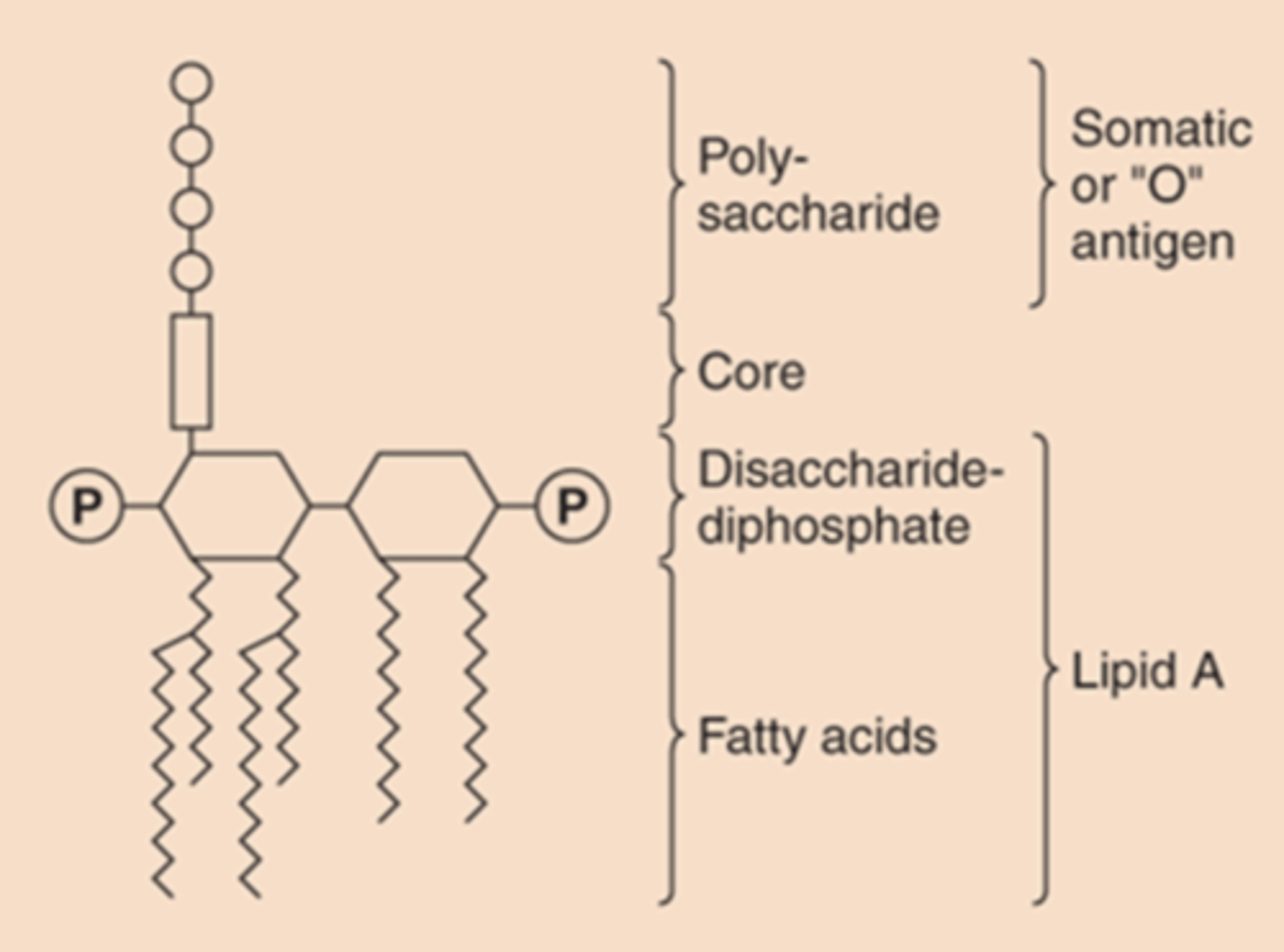
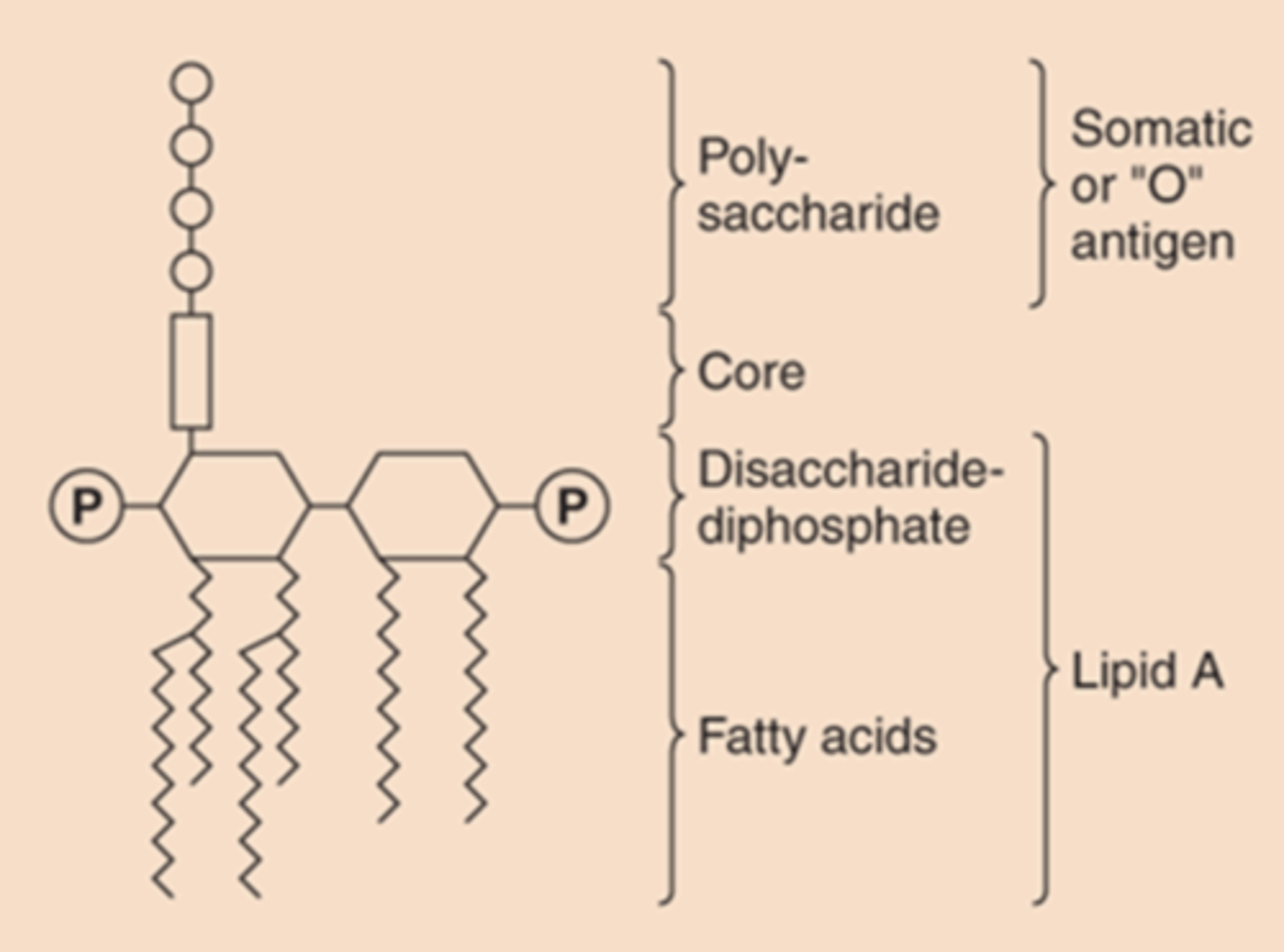
what is endotoxin responsible for when one has gram-negative bacterial disease
fever, shock
describe the 3 distinct units of Lipopolysaccharide
1. lipid A: phospholipid that causes toxicity
2. core polysaccharide linked to lipid A
3. O antigen: outer polysaccharide
fibers that extend from the outer layer of gram-positive cell wall
teichoic acid
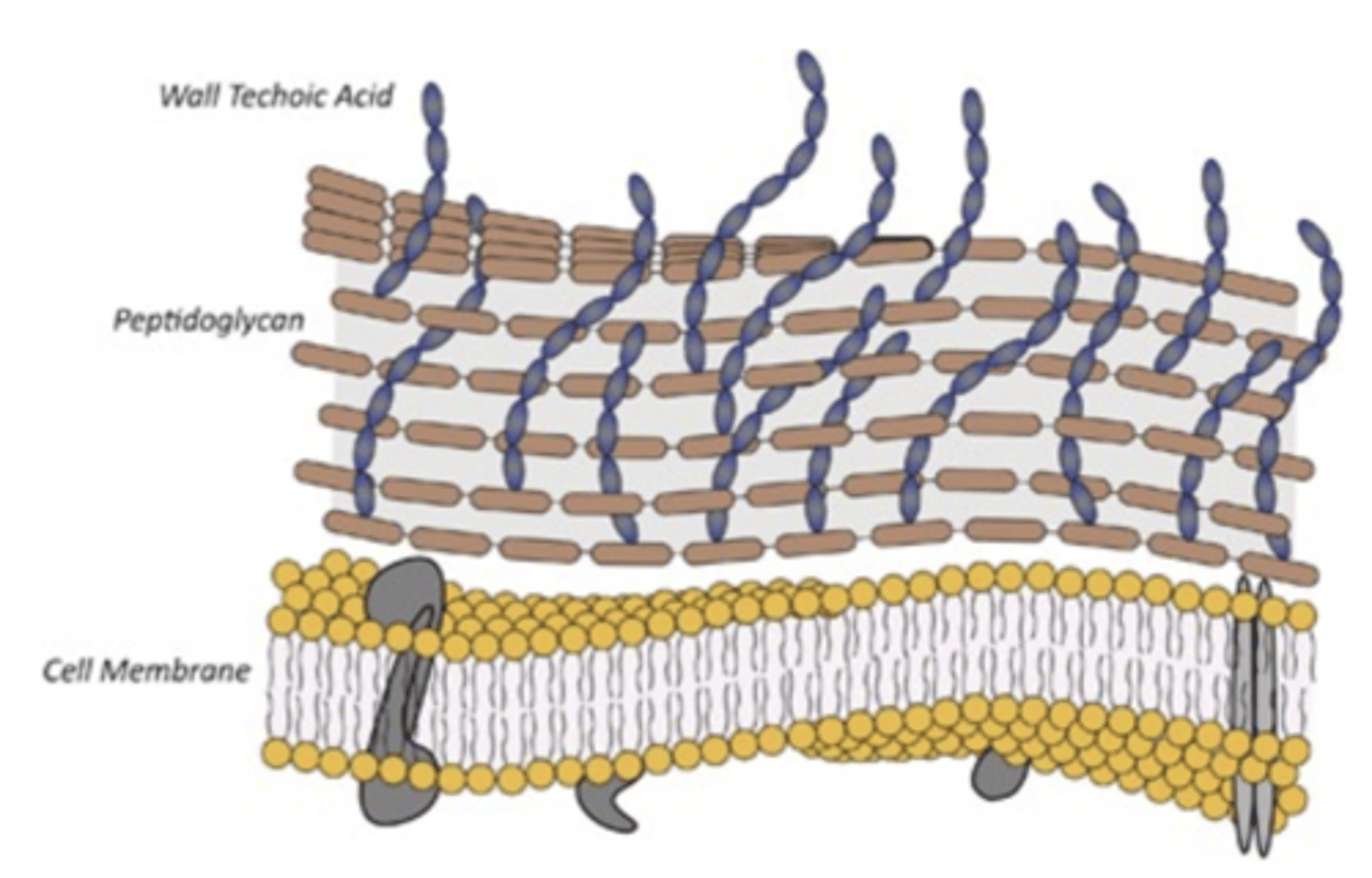
what do teichoic acids induce symptom wise
inflammation, septic shock
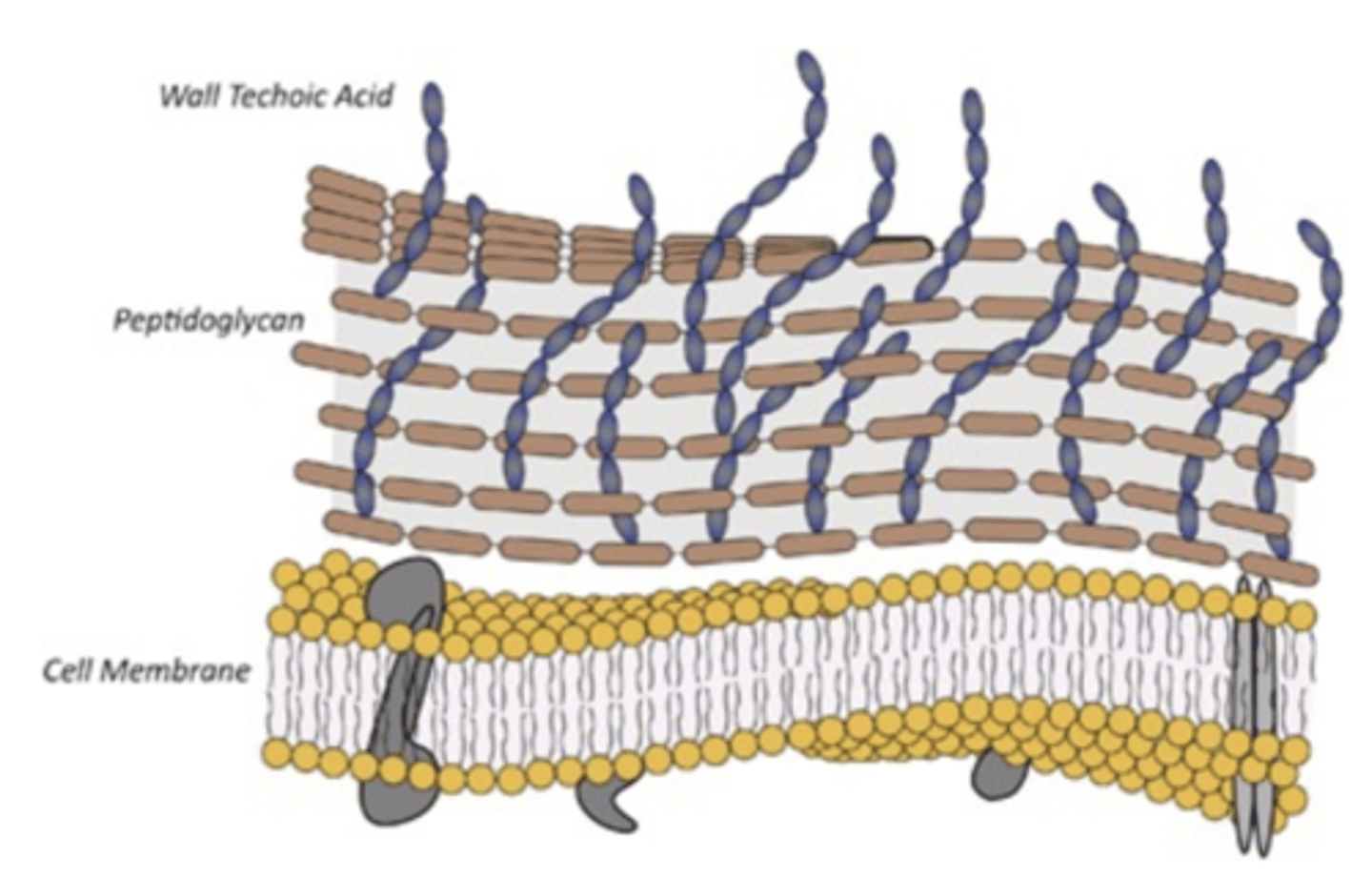
