Bones, Cartilage, and STS
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Bones and cartilage make up the ________ system
Skeletal
What are functions of bone and cartilage
gives shape and movement
Protects softer tissue
Reservoirs for fats, minerals, blood cell production
Provides connection, support, and locomotion
What is the most common pediatric skeletal malignancy
Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcomas happen in what age group?
10-30
What is the 2nd most common bone tumor in adults?
Osteosarcoma
What is the 1st most common bone tumor in adults?
Chondrosarcoma
What age group is Ewings Sarcoma most commonly seen in?
Teens and Young Adults
What is the most common bone tumor malignancy
Bone mets
Bone/Joint cancer has ______ (good/poor) prognosis with _______ (little/large) incidence
Poor; Little
Is there an exact cause of bone cancer?
No
What are suspected risk factors for Osteosarcoma
Genetics
Higher birth weight/increased height
Paget’s Disease
Hyperparathyroidism
Osteomyelitis
What is Paget’s Disease
Breakdown of old bone is interfered with new bone formation
What does Hyperparathyroidism cause
Loss in bone calcium
What gland regulates calcium in the blood
Parathyroid
What is Osteomyelitis
Infection of bone/bone marrow
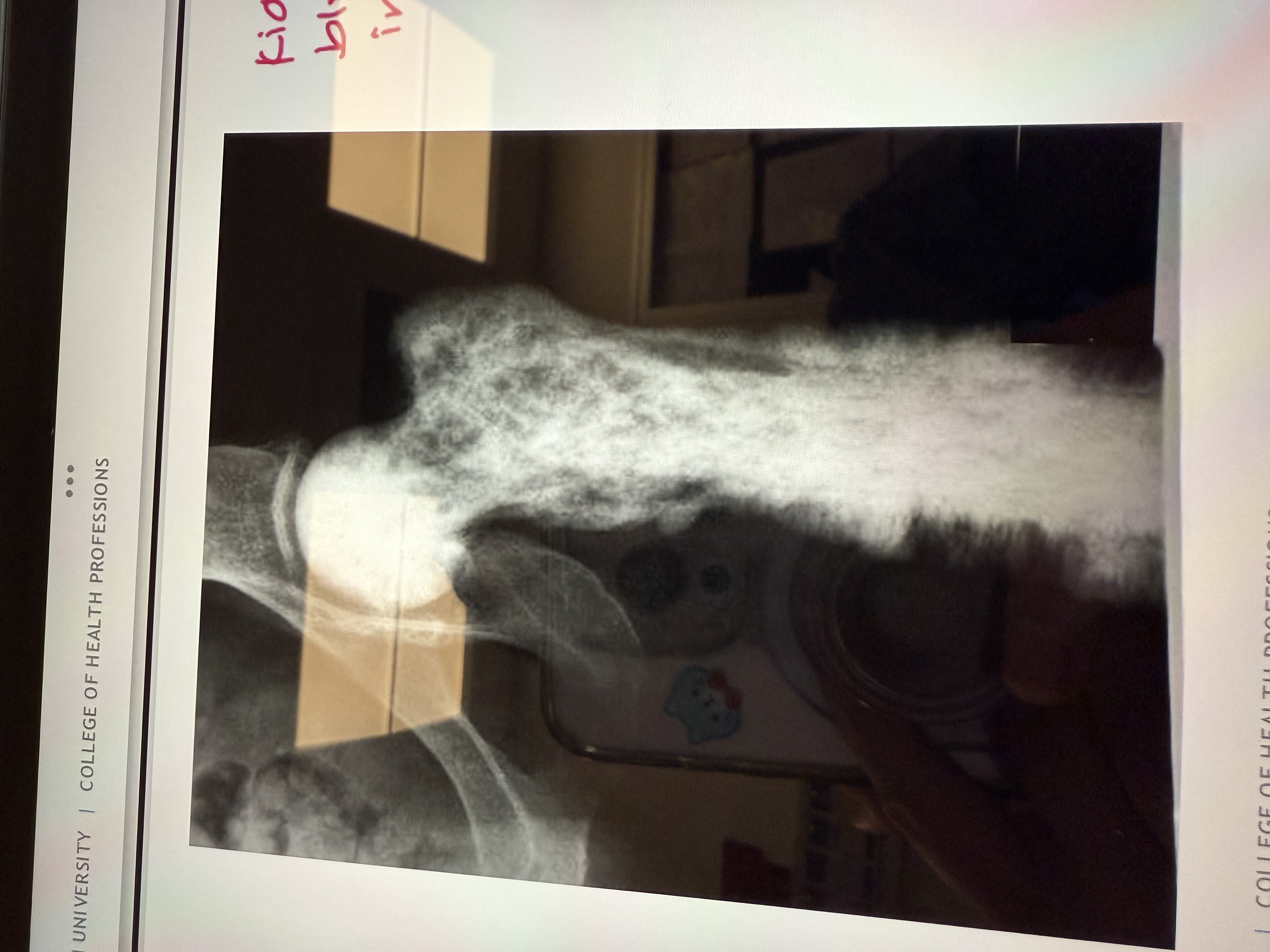
What is this
Paget’s Disease
Previous radiation can cause what bone cancers?
