Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism Overview
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Triglycerides
Hydrolyzed to glycerol and fatty acids during digestion.
Phosphoglycerides
Hydrolyzed to component substances in lipid metabolism.
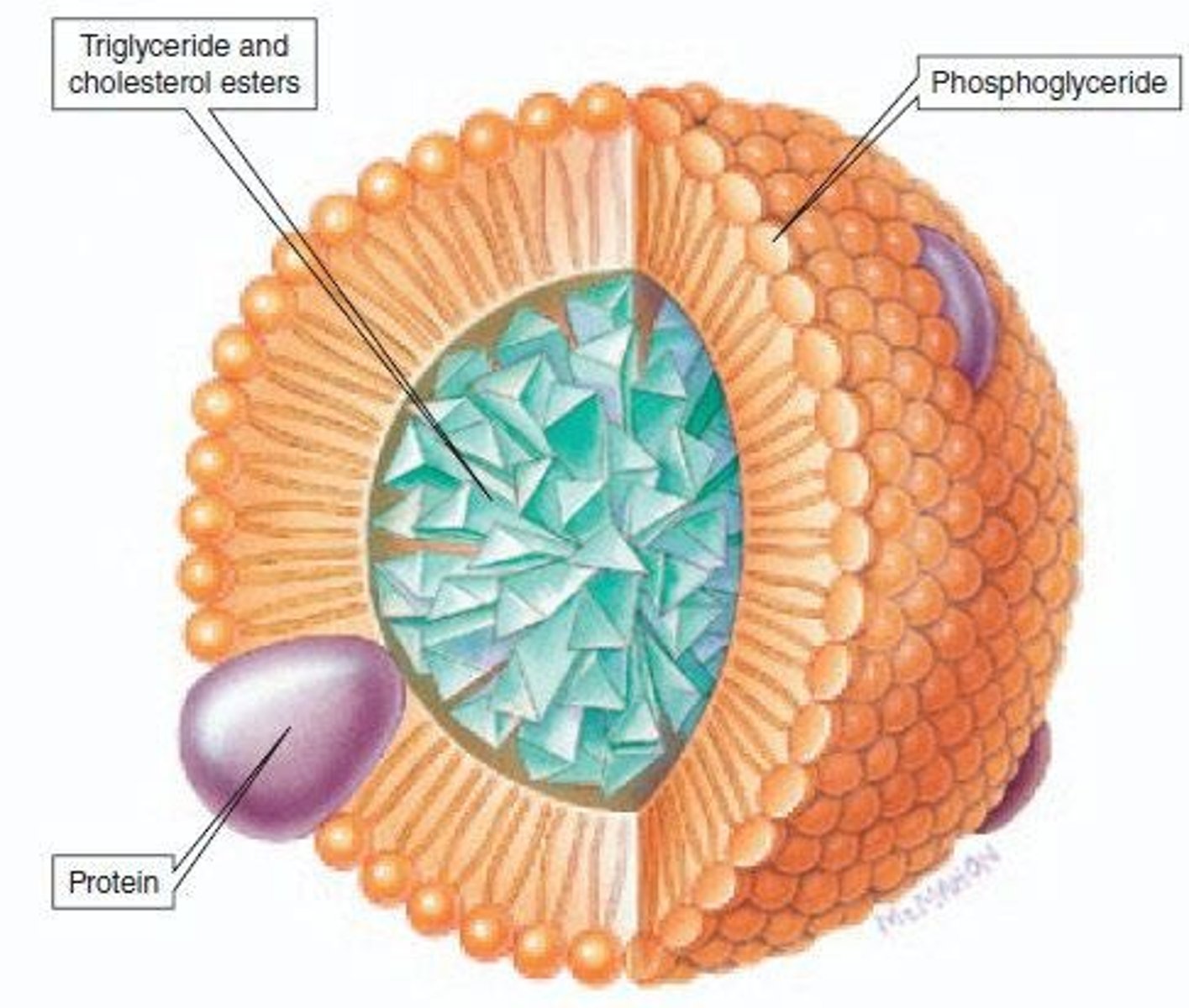
Chylomicrons
Lipoprotein aggregates for lipid transport in blood.
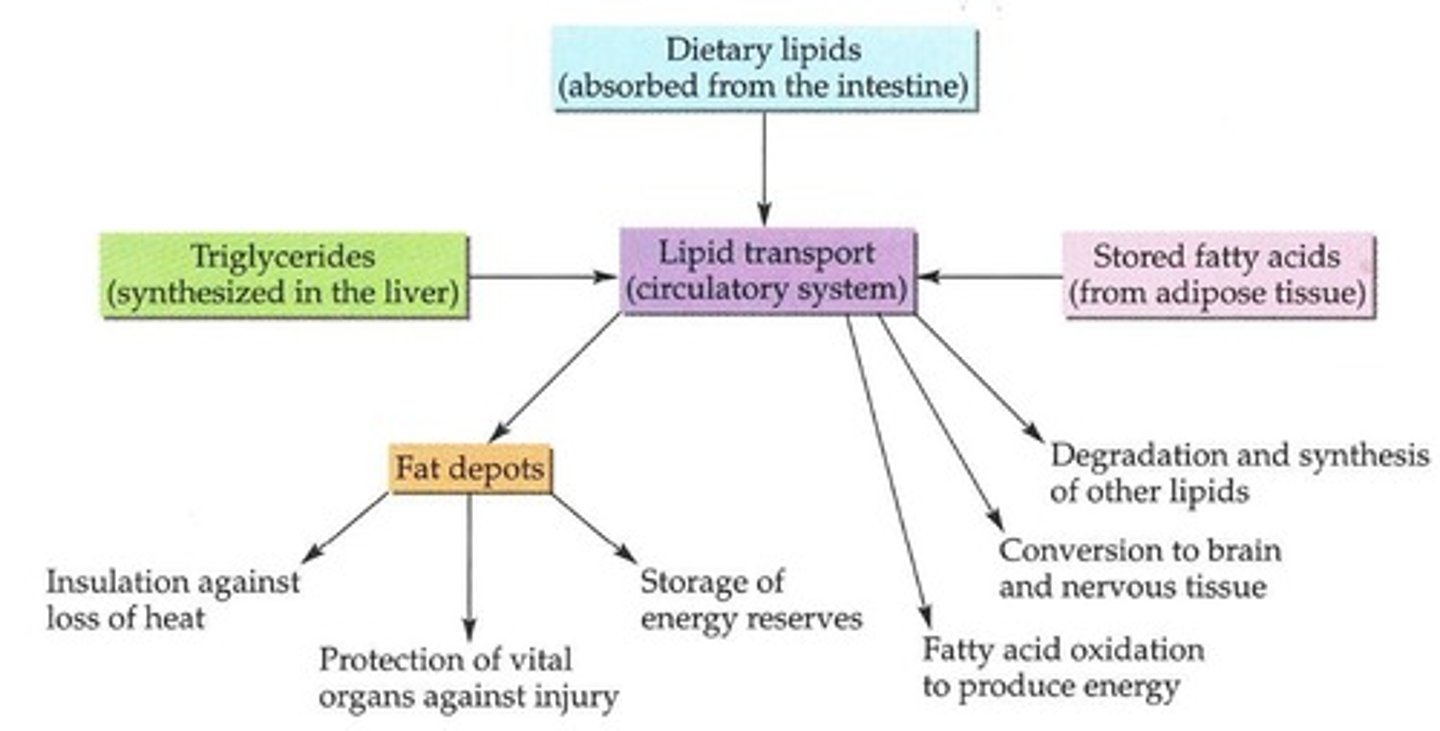
Lipoproteins
Complexes of lipids and proteins, classified by density.
VLDL
Very low density lipoprotein, rich in triglycerides.
LDL
Low density lipoprotein, associated with cholesterol transport.
