ocr a level coasts
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
system
a group of objects and the relationship between them
geomorphic processes
processes resulting in the formation and shaping of lanforms and landscapes
open systems
a type of system whose boundaries are open to both inputs and outputs of energy and matter
input
the addition of energy or materials to a system
output
the transfer of energy and/or materials out of a system
deposition
the laying down of sediment transported by rivers, waves, glaciers and wind, as energy levels decline
weathering
the in situ breakdown of rocks at, or near, the land surface by physical, chemical and biological processes.
mass movement
the downslope transportation of material under gravity.
erosion
the wearing away and/or removal of rock and other material by a moving force.
stores
the parts of a system in which material and/or energy accumulates.
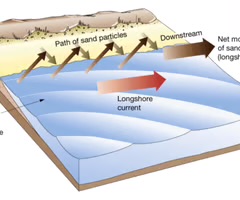
longshore drift
the movement of sediment by waves and currents along a coastline.
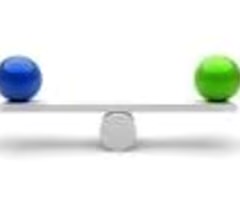
equilibrium
a long-term balance between inputs and outputs in a system.
negative feedback
an automatic response to change in a system that restores equilibrium.
sediment cell
a stretch of coastline and its associated nearshore area within which the movement of coarse sediment, sand and shingle is largely self-contained.
closed system
a system with inputs and outputs of energy, but wiothout any movement of materials across system boundaries.
fetch
the distance of open water in one direction from a coastline, over which the wind can blow.
aeolian processes
erosional, transportational and depositional processes by the wind
wave period
the time period between successive wave crests arriving at a given point
storm waves
a wave generated locally by high wind energy
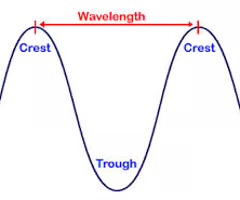
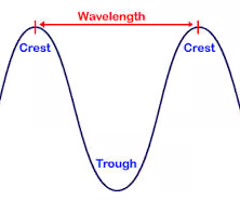
crest
the highest point of a wave

trough
the lowest point of a wave
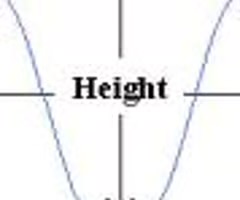
wave height
the vertical distance between trough and crest
wavelength
horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
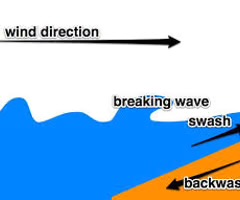
swash
the movement of water up a beach after a wave has broken
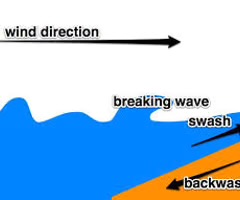
backwash
flow of water down a beach after a wave has broken
constructive waves
waves in which the swash is more powerful than the backwash
destrictive waves
waves in which the backwash is more powerful than the swash
breaker zone
near shore area where waves first begin to break
swash zone
the part of the beach dominated by swash and backwash
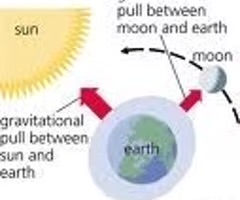
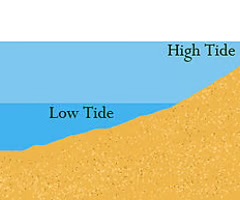
tide
the periodic rise and fall of the sea level under the gravitational pull of the moon and sun
tidal range
the vertical difference in height between consecutive high and low waters over a tidal cycle
geology
the study of the earth, specifically rocks and the planet's crust
lithology
the chemical and physical characteristics of rock types
structure
the physical characteristics of rocks, including their jointing, bedding, faulting, angle of dip etc.
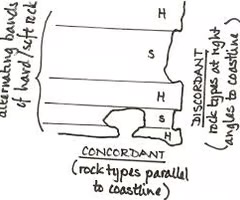
discordant
a coastline with bands of different geologies lying perpendicular to the coastline
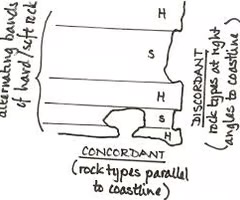
concordant
a coastline with bands of different geologies lying parallel to the coastline
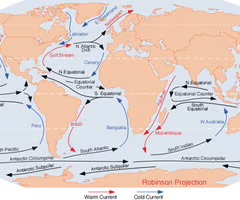
ocean currents
the large scale horizontal flow of ocean water (at the surface and at depth) driven by planetary winds and contrasts in water temperature and salinity.
sub-aerial processes
a collective term for weathering and mass movement processes
sediment budget
the balance of sediment volume entering and exiting a particular section of the coast
Physical weathering
disintegration of rocks by physical forces, like pressure release, ice wedging, freezing and thawing, exfoliation
freeze-thaw
a mechanical weathering process caused by water, confined in rock joints, expanding as it freezes, and as a result breaking rocks into smaller particles

