1: Basic Concepts of Cybersecurity
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Information
A knowledge concerning any objects, such as facts, events, things, processes or ideas, which have a special meaning in certain contexts
Heavily related to knowledge, it assumes there is a fact which is known (object), and a person who knows the fact (subject)
When we consider the practical representation of information, data
When will the practical shape of information occur?
Data
Reinterpretable formalized representation of an information in such a form which i suitable for transfer, processing and/or interpretation
The presentation of information, usually in a pre-agreed form
Digital Data Set
Presentation of information as a bit sequence, often referred to as files
Ex: A sequence of symbols 0 and 1
Format
Rule for interpreting data as information, especially as an actual type of information (text, image, sound, video, etc.)
A rule on how information is presented in digital form
True
True or False:
Any information in computers (IT equipment) is always presented in digital form in certain pre-agreed formats as datasets (files) that carry information
Pre-agreed format
What gives the data set (document) its meaning?
True
True or False:
Different data formats are usually supported by a different application software means which allow to write the file in the certain format, or to made the content of data (information) human-perceptable
False
True or False:
A typical end-user usually knows everything about different data formats and interpretation
What You See Is What You Get
The human-perceptable form prepared by software an end user receives
False
True or False:
If we possess (or process) the data then the information carried by the data has no certain value for us (for our business process)
It depends on either the information is represented by the digital nor by the paper-based data
Information/Data Security
A discipline concerning the maintaining the values/properties of information (performed in practice by the maintaining of the properties of data)
Information Availability, Information Integrity, Information Confidentiality
What are the 3 Independent Branches of Information/Data Security?
Data Protection
In Europe, it often means the protection of personal data
Availability
A timely and convenient access and usage of information carried by the data for all authorized persons and other subjects (entities)
The most important concept of data security
In business processes, this means that it actually works by planned process
Integrity
Ensuring that data (information was stored into the data) are originated by a certain source and haven’t been altered (both by an accident or by deliberate act or by the fake)
Second most important security branch
In business processes, this means that it works in a proper way as details and properties are correct
Confidentiality
Availability of the information, carried by the data, only by the authorized subjects (and strict non-availability for other subjects)
In business processes, this means that ineither the details of business process or data used inside the process must be accessible only to certain users
Security of Data
Ensured by securing the IT assets surrounding the data
IT equipment, Data communication channels, Software, Organization, Personnel, Data Carriers, Infrastructure
Examples of IT Assets?
A great but indirect value of a data, Portativity, Possibility of avoiding the physical conact, Disclosure of security losses
Main Properties of Digital IT assets?
Portativity
Data which can be stored by the very small and easily movable carriers can posses a huge value for our business process
Threat
A potential extern-influenced harm of information security
Influences the data and exploits the vulnerabilities of IT assets or components of IT system
Will determine the risk or security risk, then there will appear a security loss, breach, or incident
Threat
1?
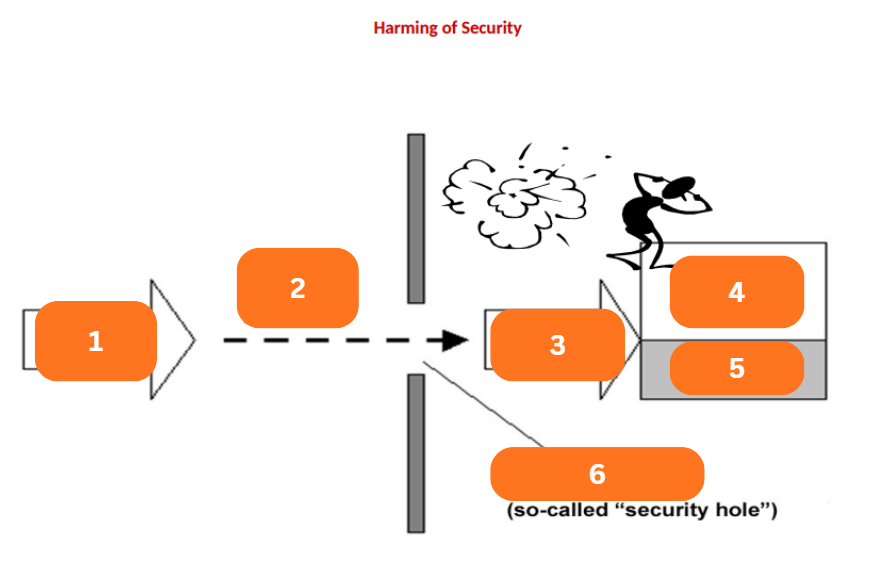
p: risk
2?