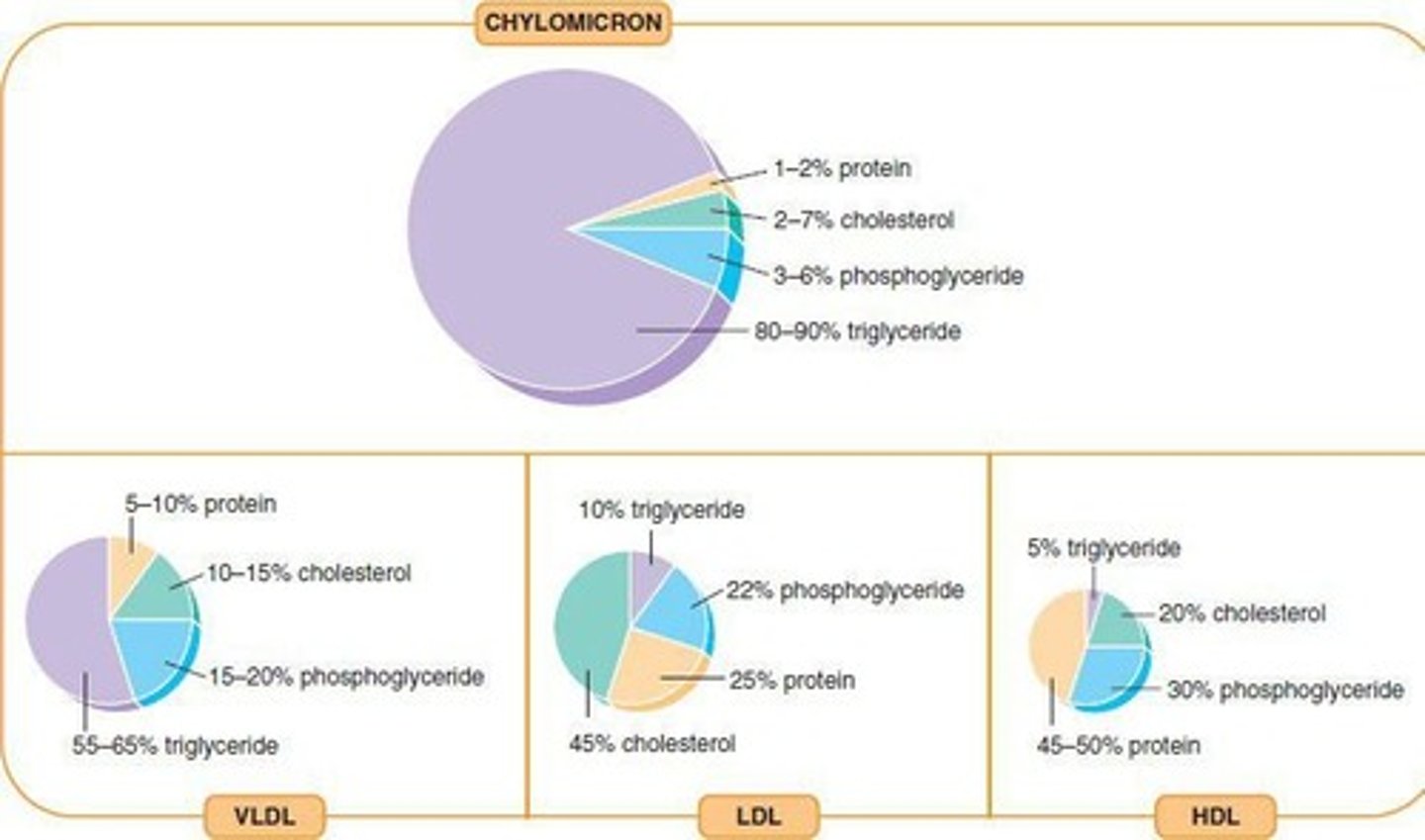
HDL
High density lipoprotein, involved in cholesterol removal.
Fat Mobilization
Hydrolysis of triglycerides for energy production.
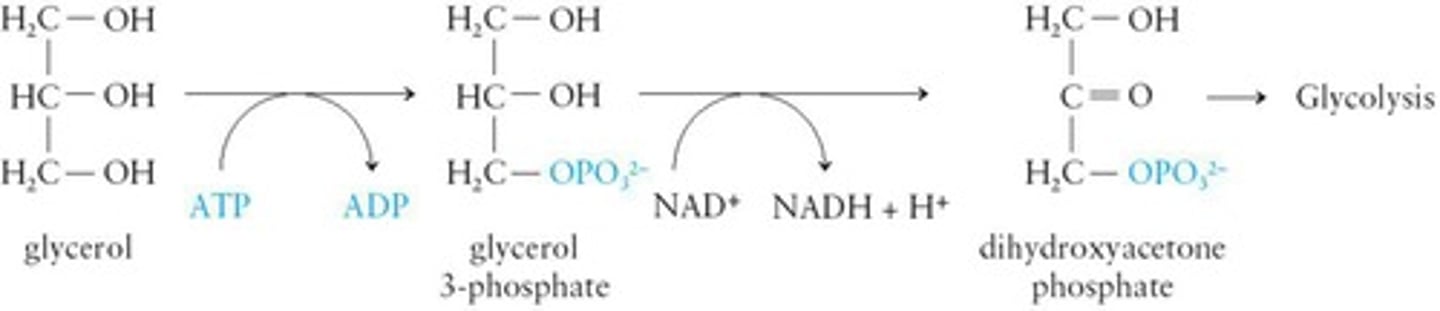
Glycerol
Converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate for glycolysis.
Fatty Acids
Mobilized for energy when glycogen stores are low.
Serum Albumin
Plasma protein that transports fatty acids in blood.
ATP Hydrolysis
Provides energy for fatty acid activation to acyl CoA.
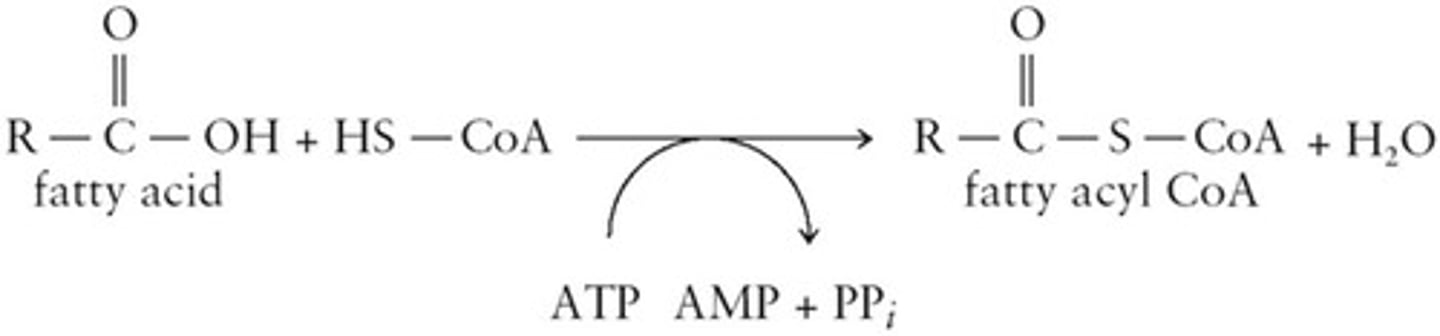
Acyl CoA Synthetase
Enzyme that catalyzes fatty acid activation.
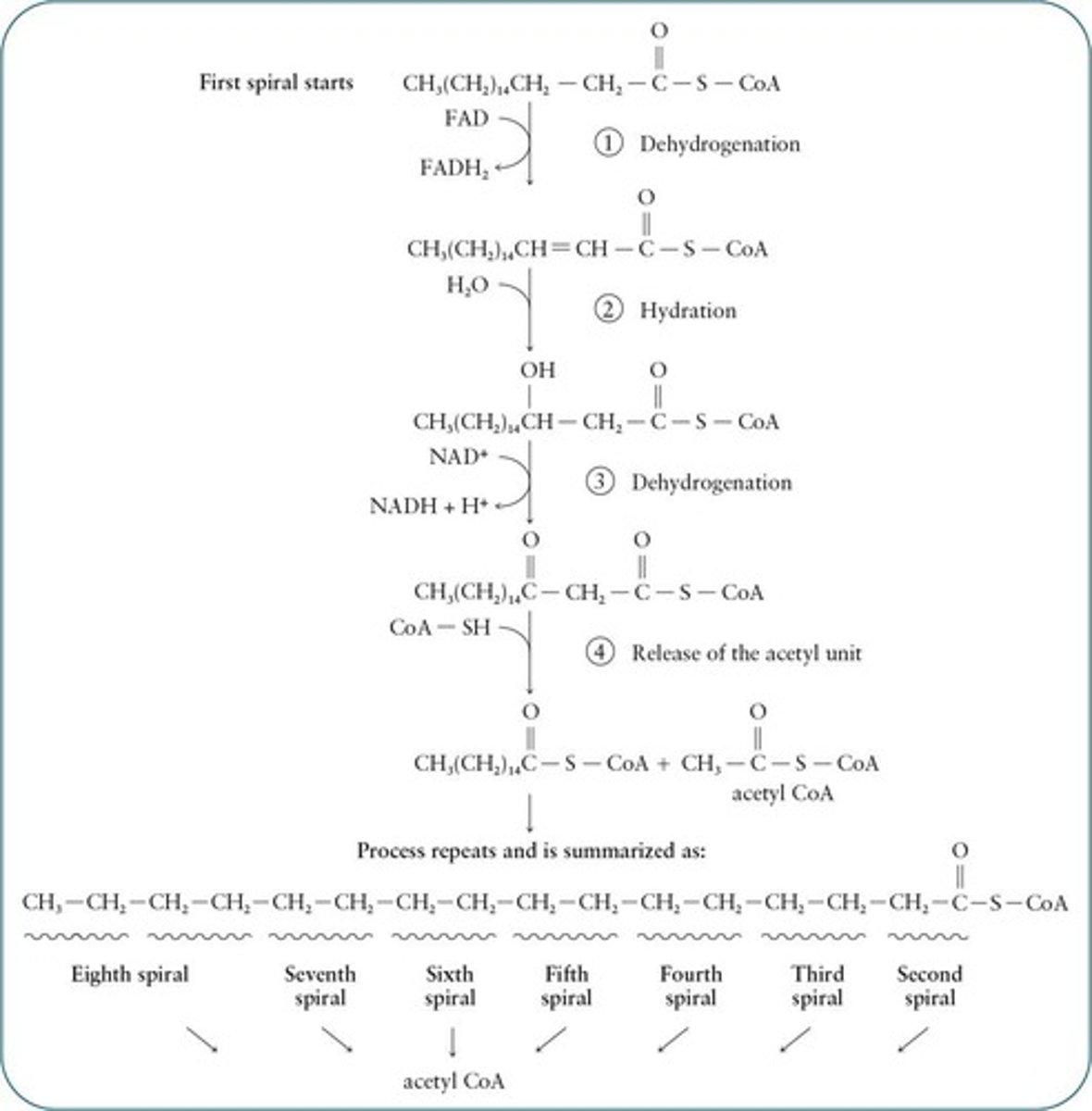
β-Oxidation
Pathway for fatty acid catabolism to acetyl CoA.
Ketone Bodies
Produced during fat metabolism under low carbohydrate conditions.
Urea Cycle
Pathway for amino acid nitrogen disposal as urea.
Transamination
Reaction transferring amino group to form new amino acid.
Deamination
Removal of amino group from amino acids.
Amino Acid Pool
Source of amino acids for protein synthesis and metabolism.
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Energy Production
Amino acids can be used for cellular energy.
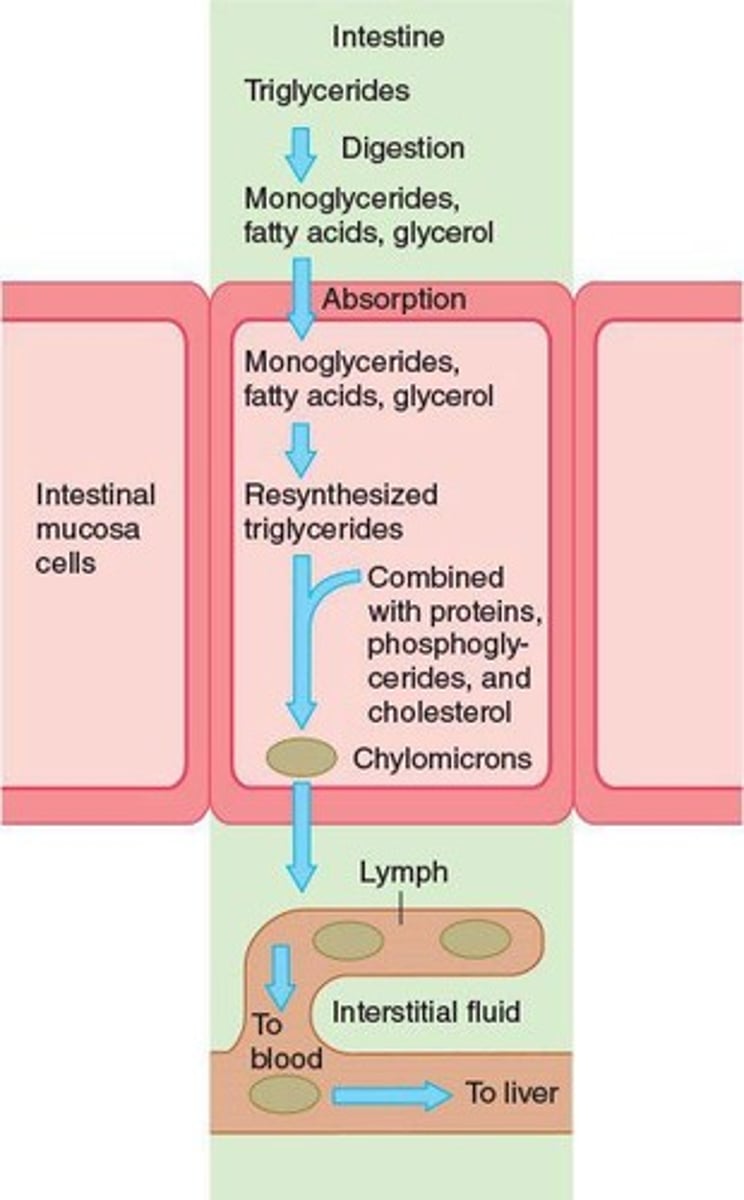
Triglyceride Resynthesis
Occurs in intestinal mucosa after lipid digestion.