pressure release
the disintegration of rocks caused by a release of pressure by the removal of overlying mass.
thermal expansion
increase in volume of water due to its rise in temperature
salt crystallisation
a mechanical weathering process whereby formation of salt crystals leads to disintegration of rocks
chemical weathering
decomposition of rocks by chemical processes leading to the creation of new chemical componds.
oxidation
a chemical process that weathers certain types of rock and involves the absorption of oxygen from either the atmosphere or water by rock minerals
carbonation
a chemical weathering process whereby carbon
solution
the chemical weathering process by which rock minerals are dissolved
hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that leads to decomposition of rocks by the addition of water.
hydration
the breakdown of rocks by cycles of wetting (expansion) and drying (contraction)
biological weathering
the breakdown of rocks through the chemical and physical action of living organisms e.g. burrowing, tree roots etc.
root action
the biological weathering process by which rock is broken apart as roots grow and expand

burrowing
the biological weathering process caused by animals digging.
chelation
a type of chemical weathering caused by acids derived from rainwater and organic material
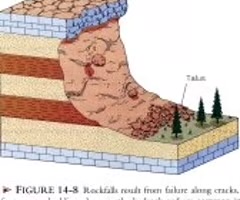
rockfall
a mass movement process affecting steep slopes over 70 degrees in angle
slide
a mass movement process where cohesive material moves downslope along a straight slip plane.

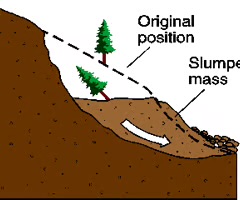
slump
a mass movement process where material moves downslope along a curved slip plane
abrasion
an erosion process whereby material being transported rubs against surfaces leading to smoothed surfaces
attrition
the erosion of sediment transported by rivers, glaciers, waves and winds leading to smaller rounder particles
hydraulic action
the erosion process by which water forces air into cracks in the rock leading to disintegration
corrosion
The decomposition of rock due to a chemical reaction with water
traction
the transport process by which large material is rolled along the river or sea bed.
saltation
the transport process by which material is hopped or bounced along the bed
suspension
the transport process by which fine material is carried by the energy of the water
solution transport
the transport process by which minerals are dissolved and carried by the water
marine processes
processes operating upon a coastline that are connected with the sea, such as waves, tides and longshore drift.
fluvial processes
processes involving the work of running water on the surface of Earth
flocculation
a process by which salt causes the aggregation (clumping) of minute clay particles into larger masses that are too heavy to remain suspended in water
erosional landforms
the category of landforms shaped predominantly by erosion processes
cliffs
rugged steep or vertical landforms found on coastlines.
shore platforms
A smooth erosional surface that develop in the surf zone adjacent to coast lines.
bay
an inlet along a coastline, usually between two headlands
headland
a promontory extending out from the coastline
wave refraction
the process by which waves slow down and wave crests bend towards due to the uneven shallowing of water.
blowholes
Formed when a joint between a cave and the land surface becomes enlarged and air can pass through it
geos
a narrow, steep sided inlet
cave
an erosional landform usually found in a headland between low water mark and high water mark
arch
an erosional landform formed when a cave is eroded through the headland.
stack
a tall erosional landform formed by the collapse of an arch
stump
a short erosional landform formed after the partial collapse of a stack
depositional landforms
the category of landforms shaped predominantly by deposition
beach
A depositional landform comprising of an accumulation of sediment on the shoreline
spring tide
The tide with the greatest tidal range (the highest high tide and the lowest low tide)
neap tide
The tide with the smallest tidal range (the lowest high tide and the highest low tide)
intertidal range
The vertical distance between high tide and low tide
wave energy
a measure of the kinetic energy carried by waves
beach profile
a cross section of beach, measured with a clinometer, tape-measure and ranging poles
beach angle
a measure of how steep or shallow a beach is
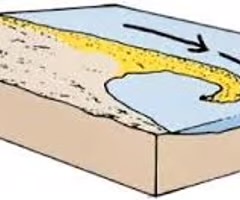
spit
a depositional landform occuring after a sharp change in the direction of the coastline. Formed by longshore drift transporting sediment and depositing it as a finger protruding out into the sea.

salt marsh
a depositional landform often forming in the lee of a spit where deposited sediment is innundated twice daily by tides. This creates a halosere which is populated by halophytic species
onshore bar
formed when a spit extends across a whole bay and rejoins the land forming a lagoon behind it

tombolo
a beach which joins the mainland to an offshore island

turbid
cloudy or muddy conditions owing to sediments held in suspension

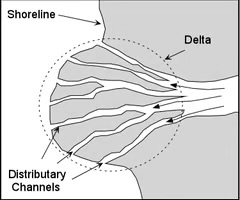
delta
a large area of sediment found at the mouth of a river.
cuspate delta
a pointed extension to the coastline caused by sediment accumulation which is shaped by regular, gentle currents from opposite directions
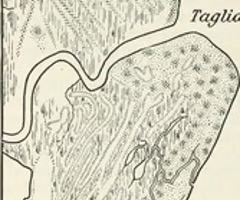
arcuate delta
a delta in which there is sufficient sediment supply for the delta to grow seawards, but wave action is strong enough to smooth and trim its leading edge.

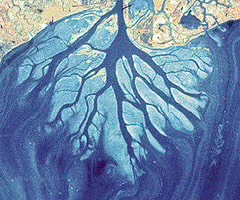
birds foot delta
a delta in which distributaries build out from the coast in a braiding pattern, with river sediment supply exceeding the rates of removal by waves and currents.
Are tides predictable?
Yes because it happens at regular intervals.
Two high and two low tides are experienced at coastal places on Earth every 24 hours.
What are the two types of currents?
Surface ocean currents (wind) and deep ocean currents (temperature/salinity)
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface