Heart Anatomy
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
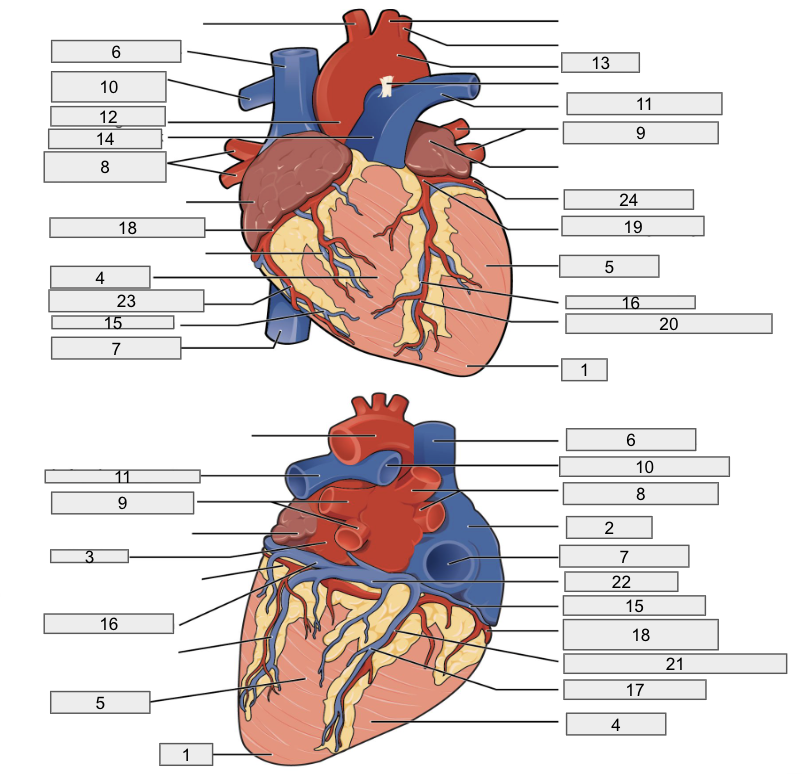
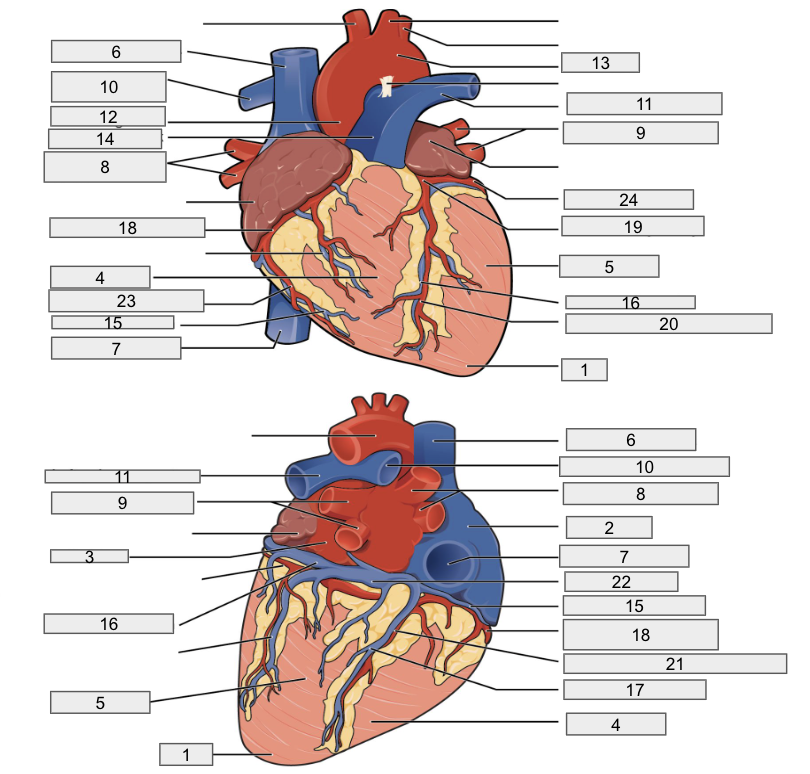
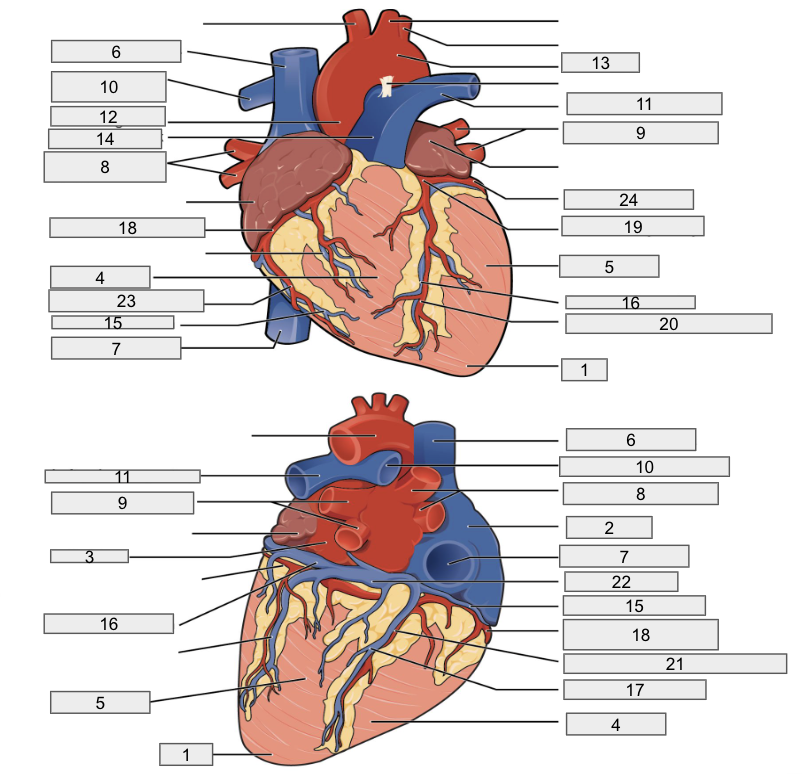
Protective outer layer of heart
Fibrous pericardium
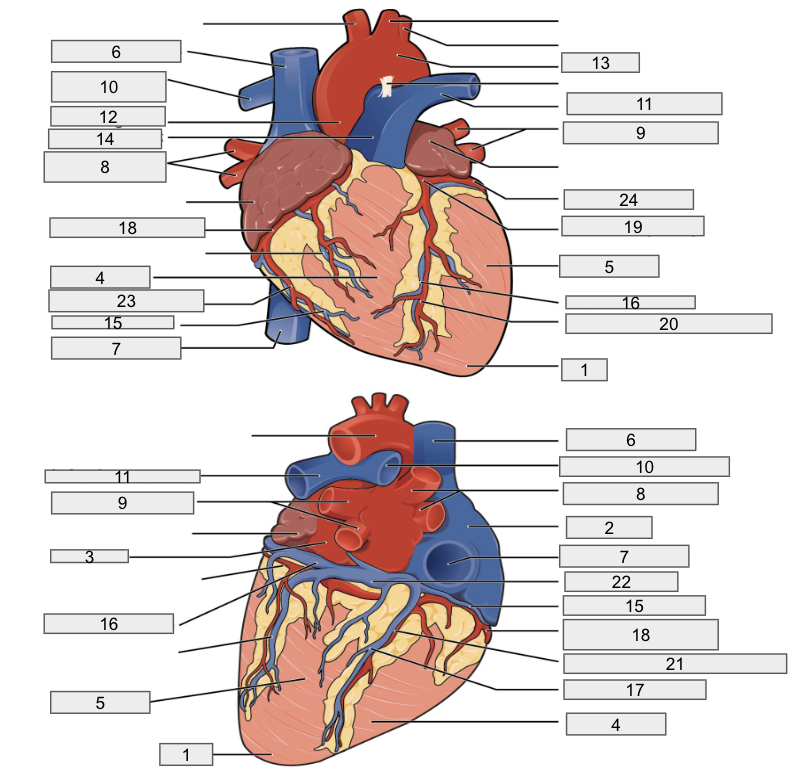
1
Apex
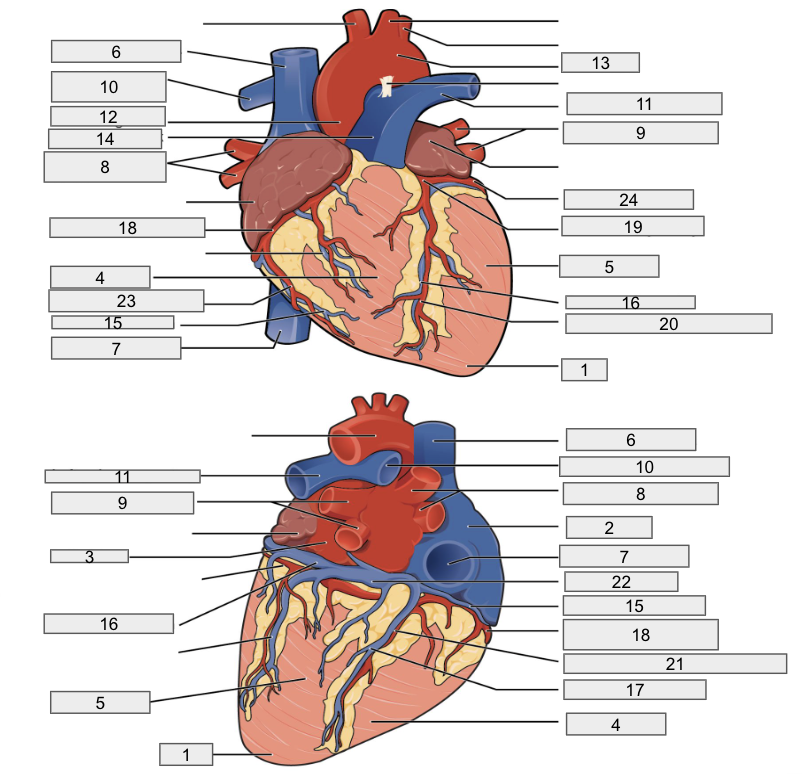
2
Right Atria
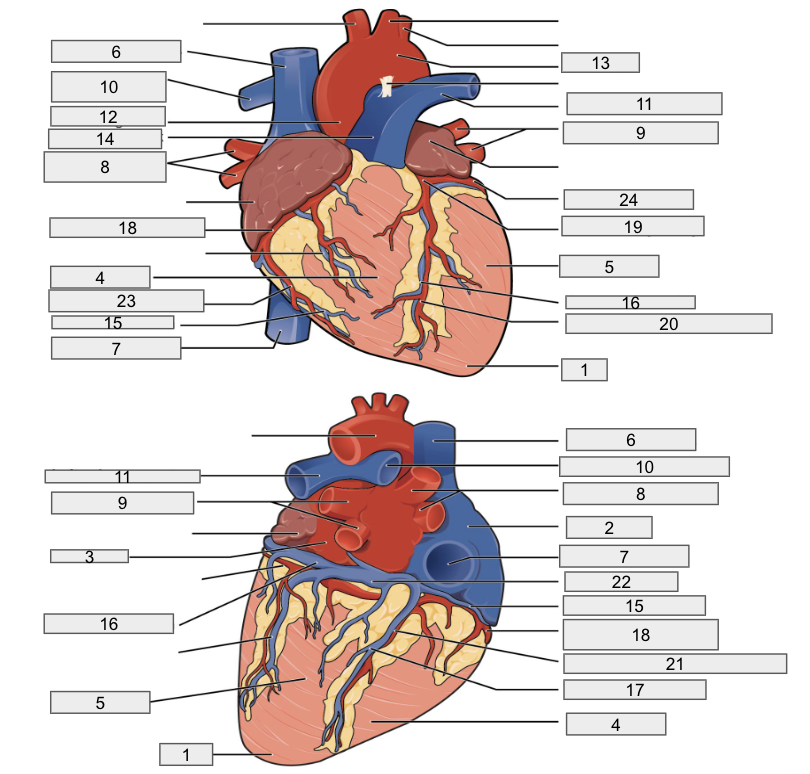
3
Left Atria
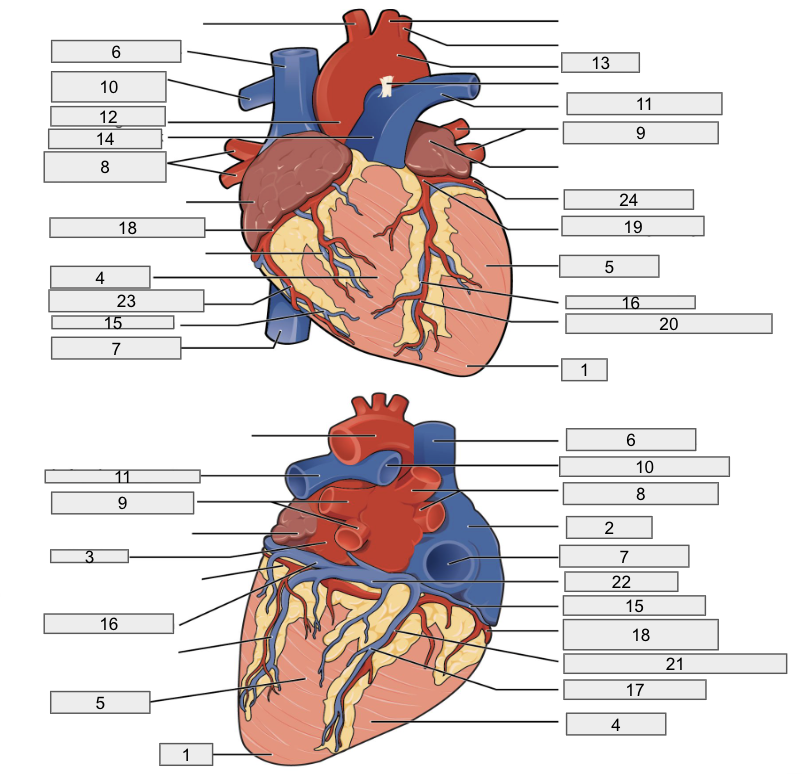
4
Right ventricle
5
Left ventricle
6
Superior vena cava
7
Inferior vena cava
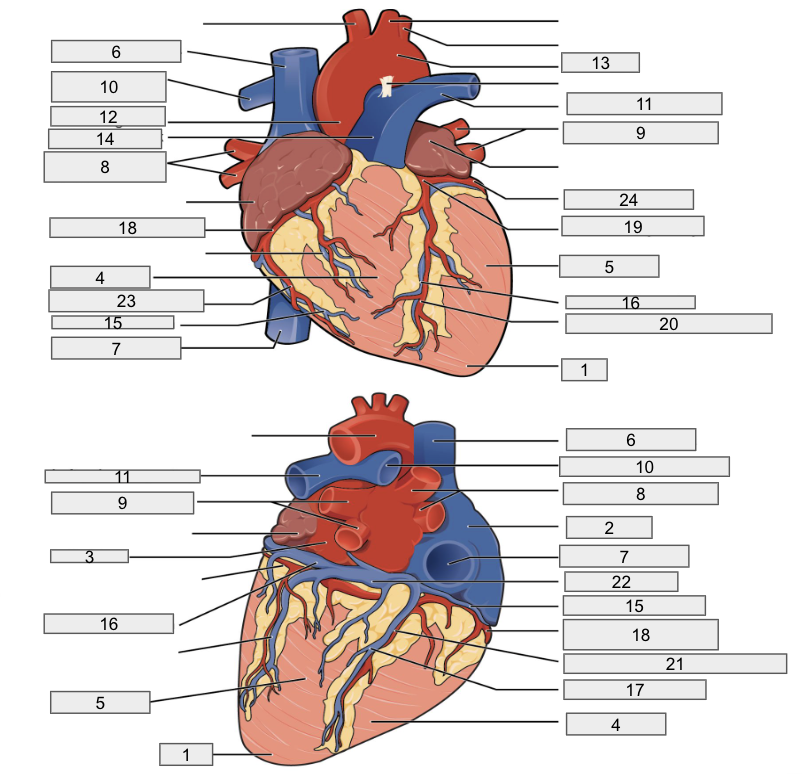
8
Right pulmonary vein
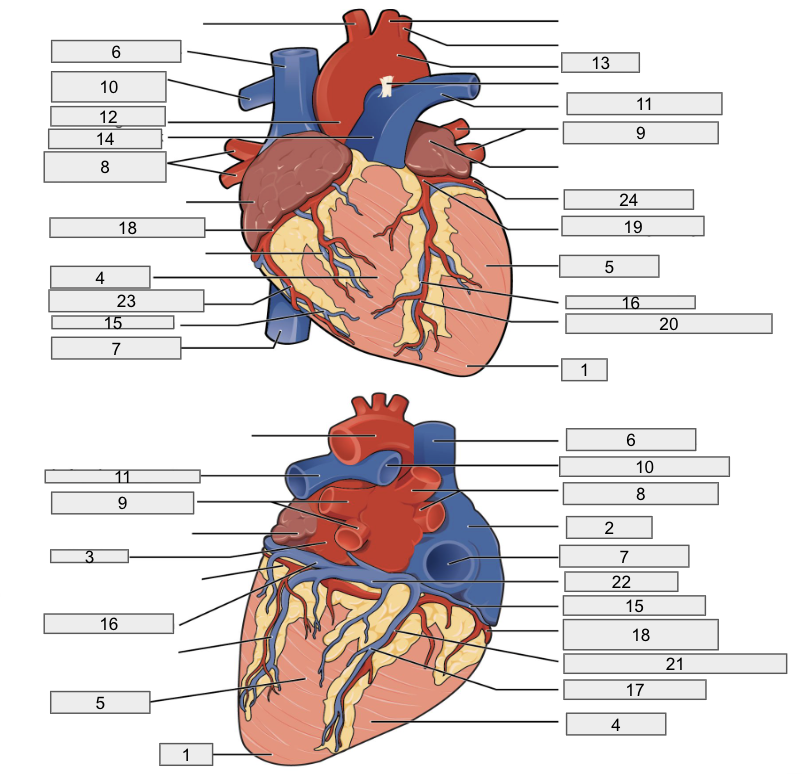
9
Left pulmonary veins
10
Right pulmonary artery