Blood Lipid Behavior
Increases after meals, normalizes through storage and oxidation.
Lipid Digestion
Triglycerides hydrolyzed to glycerol and fatty acids.
Chylomicrons
Lipoprotein aggregates transporting insoluble lipids.
Fat Mobilization
Hydrolysis of triglycerides for energy use.
Glycerol Metabolism
Converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate in glycolysis.
Fatty Acyl CoA
Activated form of fatty acids for catabolism.
Acyl CoA Synthetase
Enzyme catalyzing fatty acyl CoA formation.
ATP Hydrolysis
Energy source for fatty acid activation.
β-Oxidation
Process of fatty acid catabolism for energy.
Ketone Bodies
Produced during fat metabolism under specific conditions.
Urea Cycle
Pathway converting ammonia to urea for excretion.
Transamination
Amino group transfer between amino acids and keto acids.
Energy Production
Amino acids can generate ATP through various pathways.
Triglyceride Resynthesis
Reformation of triglycerides in intestinal mucosa cells.
Blood Lipid Behavior
Lipids increase post-meal, normalize through storage.
Lipoprotein Classification
Based on density; higher lipids, lower density.
VLDL
Very low density lipoprotein, transports triglycerides.
LDL
Low density lipoprotein, carries cholesterol to cells.
HDL
High density lipoprotein, removes cholesterol from cells.
Amino Acid Pool
Body's reservoir of amino acids for metabolism.
Nonessential Amino Acids
Synthesized from carbohydrate metabolism intermediates.
Fatty Acid Transport
Fatty acids bind to serum albumin in blood.
Fatty acyl-CoA
A substrate for subsequent Ⱦ-oxidation cycles.
Ⱦ-oxidation
Metabolic process for fatty acid degradation.
Substrate
A reactant in a biochemical reaction.
Final step
Last phase before the substrate is reused.
Next round
Subsequent cycle of metabolic processing.
β-oxidation
Process of fatty acid degradation in mitochondria.
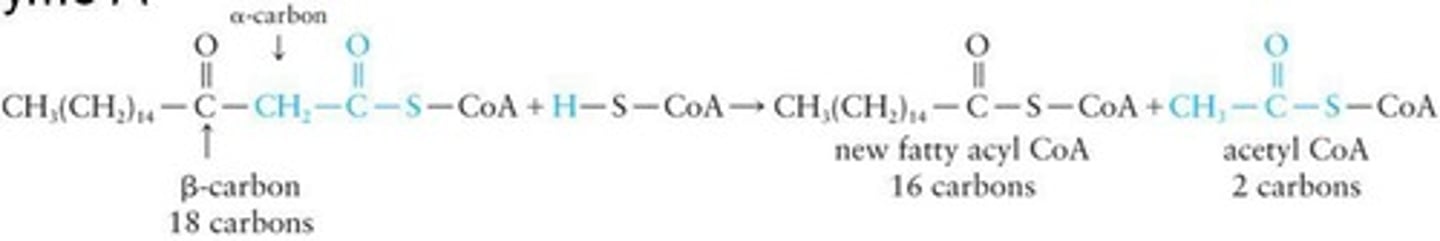
Acetyl-CoA
Two-carbon molecule produced from fatty acid oxidation.
Fatty Acid Spiral
Pathway for sequential degradation of fatty acids.
NADH
Electron carrier producing 2.5 ATP per molecule.
FADH2
Electron carrier producing 1.5 ATP per molecule.
Stearoyl CoA
Activated form of stearic acid for oxidation.
Activation Step
Initial reaction using ATP to activate fatty acids.
Citric Acid Cycle
Pathway where acetyl CoA enters for energy production.
Energy Density
Fatty acids provide more energy than carbohydrates.
