BIOL 1031 MIDTERM
1/235
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Scott Bowling @ Auburn University, Biology 1031 lab practical 1 study guide - everything from remote labs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
236 Terms
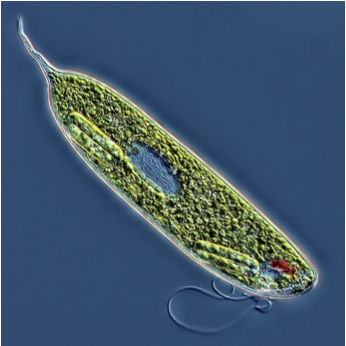
Phylum Euglenozoa
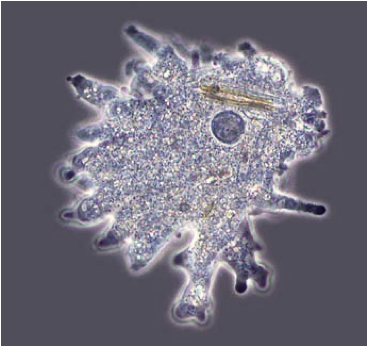
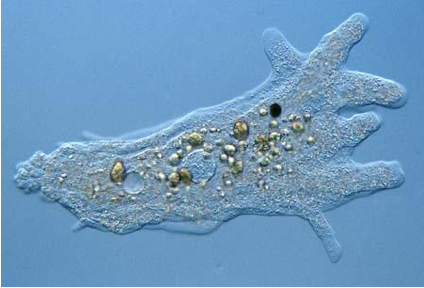
Phylum Gymnamoeba
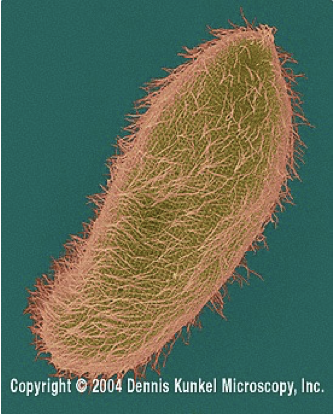
Phylum ciliophora
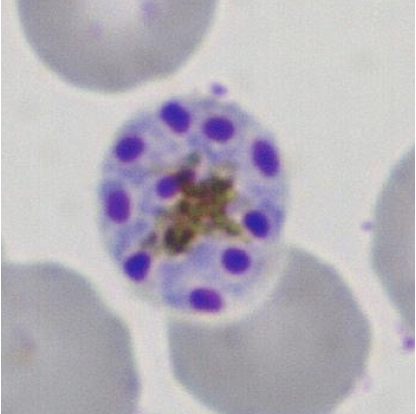
Phylum apicomplexa

Phylum foraminifera
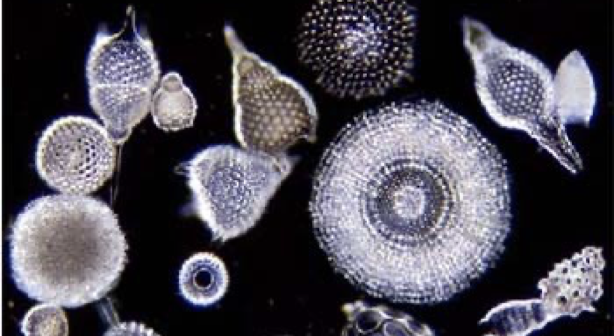
Phylum radiolaria
ciliates
have fast, smooth motion
flagellates
often slower with an almost spiraling motion
pseudopodia
slow and have an oozing, liquid movement
example of ciliophora
Paramecium