teichoic acid activates the ____ pathway as endotoxin (LPS) in gram-negative bacteria
same
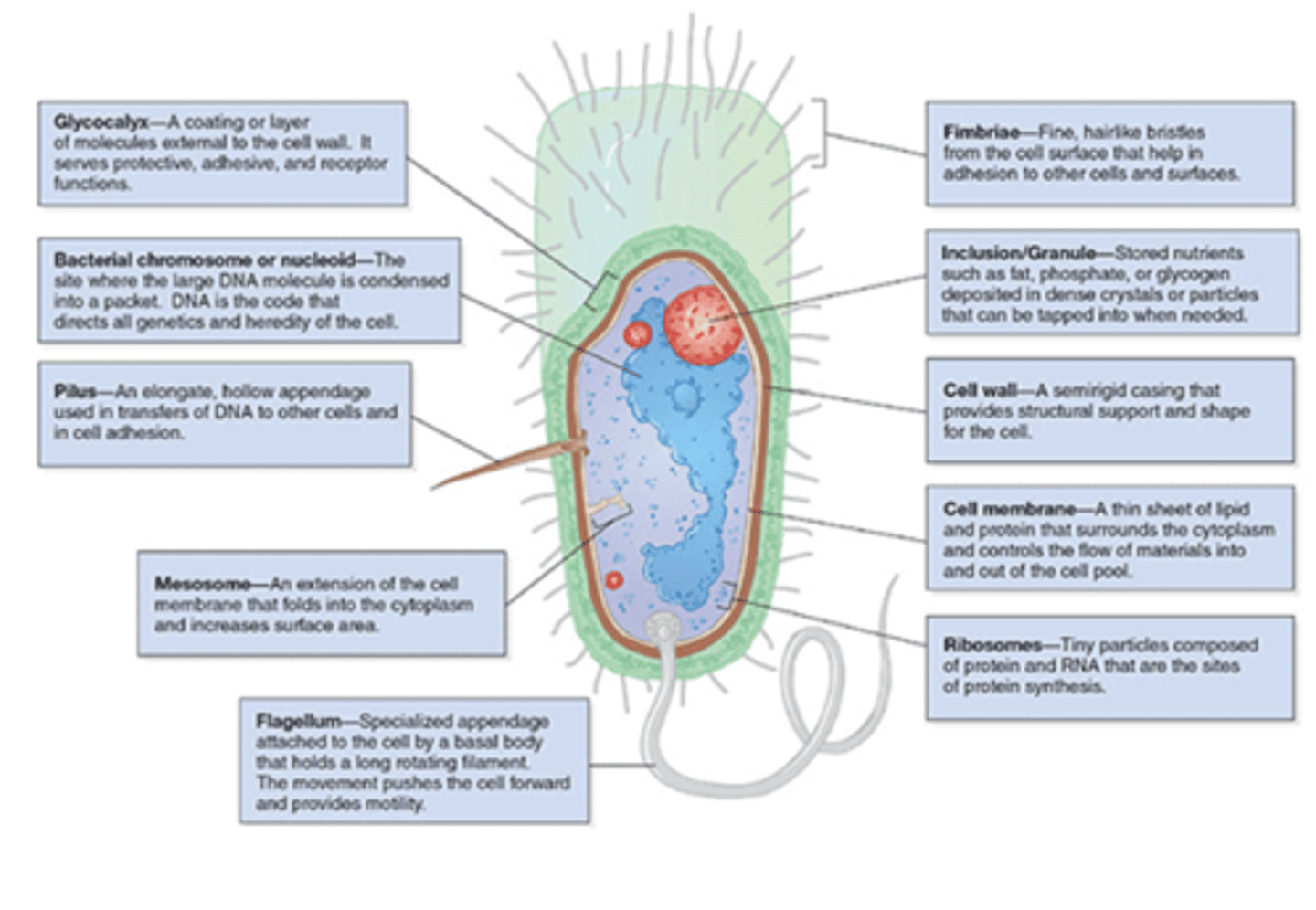
what is the role of ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
bacterial ribosomes differ from eukaryotic ribosomes in what
size and chemical composition
bacterial ribosomes are ____ in size
70S - 50S and 30S subunits
eukaryotic ribosomes are ____ in size
80S - 60S and 40S subunits
differences in the ribosomal RNAs and proteins constitute the basis of the selective action of ____ that ____ _____ ____ ____
antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis
plasmids are
double-stranded, circular DNA molecules
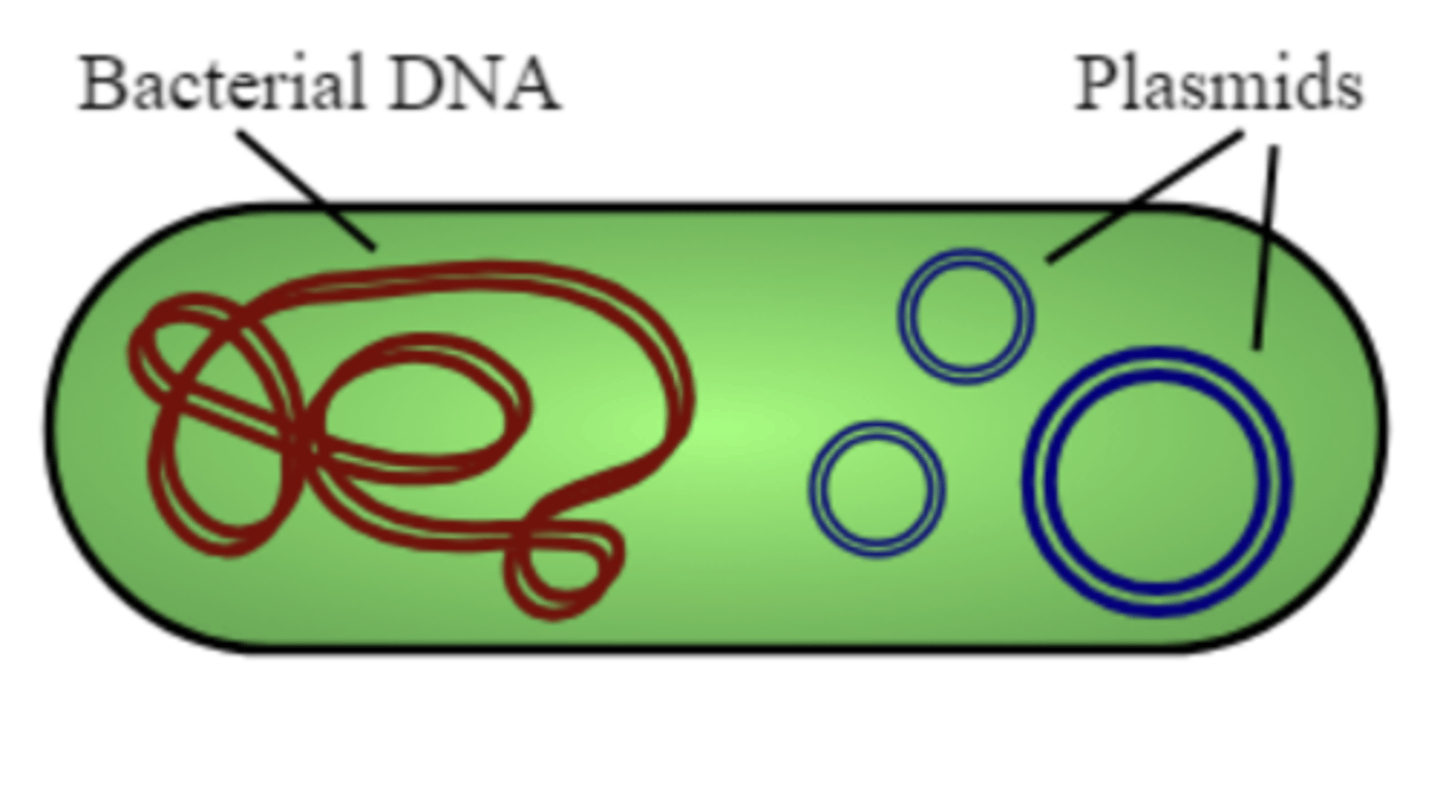
plasmids replicate ____ of the bacterial chromosome
independently
do plasmids occur in gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria
both
several ____ types of plasmids can exist in one cell
different
transmissible plasmids can be transferred to cell to cell via what
conjugation
plasmids are carriers of what
medically important genes
name the medically important genes of plasmids
1. antibiotic resistance
2. exotoxins
3. pili (fimbriae)
4. resistance to heavy metals
5. resistance to UV light
6. bacteriocins
what mediates antibiotic resistance of plasmids
variety of enzymes, such as B-lactamase
what is the role of pili (coded by plasmids)
mediate adherence of bacteria to epithelial cells
what are bacteriocins
toxic proteins produced by certain bacteria that are lethal for other bacteria
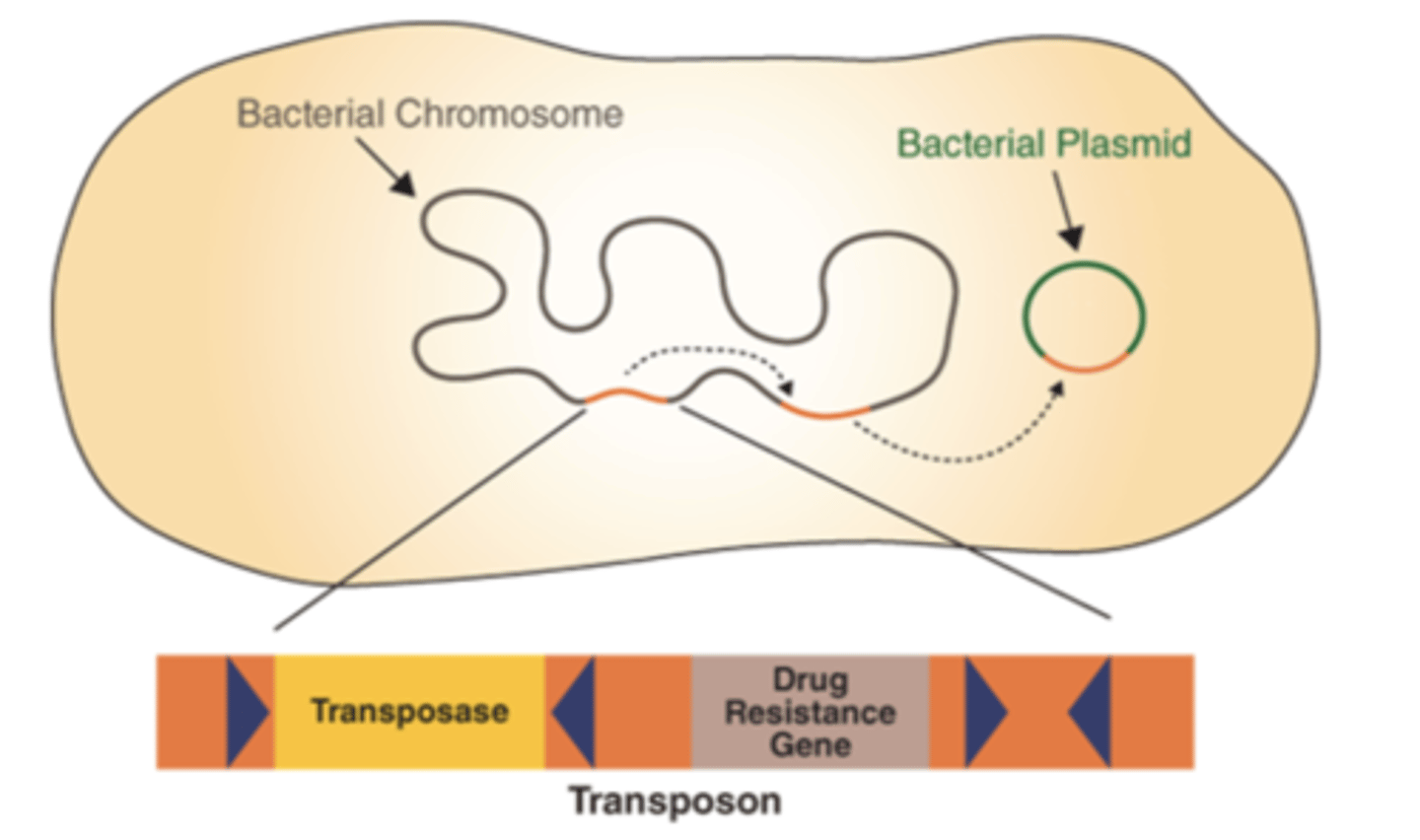
transposons are
pieces of DNA that move from one site to another within or between DNAs of bacteria, plasmids, and bacteriophages
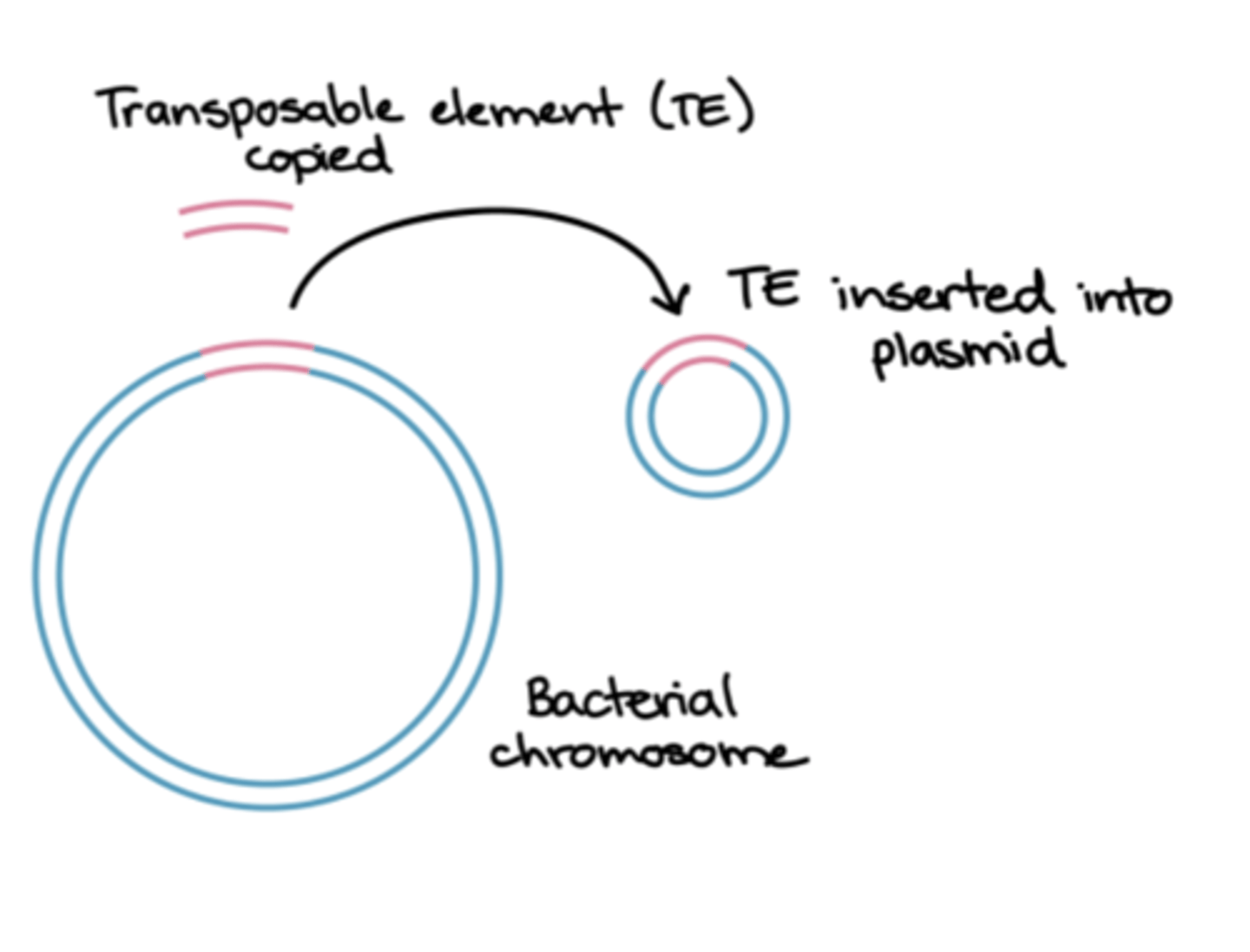
transposons are aka...
