Organic Chemistry (Nomenclature)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:03 AM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
aliphatic hydrocarbons
Long carbon chains (straight or cyclic) surrounded by hydrogen. They contain single, double, or triple bonds between carbons.
2
New cards
organic compound
Carbon-containing compounds.
* Any of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen
* Any of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen
3
New cards
inorganic compound
Does not contain C atoms.
* Exceptions: CO2, carbides, carbonates, cyanides
* Exceptions: CO2, carbides, carbonates, cyanides
4
New cards
carbon
The “element of life”: it bonds with a variety of elements in a variety of shapes, is an excellent building block due to strong bonds that are able to re-arrange themselves
5
New cards
alkanes
A class of hydrocarbon compounds that **consist entirely of atoms of carbon and hydrogen** bonded to one another by *carbon-carbon* and *carbon-hydrogen* __**single bonds**__.
* **- ane**
\
* **Not soluble** in __water__; **soluble** in __non-polar__ solvents
* **Density** is __less than that of water__
* **Boiling point** __increases__ as the __size__ of the chain __increases__
* **London Forces!!**
* **- ane**
\
* **Not soluble** in __water__; **soluble** in __non-polar__ solvents
* **Density** is __less than that of water__
* **Boiling point** __increases__ as the __size__ of the chain __increases__
* **London Forces!!**
6
New cards
alkyl groups
Smaller carbon chains attached as __**branches**__ to the parent.
* methyl, ethyl, etc.
* methyl, ethyl, etc.
7
New cards
location numbers
The longest carbon chain (parent) is numbered to show on to which carbon a branch (alkyl group, functional group) is attached. If there are multiple branches on a parent chain, numbering starts on the end closest to the branch with the highest priority.
8
New cards
alkenes
A class of hydrocarbons with **at least one** *carbon-to-carbon* __**double bond**__.
* **- ene**
\
* Slightly more reactive than alkanes due to the double bonds
* **- ene**
\
* Slightly more reactive than alkanes due to the double bonds
9
New cards
alkynes
A class of hydrocarbons which contain at least one *carbon-carbon* __**triple bond**__.
* **- yne**
* **- yne**
10
New cards
enynes
When there is a double bond and a triple bond in the same compound!
Number from the end closest to either the double or triple bond; if there’s a choice, __**the double bond gets priority**__ (lowest #)!!
* **root - # - en - # - yne"**
Number from the end closest to either the double or triple bond; if there’s a choice, __**the double bond gets priority**__ (lowest #)!!
* **root - # - en - # - yne"**
11
New cards
isomer
Molecules that have the same molecular formula, but their atoms are in __different arrangement__.
12
New cards
structural isomers
Molecules that have the SAME molecular formula, but their atoms are bonded together in a DIFFERENT sequence.
* Physical properties, such as boiling points, vary, as do their shapes.
* Physical properties, such as boiling points, vary, as do their shapes.
13
New cards
stereoisomers
Molecules that have the SAME molecular formula and their atoms are bonded together in the SAME sequence, but DIFFER in the 3D orientations of their atoms in space.
* Alkenes have double bonds that are flat and rigid because their atoms cannot rotate around the double bond.
* Two types: diastereomers and enantiomers
* Alkenes have double bonds that are flat and rigid because their atoms cannot rotate around the double bond.
* Two types: diastereomers and enantiomers
14
New cards
diastereomers
**** only for alkenes! ****
Each carbon atom involved in the DOUBLE BOND has DIFFERENT types of atoms or groups of atoms bonded to it.
The double bond prevents rotation around the carbon atoms, resulting in __two separate orientations in space__.
Two types of orientation: *cis* (D or Z) and *trans* (E)
Each carbon atom involved in the DOUBLE BOND has DIFFERENT types of atoms or groups of atoms bonded to it.
The double bond prevents rotation around the carbon atoms, resulting in __two separate orientations in space__.
Two types of orientation: *cis* (D or Z) and *trans* (E)
15
New cards
cis
The two larger or smaller atoms or groups are on the SAME side of the double bond (above or below the bond plane).
16
New cards
trans
The two larger or smaller atoms or groups are on OPPOSITE sides of the double bond (one above and one below the bond plane).
17
New cards
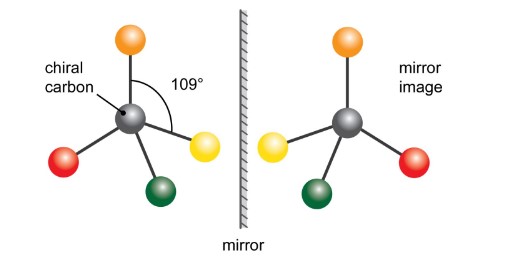
enantiomers
**** only for a single carbon!! ****
Mirror images of each other around a SINGLE CARBON atom bonded to __four DIFFERENT types of atoms or groups__.
