genetics exam 3
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
chromatin
DNA that’s packaged by proteins called histones; can exist in varying degrees of folding/compaction
eukaryotic cells only
condensation
the process of compacting and organizing chromatin during cell division
histones
basic proteins that package and compact DNA into structural units
nucelosomes
a complex of eight histone proteins
euchromatin
looser and more open; higher levels of transcription
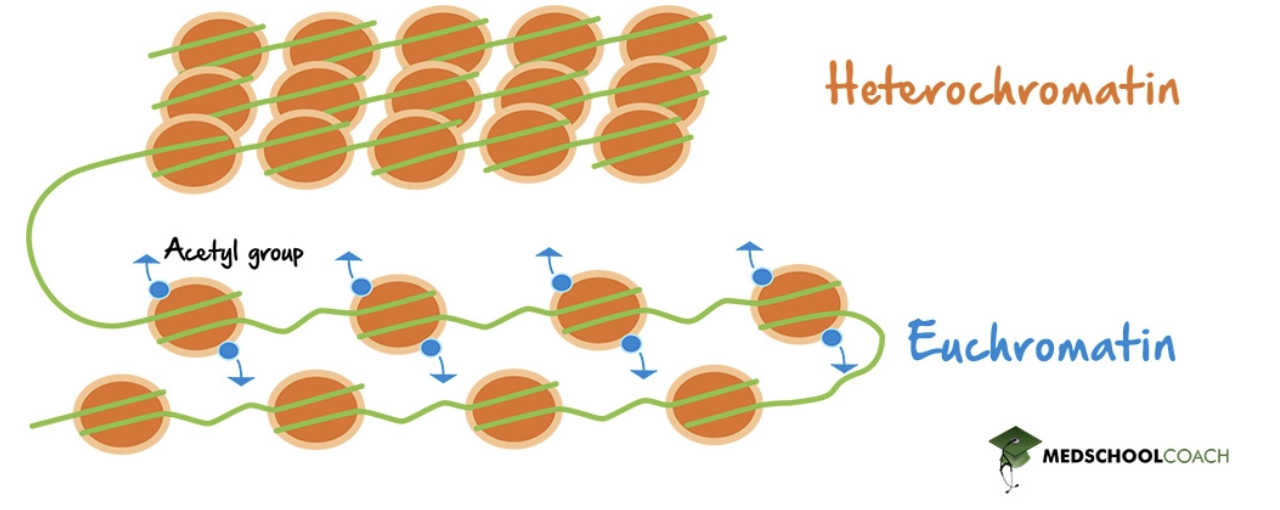
heterochromatin
more compacted, much less transcription (genes are silenced)
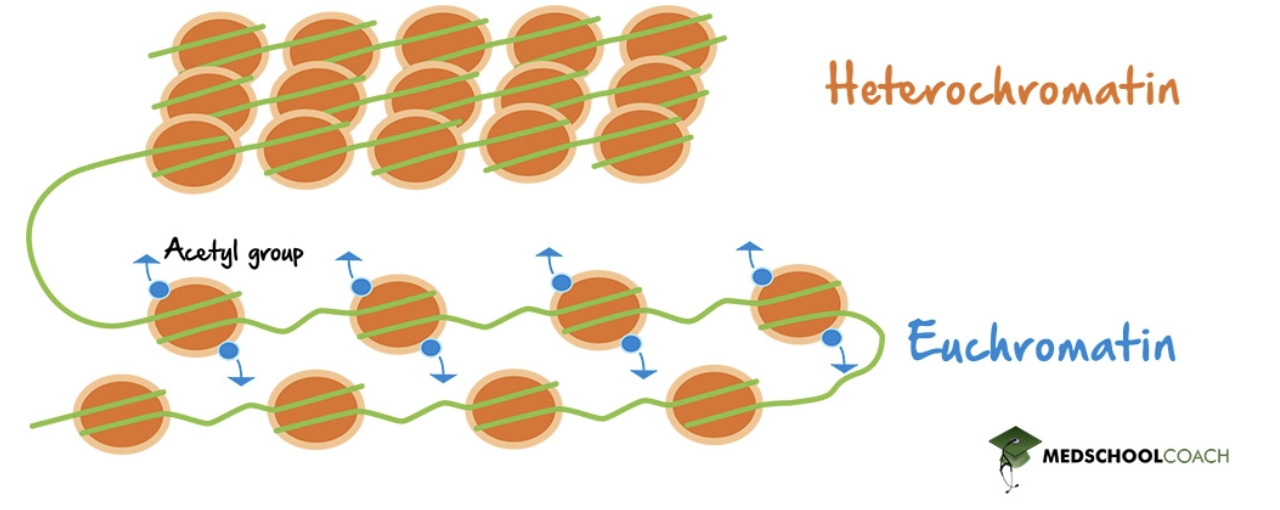
histone acetylation
a reversible process where acetyl groups are added to lysine residues on histone tails; regulates gene expression and chromatin structure, causing the chromatin to become more open
RNA interference(RNAi)
a biological process in which small pieces of RNA can shut down protein translation by binding the mRNAs that code for those proteins
double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)
required for silencing
short interfering RNA (siRNA)
20-22 nucleotides with a 3’ overhang; enters the RNA induced silencing complex and unzips the dsRNA
mRNA degredation
after the single-stranded mRNA finds a complementary strand, it gets cut up by siRNA, causing its degredation
Is transcription active or inactive in euchromatin?
euchromatin is transcriptionally active
In what way does acetylation alter transcription activity?