Osteo/Chondro/Fibrosarcomas
Can a chromosome defect from Ewing’s Sarcoma cause Osteosarcoma?
Yes
Osteosarcomas occur in areas of ______ (slow/rapid) growth
Rapid
What regions do Osteosarcomas usually develop?
Near growth plates
Where are growth plates located
In long bones where rapid cell proliferation takes place
What are the 2 most common sites of primary bone tumors
Distal Femur
Proximal Tibia
What are the 4 parts of the bone
Diaophysis
Epiphysis
Periosteum
Metaphysis
What is the main shaft of the bone
Diaphysis
Which part of the bone is knob-like at either end
Epiphysis
Which part of the bone is the hard, sense covering
Periosteum
Which part of the bone is the neck?
Metaphysis
The epiphysis contains what kind of bone?
Spongy
The Metaphysis has what kind of bone marrow
Red
The Diaphysis has what kind of bone marrow?
Yellow
What are the 7 primary bone tumors
Osteosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Fibrosarcoma
Ewing’s Sarcona
Multiple Myeloma
Giant Cell Tumor
Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma
Most common anatomical sites of Osteosarcomas
Proximal Tibia
Proximal Humerus
Distal femur
T/F: Osteosarcomas frequently occur in distal extremities
False
Chondro = _____ (adult/kid)
Adult
Osteo = _______ (adult/kid)
Kid
Average age of Chondrosarcoma incidence
60
Most common anatomical sites of Chondrosarcoma
Femur
Shoulder/Proximal Humerus
T/F: Chondrosarcomas rarely occur in distal extremities
True
Fibrosarcomas often occur in ________ bones
Tubular
Examples of tubular bones
Tibia
Femur
Fibrosarcomas can affect ________ and _______ ________
Bone; Soft tissue
Do Fibrosarcomas often occur in kids?
No
Ewing’s Sarcoma accounts for 3% of all _________ (childhood/adult) cancers
Childhood
Can Ewing’s Sarcona occur in any bone?
Yes
Which part of the body does Ewing’s Sarcoma most commonly occur?
Lower half
What part of the bone does Ewing’s Sarcoma most commonly occur in?
Diaphysis
What cell characteristics does Ewing’s Sarcoma represent
Small, blue, round
Multiple Myeloma is the malignancy of ________ cells
Plasma
What does Multiple Myeloma cause in the bone?
Bone resorption = painful osseous lesions
Where does Multiple Myelona arise
B-Lymphocytes in Bone Marrow
As single lesion of Multiple Myeloma is called?
Plasmacytoma
T/F: Giant Cell tumors are usually malignant
False
Are giant Cell tumors aggressive
Yes
Where on the bone do giant cell tumors occur most?
Metaphysis
Epiphysis
What do Giant cell tumors cause
Bone destruction
Mets disease gets what kind of XRT
Palliative
What are most common sites of bone mets
Vertebral bodies
Pelvic bones
Ribs
Distal lesions for bone cancer occur more in the ______ than the _______
Feet; hands
Distal bone lesions are usually due to what malignancy?
