Earth Science 10: Antarctica
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
Latitude
angular measure of how far North or South a location is from the equator
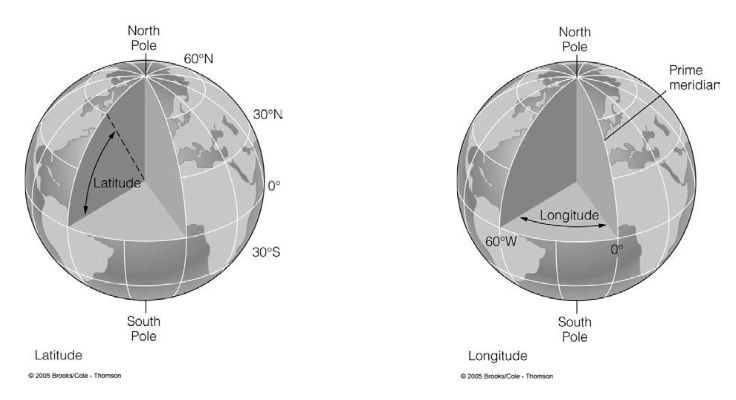
Longitude
angular measure of how far North or South a location is from the Prime Meridian
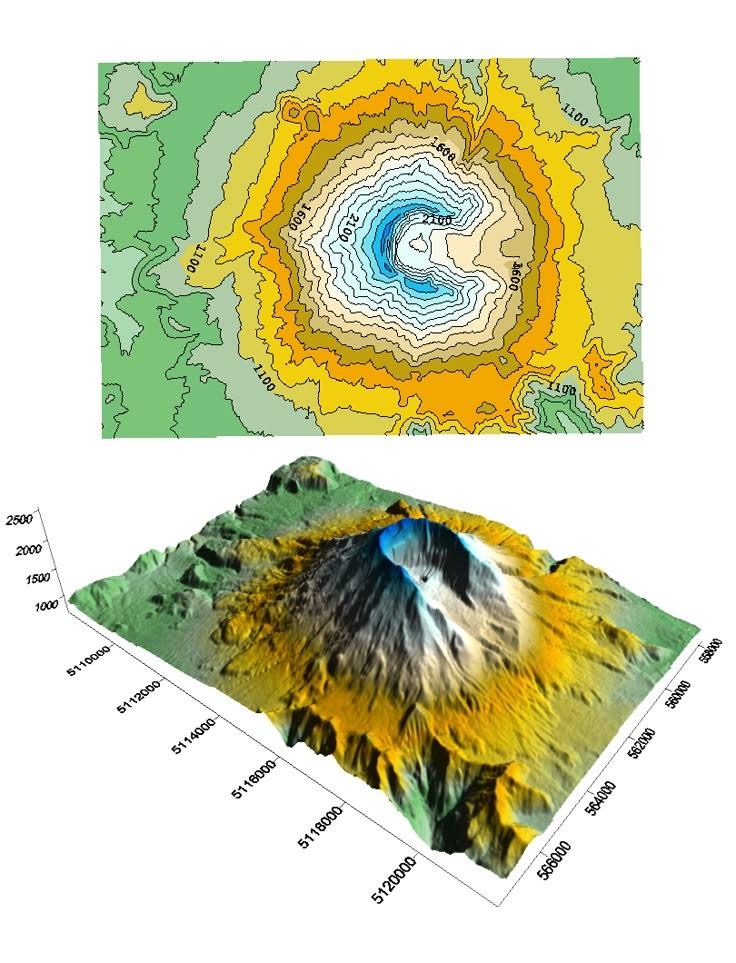
Contour Lines
- show elevation 2D map
- connects all points that have the same elevation
- when the lines get closer together the ground is steeper
What is a map? and 3 basic map projection schemes
A map is a 2D projection of a 3D globe. 3 basic map projections schemes
1) Cylindrical projections
2) Conic projections
3) Azimuthal projections
East Antarctic Ice Sheet
- Terrestrial ice sheet
- 60m sea level equivalent
West Antarctic Ice Sheet
- Marine based ice sheet
- 6m sea level equivalent
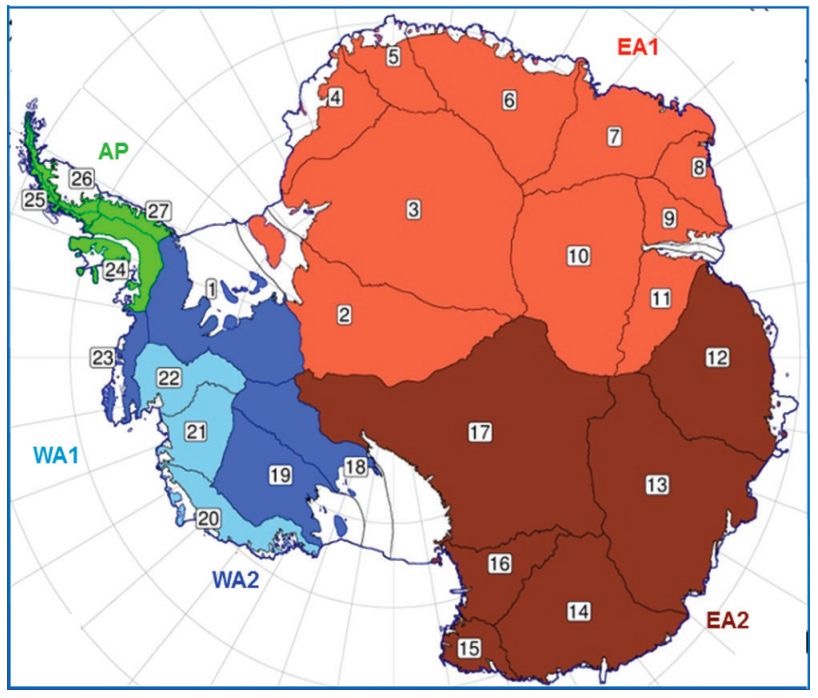
Drainage Basin View of Antarctica
the topography of Antartica influences the size and distrubution of the ice sheets. East Antarctic ice sheet, West Antarctic ice sheet, Antarctic Peninsula Ice Sheet
Ice Sheet
massive land-based glacier
west Antartica and east Antartica are separated by mountain range
e.a ice sheet is much thicker
becomes a glacier when covering more than 50k km²
Underlying topography
influences size and sheet of ice sheets
Terrestrial Ice Sheet and Marine-based Ice Sheet
Terrestrial Ice Sheet: bed of ice is mostly above sea level
Marine-based Ice Sheet: bed of ice is mostly sea level
more susceptible to melting from a warming/rising ocean
Transantartic Mountains
3500 km long
important geologic boundary
splits east & west ice sheets
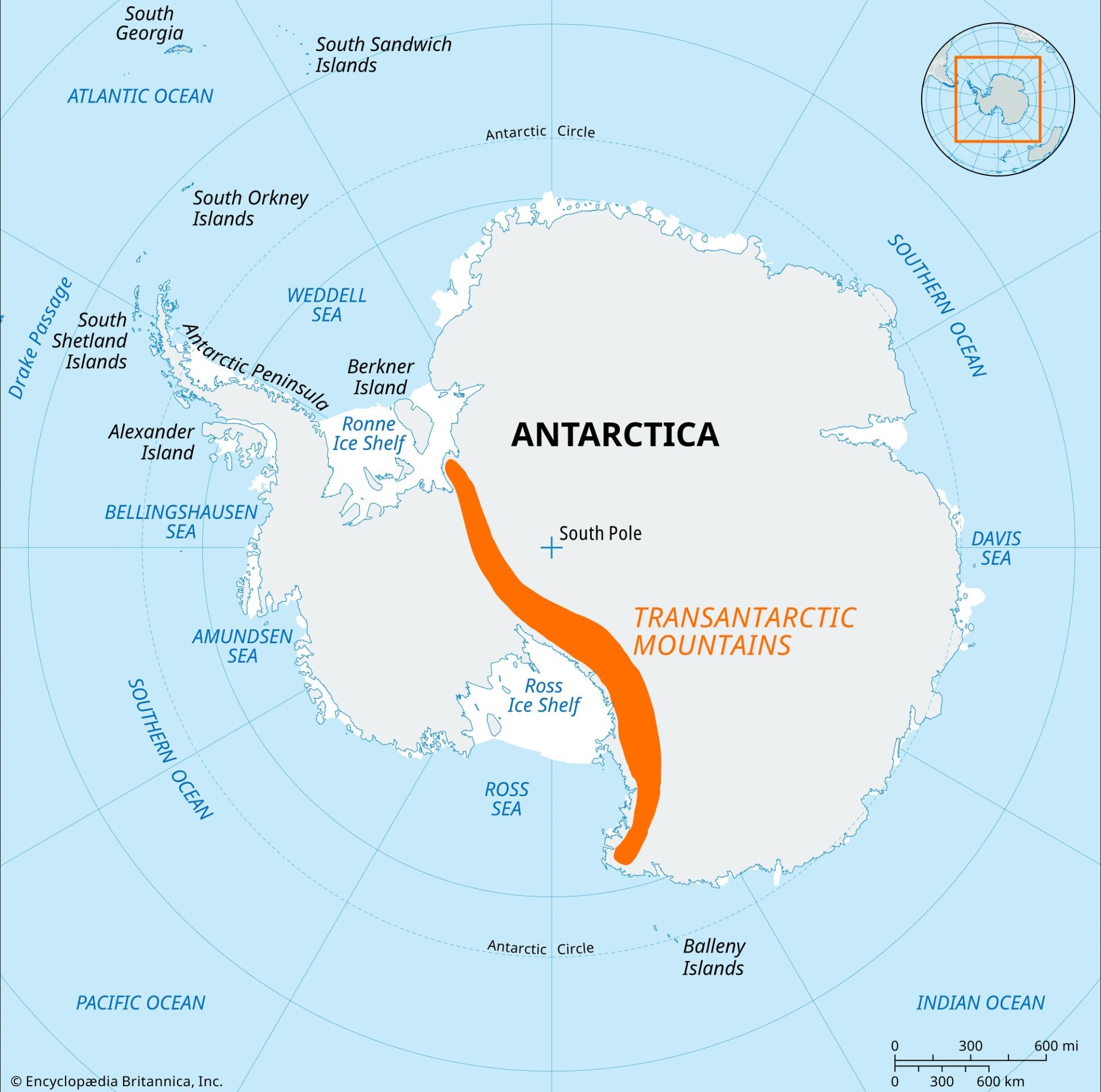
Ellsworth Mountains
highest mountains in Antartica
highest peak - Vinson Massif
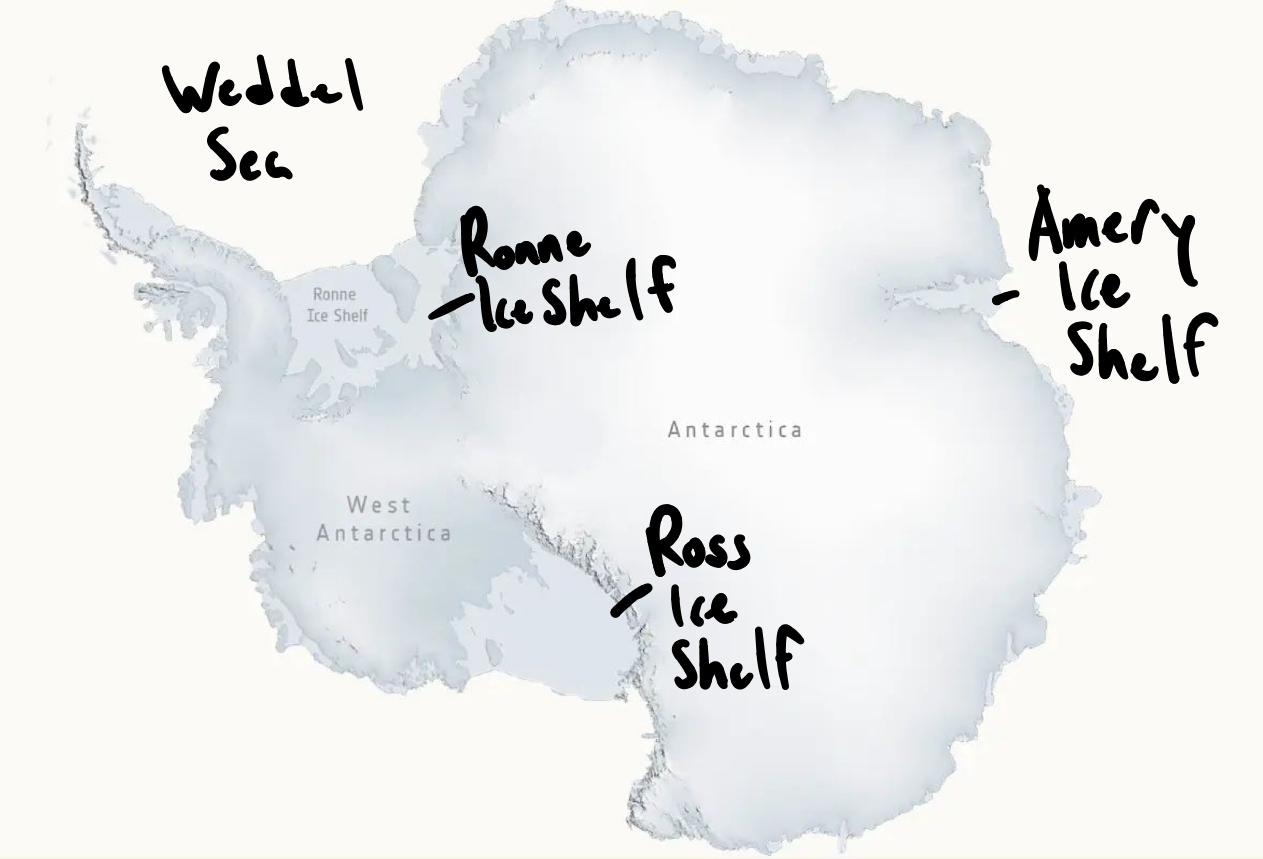
Major Seas
Weddel Sea - adjacent to Antarctic Peninsula, includes the Ronnie ice shelf
Ross Sea - includes the ross ice shelf
Surrounding Ocean - Antarctica is surrounded by the Southern Ocean, the crossing between the tip of South America and the Antarctic Peninsula is called the Drake Passage
Ice Shelves
floating extensions of ice sheets
attached to ice sheet but no longer resting on land
the grounding line separates an ice sheet from an ice shelf
Antarctic Ice Shelves
Ross Ice Shelf
Ronne Ice Shelf
Amery Ice Shelf
Iceberg
formed when an ice shelf towers out of the water and breaks
Antarctica Sea Ice
crucial for life on antarctica
provides food(algae) and shelter(penguins/seals)
forms from the surface of the sea freezing
grows thick by accumulation, repetitive freezing, and snow accumulation
in the winter, continent doubles in size due to sea ice growth
First to arrive? to Antarctica
Polynesian people: oral history suggest that Hui Te Rangiora of Rarotanga (Cook Islands) sailed south at ~750 CE & hit Ice
by canoe
debated and no archeological evidence
Ancient Hypothesis: Terra Australis exists.