They are ***non-superimposable*** mirror images of each other (have different spatial arrangement).
* For example, our hands!
Mirror images of each other around a SINGLE CARBON atom bonded to __four DIFFERENT types of atoms or groups__.
They are ***non-superimposable*** mirror images of each other (have different spatial arrangement).
* For example, our hands!
18
New cards
alkyl halide hydrocarbons
Has at least __one halogen side group__.
* Generally colourless and odourless compounds
* They are hydrophobic in nature
* __Boiling point__ is higher than alkanes if the number of carbon atoms is the same in both
* Generally colourless and odourless compounds
* They are hydrophobic in nature
* __Boiling point__ is higher than alkanes if the number of carbon atoms is the same in both
19
New cards
nitro hydrocarbons
Has at least __one nitro side group__.
20
New cards
cyclic hydrocarbons
General formula: C*n*H*2n, r*epresented by POLYGONS.
* *** If you have one that is not the main chain, then you name it as a branch! The ending is changed to “yl”.**
* *** If you have one that is not the main chain, then you name it as a branch! The ending is changed to “yl”.**
21
New cards
aromatic hydrocarbons
Have a BENZENE ring, C*6*H*6* - a six carbon, six hydrogen ring with alternating single & double bonds.
* All six carbon-carbon bonds are intermediate in length between a single and double bond due to resonance (delocalized electrons are shared by all six carbon atoms).
* All six carbon-carbon bonds are intermediate in length between a single and double bond due to resonance (delocalized electrons are shared by all six carbon atoms).
22
New cards
benzene
C*6*H*6*, a six carbon, six hydrogen ring with alternating single & double bonds.
23
New cards
phenyl
***** **If you have a benzene ring attached to a straight or cyclic hydrocarbon chain that is larger than the ring itself (more than 6 carbon atoms), the benzene ring is the side group and you name it as a branch!**
24
New cards
alcohols
Contains a __hydroxyl group__ (-OH) attached to a carbon chain (NOT hydroxide; the -OH group is covalently bonded rather than ionically bonded).
* Higher boiling points than haloalkanes that remain associated with intermolecular hydrogen bonding
* Higher boiling points than haloalkanes that remain associated with intermolecular hydrogen bonding
25
New cards
phenol
A __hydroxyl group__ (-OH) attached to a benzene ring.
26
New cards
ethers
An oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms by single bonds.
* **“-oxy”** ending
\
* The boiling point is comparable to alkanes but much lower than that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass despite the polarity of the C-O bond
* **“-oxy”** ending
\
* The boiling point is comparable to alkanes but much lower than that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass despite the polarity of the C-O bond
27
New cards
aldehydes
At least one H atom is attached to a carbonyl group (on the end of a carbon chain).
* Have __strong odors__
* Are __polar compounds__
* Only dipole-dipole interactions (NO hydrogen bonding)
* __Low boiling points__ compared to amines and alcohols, higher than hydrocarbons
* __Soluble__ in water (not soluble in nonpolar compounds)
* Have __strong odors__
* Are __polar compounds__
* Only dipole-dipole interactions (NO hydrogen bonding)
* __Low boiling points__ compared to amines and alcohols, higher than hydrocarbons
* __Soluble__ in water (not soluble in nonpolar compounds)
28
New cards
ketone
Two carbon groups are attached to a carbonyl group (in the middle of a chain).
* Have __pleasant odors__
* Are __polar compounds__
* Only dipole-dipole interactions (NO hydrogen bonding)
* __Low boiling points__ compared to amines and alcohols, higher than hydrocarbons
* __Soluble__ in water (not soluble in nonpolar compounds)
* Have __pleasant odors__
* Are __polar compounds__
* Only dipole-dipole interactions (NO hydrogen bonding)
* __Low boiling points__ compared to amines and alcohols, higher than hydrocarbons
* __Soluble__ in water (not soluble in nonpolar compounds)
29
New cards
carboxylic acids
**** TOP OF PRIORITY SHEET!!!!! **** → will ALWAYS be the parent group if they are present.
Contains a __carboxyl group__, which is a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group (-COOH).
The common names use prefixes “form- and “acet-” for the first two carboxylic acids.