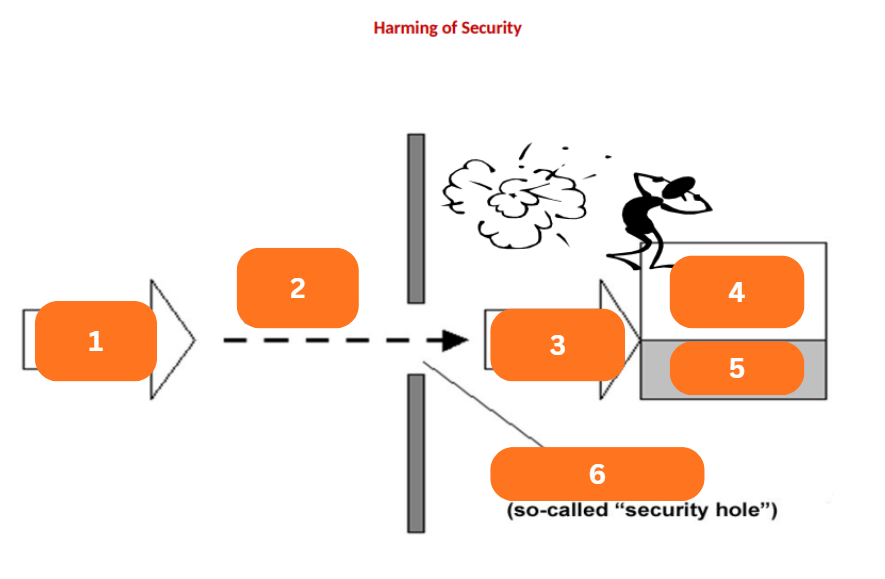
Influence
3?
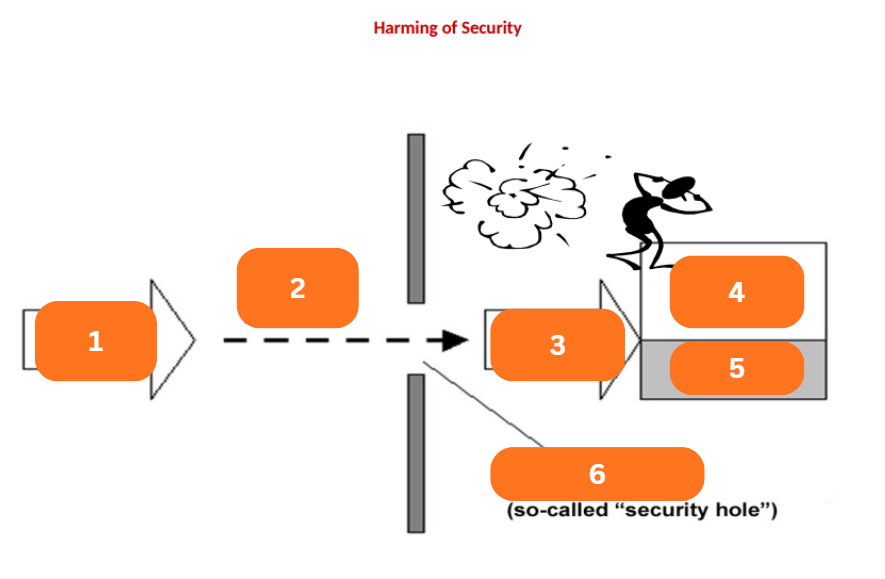
Assets
4?
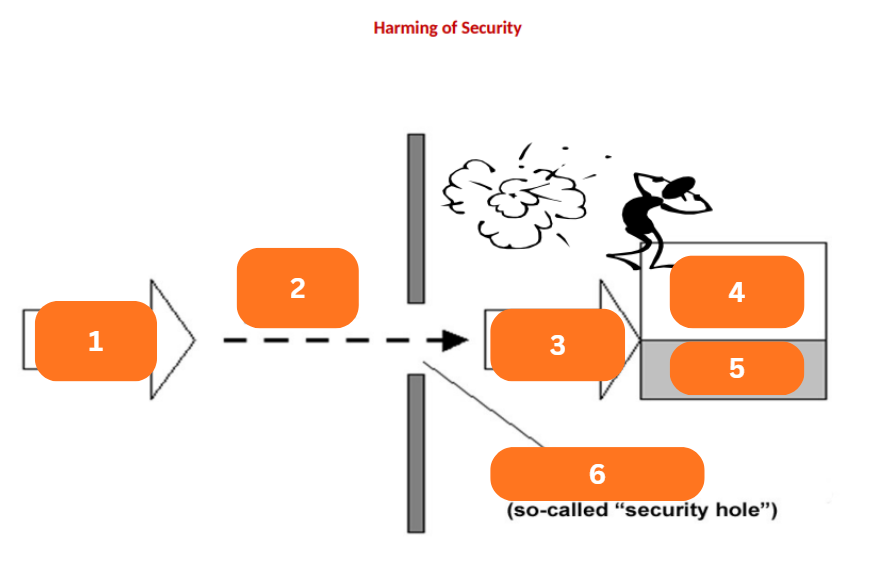
Damage
5?
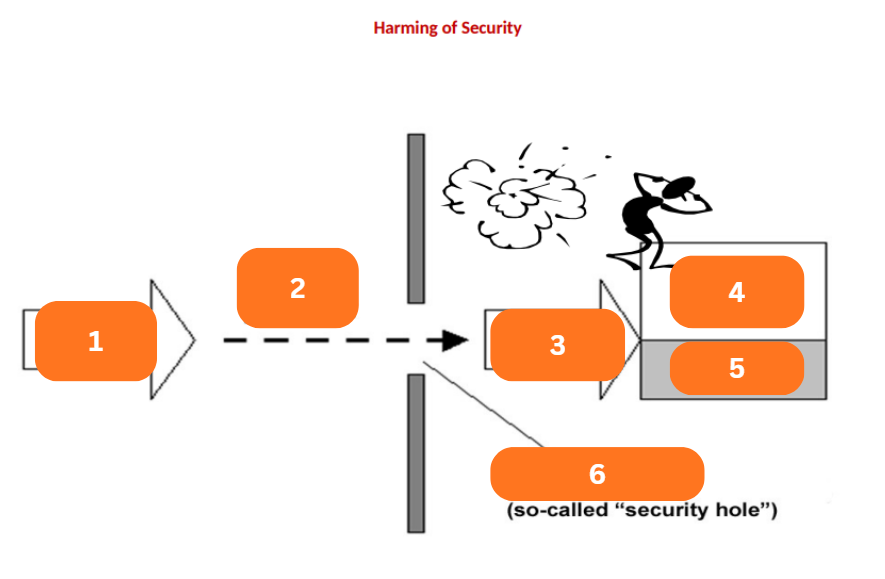
Vulnerability
6?
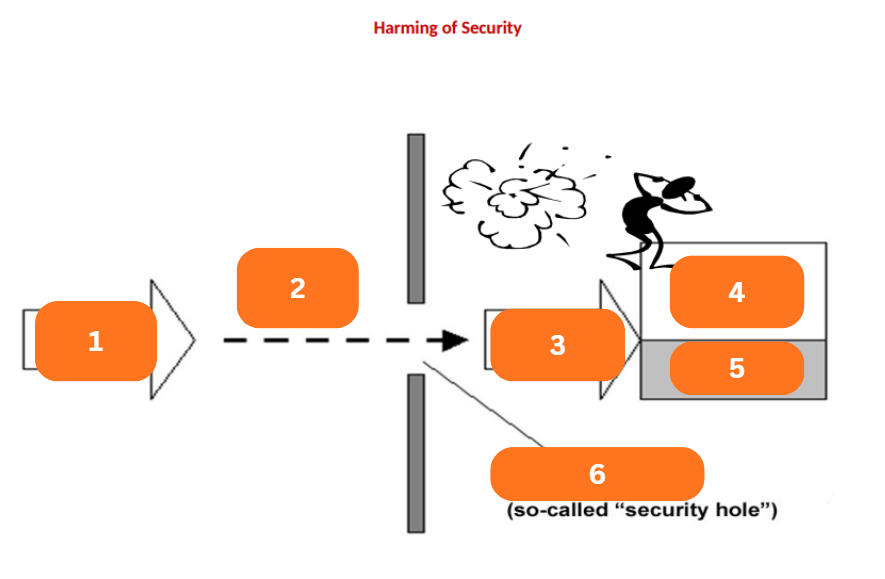
Safeguards, Security Measures
A modification of IT assets that will minimize the risks and rate of vulnerabilities of assets
Safeguards
What was added to minimize vulnerabilities and residual risk?
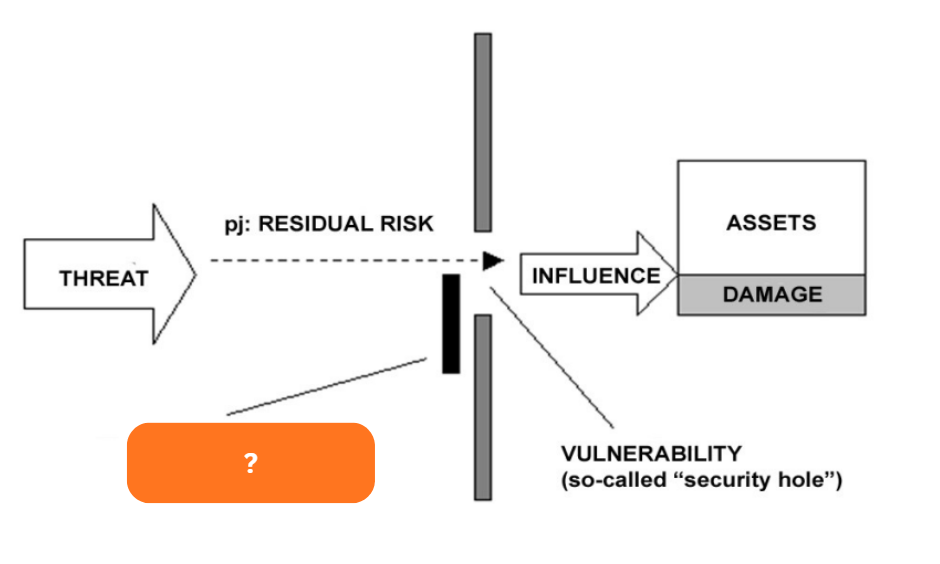
Vulnerability
The property of each IT asset (component) from the point of view of external threats
Risk
A probability that an actual threat can exploit the certain vulnerability and will realize
Security Loss
An event when the security availability, integrity and/or confidentiality of some IT assets will be harmed
A realized risk
Integrity Loss
Integrity, Availability or Confidentiality Loss:
Failure of equipment
Availability Loss
Integrity, Availability or Confidentiality Loss:
Theft of equipment
Integrity Loss
Integrity, Availability or Confidentiality Loss:
Unauthorized modifying of register
Availability Loss
Integrity, Availability or Confidentiality Loss:
Destroying of office rooms by fire
Confidentiality Loss
Integrity, Availability or Confidentiality Loss:
Wiretapping of non-encrypted data cables
Organizational Security
In order to protect data used in a business process (information assets), data security must be handled by the organization or organizations involved in the entire business process
Acceptable Residual Risk
A situation where the total price of all implemented safeguards is approximately equal to the forecasted total loss of security
Risk Management
To standardize different security levels i.e. different availability, integrity and confidentiality levels
To create a system which is able to determine standardized actions (safeguards), for different security levels, which result ensures us to approximately achieve the optimum point (to achieve the acceptable residual risk situation