Ptolemy (2nd century ce): North vs. South land masses should balance. Africa may extend to South Pole
First Oceanographer
James Cook, a commander in the British Royal Navy led 3 voyages(1768-1780) across the globe.
charted New Zealand and the Great Barrier Reef, Tonga and easter islands
sampled marine life, plants, and animals
The first expedition to reach the South Pole was led by _____, followed shortly thereafter by the expedition led by ____
Roald Amundsen then Robert Scott
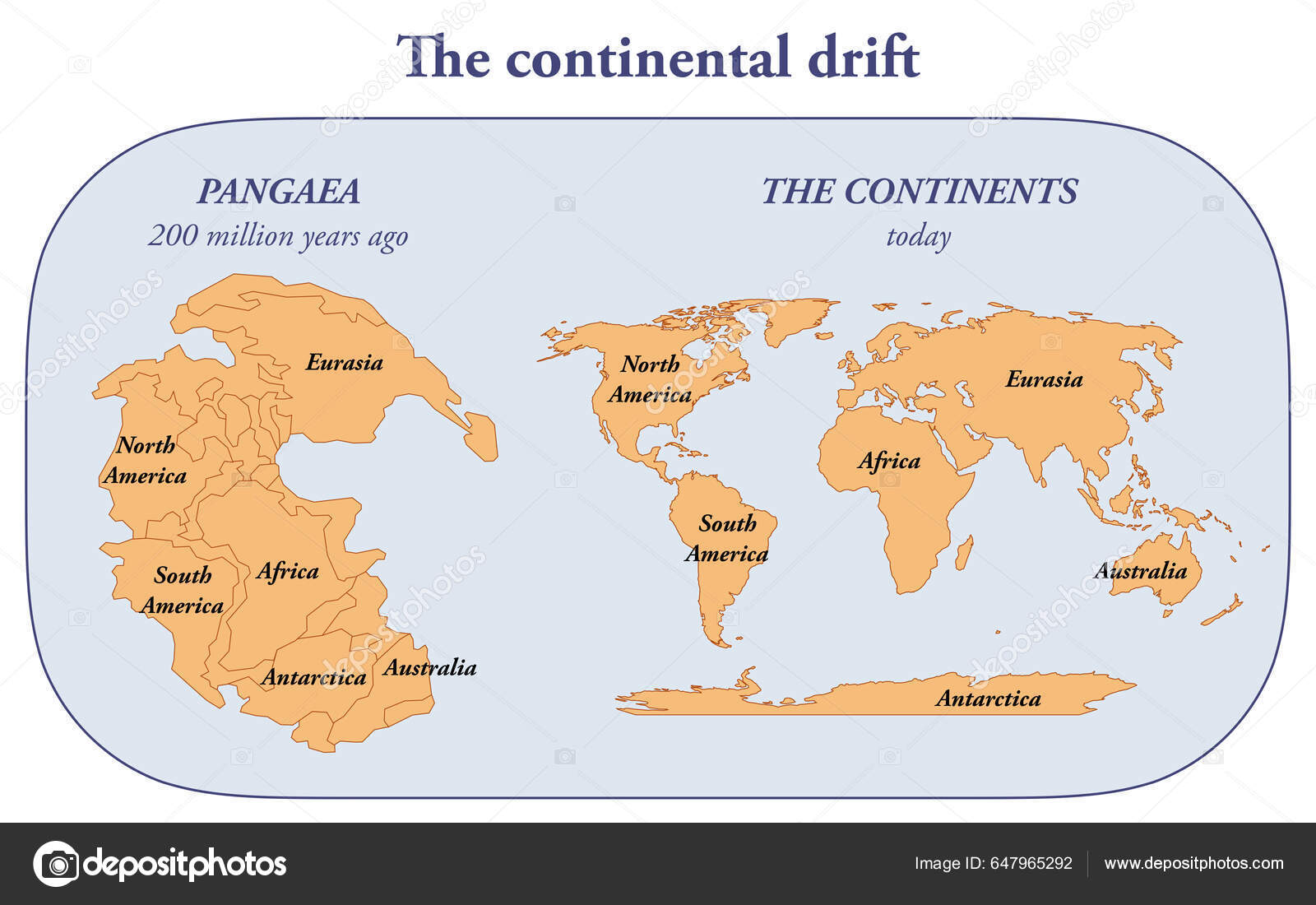
Kontinentalverschiebung
continental drift: hypothesis that continents were mobile based on:
1) fit of continents
2) glaciations at low latitudes
3) Paleoclimate belts
4) fossil distribution
5) rocks matching across oceans
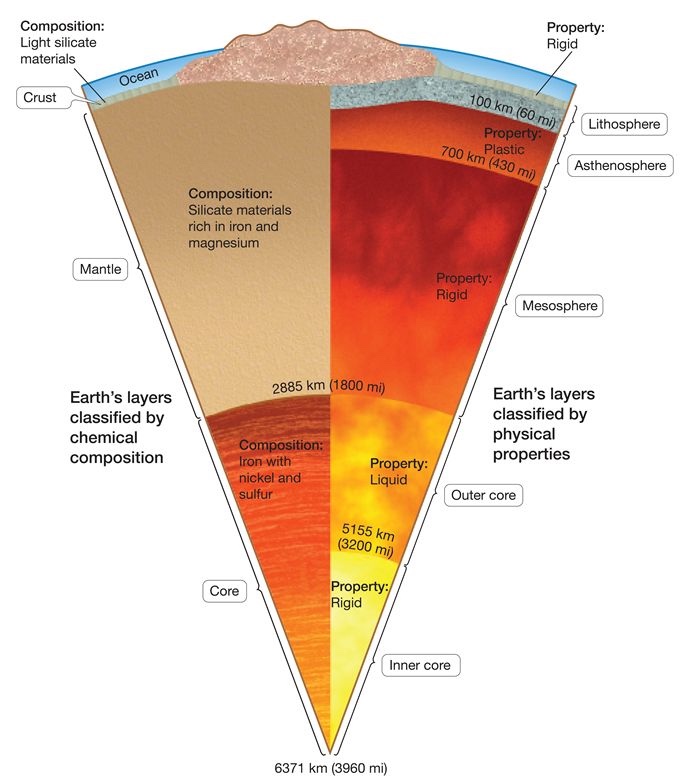
Crust
thin rocky shell that we walk around
continental (high elevation)
oceanic(low elevation)
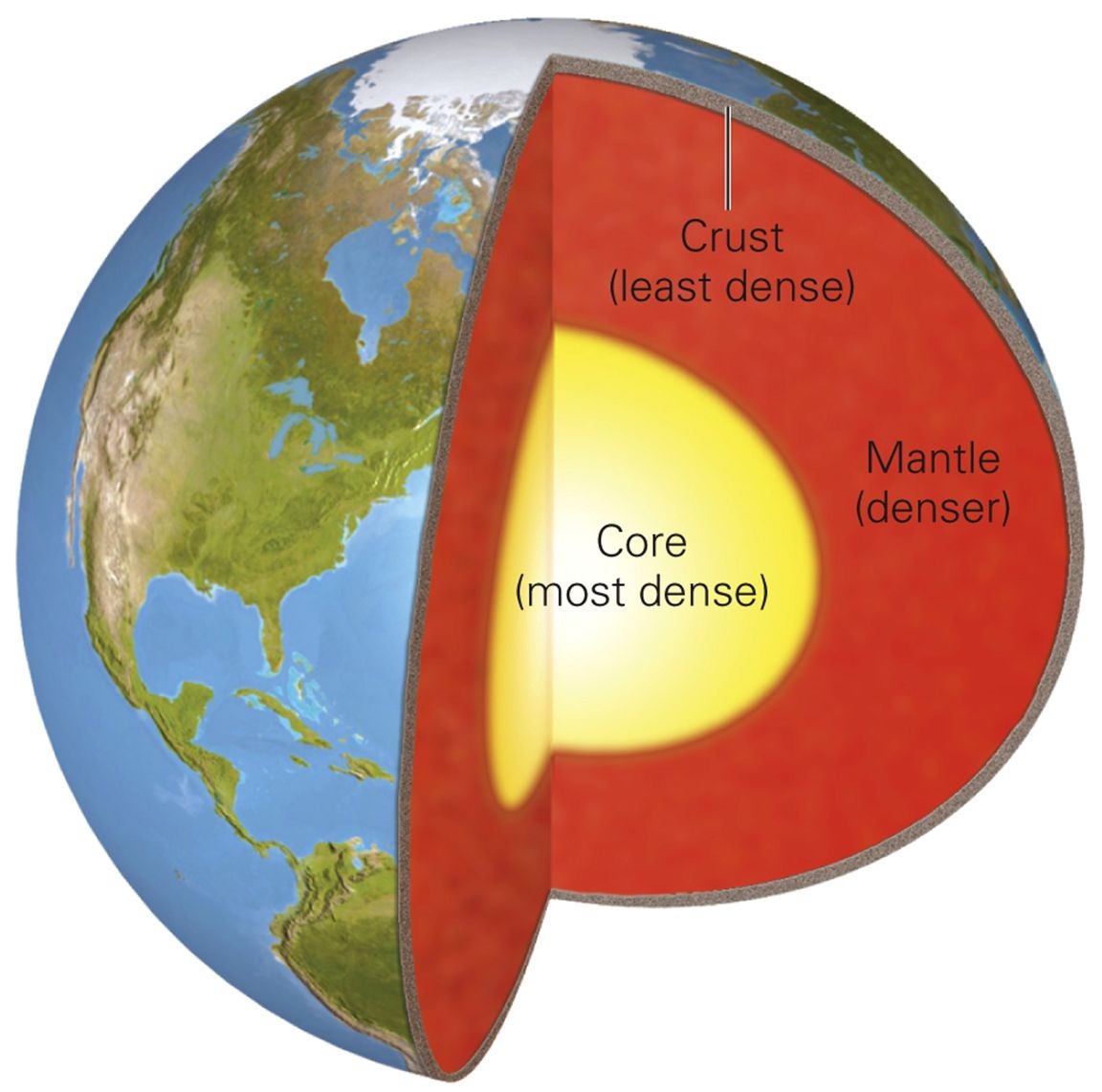
Mantle
made of solid silicate rock … but certain areas can flow
Core
made of metallic iron/nickel
outer core(fluid) = liquid
due to high heat
inner core(rigid) = solid
rigid due to high pressure
4 main physical layers
lithosphere
asthenosphere
mesosphere
core
Lithosphere(rigid)
cold rigid outer shell (~100km thick)
includes crust and upper mantle
lithospheric plates move atop the ductile Asthenosphere
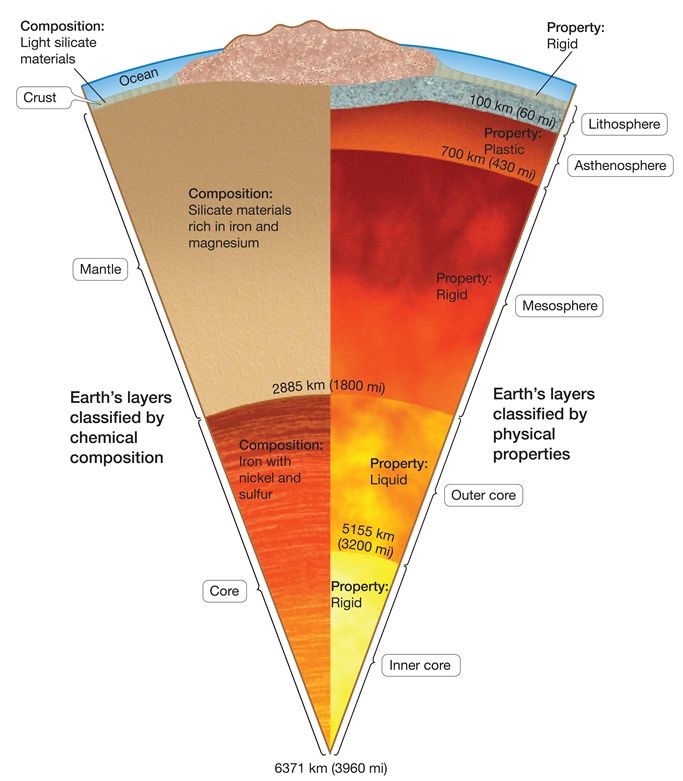
Asthenosphere(plastic)
hot, ductile layer that flows with a high viscosity
extends from base of the lithosphere to ~700km deep
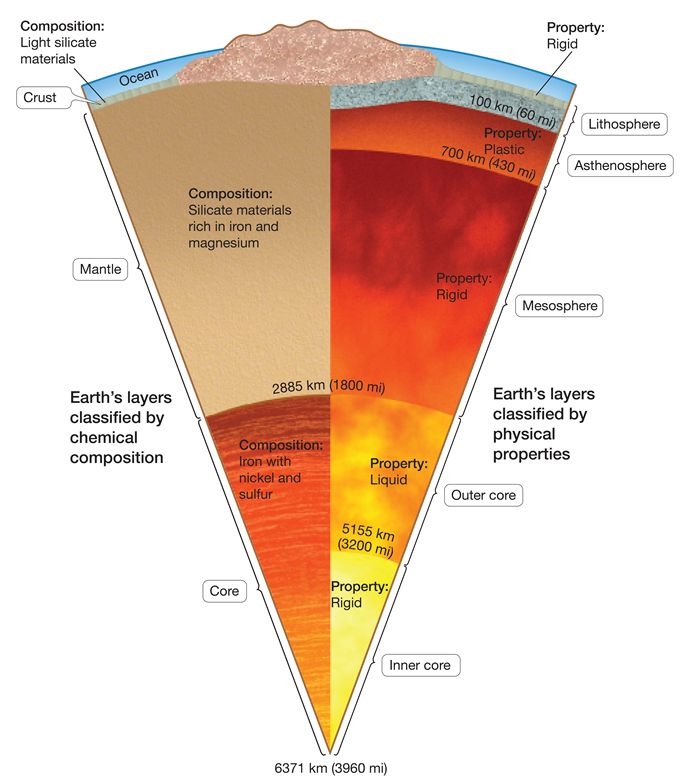
Mesosphere(rigid)
rigid due to increased pressure at depth
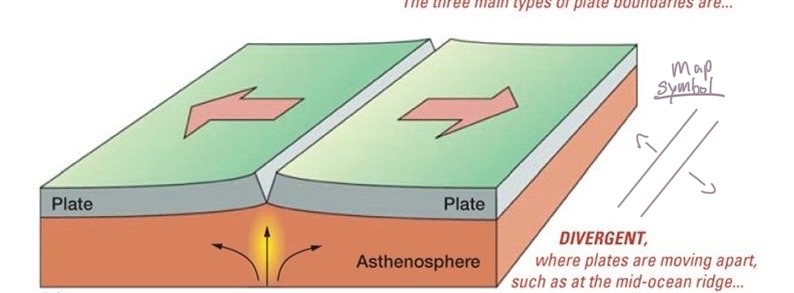
Divergent Plate Boundaries
mid-ocean ridges
continental rifts
new lithosphere is created via the process of spreading/rifting
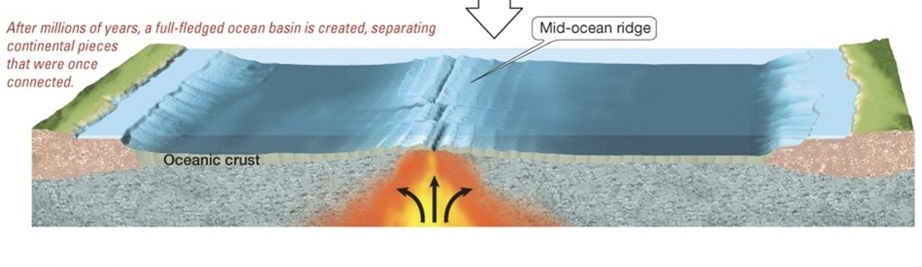
Formation of ocean crust?