Acetylation promotes transcription by neutralizing the positive charge of histone tails, weakening their interaction with DNA and making chromatin more accessible to transcription machinery.
true-breeding
pollination results in 100% of the parent phenotype for all filial levels
alleles
alternative forms (variants) of a gene
trait
a specific characteristic or feature of an organism that’s genetically determined
homozygous
genotype with two alleles that are the same (SS, ss)
heterozygous
genotype with two alleles that are different (Ss)
dominant trait
a trait that is displayed by an individual that is heterozygous
recessive trait
a trait that is not displayed by an individual that is heterozygous
monohybrid cross
a genetic cross between two true breeding individuals that differ in only one trait; allows for the study of the inheritance patterns of a single gene
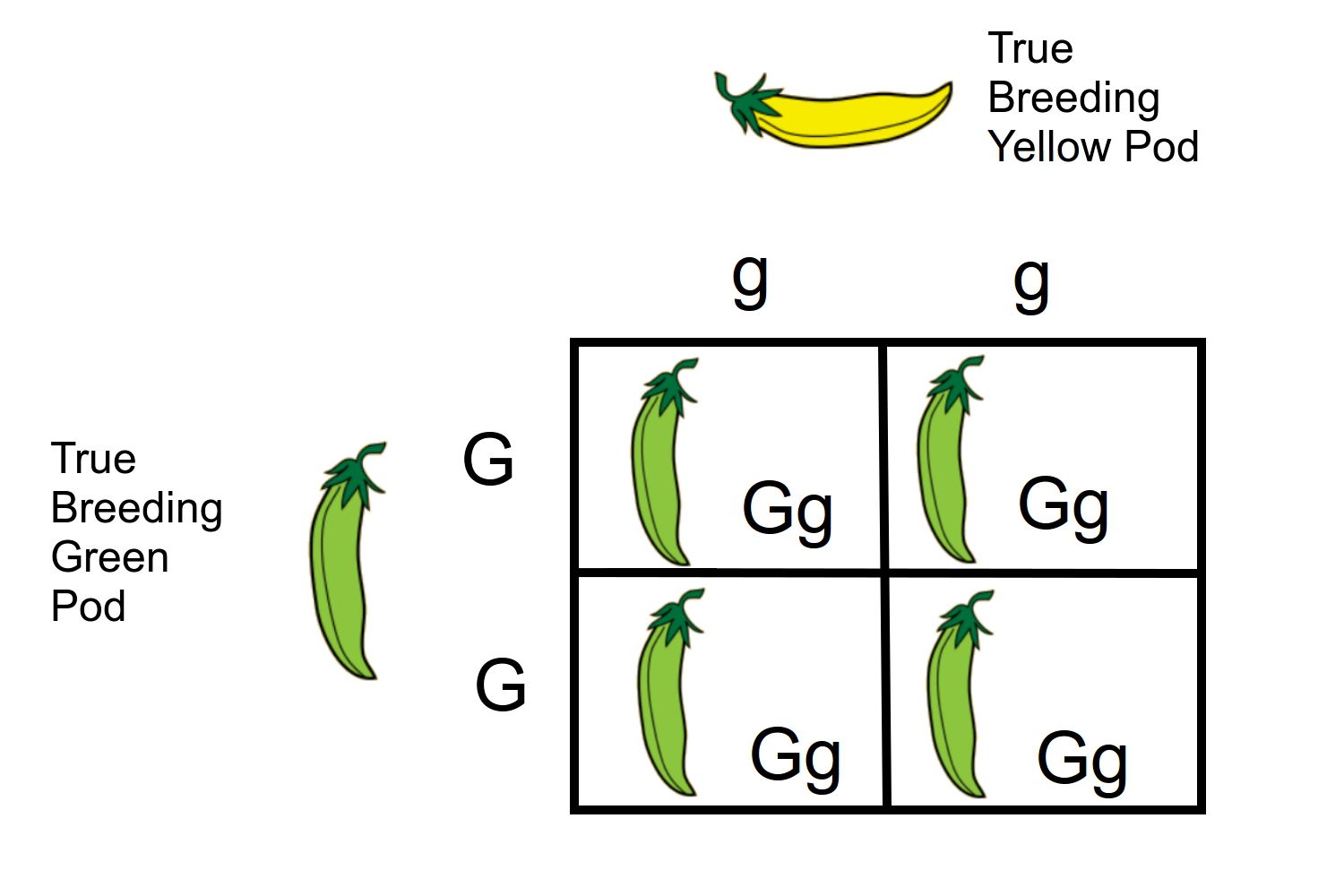
dihybrid cross
a genetic cross between two individuals with two observed traits that are controlled by two distinct genes
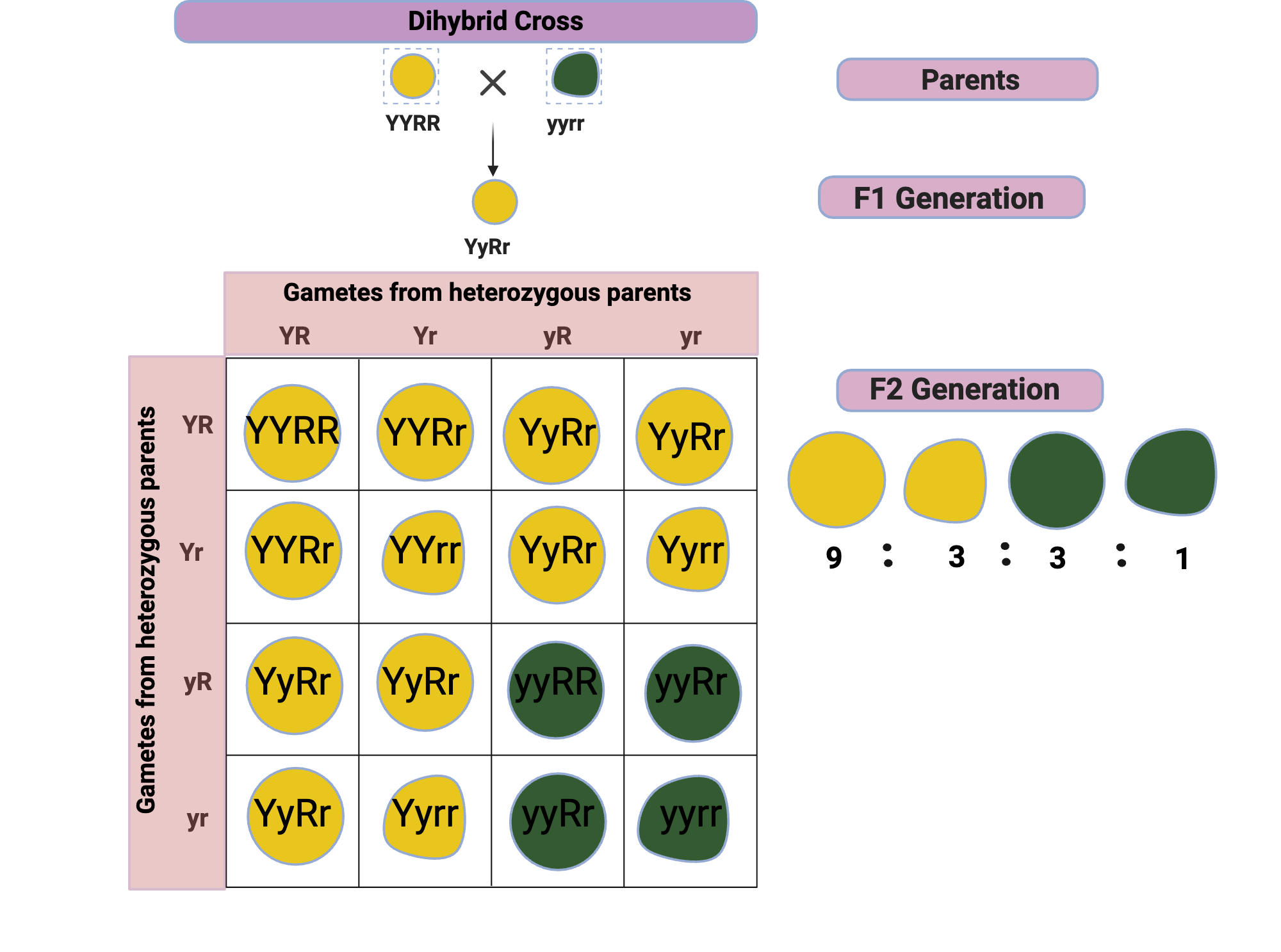
test cross
a genetic cross of an individual organism of dominant phenotype but unknown genotype and an organism with a homozygous recessive genotype/phenotype
law of segregation (Mendel’s 1st law)
during gamete formation, the two alleles for one trait seperate from one another
at fertilization, only one allele is inherited from each parent, and allele choice is random
law of independent assortment (Mendel’s 2nd law)
during gamete formation, alleles for different traits assort independently
product rule
for independent events A and B, the probability of both A and B occuring is the product of their individual probabilities [p(A and B) = p(A) x p(B)]
sum rule
the probabi;ity of either event A or event B occurring is the sum of their individual probabilities [p(A or B) = p(A) + p(B)]
family pedigrees
a visual representation of a family’s genetic history highlighting relationships and patterns of inheritance for specific traits and conditions
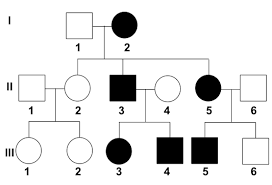
hallmarks of pedigrees for dominant traits
dominant traits can be displayed by an individual who is heterozygous or homozygous
affected individuals always have an affected parent
trait shows up at every generation - vertical pattern
hallmarks of pedigrees for recessive traits