* The carboxyl group contains __three__ __**polar covalent bonds**__: C=O, C-O, and O-H; so they are __**polar**__
* Have __higher boiling points__ than other types of organic compounds (with the same molecular weight) because of __**hydrogen bonding**__
* __More soluble__ (!!!) in water than alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and ketones because of __**stronger hydrogen bonding**__
* Liquid forms have __sharp and disagreeable odors__
* __THEY TASTE SOUR__ (exist in pickle, lime, and lemon)
Contains a __carboxyl group__, which is a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group (-COOH).
The common names use prefixes “form- and “acet-” for the first two carboxylic acids.
* The carboxyl group contains __three__ __**polar covalent bonds**__: C=O, C-O, and O-H; so they are __**polar**__
* Have __higher boiling points__ than other types of organic compounds (with the same molecular weight) because of __**hydrogen bonding**__
* __More soluble__ (!!!) in water than alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and ketones because of __**stronger hydrogen bonding**__
* Liquid forms have __sharp and disagreeable odors__
* __THEY TASTE SOUR__ (exist in pickle, lime, and lemon)
30
New cards
esters
**** FAVOURITE ON TESTS & EXAMS, LOTS OF REACTIONS!!!! ****
**** 2nd ON PRIORITY LIST ****
The H in the carboxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced with an alkyl group.
* Give flowers and fruits their pleasant fragrances and flavours.
**** 2nd ON PRIORITY LIST ****
The H in the carboxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced with an alkyl group.
* Give flowers and fruits their pleasant fragrances and flavours.
31
New cards
hydrolysis
Reaction with water; breaking a bond and adding the elements of water.
32
New cards
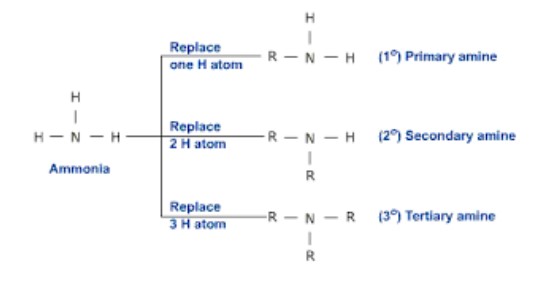
amines
Organic derivatives of ammonia (NH*3*), in which one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aromatic groups replace hydrogen and bond to the nitrogen atom.
Classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary (similar to alcohols) → __the__ __**number of carbon groups**__ that are bound to the nitrogen atom.
The **-NH*****2*** group of a primary amine can be thought of as an **“amino group”** (a BRANCH).
* State: tend to be **gases** for low molecular weight cases, many **heavier ones** are **liquids** are room temperature
* Tend to exhibit **strong odors**, some have a “fishy” smell!
* __Boiling points__ are intermediate to those for alcohols and alkanes of similar molar mass; because of the presence of **N-H** bonds in primary + secondary, *H-bonding is sometimes possible;* however, because __***N is not as electronegative as O, the N-H bond is not as polar as an O-H bond***__ (hence __***weaker H-bonding***__)
* Tend to be **water-soluble** because of H-bonding interactions with water molecules; in fact, those with fewer than six carbon atoms are infinitely water-soluble
* Water-solubility decreases as chain length increases and as the **degree of N-substitution increases**
Classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary (similar to alcohols) → __the__ __**number of carbon groups**__ that are bound to the nitrogen atom.
The **-NH*****2*** group of a primary amine can be thought of as an **“amino group”** (a BRANCH).
* State: tend to be **gases** for low molecular weight cases, many **heavier ones** are **liquids** are room temperature
* Tend to exhibit **strong odors**, some have a “fishy” smell!
* __Boiling points__ are intermediate to those for alcohols and alkanes of similar molar mass; because of the presence of **N-H** bonds in primary + secondary, *H-bonding is sometimes possible;* however, because __***N is not as electronegative as O, the N-H bond is not as polar as an O-H bond***__ (hence __***weaker H-bonding***__)
* Tend to be **water-soluble** because of H-bonding interactions with water molecules; in fact, those with fewer than six carbon atoms are infinitely water-soluble
* Water-solubility decreases as chain length increases and as the **degree of N-substitution increases**
33
New cards
amides
Possess a functional group that consists of a __**C=O (carbonyl) directly bonded to a nitrogen atom**__.
Classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary.
* The simplest ones are **liquids** at room temperature, and all unbranched having 2 or more carbons on their C-chain side are **solids**
* Secondary and tertiary have lower melting points, with tertiary amides having lower melting points than secondary amides (__***less opportunity for H-bonding)***__*.*
Classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary.
* The simplest ones are **liquids** at room temperature, and all unbranched having 2 or more carbons on their C-chain side are **solids**
* Secondary and tertiary have lower melting points, with tertiary amides having lower melting points than secondary amides (__***less opportunity for H-bonding)***__*.*