in a mid-ocean ridge (spreading center), molten rock arises from the mantle and forms new oceanic crust. this then moves apart, allowing newer oceanic crust to be formed
Youngest seafloor rocks are closet to what?
spreading centers
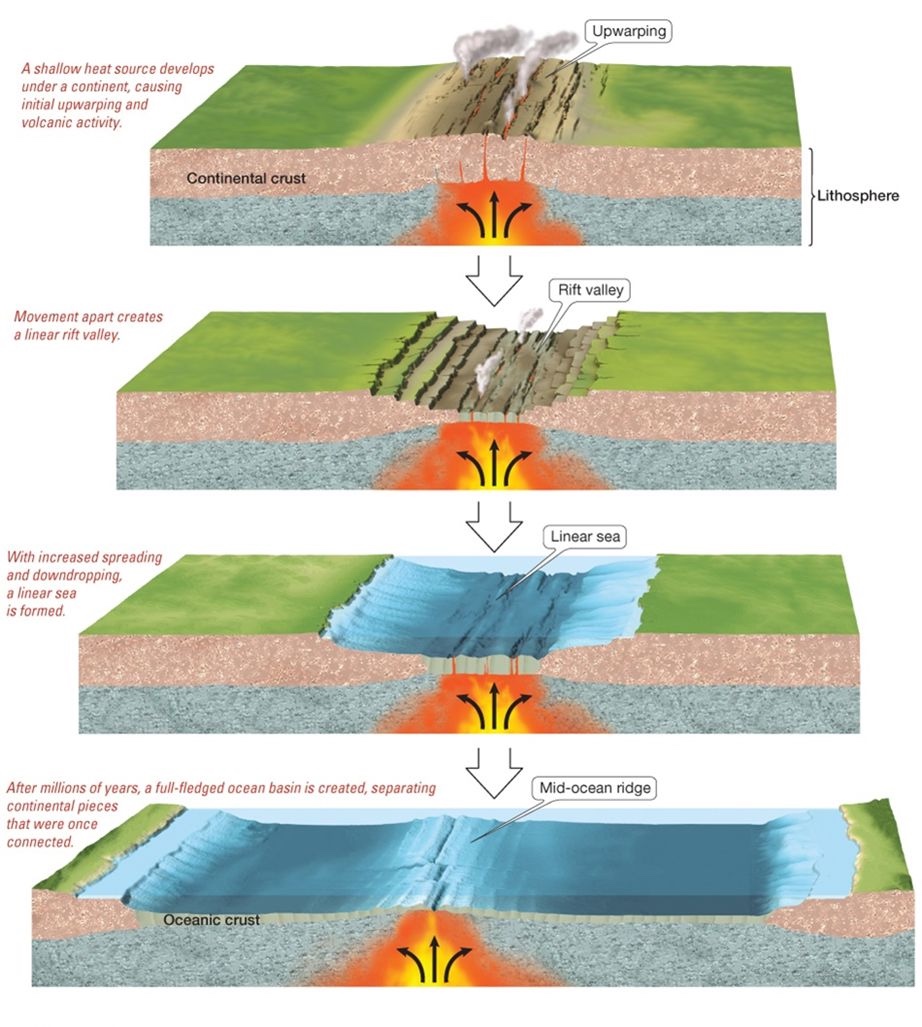
How to create an ocean basin
1) Upwarping
2) Rift Valley (ex: Great Rift Valley in East Africa)
3) Linear Sea (ex: the Red Sea)
4) Mid-ocean Ridge in fully fledged ocean basin
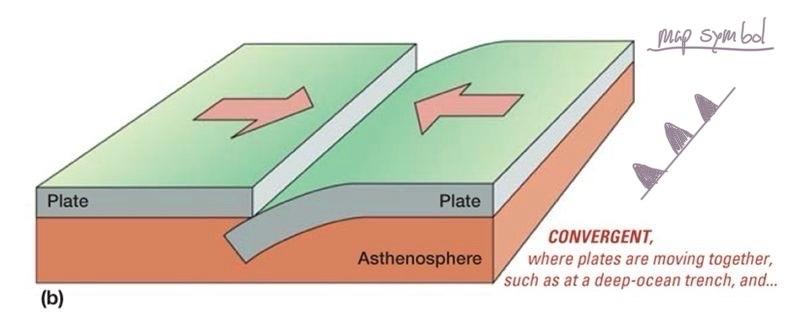
Convergent Boundaries
subduction zones
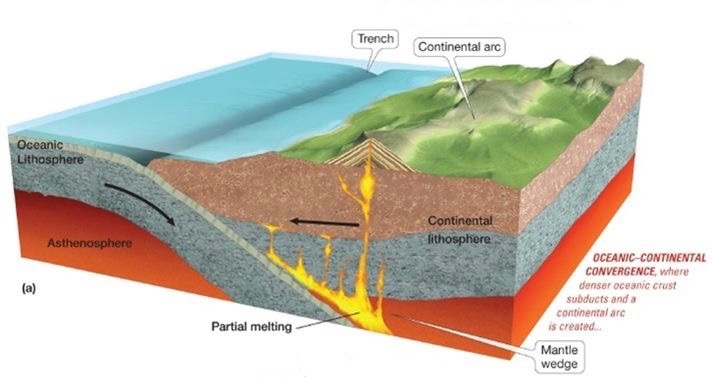
Ocean-Continent Convergence
Ocean crust subjects beneath a continent
Continental volcanic arc forms
ocean crust (denser) subducts beneath continental crust (less dense)
deep trench forms at collision zone
volcanoes form on continent above the subductin plate
subduction leads to magma generation
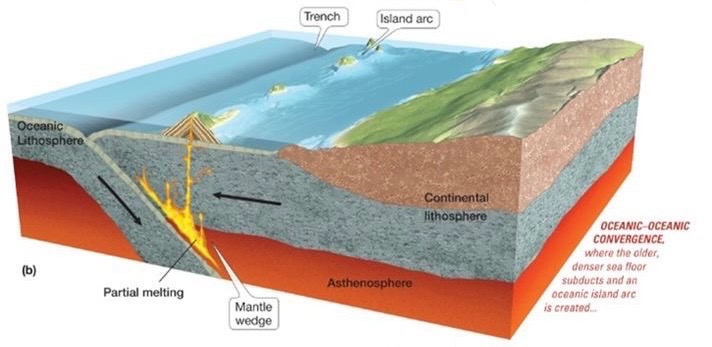
Oceanic-Oceanic convergence
Ocean crust subduction beneath ocean crust
Ocean volcanic island arc forms
more dense oceanic crust subduction beneath less dense oceanic crust
deep trench forms at collision zone
volcanic island arc forms on overriding plate
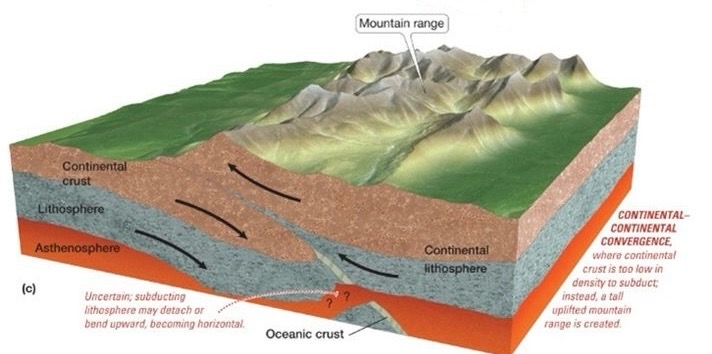
Continent-Continent convergence
continental crust collides
neither plate fully subjects, mountains form
Transform Boundaries
San Andreas fault, etc
Oceanic transform faults
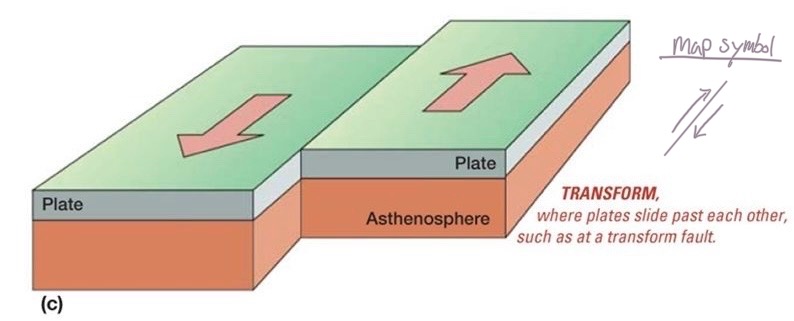
Oceanic Transform faults
spreading centers don’t form in a perfect line
where they are offset, oceanic transform faults occur

The vast majority of the Antarctic plate is surrounded by _____ in the form of _____
divergent boundaries, mid-ocean ridges
Continental Transform faults
occurs when two plates move past another
example: the san Andreas fault
South Sandwich Islands
example of a volcanic island arc
formed by oceanic-oceanic convergence
trench also present
What large mountain ranges of West Antarctica was formed during rifting?