11
Left pulmonary artery
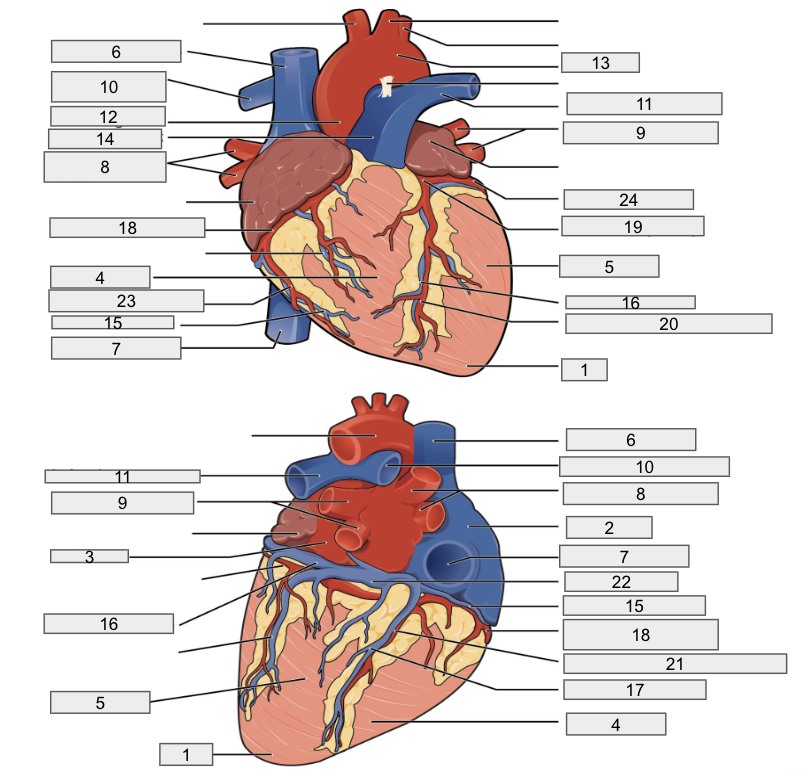
12
Ascending aorta
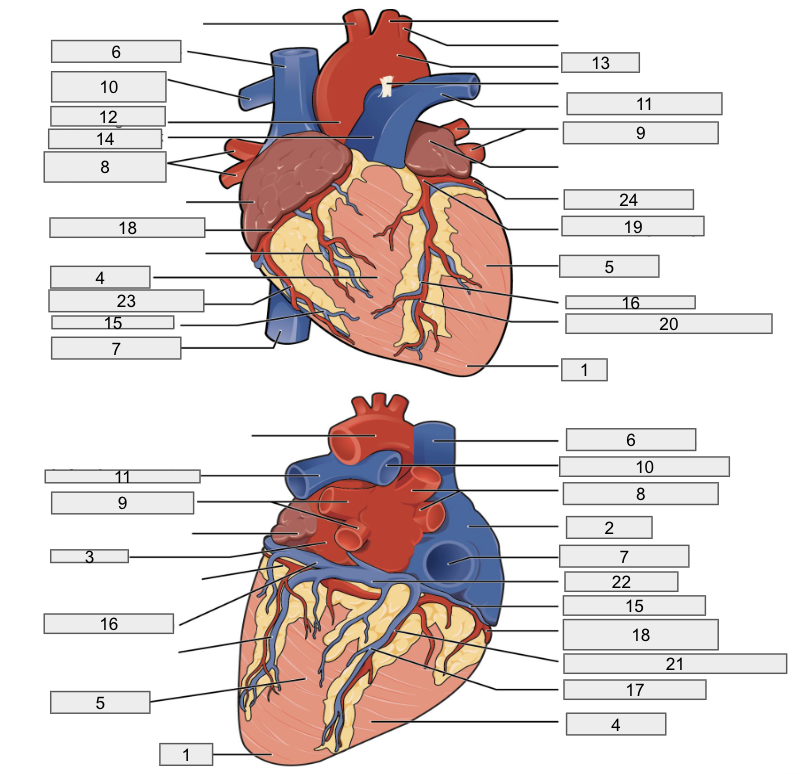
13
Aortic arch
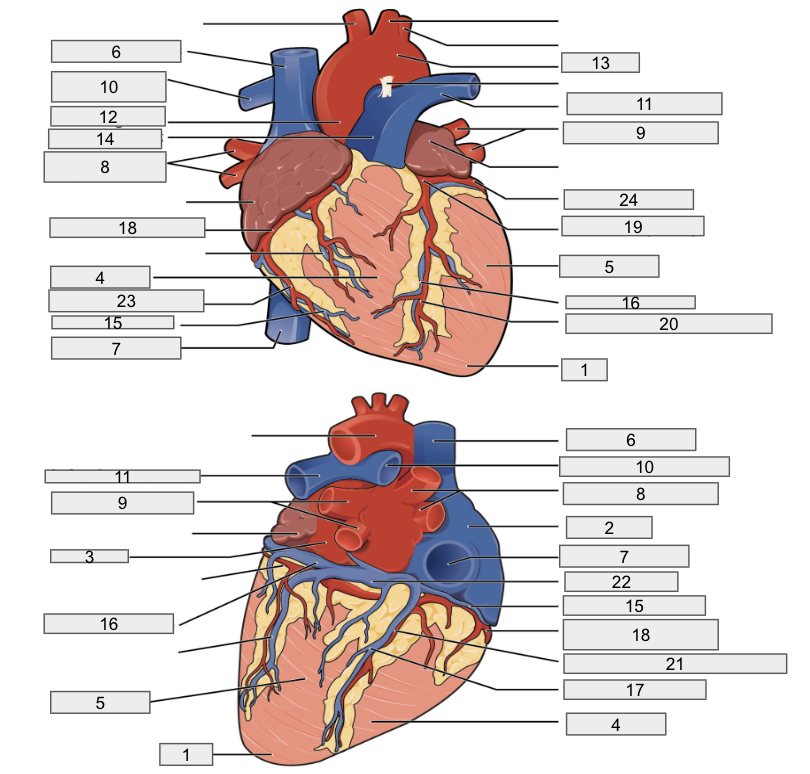
14
Pulmonary trunk artery
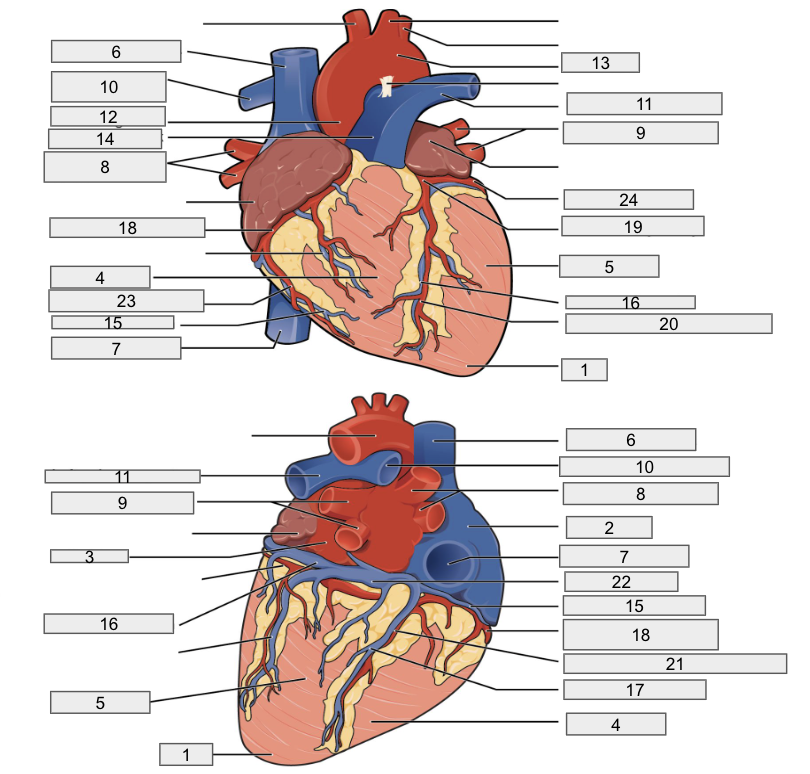
15
Small cardiac vein

16
Great cardiac vein
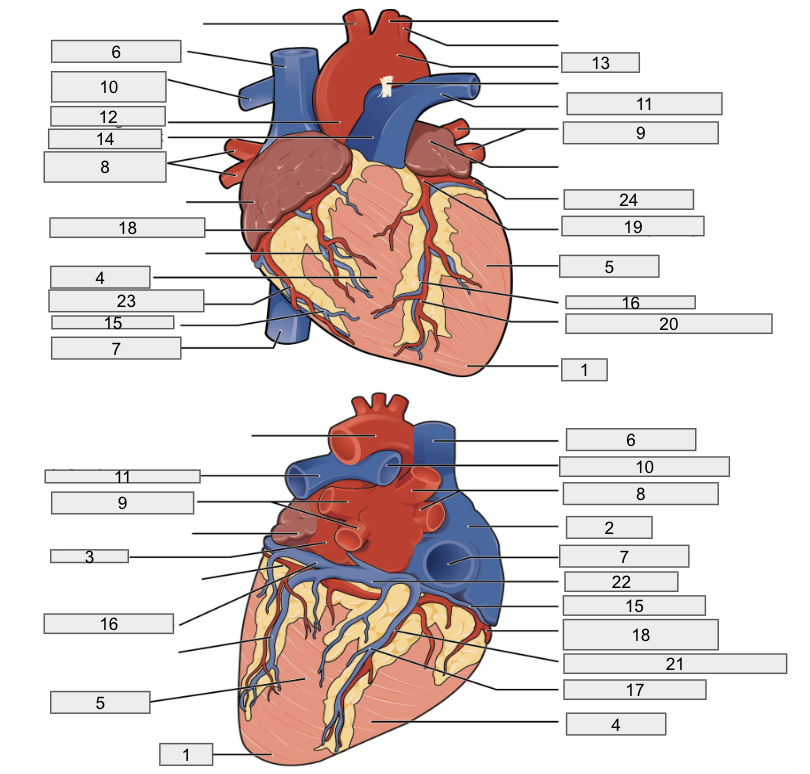
17
Middle cardiac vein
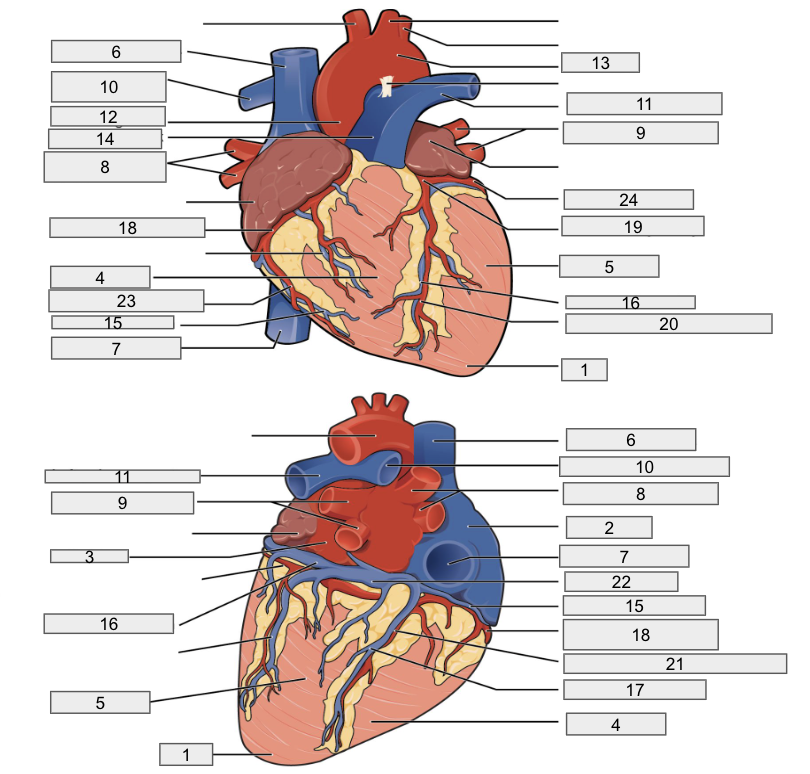
18
Right coronary artery
19
Left coronary artery
20
Anterior interventricular artery
21
Posterior interventricular artery

22
Coronary sinus
23
Right marginal artery
24
Circumflex artery
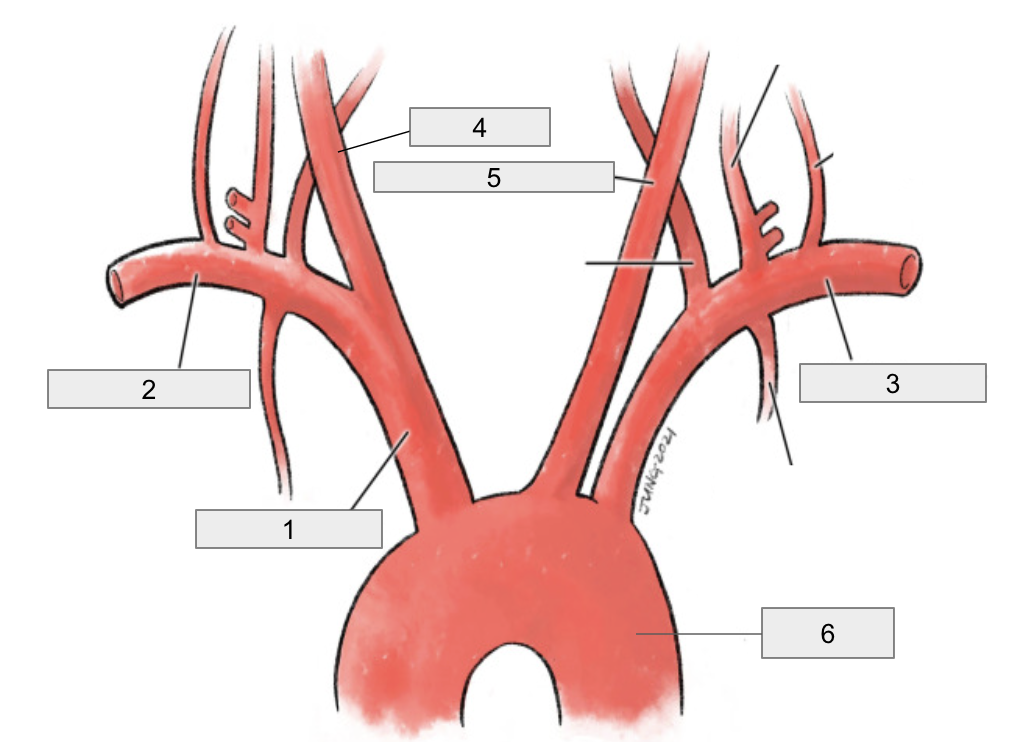
1
Brachiocephalic artery