Lung cancer
What is the most common presentation of bone cancer
Pain
Pain is often correlated with tumor ______
Size
T/F: Early detection of bone cancers is easy
False
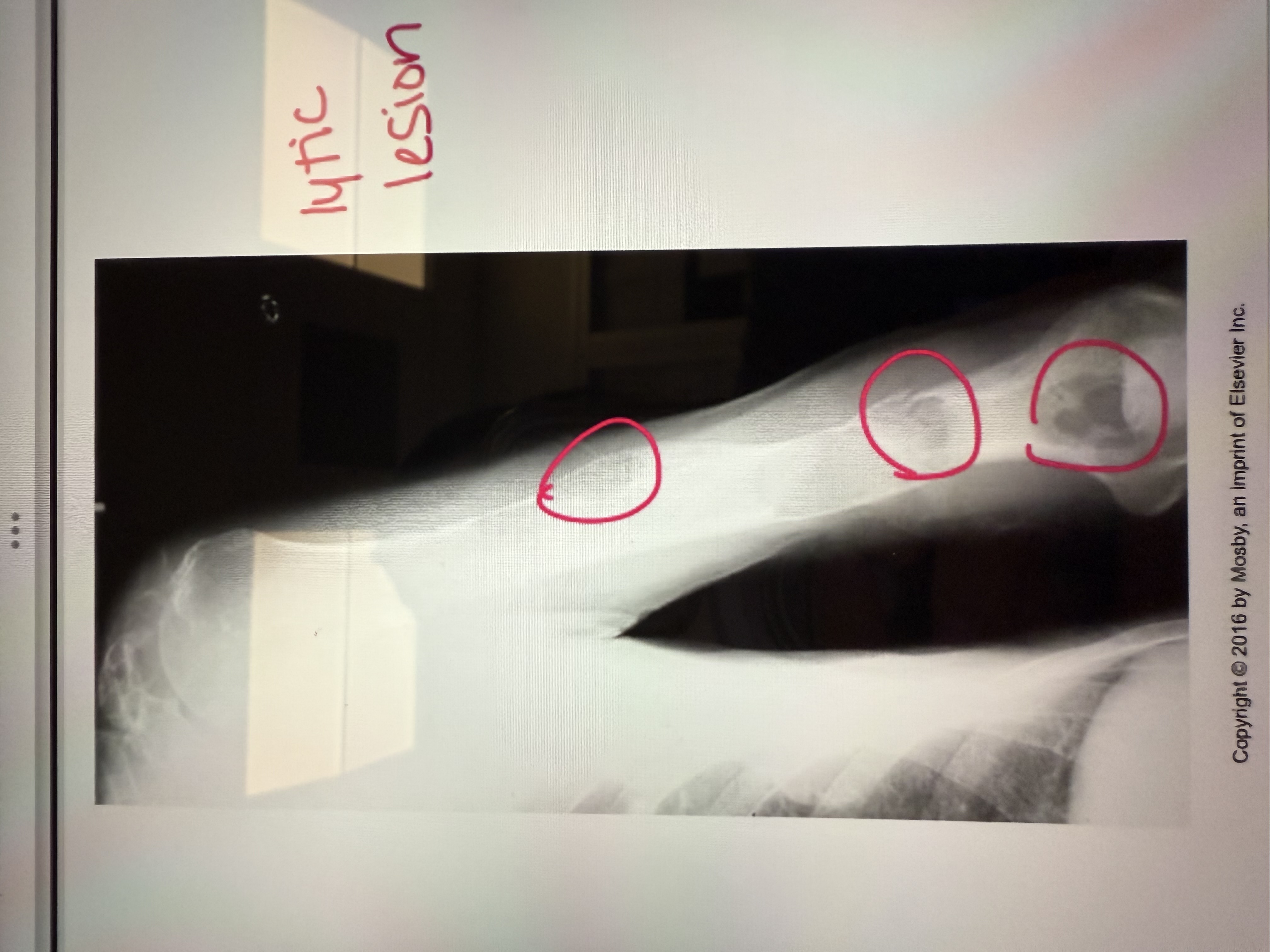
Lytic or blastic?
Lytic
What is the most important tool for bone cancer detection
Radiograph
Why is CT gradually being replaced by MRI?
MRI shows disease growth and neurovascular structure relationship
What isotope do they use for bone scans?
Technetium-99m (Tc-99m)
What is important for determining radiosensitivity of bone lesions?