Transantarctic Mountains
Ellsworth Mountains
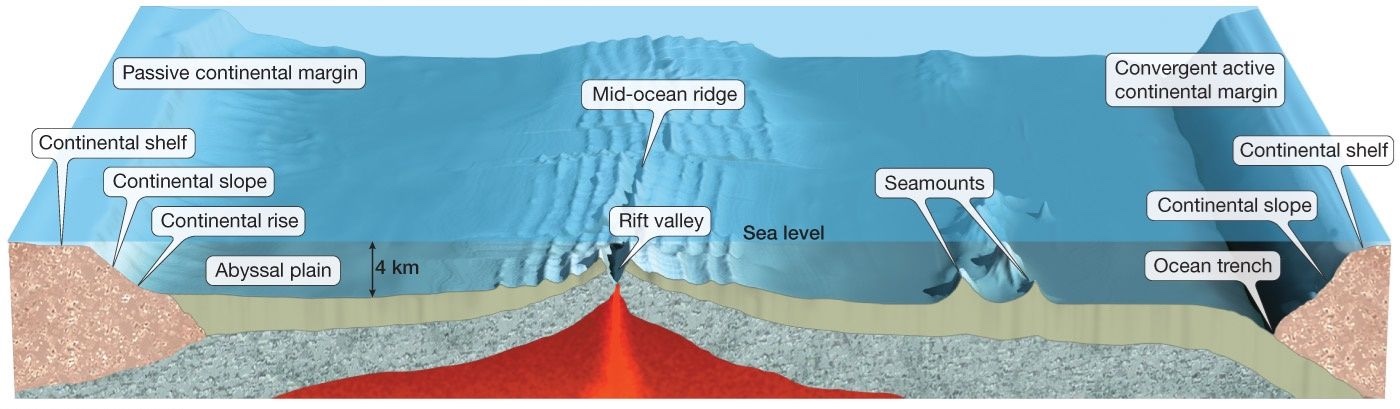
Continental Margins
location where oceanic crust meets continent crust
Active continental margin
Left Side of the image
oceanic plate subjecting beneath the continent
Passive continental margin
Right Side of the image
Oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere are attached
no tectonic plate motin between continent and ocean lithosphere
most of antarctica has passive margins
an exception is the northern tip of the antarctic peninsula
Time Scale 4 units ranking: largest to smallest
Eons
Era
Period
Epoch
these divisions are largely based on fossil evidence of the evolution of life and the timing of mass extinctions
When did the Earth form?
~4.6 billions year ago
When did the Cambrian Explosion happen?
~540 million years ago
When did the first mammals exist?
~220 ma
When did the avian dinosaurs go extinct?
66 millions year ago
When did the first Homo sapiens exist?
300k years ago
When did the first ancient civilizations & cities exist?
~5k years ago
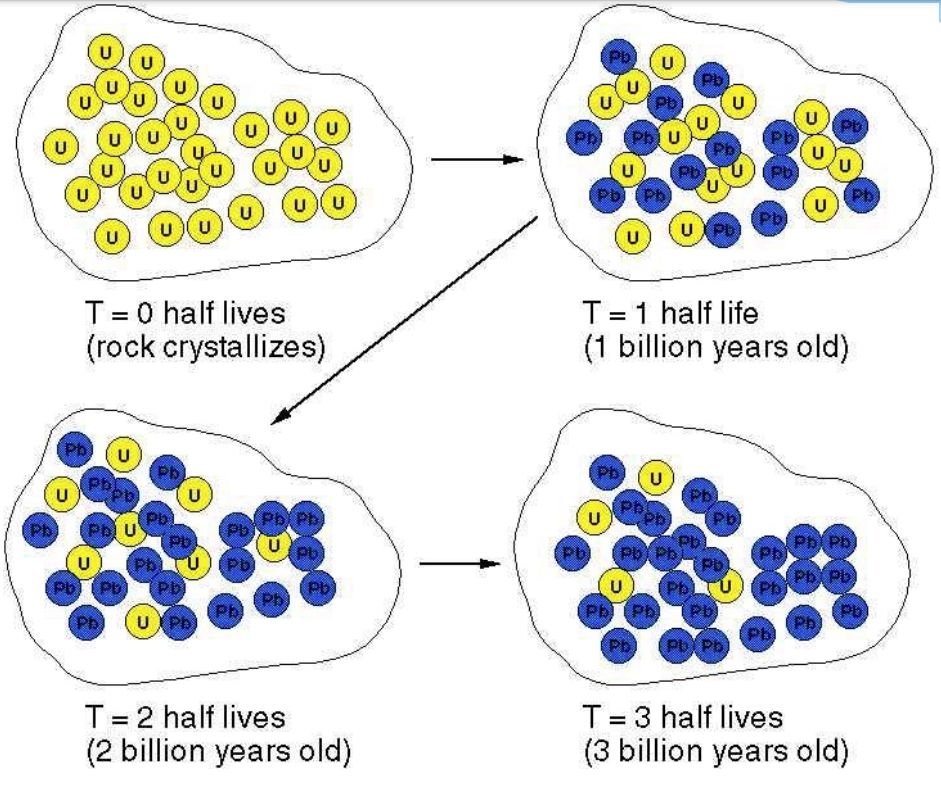
Absolute Dating
using radioactive isotopes to determine when a rock/substance formed
Relative Dating
using the spatial relationships between geologic features to the sequence of geologic events
Index fossils
using specific fossils of a known age to determine when a rock was deposited
fossil: evidence of prehistoric life
fossilized organisms sucked each other through time in a definite and recognizable order. Therefore relative ages of rocks can be recognized based on their fossil content
Index Fossil: a fossil that indicates the age of the rocks containing it
Body Fossils
fossil remnant showing the body of an organism

Trace Fossils
Fossil remnant showing the behavior of an organism
footprint, burrow, trail, or other “trace” of an organism
nearly all fossils are preserved within sedimentary rocks

Igneous rocks
rocks that form from the solidification of molten rock
Form at volcanoes or in magma chambers
Common igneous rocks: Granite, basalt, rhyolite, Andesite, and many many more
Typically associated with subduction zones and rifts

Sedimentary rocks
form from the lithification (lithos = rock) of sediment
Form within basins (large sediment traps/catchments)
Common sedimentary rocks: Sandstone, mudstone, limestone (i.e. coral reefs), and many more
Associated with oceans, lakes, rivers
Metamorphic rocks
rocks that form due to high heat and pressure within the earth
Form deep within the earth or at convergent tectonic boundaries
Gneiss, Schist, Marble, and many more
Presence of metamorphic rocks at surface usually indicates large
mountain building events
Water molecules have ____ polarity
electrical
because both H atoms are on the same side of the molecule, the electrical charge of the molecule is unevenly distributed
Cryosphere
regions of Earth’s surface where water is in the solid form
includes sea ice, lake ice, river ice, snow cover, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground(permafrost)
The cryosphere participates in many climate feedback loops
solar energy absorption/reflection
cloud creation and precipitation
atmospheric/ocean circulation
Antarctica is Earth’s largest reservoir of continental
ice
Katabatic Wind
Pushes sea ice away from the ice shelf because they occur when the slope surface is cold, cooling the air making it more dense than the air at the bottom of the slope.
Polyna
the space between the ice shelf and the sea ice
Glacier
a slowly moving mass of ice that forms from the accumulation and compaction of snow
grows when more snow accumulates in winter than melts in summer
as many layers of snow accumulate, those at the bottom compress and turn into ice
How to make a glacier?
accumulation of snow - more snow accumulates in winter than melts in summer, requires
lots of snow
low summer temperatures
gentle slope
protected from wind
after the snow accumulates
burial
compaction
recrystalization
Mountain glacier
Glacial systems that form in the valleys of mountain ranges
multiple types: valley, tidewater, Piedmont, rock, and hanging glacier
Valley Glacier
a major outflowing glacier of a mountain glacier system
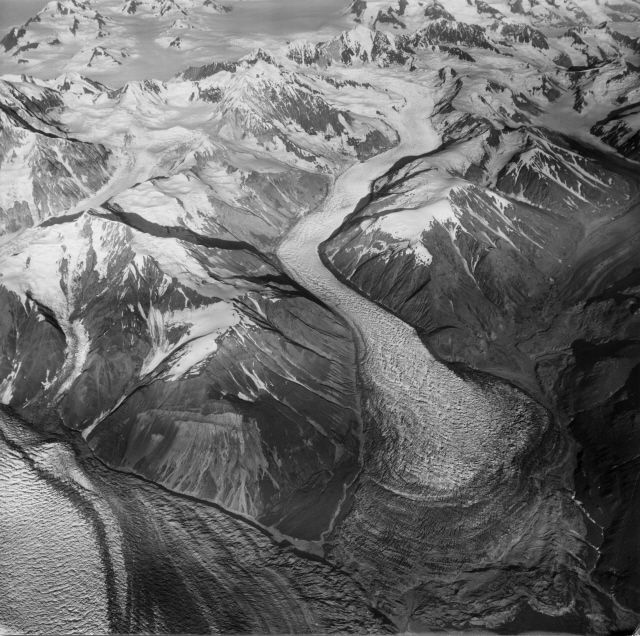

Tidewater glacier
Mountain/valley glacier that end in the ocean

Piedmont glacier
a steep mountain/valley glacier that spills and spreads into flat plains

Hanging glacier
a “stranded” glacier that ends at a steep cliff

Rock glacier
a mountain glacier composed of more rock than ice
Ice Cap
continental glacier covering less than 50k km²
Ice flows because?