affected individuals are always homozygous
affected individuals can have two unaffected parents
when rare, recessive traits can appear without family history - horizontal pattern
“carrier” for an allele
an individual who has a particular allele; term most often used for individual who has the allele but does not show the trait
At a biochemical level, how can we explain the smooth or wrinkled pea phenotypes? Why is the smooth trait dominant and the wrinkled trait recessive?
The S (smooth) allele allows for translation of SBE1 which builds up branched starch in the organism, allowing it to retain water better. The s (wrinkled) allele does not allow for formation of branched starch and is therefore unable to retain water as well.
Heterochromatin is…
a. more condensed
b. less condensed
a. more condensed
A short interfering RNA (siRNA) triggers RNAi. This molecule is…
a. single-stranded, antisense
b. single-stranded, sense
c. double-stranded
c. double-stranded
According to Mendel, a parent possess how many “particles” (alleles) of information for a trait?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
b. 2
According to Mendel, how many alleles for a trait does a parent pass along to their child?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
a. 1
True or False
Heterochromatin is an open structure that leads to transcription activation.
False
True or False
Euchromatin does allow for gene transcription.
True
True or False
DNA is wrapped around proteins called nucleosomes.
True
How many histone proteins compose a nucleosome?
a. 2
b. 6
c. 8
d. 10
c. 8
True or False
Histone tails are acetylated to convert heterochromatin into euchromatin.
True
True or False
Fire and Mello’s experiment concluded that double-stranded RNA stimulates gene silencing.
True
What is a structural characteristic of siRNA?
a. 20-22 nucleotides long
b. double-stranded RNA
c. 3’ overhang
d. all of the above
d. all of the above
True or False
In RNAi, short interfering RNAs are designed to complement the target sequence/gene they must silence.
True
In eukaryotic genomes, regions of _____ are transcriptionally active while regions of _____ are transcriptionally silent.
a. heterochromatin, euchromatin
b. euchromatin, heterochromatin
c. none of the above
b. euchromatin, heterochromatin
True or False
We would expect histones with euchromatin to be acetylated.