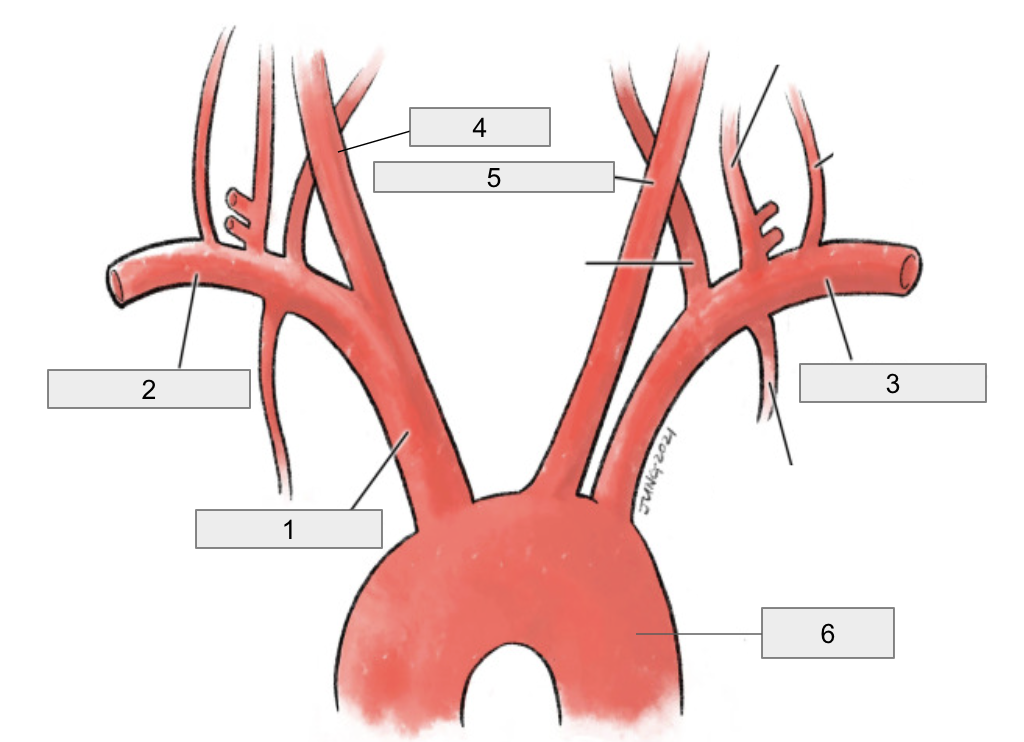
2
Right subclavian artery

3
Left subclavian artery
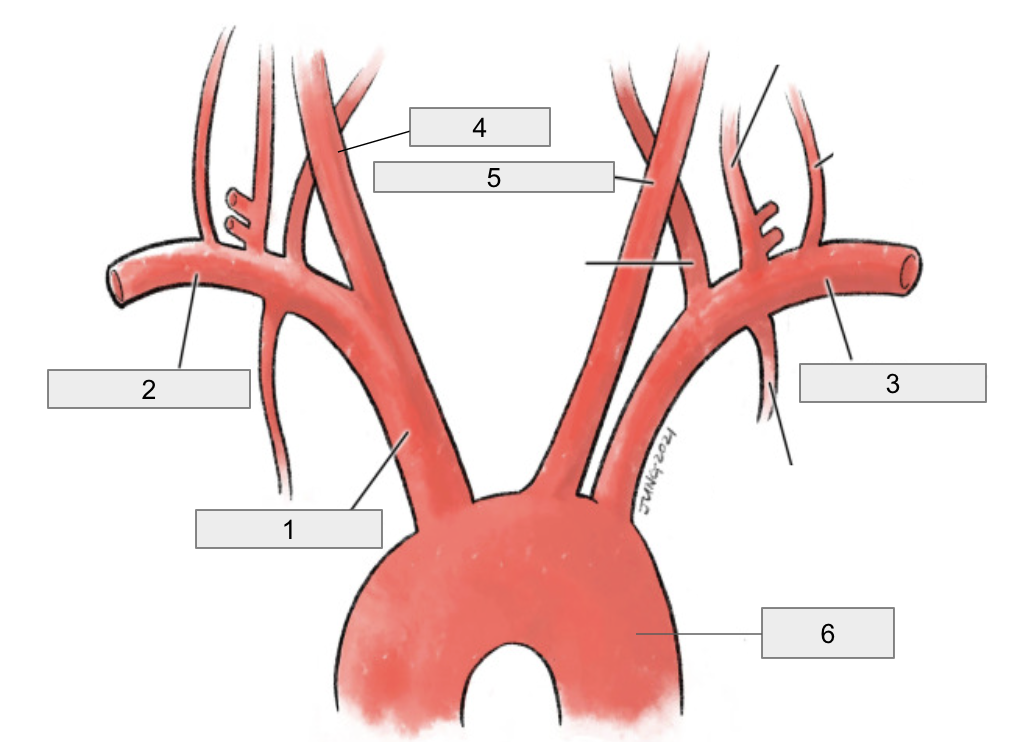
4
Right common carotid artery
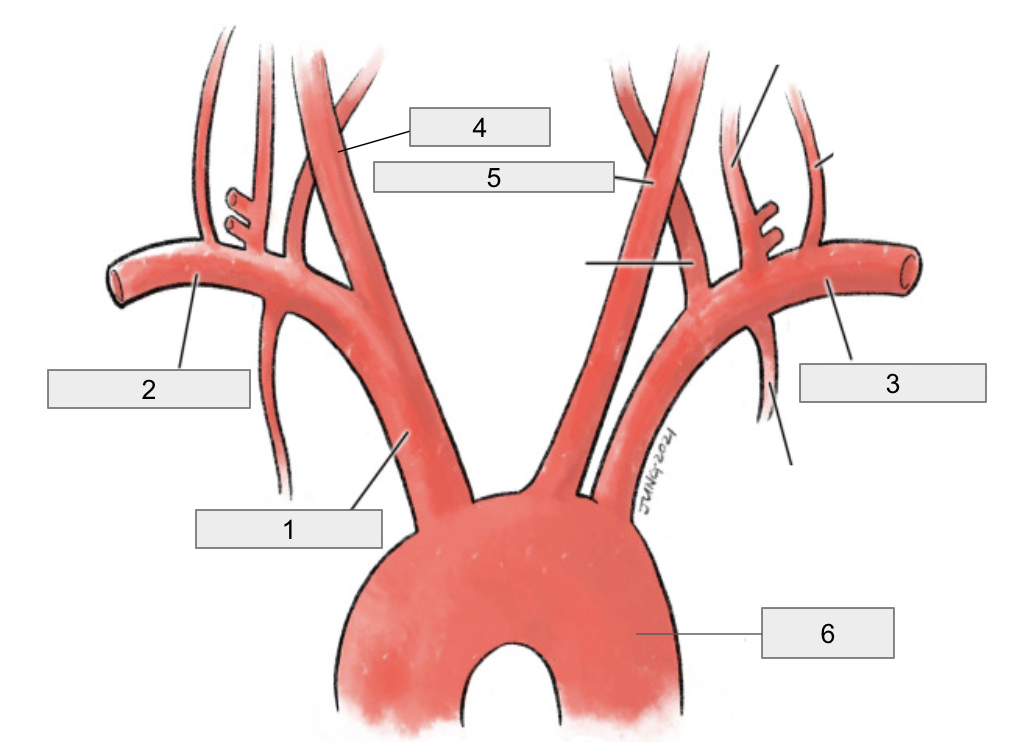
5
Left common carotid artery
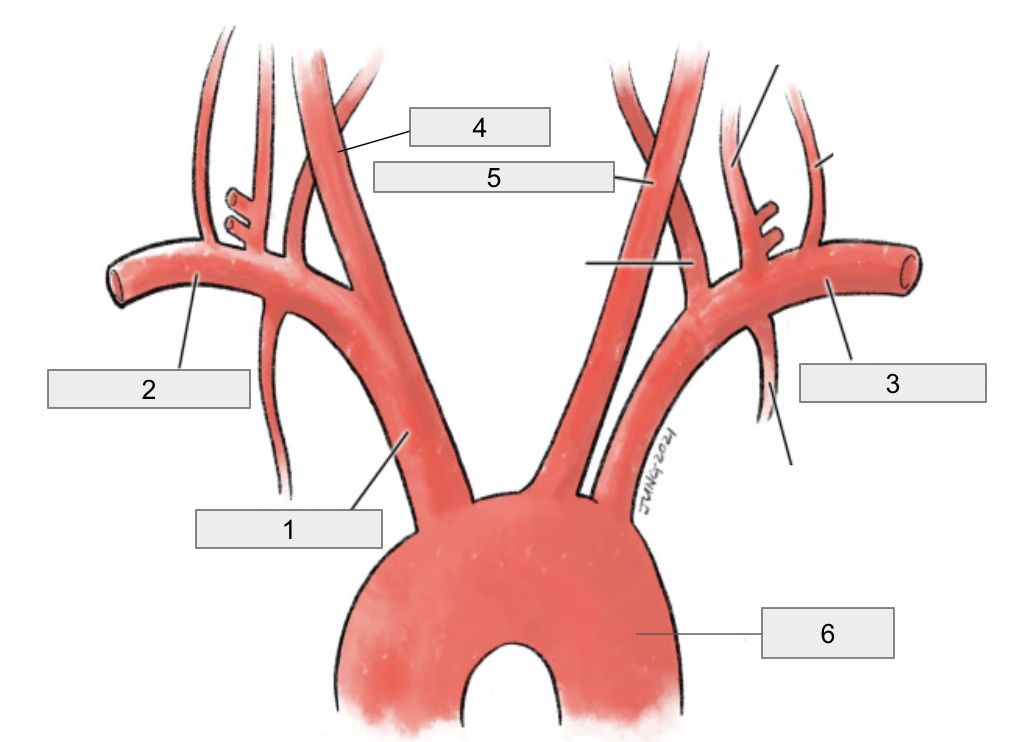
6
Descending aorta
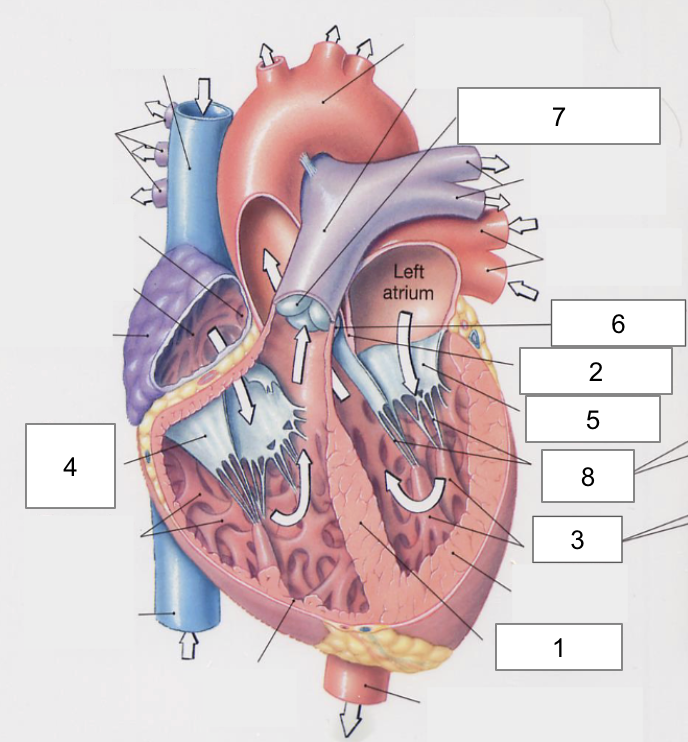
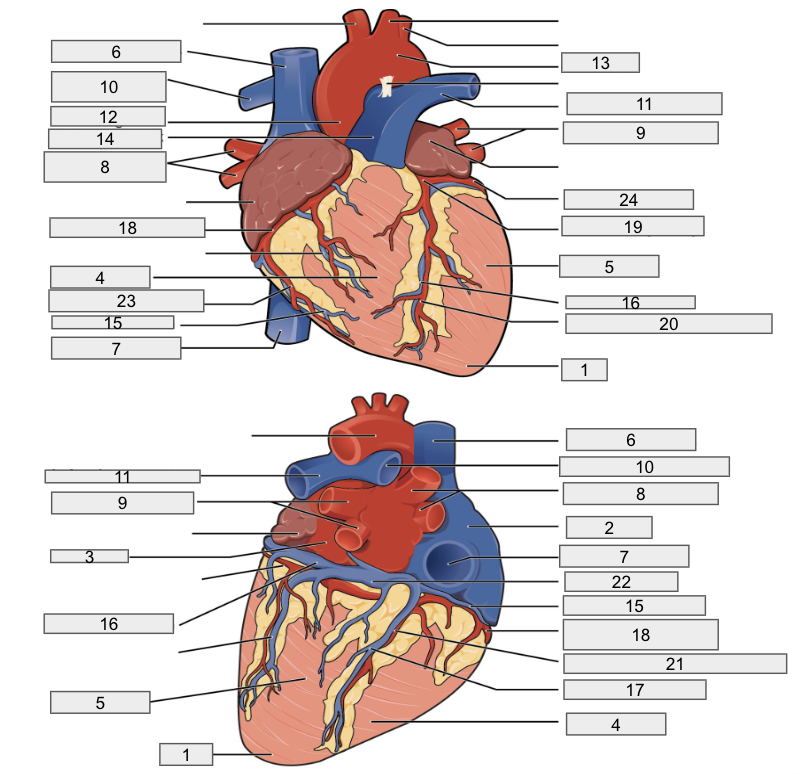
1
Interventricular septum
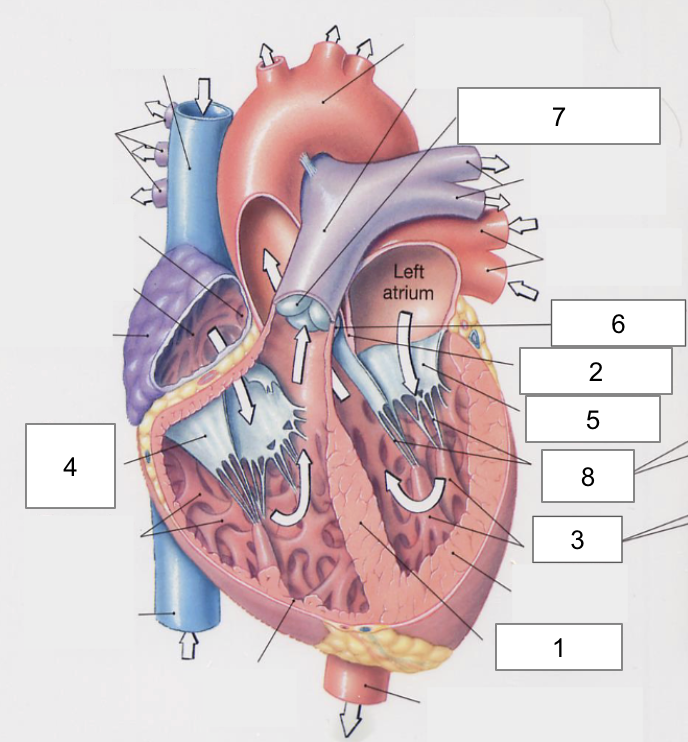
2
Interatrial septum
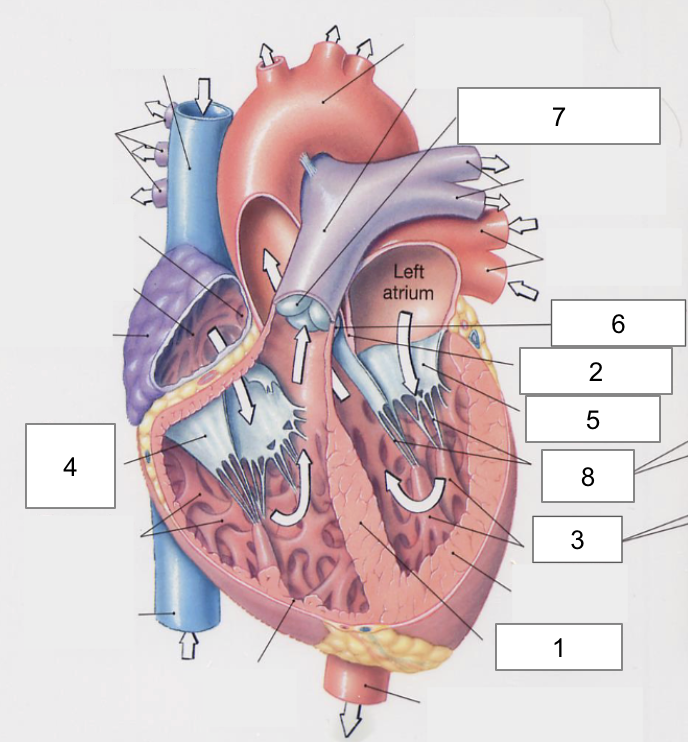
3
Papillary muscles
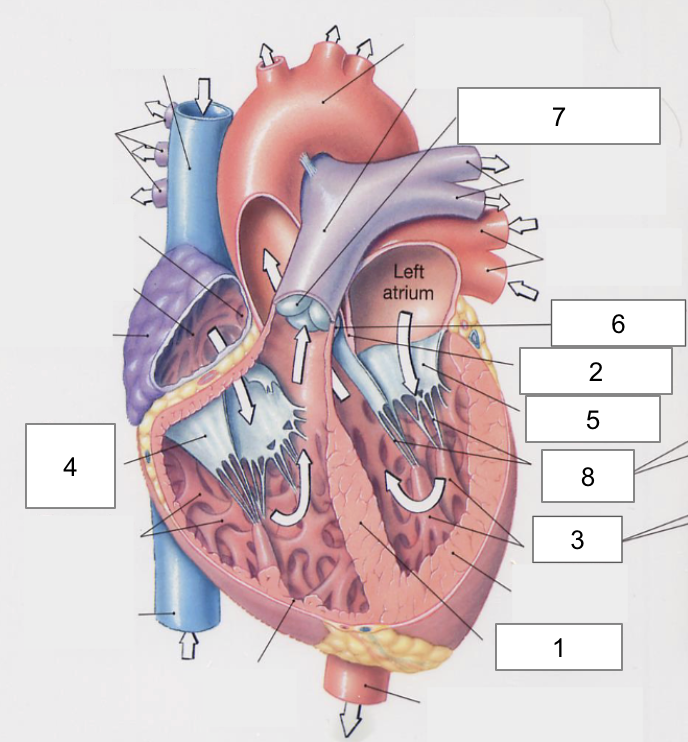
4
Tricuspid Valva
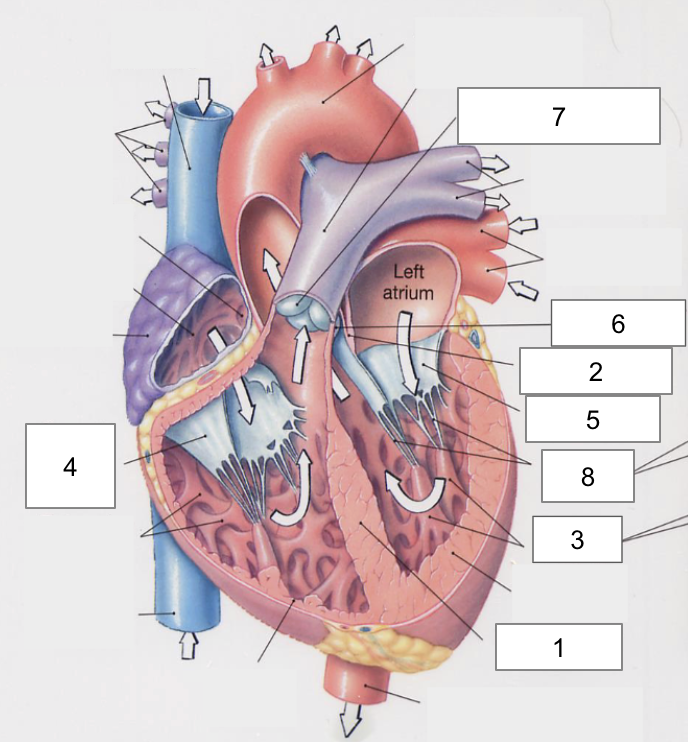
5
Bicuspid Valve
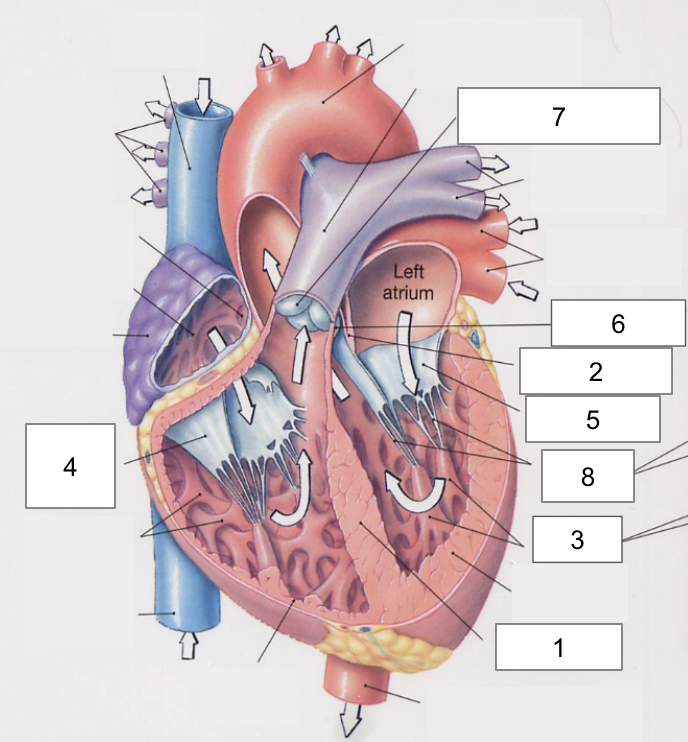
6
Aortic valve
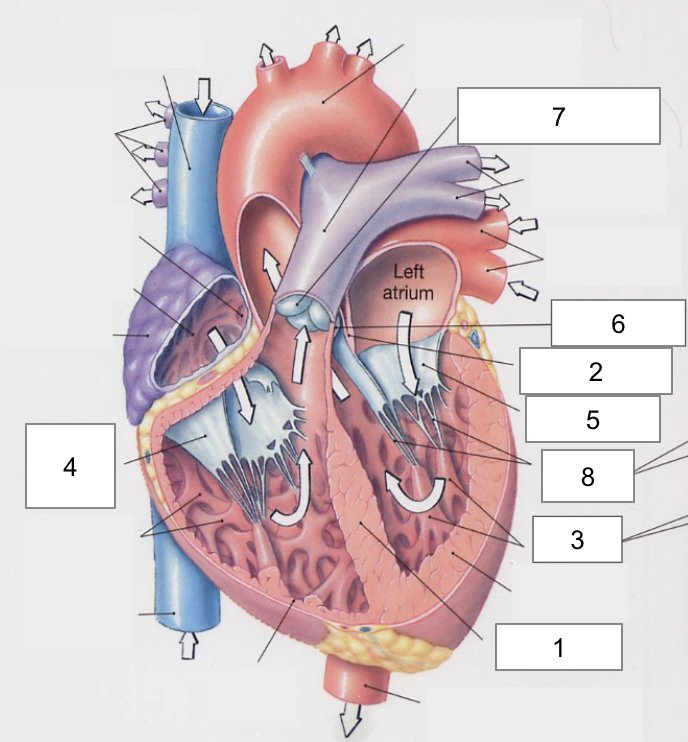
7
Pulmonary valve
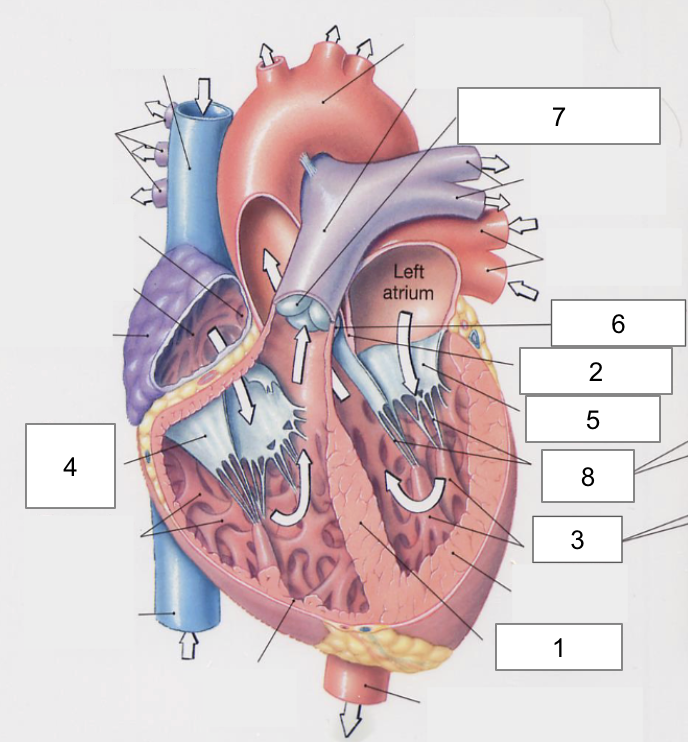
8
Chordae tendinae
Serous pericardium
Parietal layer on fibrous pericardium
Visceral layer on the heart muscle
Layers of the heart
Epicardium: visceral serous pericardium
Loose connective tissue
Myocardium: muscle layer
Muscle tissue
Endocardium: epithelium and connective tissue, inner most layer
Loose connective tissue
Atria, Right and Left chamber of the heart
Receive blood
Thin walled
Auricles
Ventricles, Right and Left Chamber of the heart
Pump blood
Thick walled
Trabecula carnae
Papillary muscles
Veins of the heart function
Bring blood to the heart
Arteries of the heart function
Carry blood away from the heart
Brings blood to the right atrium
Superior and inferior vena cava
Brings blood to the left atrium
Right and left pulmonary veins
Carries blood to the lungs
Pulmonary trunk, left and right pulmonary aortas
Carries blood to the body
Ascending aorta, Aortic arch, descending aorta
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Prevents blood flow back into the right ventricle
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Prevents blood flow back into left ventricle
Systole
contracting
Diastole
Resting and expanding
Lubb
AV valves closing
Dubb
Semilunar valves closing. This is the loudest sound
Coronary Vessels
Supply myocardium with blood and start at the base of aorta (aortic sinus)
Anterior Right Coronary Arteries
Right Coronary Artery
Marginal artery
Posterior interventricular artery
Anterior Left Coronary Arteries
Left Coronary Artery
Anterior interventricular artery
Circumflex artery
Posterior Coronary Vessels
Anastamoses
Atherosclersosis
Arteriosclerosis
Coronary Veins
Drain deoxygenated blood for the myocardium
Anterior View of Coronary Veins
Great cardiac vein
Small cardiac vein
Posterior view of Coronary Veins
Middle Cardiac Vein
Posterior cardiac Vein
Coronary sinus
Sinoatrial Node
Isolated SA node cells depolarize at 80-100 times per minute.
Parasympathetic nervous system affects. SA node to lower resting Heart Rate (HR)
to 70-80 beats per min.
Bradycardia = slower than normal HR
Tachycardia = higher than normal HR
Impulse Pathway
SA node fires → atria contract
Signal reaches AV node → brief pause (allows ventricular filling)
Impulse travels through:
AV bundle (Bundle of His)
Bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Ventricles contract
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
P wave: atrial depolarization (atrial contraction)
QRS complex: ventricular depolarization (ventricular contraction)
T wave: ventricular repolarization
Heart rate and the CNS
Parasympathetic system to slow the heart rate (vagus nerve)
Sympathetic system to increase heart rate
Tunica Interna
Endothelium
Elastic fibers
Tunica media
Smooth muscle
Controls vasoconstriction & vasodilation
Tunica externa (adventitia)
Connective tissue
Contains vasa vasorum (vessels that supply vessels)
Types of Arteries
Elastic arteries: conducting; act as a “2nd pump” (aneurysms common)
Muscular arteries: distributing
Arterioles: regulate blood flow into capillaries
Capillaries: exchange vessels
Types of Veins
Venules
Veins
How does blood return to the heart?
Skeletal muscle contractions + one-way valves
Negative pressure in thoracic cavity during inspiration