gravity
2 flow drivers:
1) ice will flow downhill
primary driver of mountain glacier
2) ice wants to flatten out
driver of ice sheets
Brittle Zone
Ice flows via fracturing/breaking
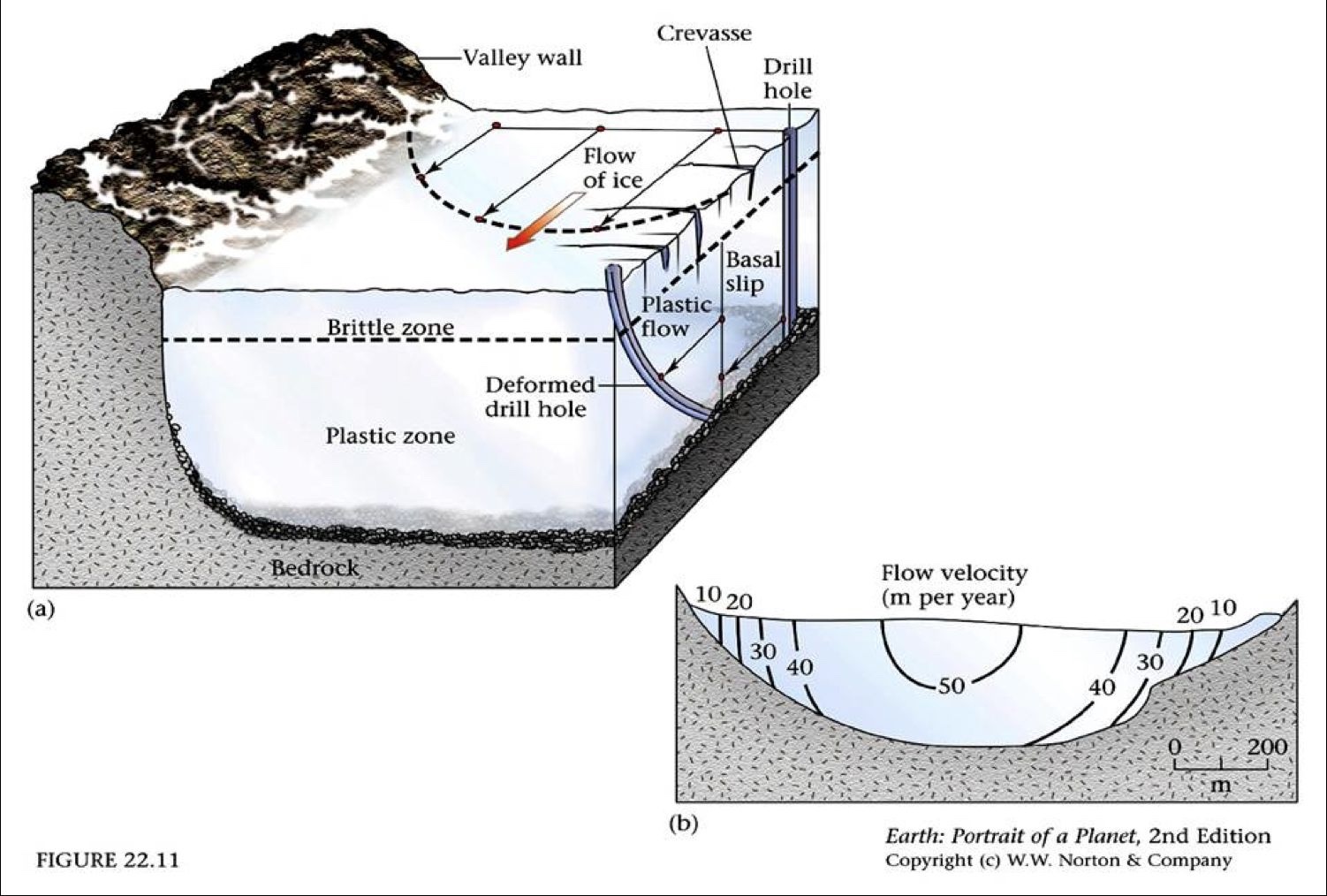
Plastic zone
ice flows via ductile deformation
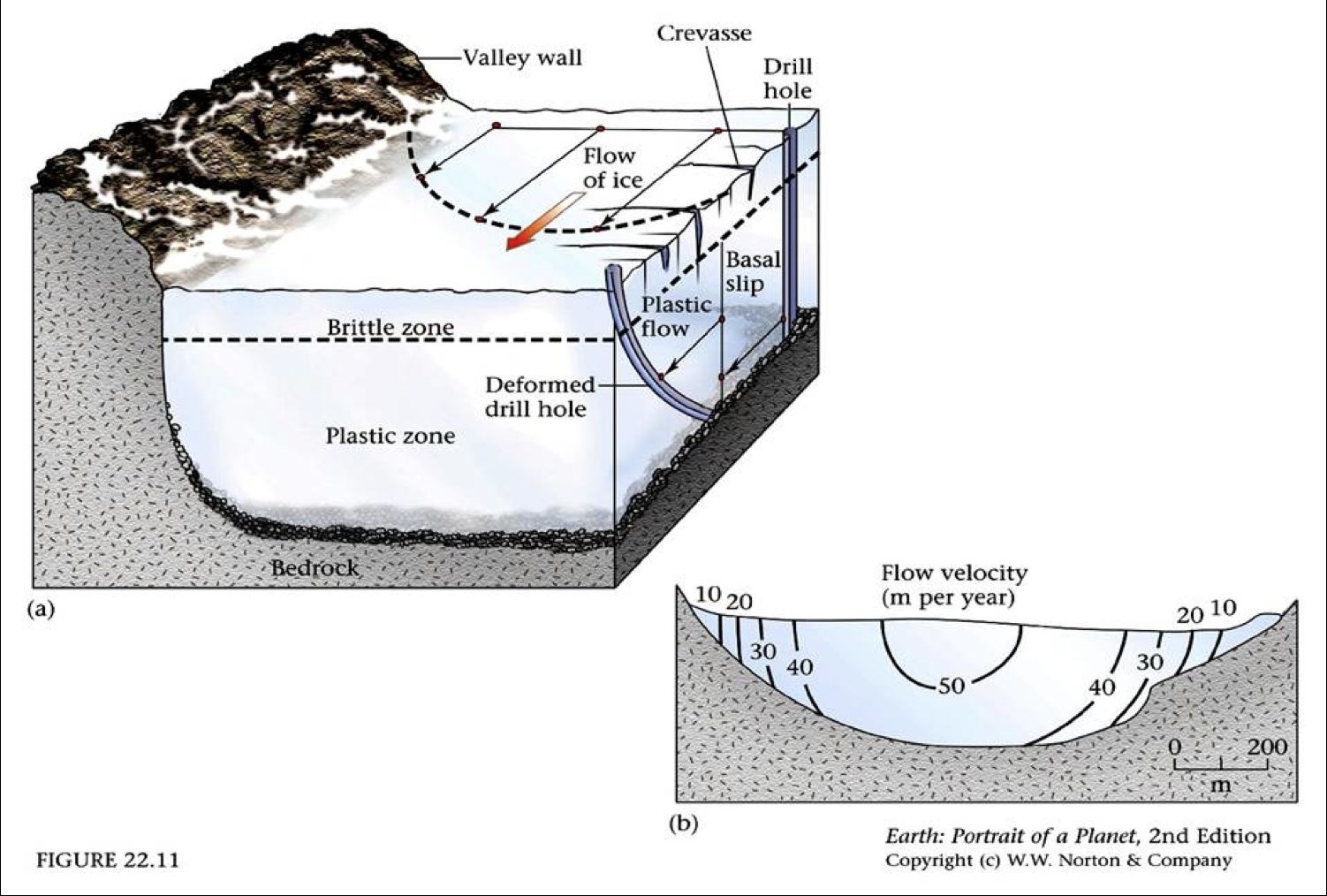
Basil slip
ice “slips” atop underlying bedrock
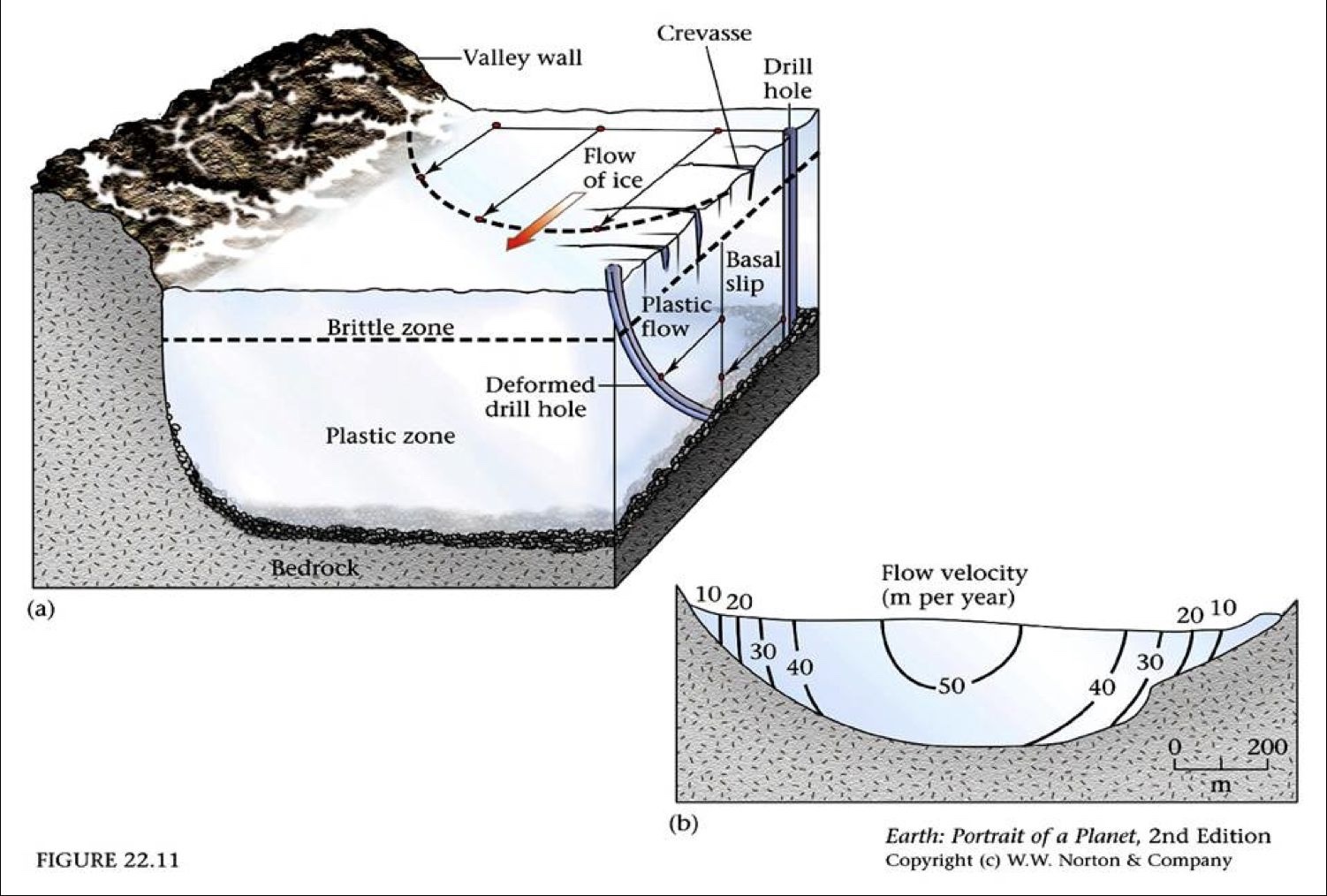
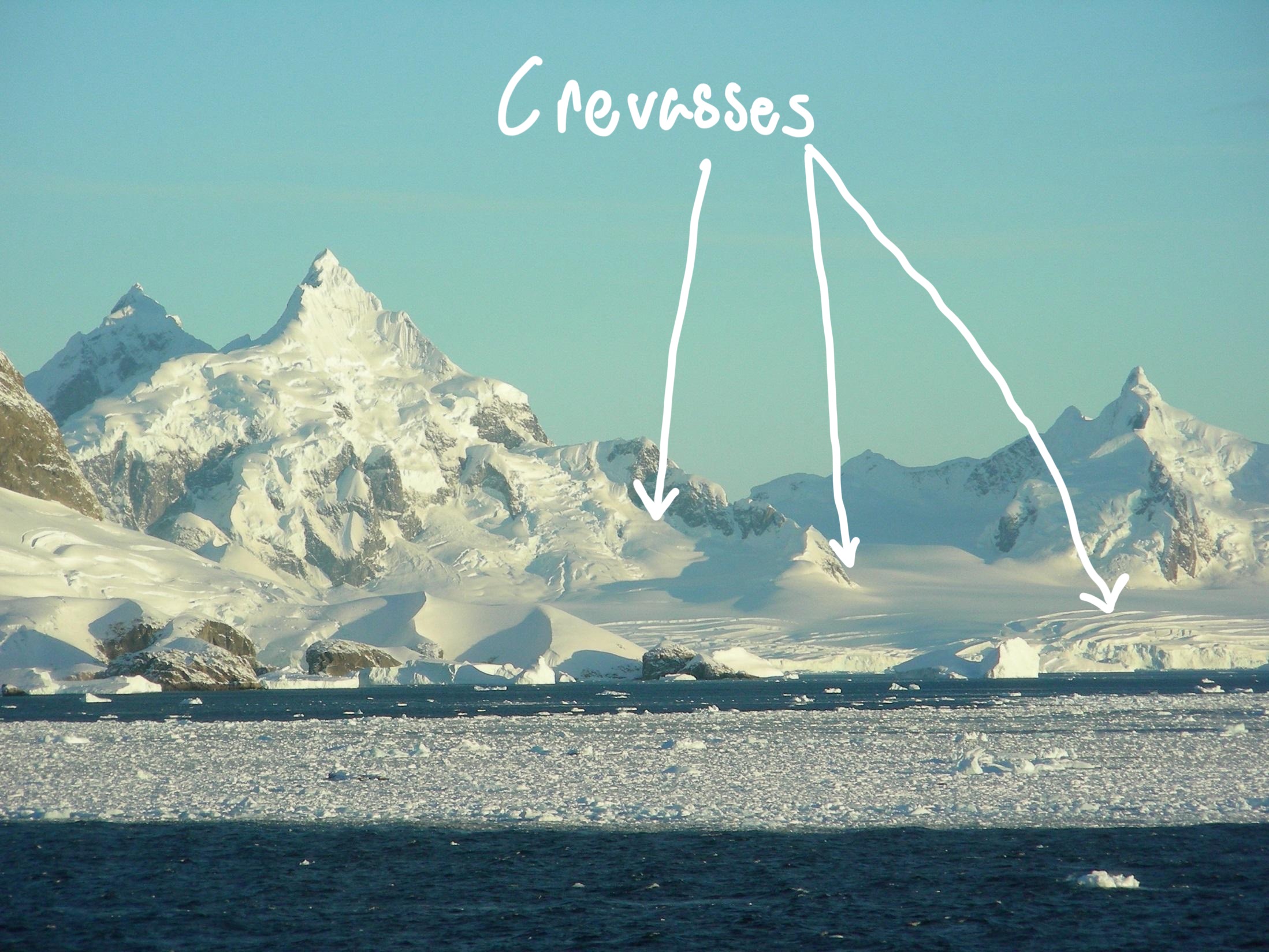
Brittle zone - Crevasses
crevasses are cracks in the upper part of the glacier
brittle fracturing that form as ice flows
fractures mark topographic changes of underlying bedrock

Ice Fall
if underlying topography gets very steep
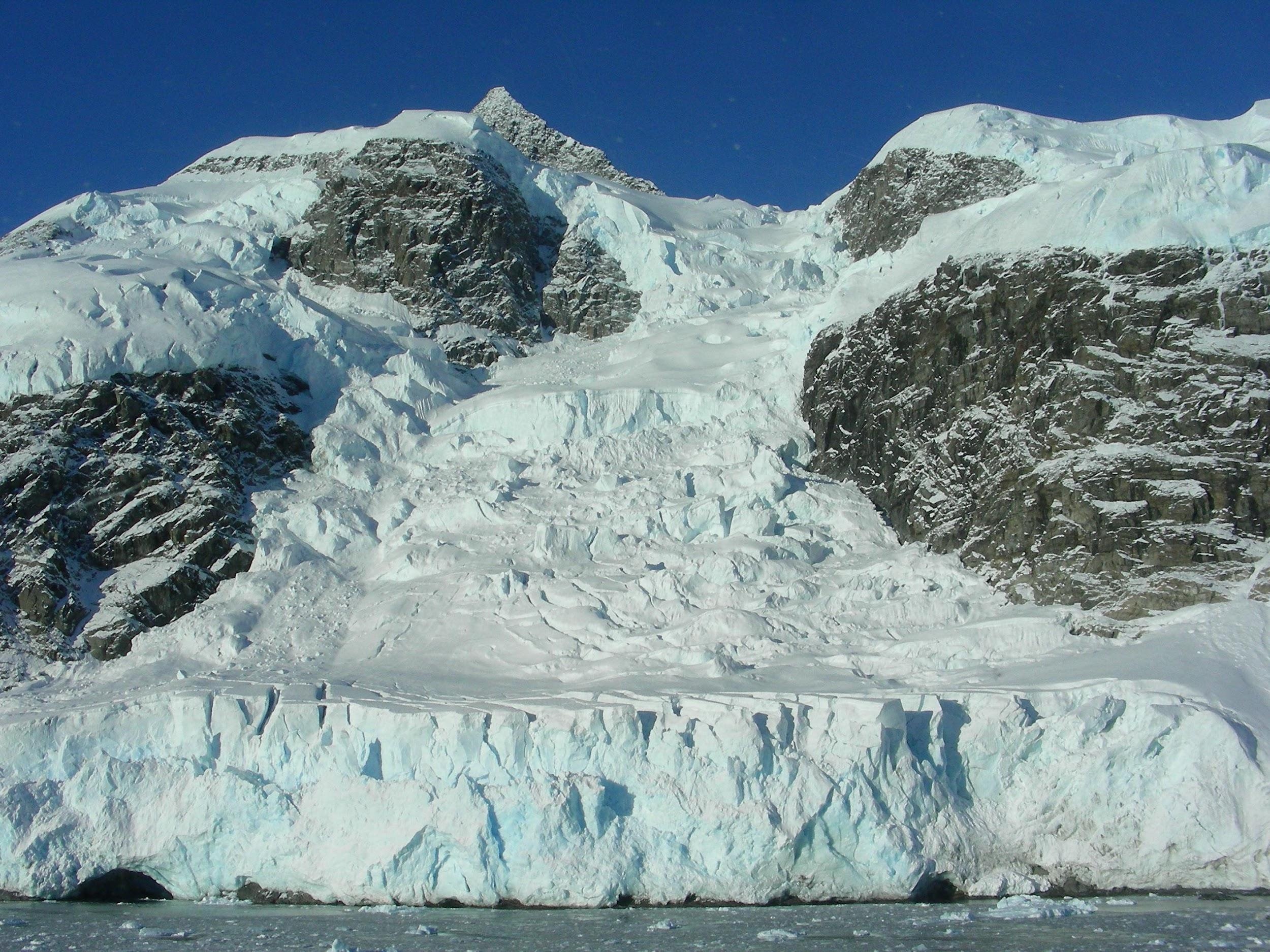

Ductile flow (aka internal deformation)
glacial movements accommodated by the shape change of ice crystals
Basil Slip
base of glacier slides across bedrock
often aided by melting at glacier/rock interface
What typically exhibits ductile flow and minimal basal slip?