True
Which of the following is NOT a method of eukaryotic gene regulation?
a. histone acetylation
b. chromatin compaction
c. RNA interference
d. all of the above are methods of eukaryotic gene regulation
d. all of the above are methods of eukaryotic gene regulation
In eukaryotes, histone acetylation leads to:
a. no change in chromatin organization
b. chromatin condensation
c. chromatin decondensation
c. chromatin decondensation
Which of the following is true of a short interfering RNA (siRNA)?
a. short length (19-22 nt)
b. 3’ overhangs on each end
c. RNA-RNA base-pairing
d. all of the above
d. all of the above
The molecule that triggers RNA interference is:
a. single-stranded sense RNA
b. single-stranded antisense RNA
c. double-stranded RNA
d. none of the above
c. double-stranded RNA
True or False
In eukaryotes, some mRNAs are not translated because they are silenced by RNA interference.
true
chromosome
a thread-like structure made of DNA and protein
haploid
a cell containing one of each chromosome (1n)
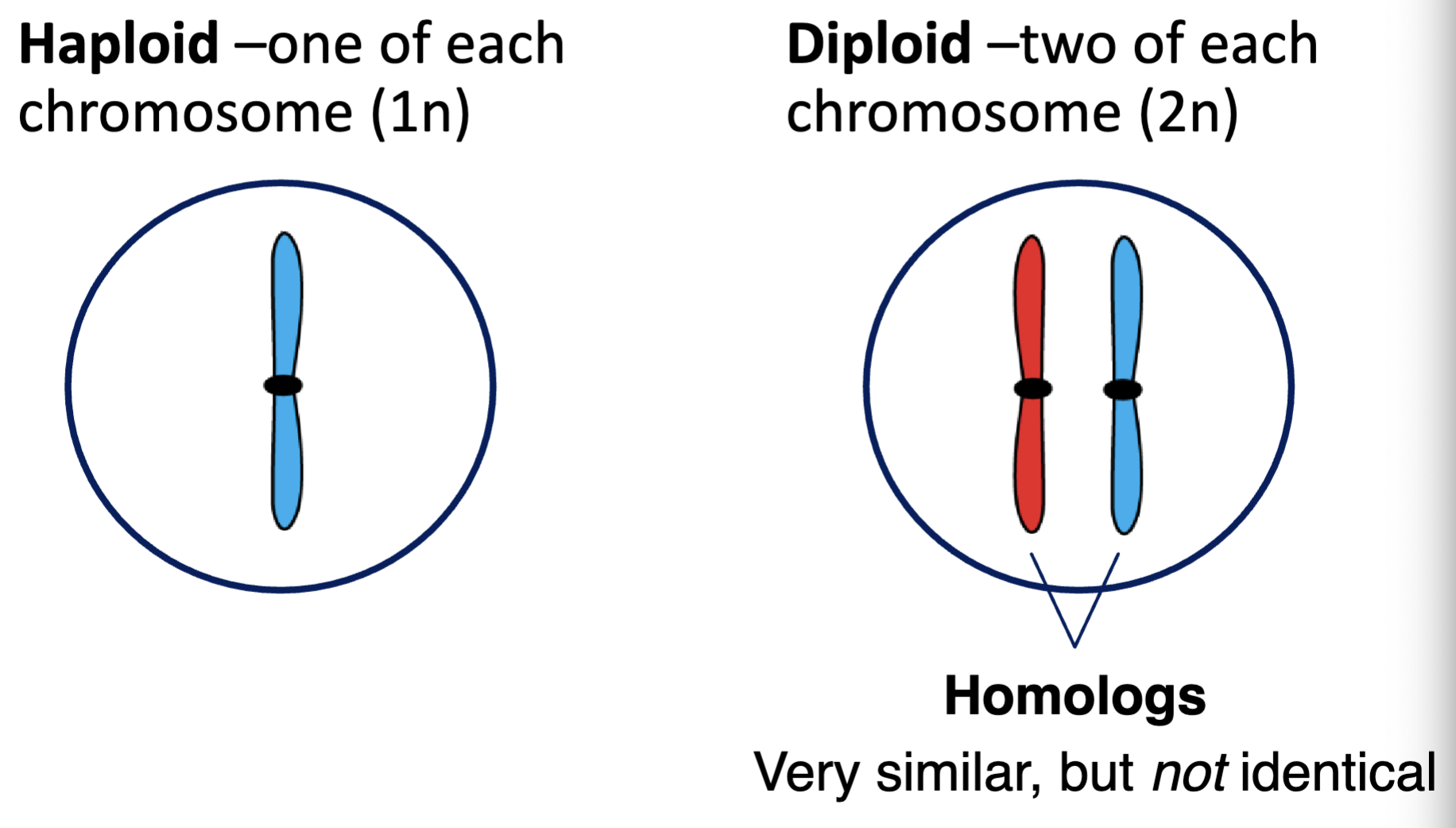
diploid