Surgical bx
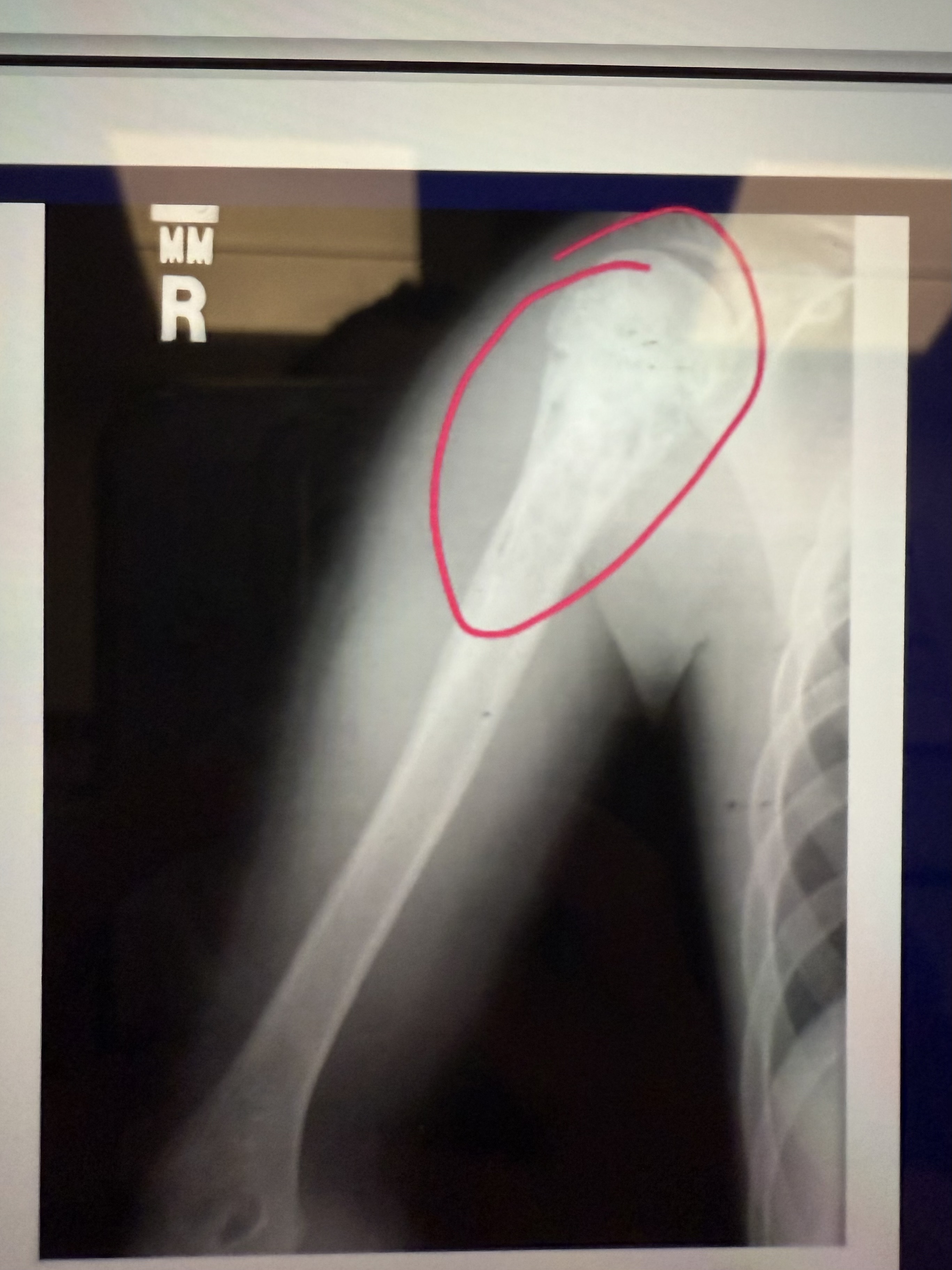
What is this
Ewing’s Sarcoma of Upper Right Humerus
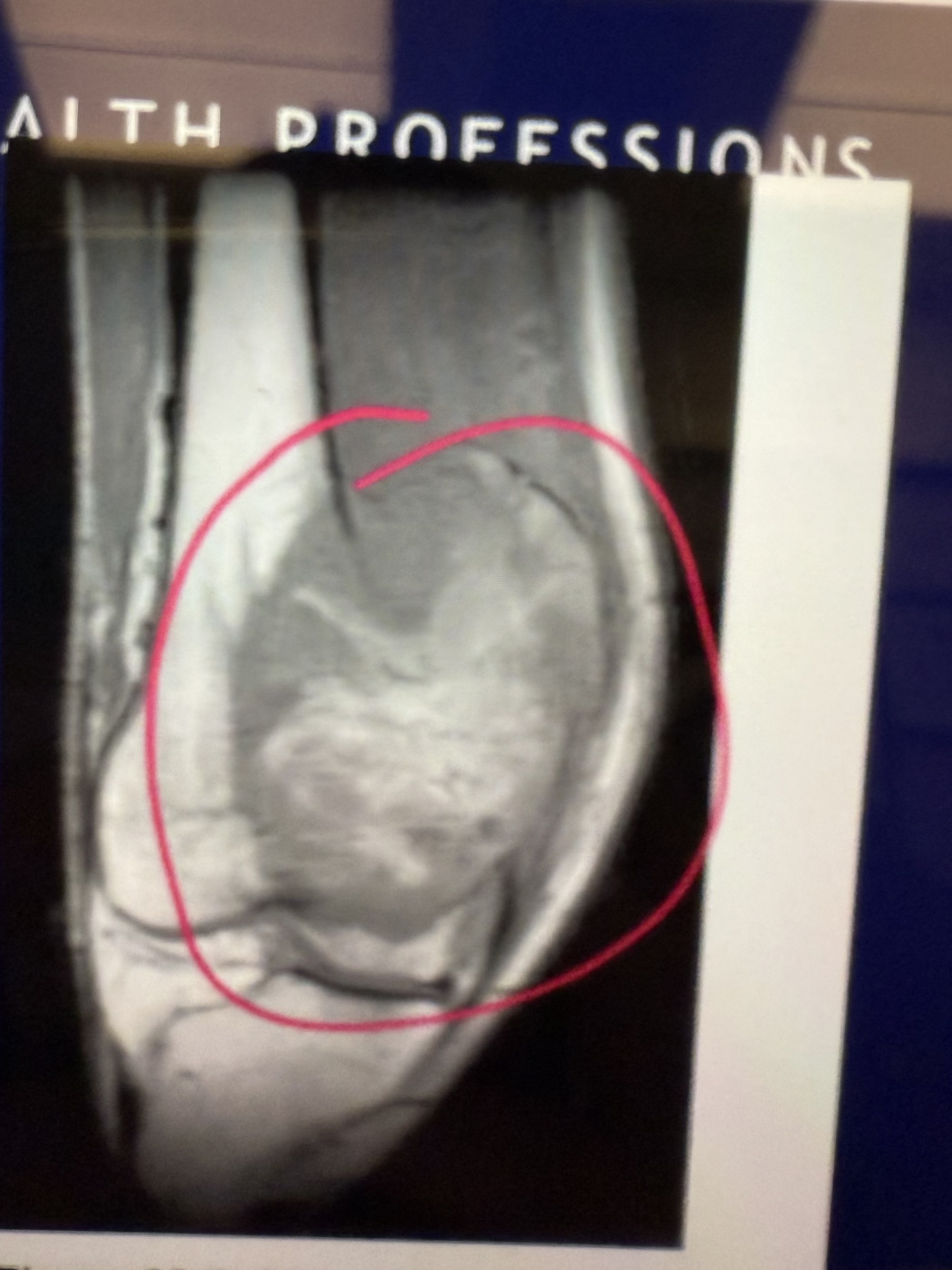
what is this
Osteosarcoma of Distal Femur
Which organs have normal uptake of FDG
Brain
Bladder
Kidneys
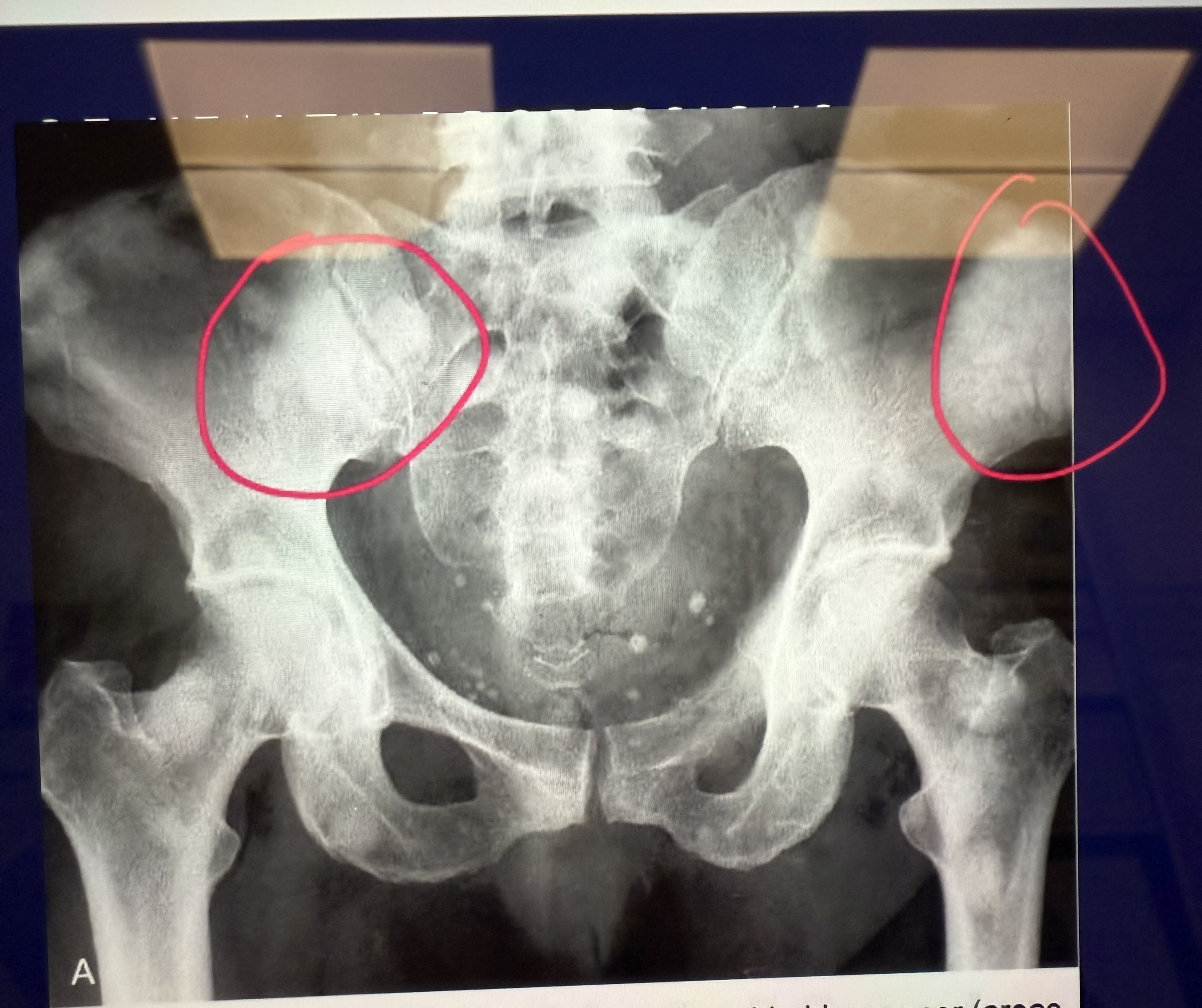
Lytic or blastic?
Blastic
Blastic lesions look _____ (black/white)
White
What Grading system is used for bone lesions
AJCC Grading
Describe AJCC Grading
G1 = Low grade
G2 = High grade
Higher grade = (better/worse) prognosis
Worse
High grade sarcomas typically spread ____________ to the peripheral lung
Hematogenously
Where do high grade sarcomas typiy spread to?
Peripheral lung
80% of Osteosarcomas spread to the _______
Lungs
Low grade sarcomas grow ________ (slow/fast) and are ________ (easy/hard) to control
Slow; Easy
Can low grade sarcomas recur and become high grade?
Yes
T/F: Sarcomas can spread via Skip Mets
True
What is Skip Mets
Cancer cells get into the LN and travel to a different region/organ of the body
What are 2 ways sarcomas can be staged?