Polar glaciers
What typically exhibit ductile flow + basal slip?
Temperate glaciers
Why might water melt at the base of a glacier
hydrogen bonds
regelation- pressure melting of ice
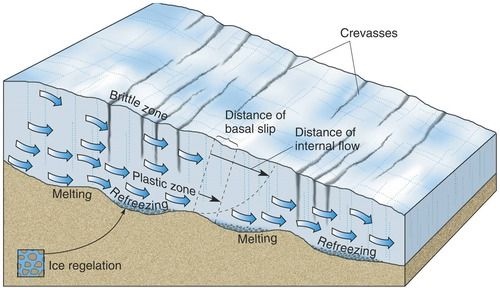
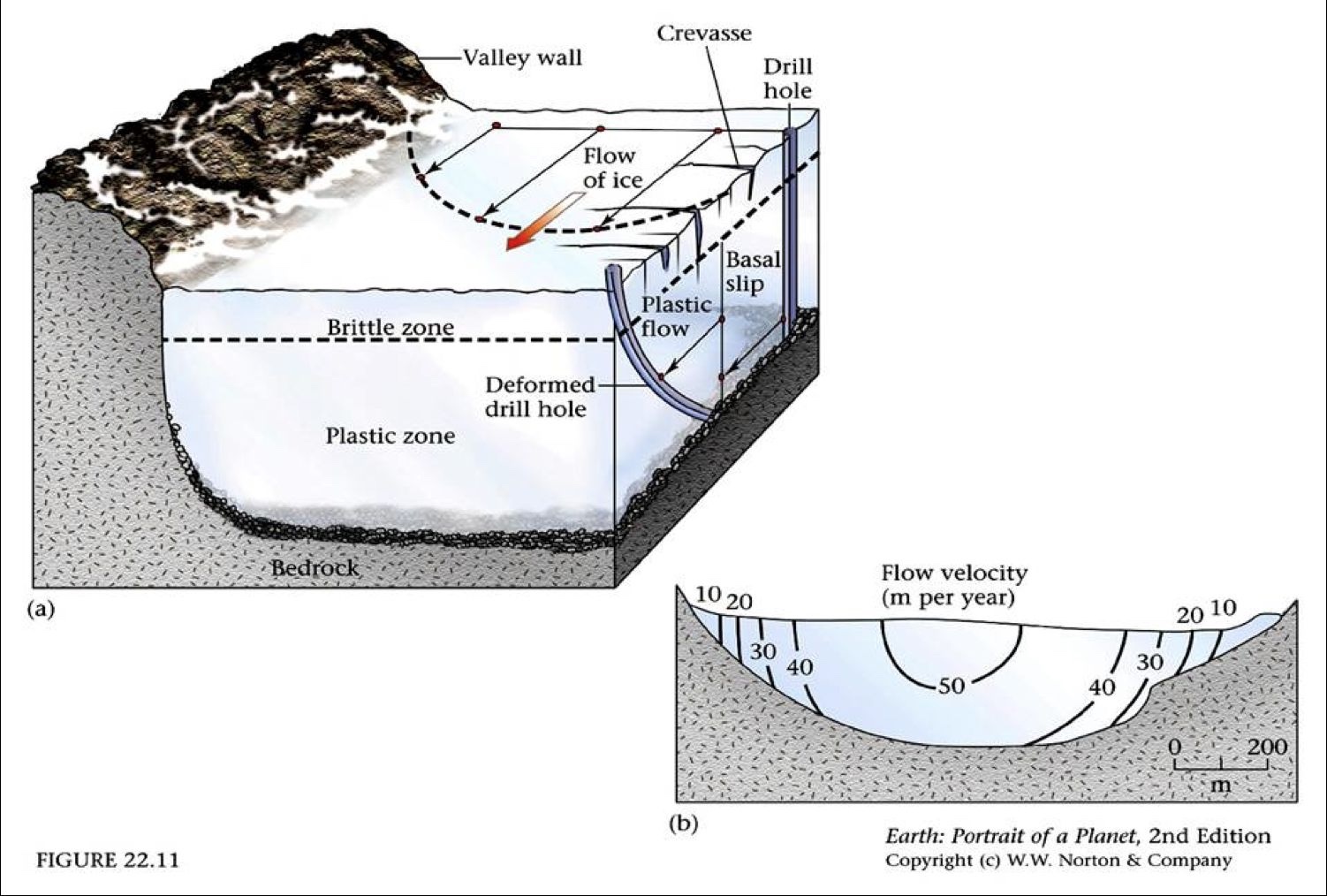
Where do glaciers flow the fastest?
Fastest = top-middle
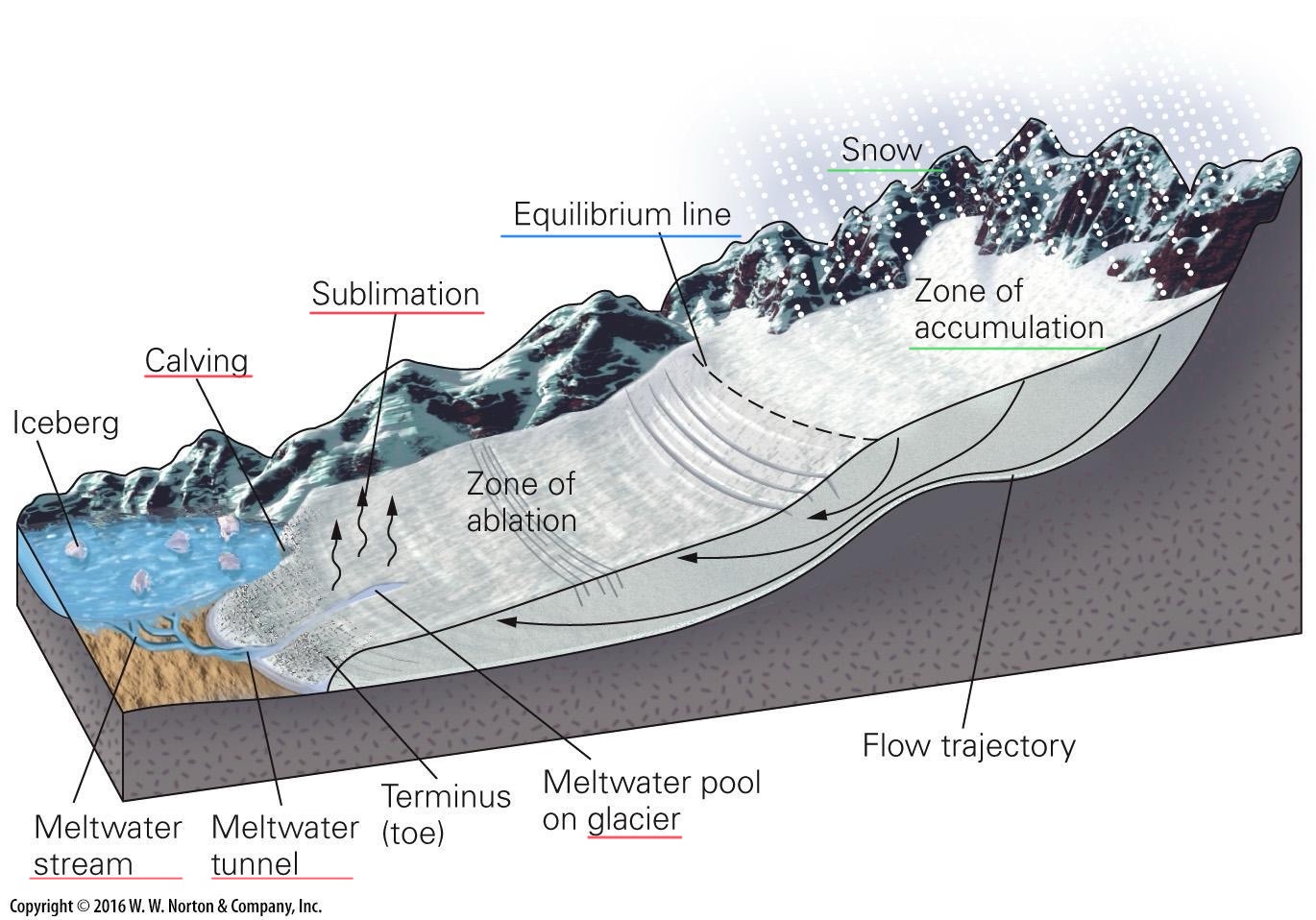
Terminus
End of the glacier
point where flow of glacier cannot keep balance within ablation
Calving
the process where large pieces of ice break off from the edge of glaciers, ice shelves, and ice fronts, forming new icebergs that then drift into the ocean
Ice Stream
sharp margins and can move much faster than the surrounding ice
In antarctica, 90% of ice and sediment discharge happens through ice streams