a cell containing two of each chromosome (2n)
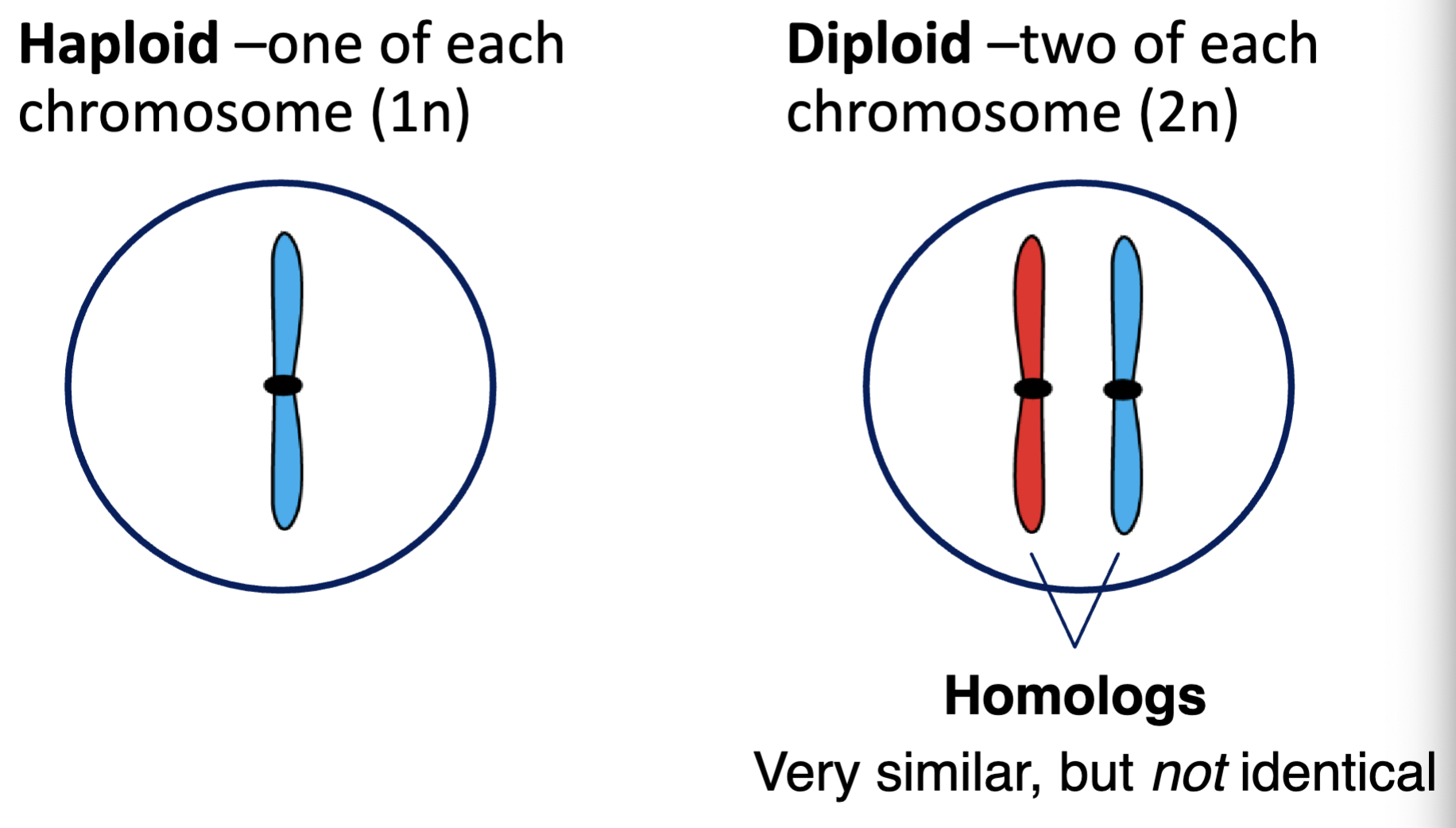
homolog (or pair of homologs)
pairs of chromosomes that have the same genes in the same order, but may have different alleles of those genes
chromatid
one of the two identical halves of a homologous pair that has been replicated in preparation for cell division
sister chromatids
the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome that are formed during DNA replication; separated during cell division
centromere
constricted regions on chromosomes that serve as the attachment point for spindle fibers and linking sister chromatids
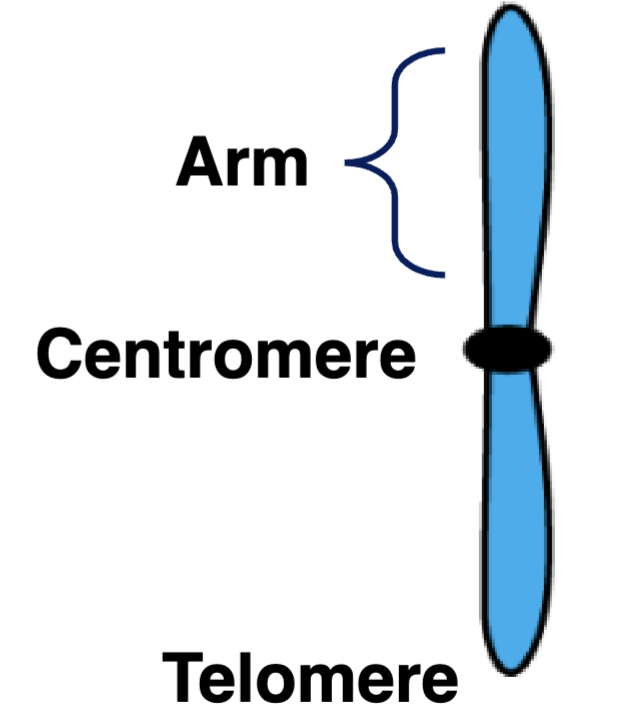
chromosome arm
two arms on a chromosome that are separated by the centromere
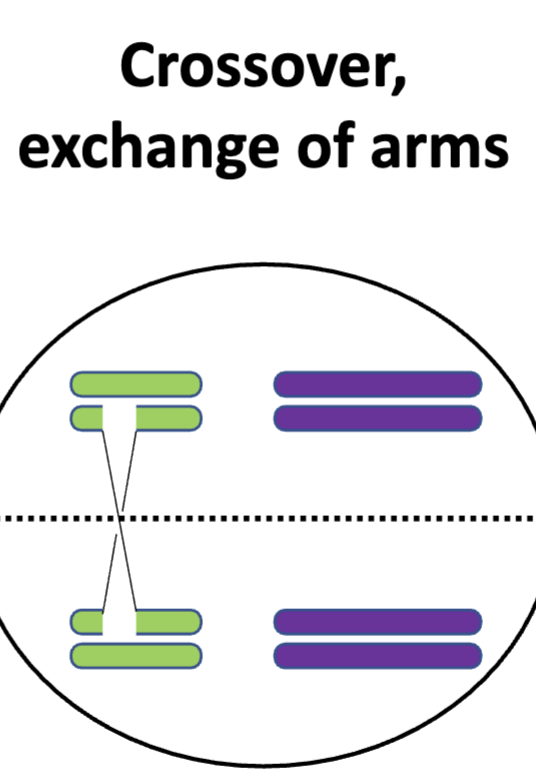
crossover
exchange of the arms of the chromosomes between two homologous chromosomes’ non-sister chromatids; meiosis only
Cohesin protein
a protein that holds together the two chromosomes of a sister chromatid (shown in yellow on slides)
Separase enzyme
“pac-man” enzyme that cuts cohesin once spindle tension is present
segregation
meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, allowing for only one homolog per gamete
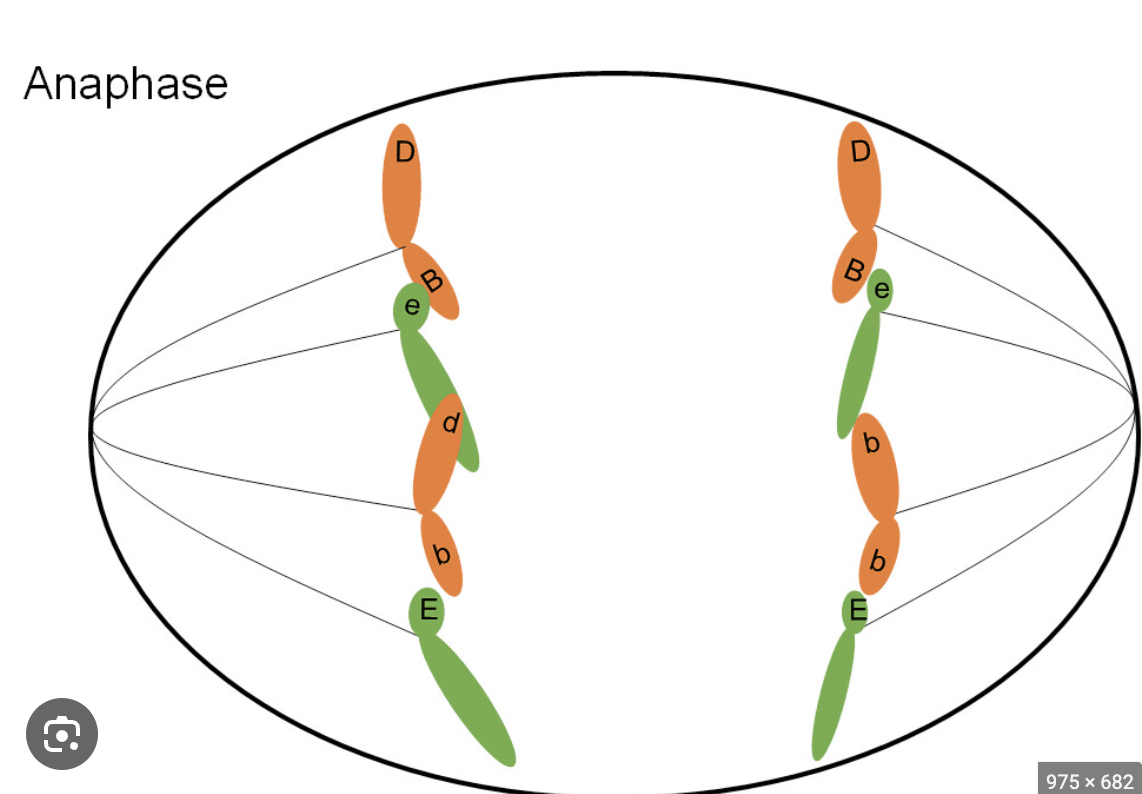
spindles
attach to the centromere and pull sister chromatids and individual chromosomes apart during mitosis and meiosis
microtubule organizing centers
a cellular structure that nucleates and organizes microtubules
S phase
part of the cell cycle where DNA replication occurs, ensuring each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes
mitosis
a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell; maintains chromosome number; haploid and diploid cells can unde
meiosis I
sister chromatids exchange arms (crossovers) between homologs; each pair of homologs attached to both poles and aligned at cell equators; regulated cutting of cohesin at arms via separase enzyme
meiosis II
sister chromatids align at equator and separate
daughter cell
either of the two cells formed when a cell undergoes mitosis
gamete
eggs and sperm; a haploid cell
What is segregated at mitosis?
sister chromatids
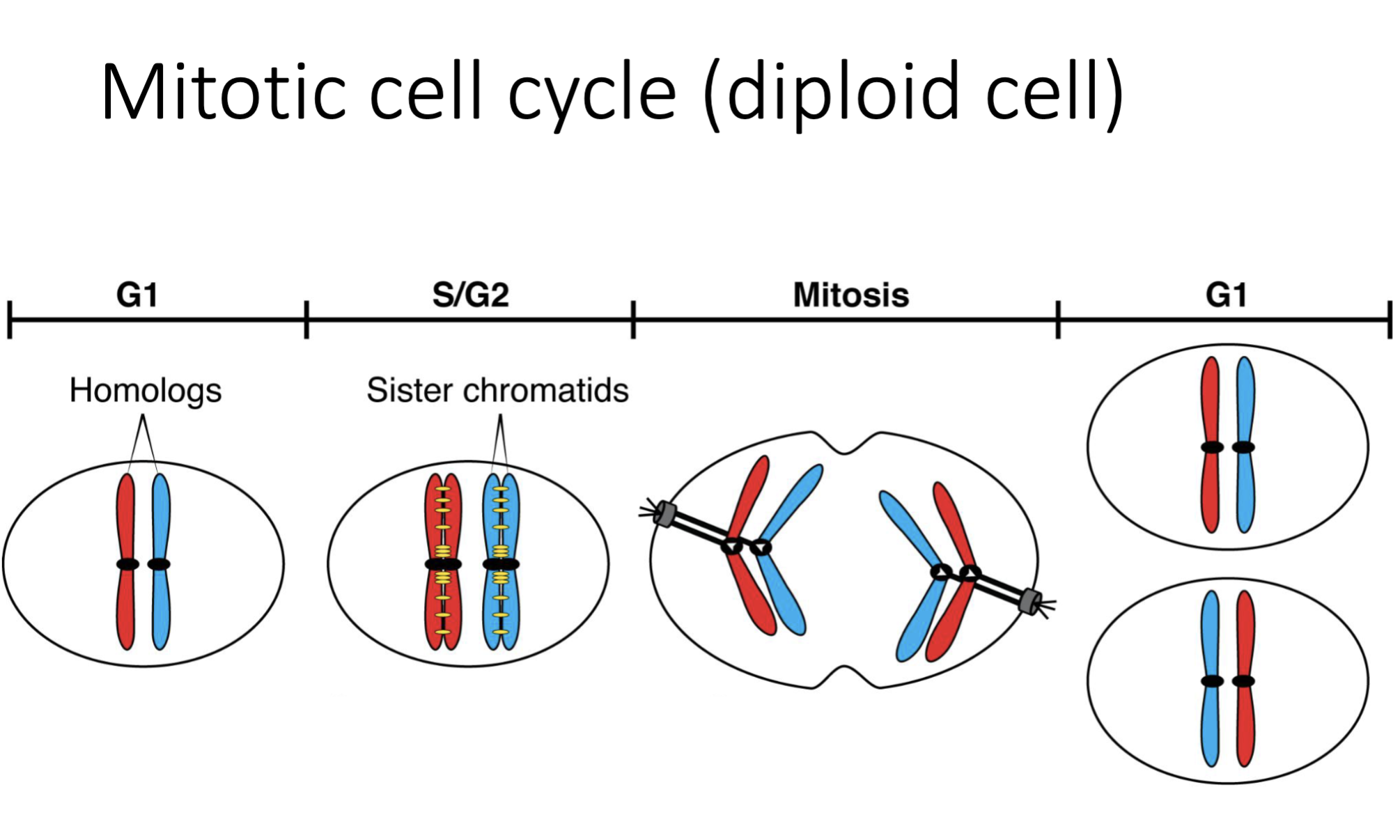
Describe the products of mitosis (include picture)
two genetically identical daughter cells
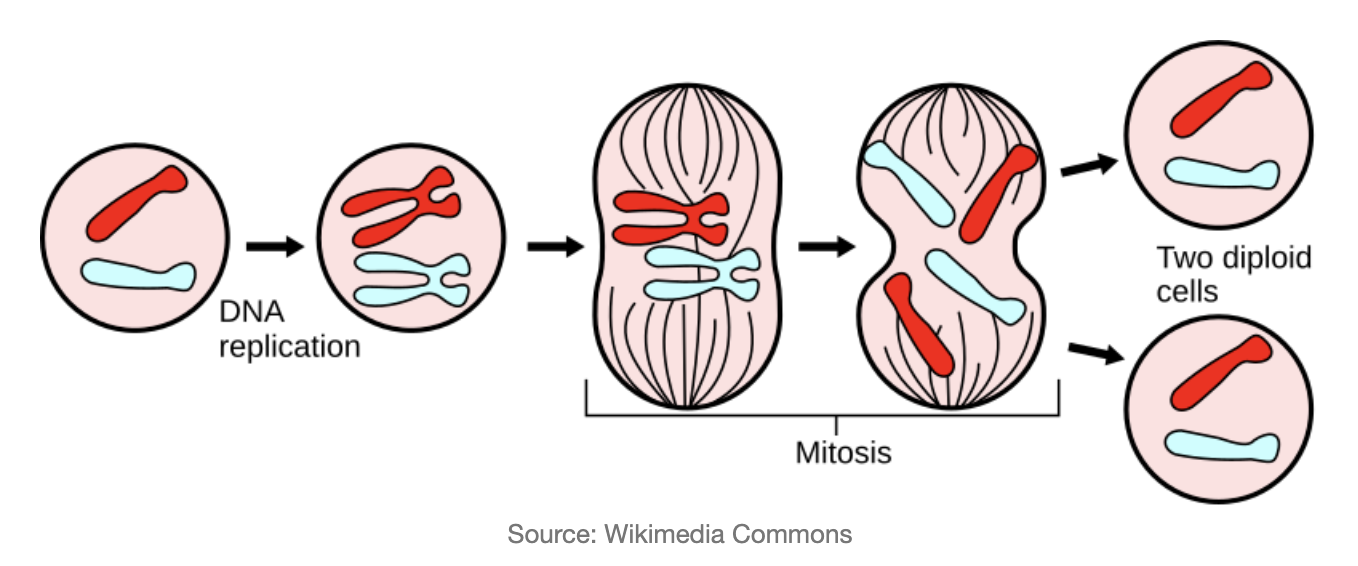
What is segregated at each phase of meiosis? What are the products of meiosis?
1) homologous pairs separate producing two haploid cells
2) sister chromatids separate to produce four haploid daugter cells
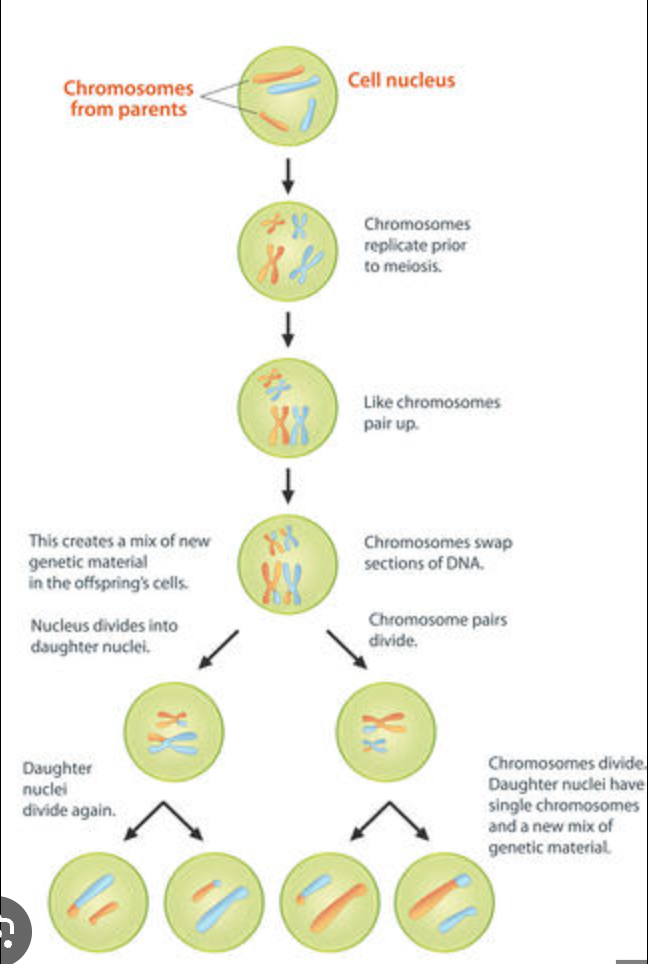
What happens in meiosis that allows a doubly heterozygous parent to produce gametes with all possible combinations?
Crossovers and alternative alignments
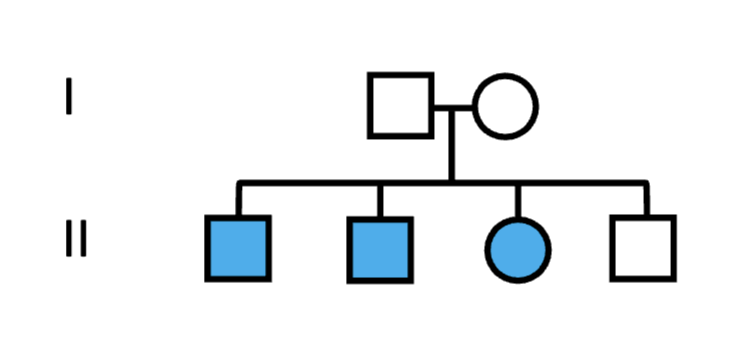
This trait must be…
a. dominant
b. recessive
c. could be either
b. recessive
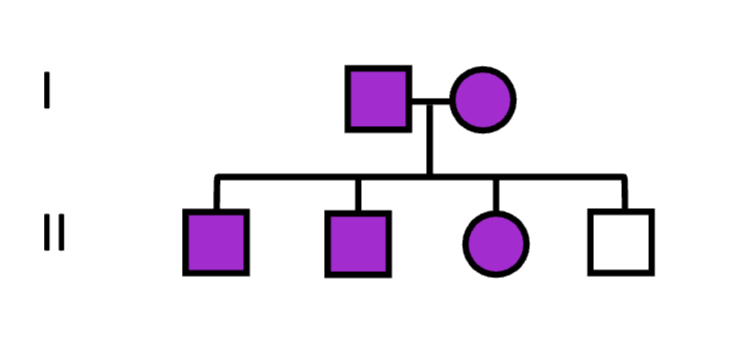
Both parents must be…
a. homozygous
b. heterozygous
c. could be either
b. heterozygous
The probability of producing a Smooth pea from a cross between heterozygous parents is…
a. 0.25
b. 0.50
c. 0.75
d. 1.00
c. 0.75
True or False
Alleles are alternative forms of genes.
true
In eukaryotes, how many total alleles does an individual possess per trait?
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
b. two
In eukaryotes, how many total alleles does an individual receive from a parent?
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
a. one
What term refers to the combination of alleles that an individual possesses?
a. phenotype
b. genotype
b. genotype
True or False
A phenotype corresponds to an observable trait or characteristic.
true
True of False
If an individual has a homozygous genotype, that means both alleles are different.
false
Which law explains how members of different gene pairs are independently assorted into each gamete?
a. Mendel’s first law
b. Mendel’s second law
b. Mendel’s second law
Which of the following statements explains Mendel’s first law?
a. two alleles for one trait will separate from each other
b. only one allele is randomly inherited from each parent
c. both statements are correct
d. neither statement is correct
c. both statements are correct
True or False
In dominant traits, a heterozygous individual WILL display the trait.
true
True or False
Wild-type traits will always be dominant.
false
True or False
An autosomal trait is a trait located on a sex chromosome.
false
Which of the following is a hallmark of recessive traits in pedigrees?
a. affected individuals are always homozygous
b. affected individuals may be heterozygous or homozygous
a. affected individuals are always homozygous
Which of the following is another hallmark of a recessive trait in pedigrees?
a. affected individuals always have an affected parent
b. affected individuals can have two unaffected parents
b. affected individuals can have two unaffected parents
Pedigrees that express a dominant trait display
a. vertical pattern
b. horizontal pattern
c. no pattern
a. vertical pattern
hallmarks of X chromosome-linked traits
an allele located on the X chromosome
affected father will never pass to sons
affected father will pass allele to all daughters
males only have 1 x-linked allele so they will display the recessive trait
parental type
progeny with the same allele combination as either parent
recombinant type
progeny with a different allele combination than both parents
recombination frequency (RF)
measures the likelihood of two genes being separated during meiosis
RF = (# recombinant progeny / # total progeny) x 100
unlinked and linked genes
when two alleles are linked, they tend to be inherited together
rule for linked genes: # parental > > > # recombinant
map unit
measure of distance between two genes on the chromosome
1% RF = 1 map unit
single crossover
double crossovers