jumping genes
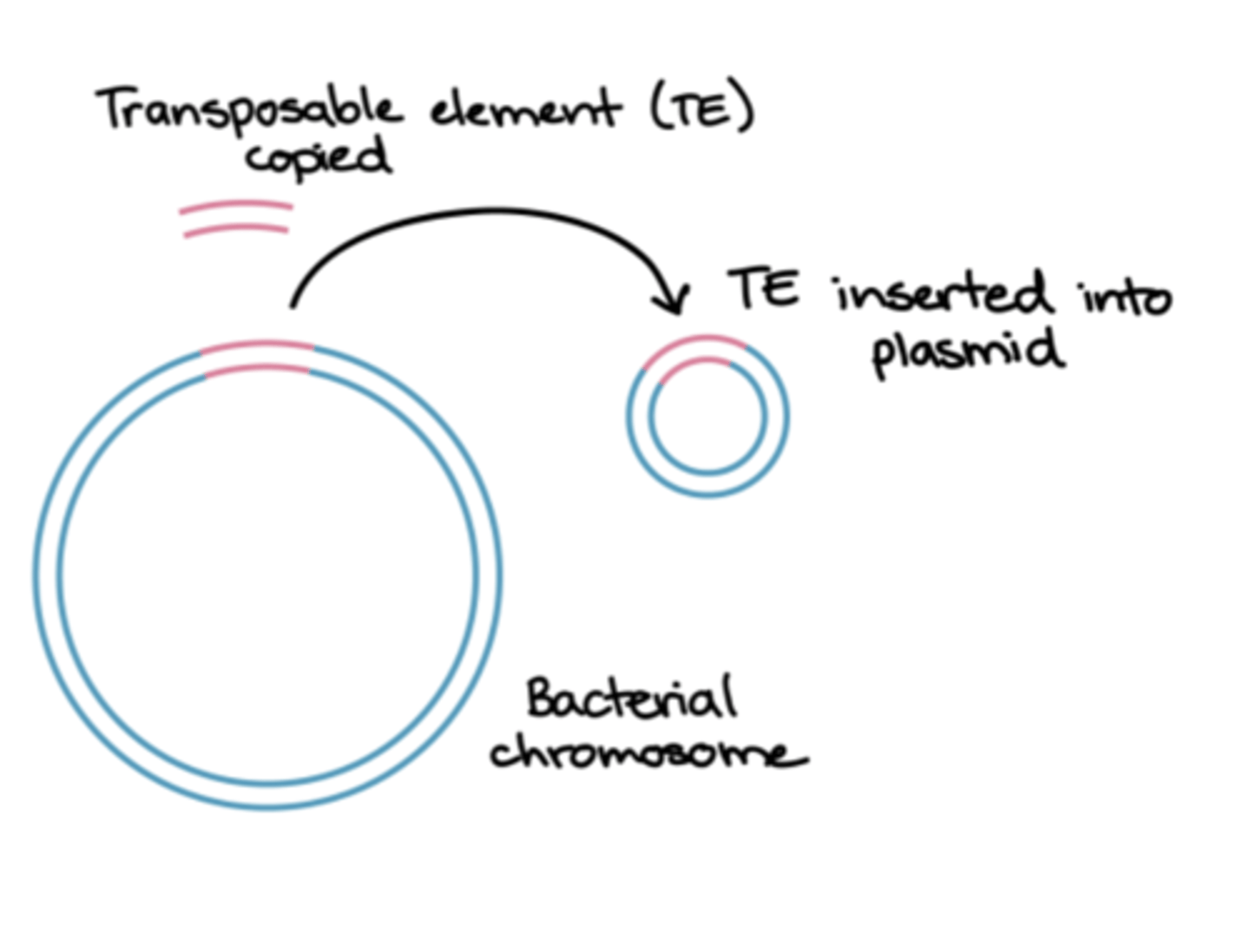
what do transposons code for
drug-resistant enzymes, toxins, or metabolic enzymes
are transposons capable of independent replication
no
how do transposons replicate
they replicate as part of the DNA in which they are integrated
photo showing how transposons can transfer to plasmids
what is the capsule
gelatinous layer covering the entire bacterium
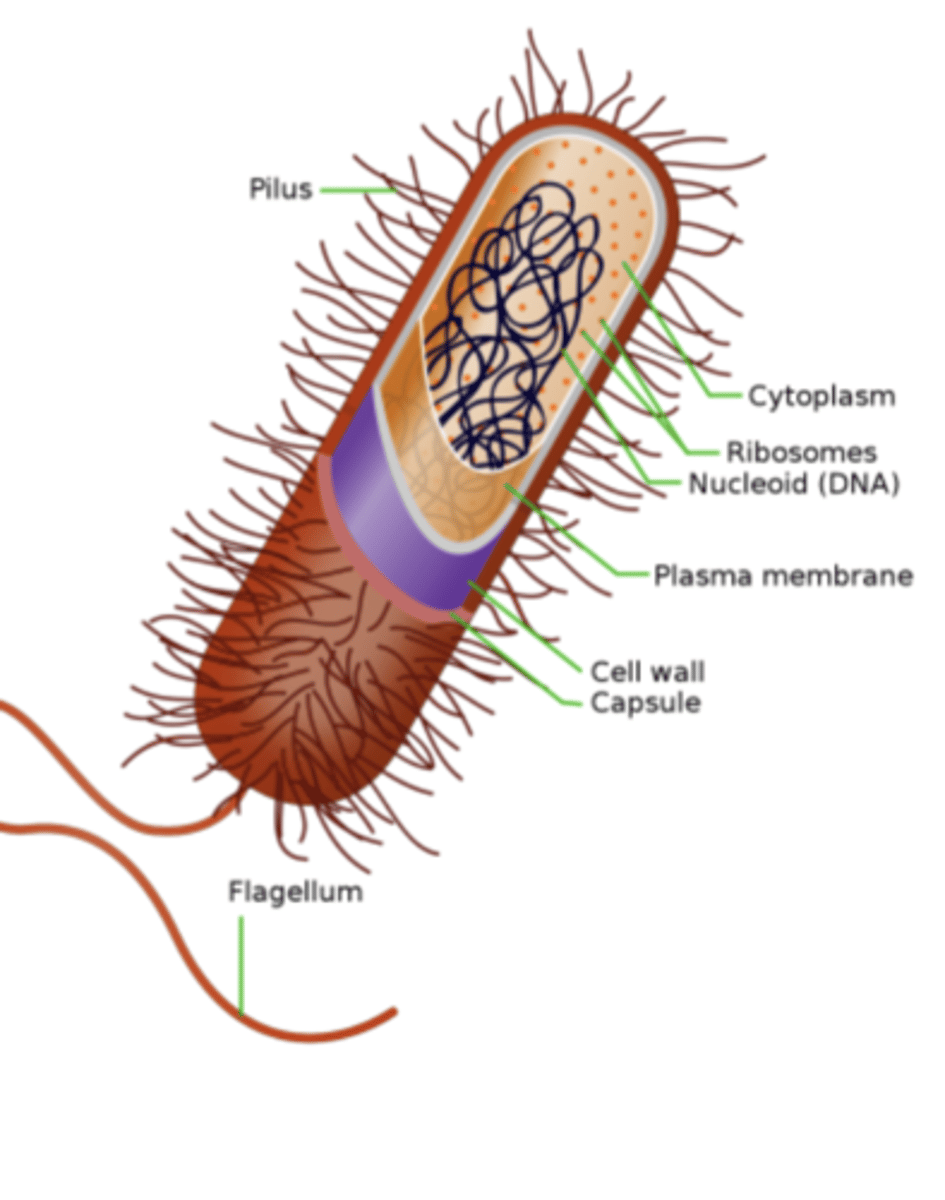
what is the medical importance of the capsule
it is a determinant of virulence - limits the ability of phagocytes to engulf bacteria
capsules are used as ____ in some vaccines
antigens - can elicit protective antibodies
name 3 bacteria that have vaccines that were made using capsules
1. streptococcus pneumoniae
2. neisseria meningitidis
3. haemophilus influenzae
capsules may play a role in ____ of bacteria to human tissues
adherence
what is an important initial step in causing infection (hint: the capsule helps with this)
asherence
flagella are
long, whip-like appendages

what is the role of flagella