by Grade
TNM
What does the staging of sarcomas depend on
Histology
What is important to do when treating sarcomas with XRT
Do skin sparing strips to prevent lymphedema
T/F: Osteosarcomas are the most common malignant bone tumor
True
Who is at increased risk of osteosarcoma
<35 yrs old
Tall
Equal in children for gender
2:1 Male/Female >15
Osteosarcomas are chemo________ but radio________
Sensitive; Resistant
What is the tx of choice for Osteosarcomas
Chemo and Surgery
5 year survival Osteosarcoma
60-70%
When is XRT used for Osteosarcomas
Chemoadjuvant
Unresectable/Partially Resected tumor
Positive margins
Dose for post-op Osteosarcoma
55 Gy
Boost: 64-68 Gy
Dose for Unresectable Osteosarcoma
60-70 Gy
What is important to keep in tx field for Osteosarcomas
Scar, Spare 1-3 cm margin
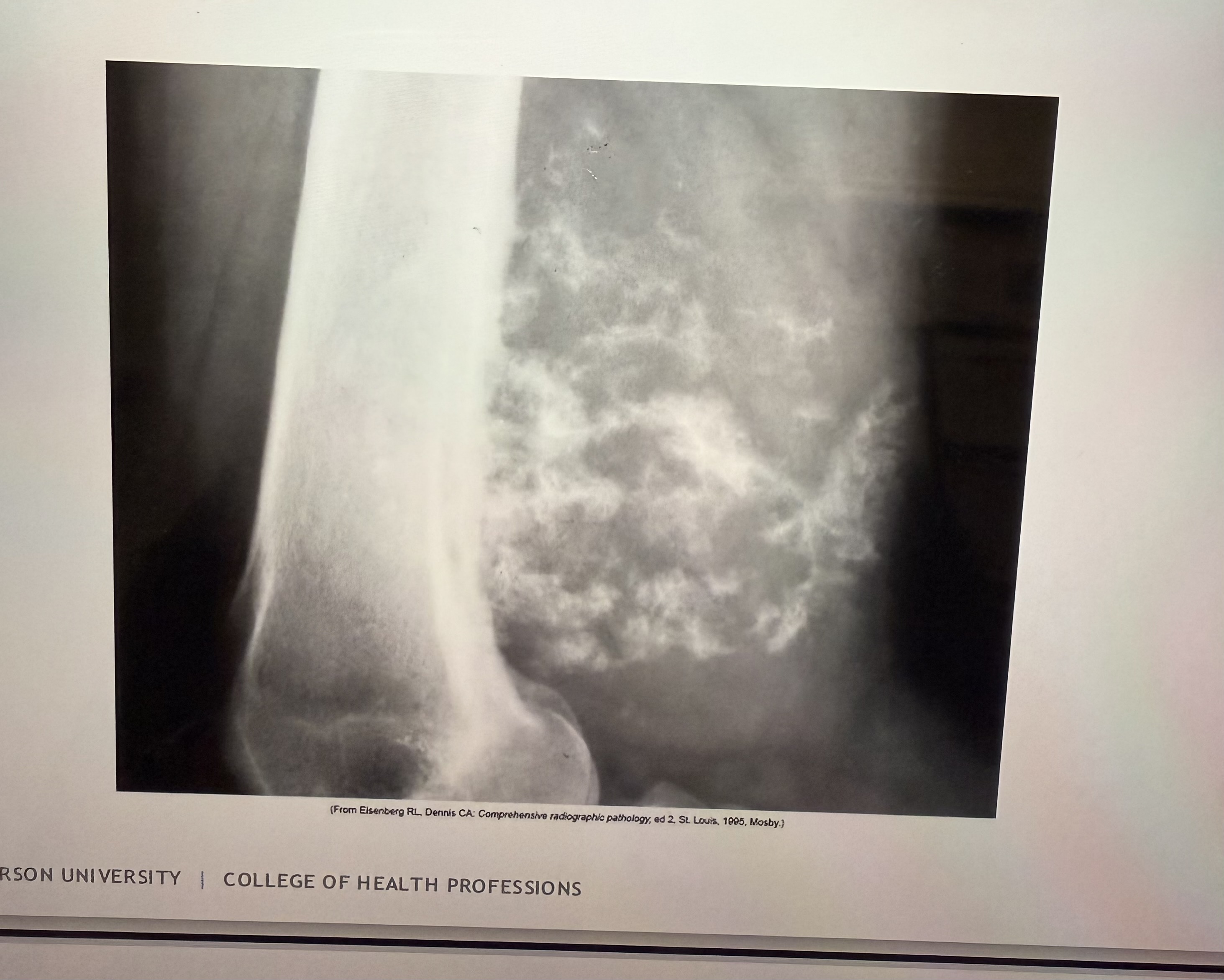
What is this
Chondrosarcoma
T/F: Chondrosarcoma is the 2nd most common bone tumor overall
True
What is the most common bone tumor in adults
Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcomas arise from _________ elements of bone
Mesenchymal
Where can chondrosarcomas form
Any cartilage forming bone
What is important for Chondrosarcoma prognosis
Location
Grade