most ice shelves are fed by ice streams
Zone of accumulation
snowfall
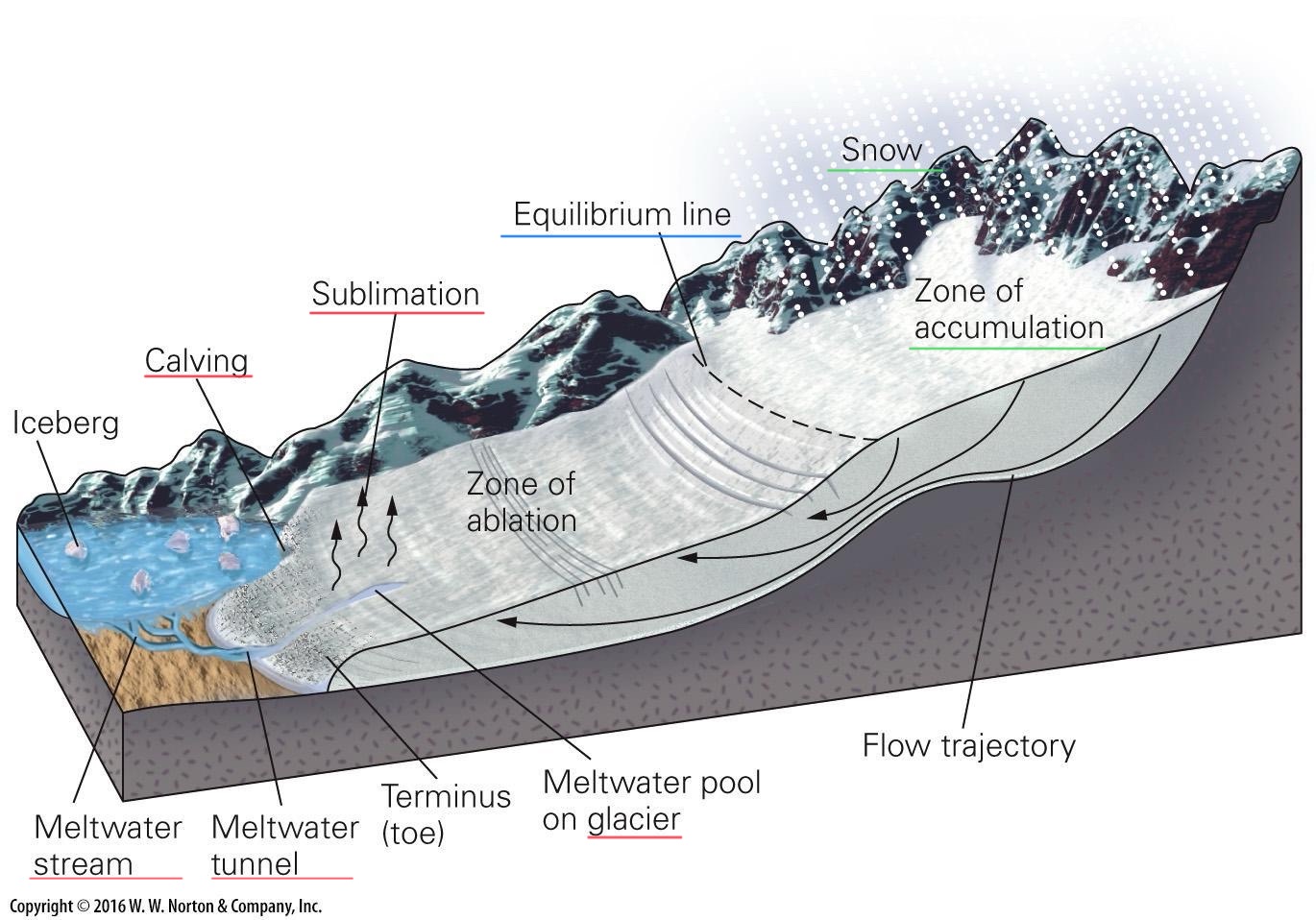
Zone of ablation
melting
calving
sublimation
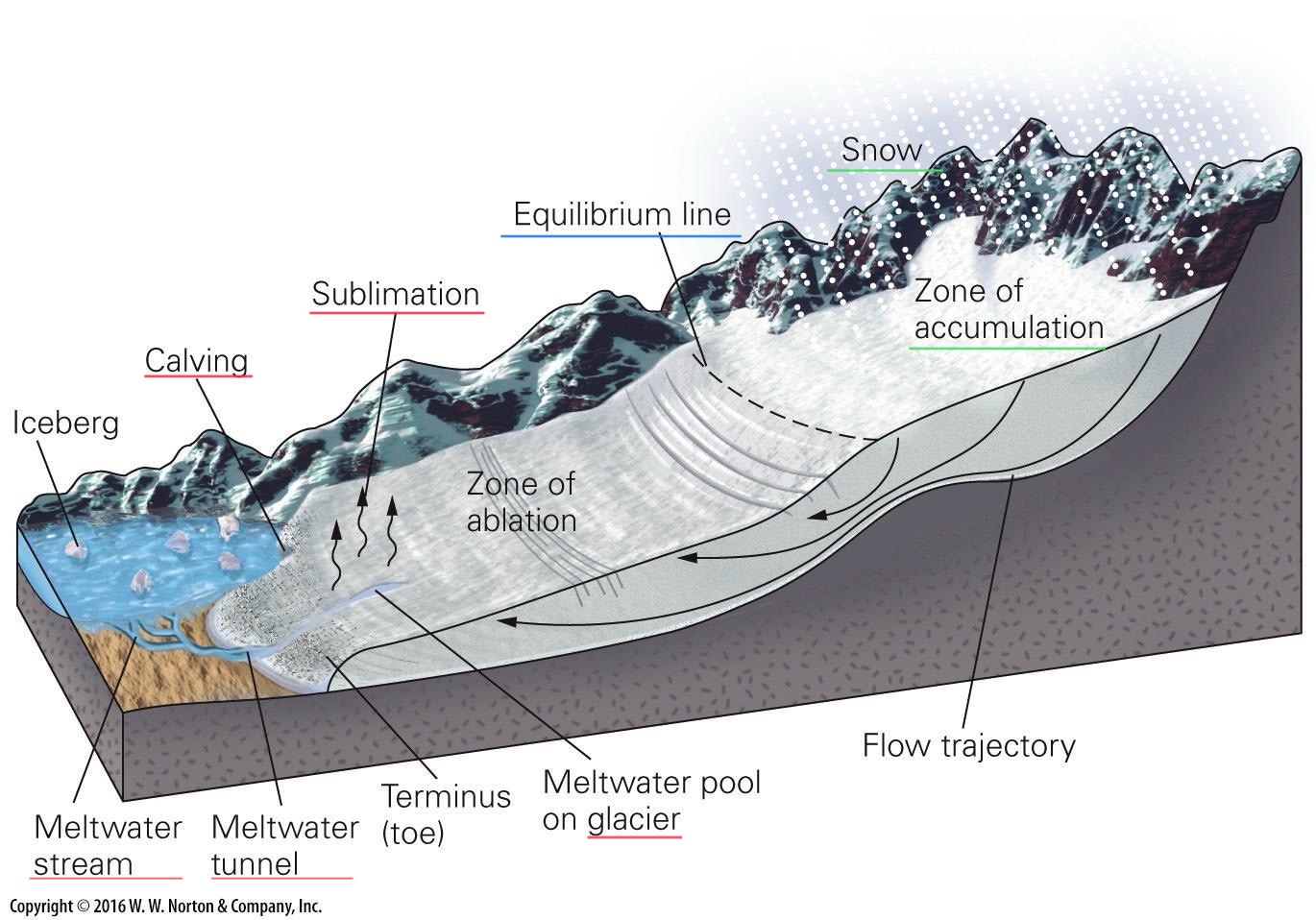
Equilibrium line
elevation where accumulation and ablation (loss) are equal
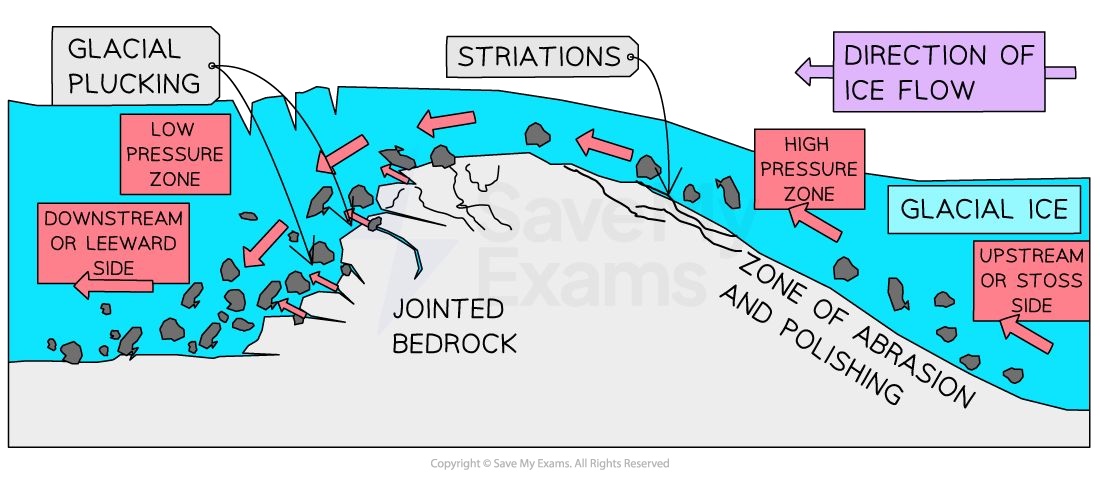
Abrasion
rock debris in base scrapes the bed
striations
grooves
polished surfaces
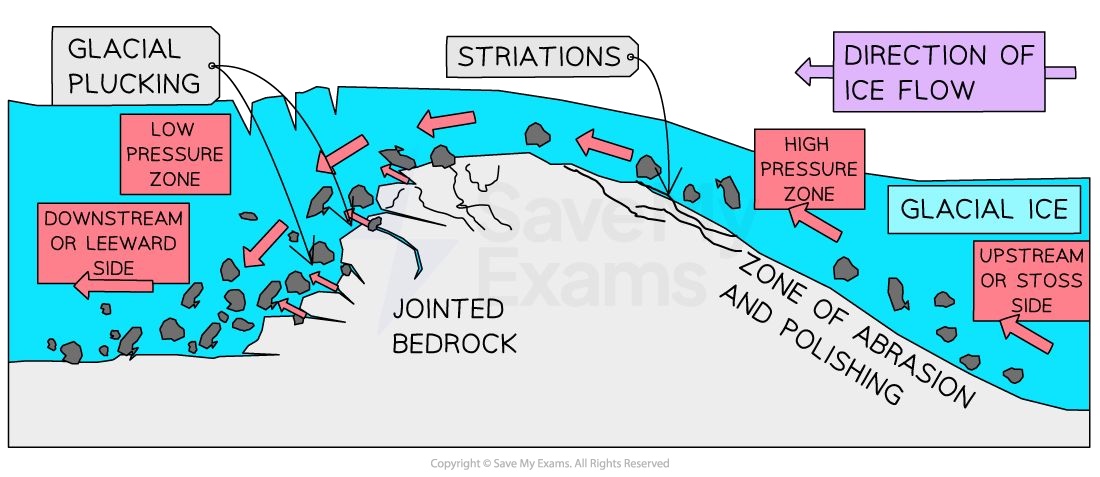
Plucking
glacier freezing to bed, moves pulls fragments away
fractures facilitate this process
chattermarks: depressions carved from the removing of rock flakes
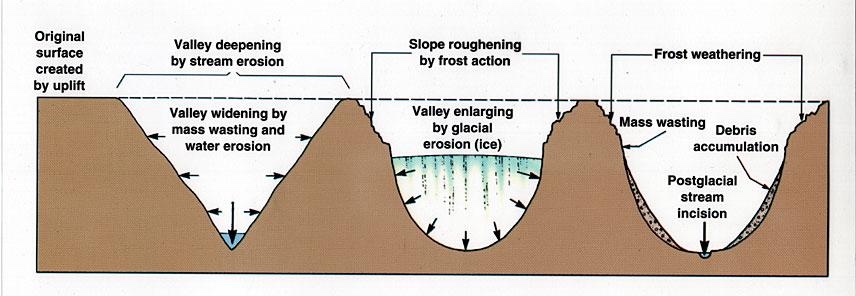
U-Shaped valleys
rivers form v-shaped valleys, or gorges or canyons