move bacteria toward nutrients (chemotaxis)
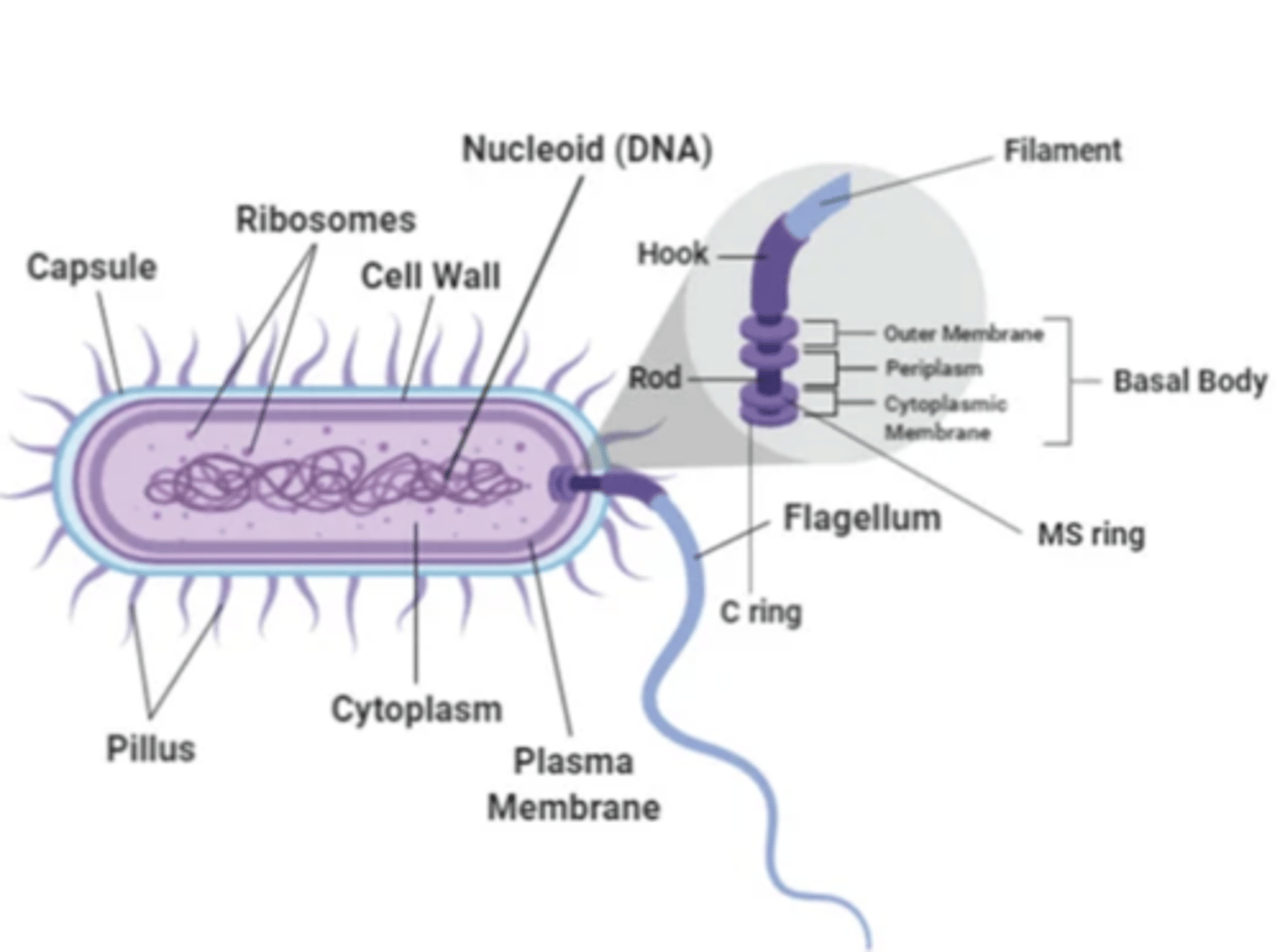
medical importance of flagella
some species of motile bacteria are common causes of UTIs as flagella propel the bacteria up the urethrae into the bladder
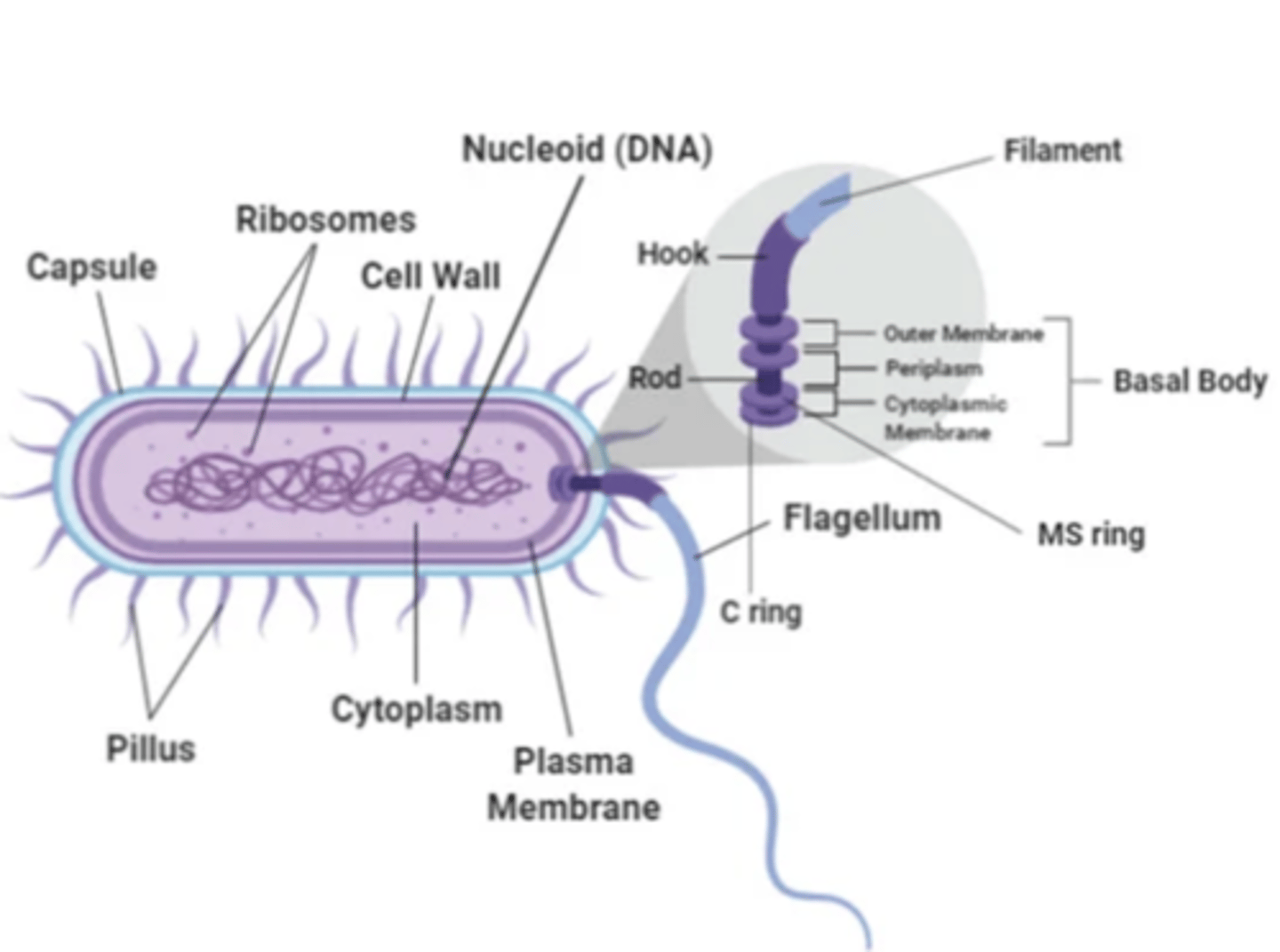
2 common bacteria species with flagella that often cause UTIs
1. Escherichia coli
2. Proteus
Pili (fimbriae) are
hairlike filaments that extend from the cell surface
pili are found mainly on gram-____ organisms
negative
medical importance of pili
1. mediate the attachment of bacteria to receptors on human cell surface (necessary step in the initiation of infection for some organisms)
2. specialized pilus (sex pilus) forms the attachment between the donor and recipient bacteria during conjugation (transmissible plasmids can be transferred from cell to cell by conjugation)
role of sex pilus
attachment between donor and recipient bacteria during conjugation
the glycocalyx is
polysaccharide coating that is secreted by many bacteria (covers surfaces like a film)
glycocalyx allows the bacteria to ___ firmly to various structures
adhere
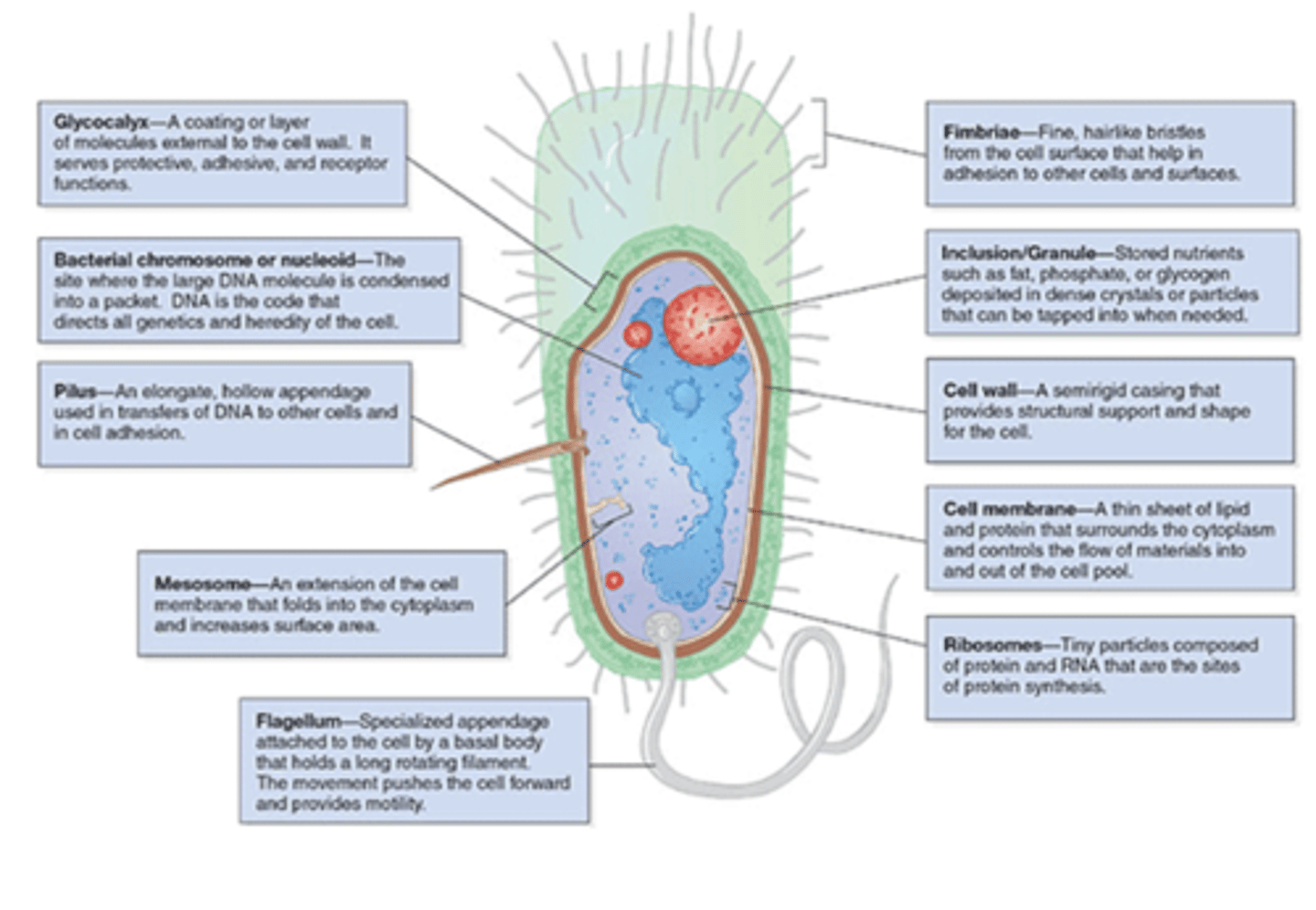
list some structures that the glycocalyx will allow bacteria to adhere to
skin, heart valves, prosthetic joints, and catheters
glycocalyx is an important component of what
biofilms
medical importance of glycocalyx
1. glycocalyx-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis and viridans streptococci cause endocartitis
2. plaque formation on teeth
bacterial spores are ____ resistant structures
highly
bacteria spores are formed by which 2 genera of gram-positive rods
1. bacillus
2. clostridium
when does spore formation occur
when nutrients are depleted
where do spores form in regards to the cell
inside the cell
what do bacterial spores contain
bacterial DNA, a small amount of cytoplasm, cell membrane, peptidoglycan, and a thick-coat
what does the thick, keratin-like coat of spores allow
resistance to heat, dehydration, radiation, and chemicals
spore has no ____ activity and can remain ___ for many years
metabolic, dormant