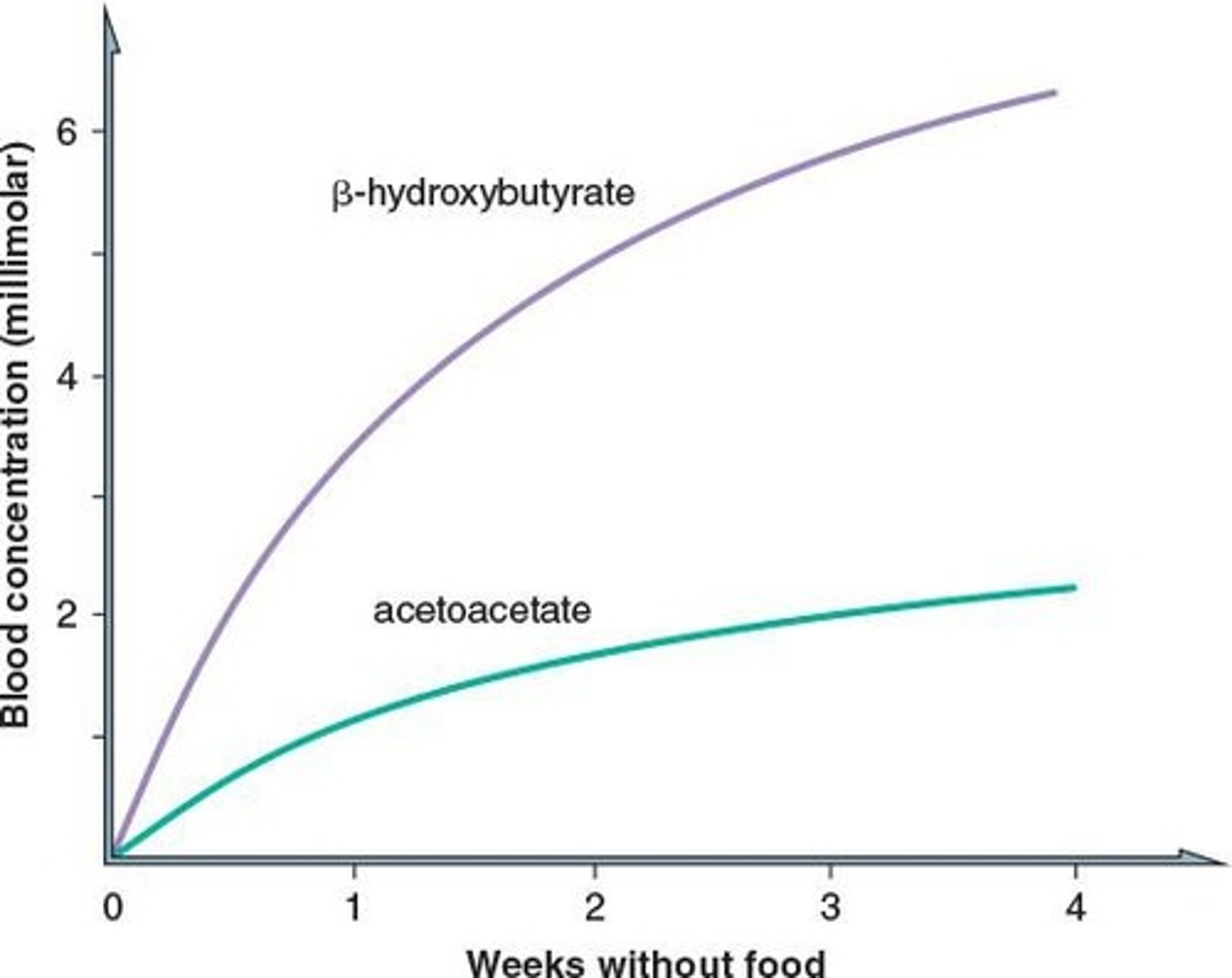
Ketonemia
Elevated ketone bodies in blood over 20 mg/100 mL.
Ketonuria
Presence of ketone bodies in urine.
Acetone Breath
Detection of acetone in breath indicating ketosis.
Ketosis
Condition with ketonemia, ketonuria, and acetone breath.
Ketoacidosis
Low blood pH due to high ketone levels.
Insulin Treatment
Used to manage diabetes-related ketosis.
Sodium Bicarbonate
Used to restore acid-base balance in severe ketosis.
ATP Calculation
Determining ATP yield from fatty acid oxidation.
Citrate Transport
Process of moving acetyl CoA to cytoplasm.
Oxaloacetate
Intermediate for transporting acetyl CoA to cytoplasm.
Butyryl CoA
Four-carbon chain entering the β-oxidation sequence.
Total ATP from Stearic Acid
120 ATP produced from complete oxidation.
Energy Comparison
Lipids are 25% more efficient than carbohydrates.
Hydrolysis of ATP
Releases energy for fatty acid activation.
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Opposing process of fatty acid degradation in cytoplasm.
Fatty Acyl-CoA
Activated fatty acid ready for β-oxidation.