glaciers create U-shaped valleys
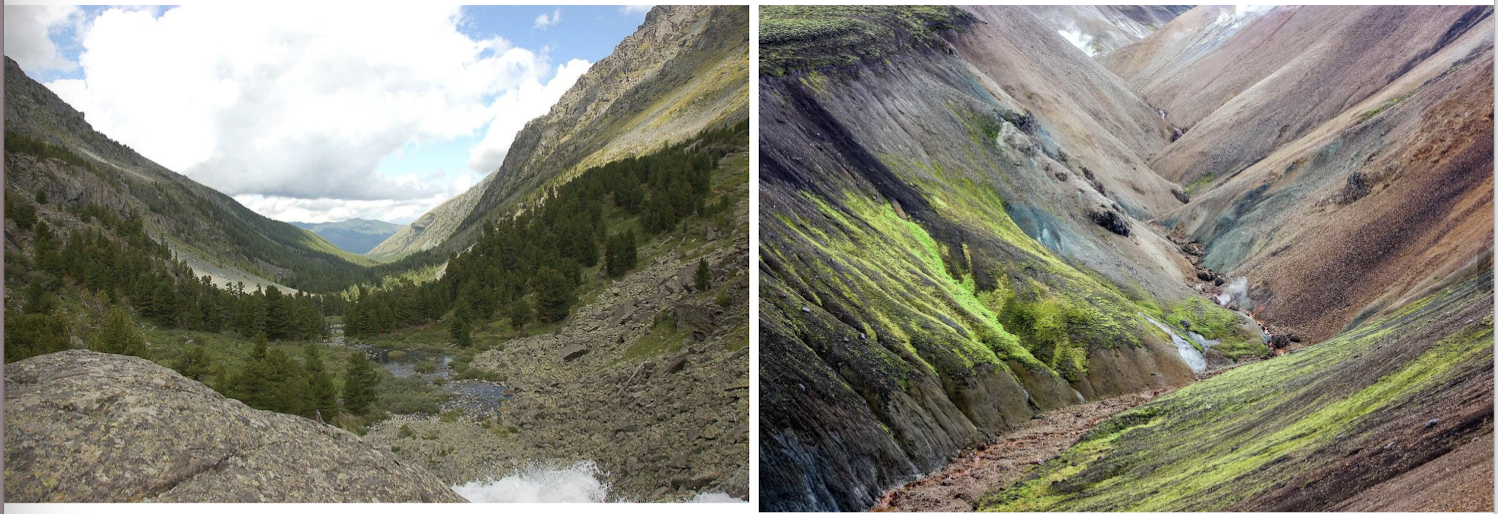


Moraines
Glacial moraines are accumulations of rock/debris at the edges, or within, a glacier
sediment in moraines are often angular, highlighting they weren’t transported by rivers
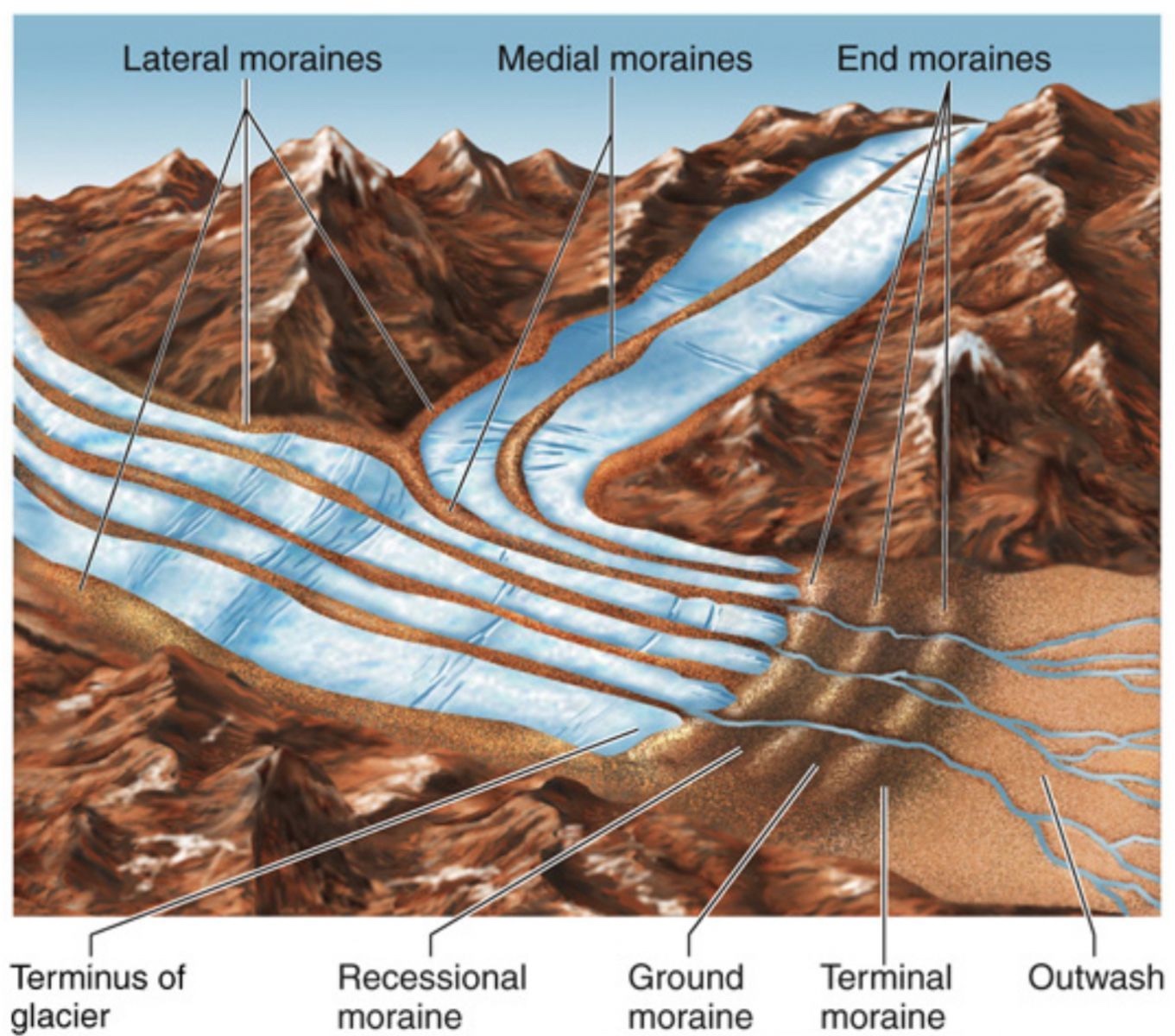
mapping ___, we can learn about where ice sheets extended to in the past
moraines
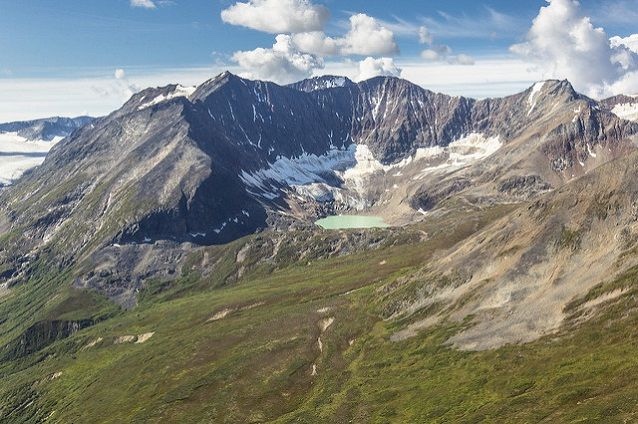

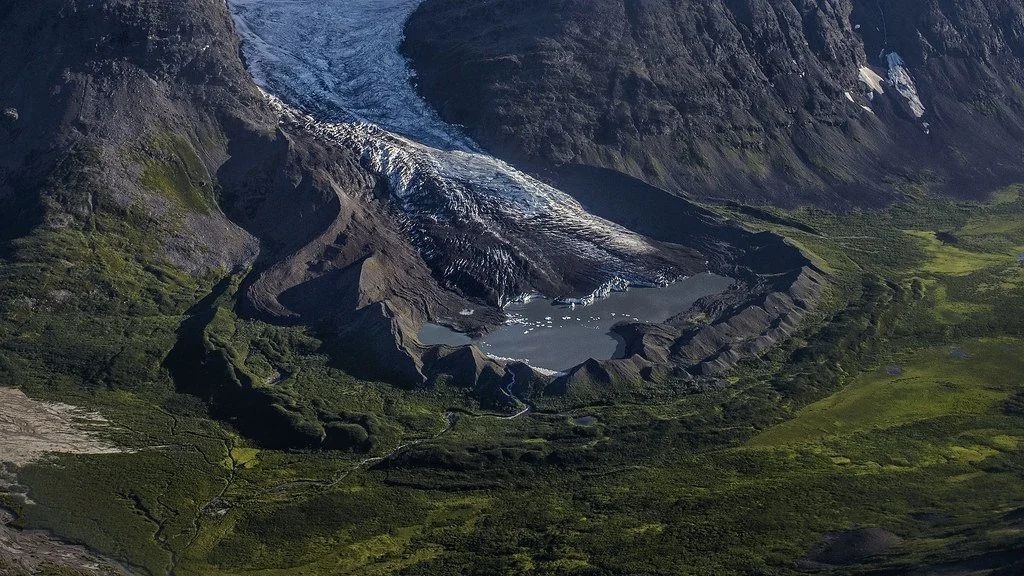
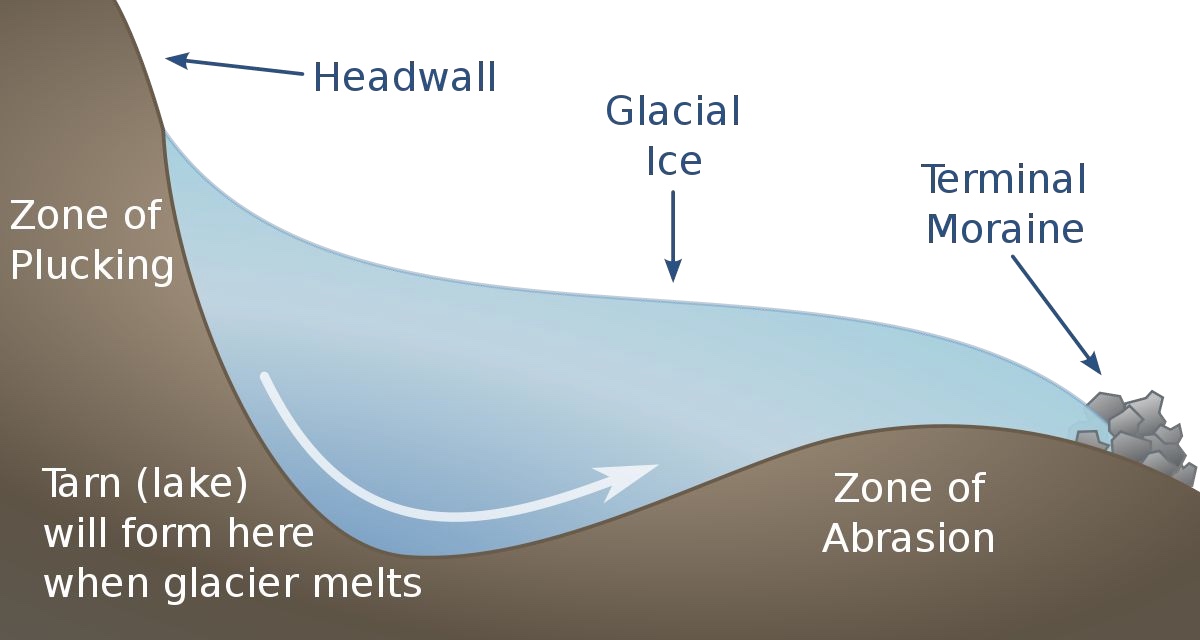
Cirques
Bowl-shaped, amptitheatre- like depressions formed at the accumulation zone of a glacier

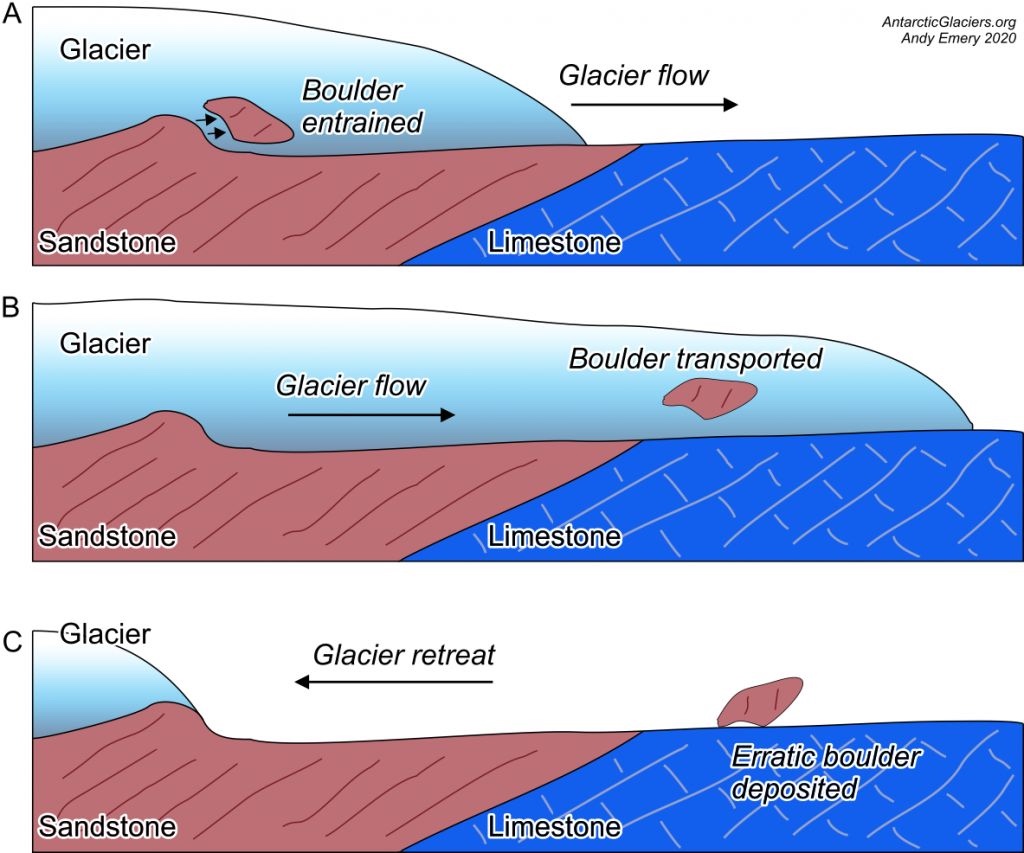
Erratics
a boulder that is out of place
studying erratics led to Ice Age discovery