upon exposure to water and nutrients, what will occur in regards to the spore
specific enzymes will degrade the coat, water and nutrients will enter and germination into a pathogenic bacterial cell will occur
medical importance of spores
1. sterilization cannot be achieved by boiling
2. autoclaving is required to ensure the sterility of products for medical use
2. hand sanitizer does not kill spores; must wash hands
bacteria reproduce via what
binary fissionn
4 phases of growth cycle of bacteria
1. lag phase
2. log phase
3. stationary phase
4. death phase
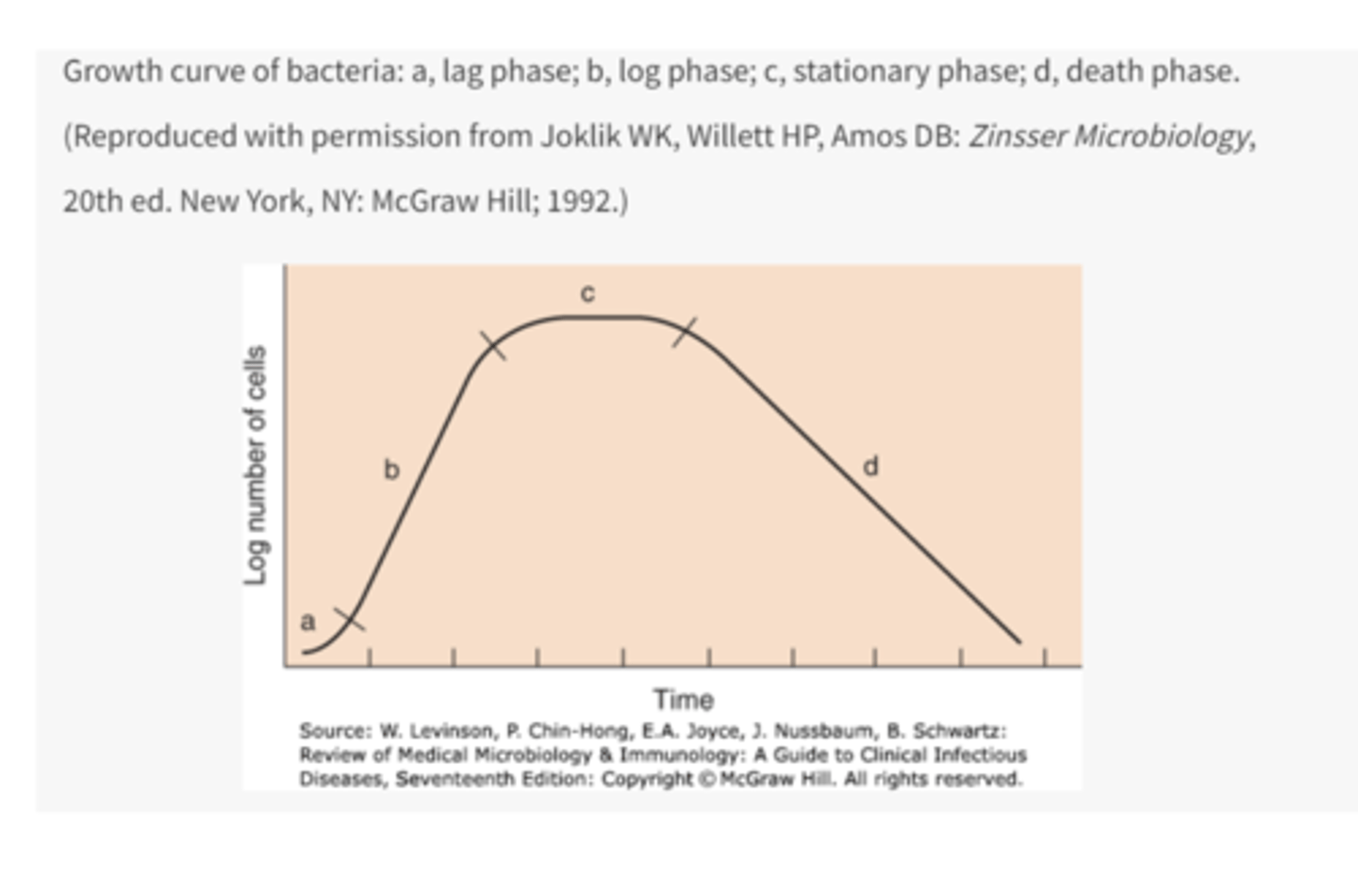
what occurs in the lag phase
metabolic activity occurs but cells do not divide
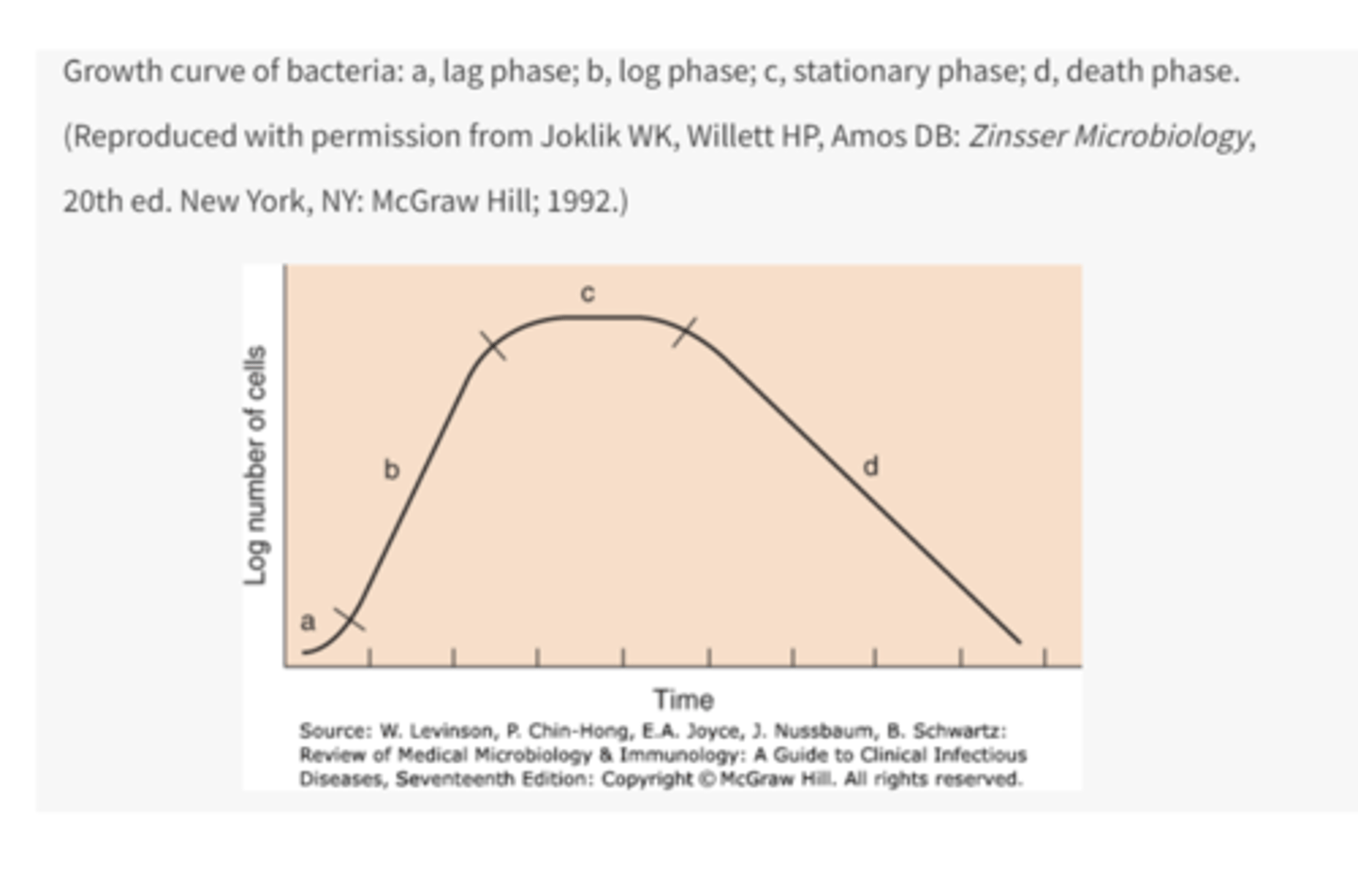
what occurs in the log phase
rapid cell division occurs
what occurs in the stationary phase
nutrient depletion or toxic products cause growth to slow (number of new cells produced balances the number of cells that die)
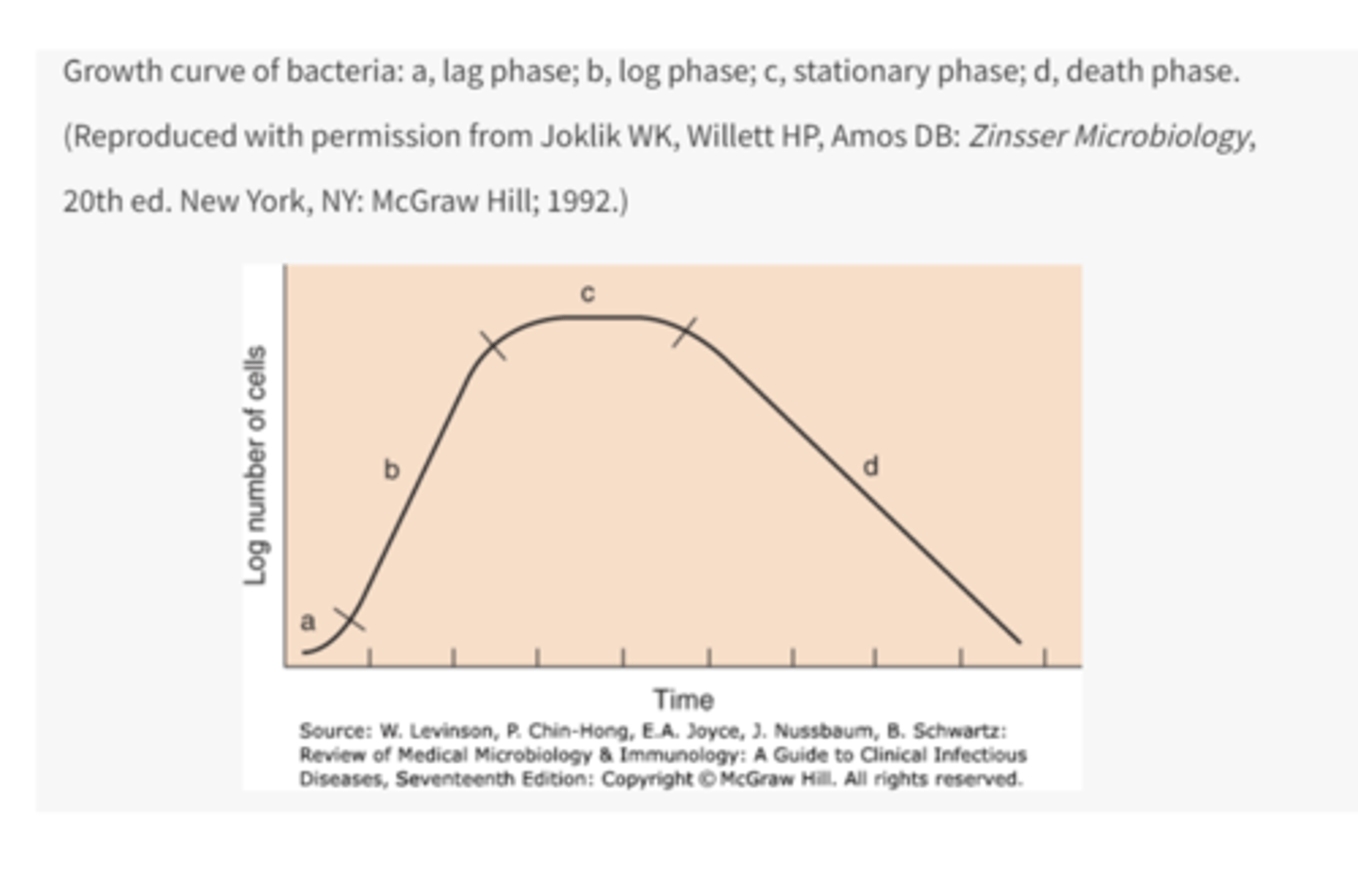
what is the stationary phase also referred to as
steady state