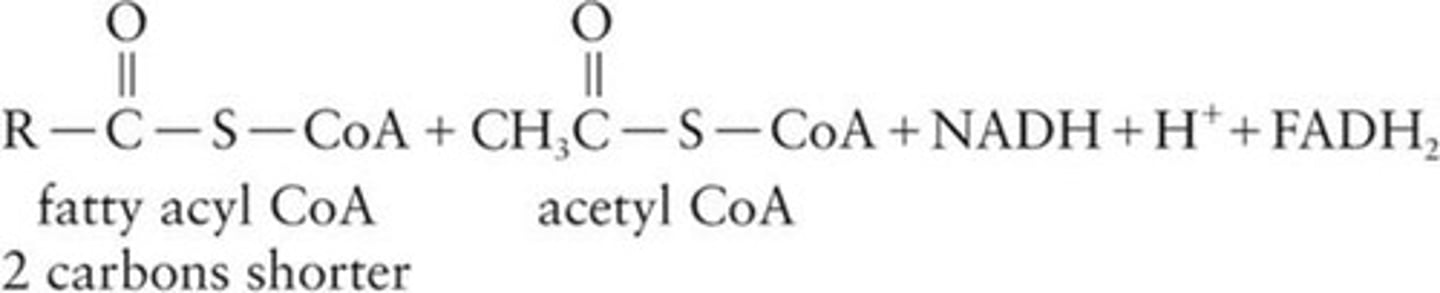
NADH
Electron carrier produced during β-oxidation.
FADH2
Another electron carrier generated in β-oxidation.
Fatty Acid Spiral
Cyclic pathway for fatty acid degradation.
Activation Step
Initial reaction forming fatty acyl-CoA from fatty acid.
Stearoyl-CoA
Fatty acyl-CoA derived from stearic acid (C18).
Energy Yield
Total ATP produced from stearic acid oxidation.
Citric Acid Cycle
Pathway where acetyl-CoA enters for further energy production.
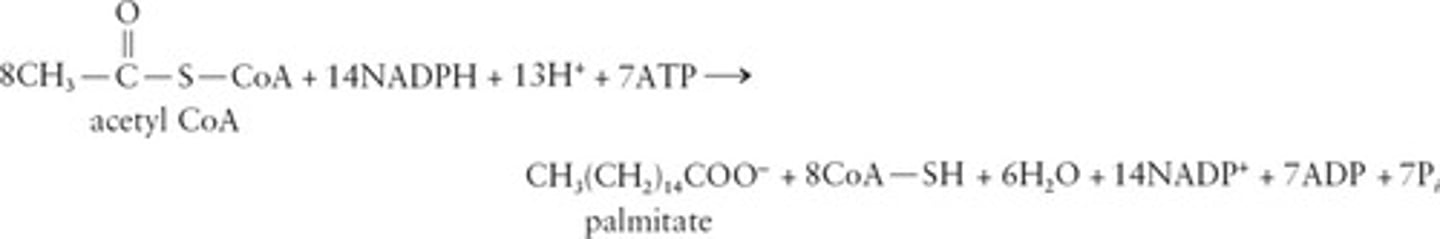
ATP Production
10 ATP per acetyl-CoA in citric acid cycle.
Ketonemia
Elevated ketone bodies in blood (over 20 mg/100 mL).
Insulin Treatment
Restores glucose metabolism, reduces ketone formation.
Sodium Bicarbonate
Used to treat dehydration and acid-base imbalance.
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Opposing process to fatty acid degradation in cytoplasm.
Citrate Transport
Mechanism transporting acetyl-CoA to cytoplasm.
Oxaloacetate
Molecule that combines with acetyl-CoA for transport.
Butyryl-CoA
Four-carbon fatty acyl-CoA in final β-oxidation step.
Energy Density
Lipids contain more energy than carbohydrates.
ATP Multipliers
Conversions: 10 ATP per acetyl-CoA, 2.5 per NADH, 1.5 per FADH2.
Malonyl-ACP
Carries carbon atoms in fatty acid synthesis.
Fatty Acid Synthetase System
Multienzyme complex catalyzing fatty acid synthesis.
Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)
Protein that holds growing fatty acyl chain.
Triglycerides
Stored form of fat in adipose tissues.
Adipose Tissue
Body tissue that stores fat as triglycerides.
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Cannot be synthesized by the human body.
Linoleic Acid
Dietary fatty acid converted to other polyunsaturates.
Linolenic Acid
Dietary fatty acid also converted to polyunsaturates.
Glucose to Fatty Acids
Human body can convert glucose into fatty acids.