Example of gymnamoeba
Amoeba
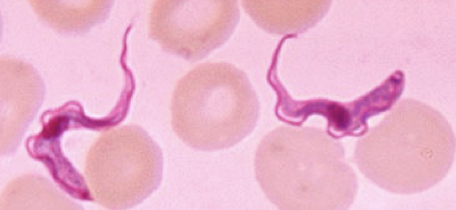
Example of euglenozoa
Trypanosomes
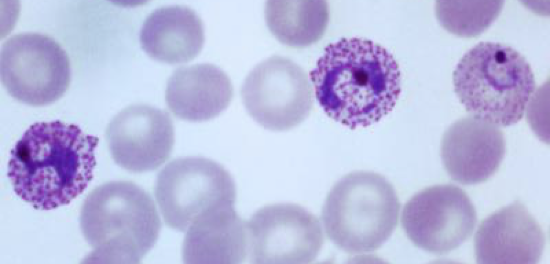
Example of apicomplexa
Plasmodium
example of ciliophora
stentor
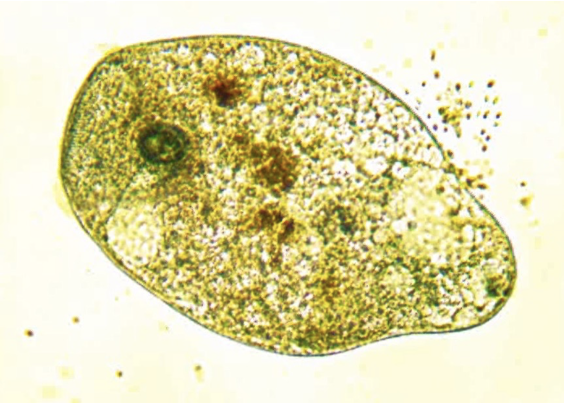
example of foraminifera
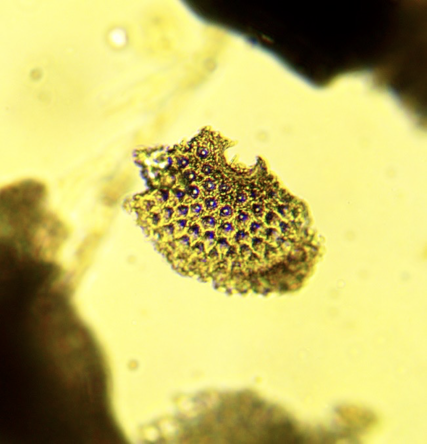
example of radiolaria
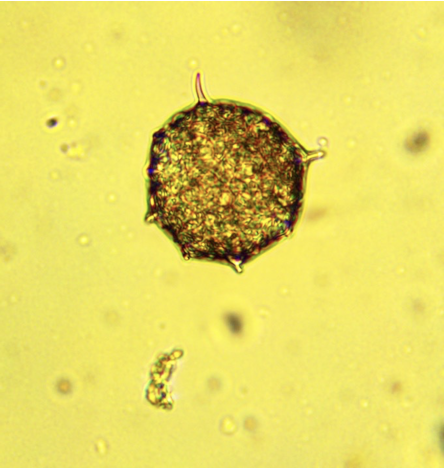
Phylum chlorophyta
Green algae
Phylum phaeophyta
brown algae

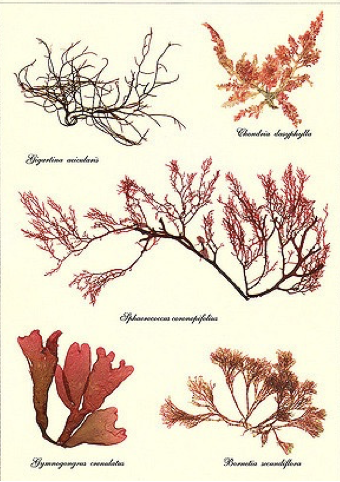
Phylum rhodophyta
red algae
Phylum Bacillariophyta
diatoms

Thallus bearing
looks like a plant but isn’t really
largest phylum of algae
chlorophyta
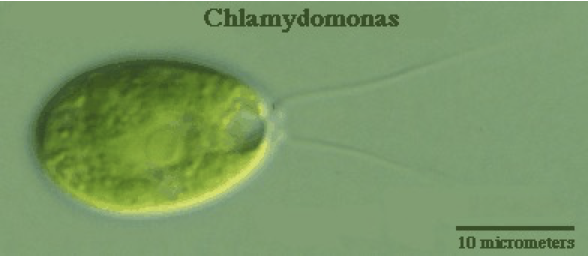
chlamydomonas characteristics
part of chlorophyta
unicellular; motile, with two anterior flagella
cup shaped chloroplast, pigmented eyespot and clear nucleus
life cycle is zygotic meiosis
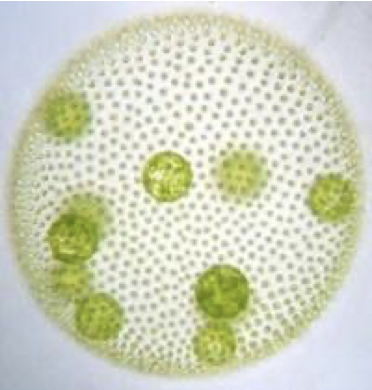
Volvox characteristics
chlorophyta
motile, colonial
large sphere colonies
daughter colonies within sphere
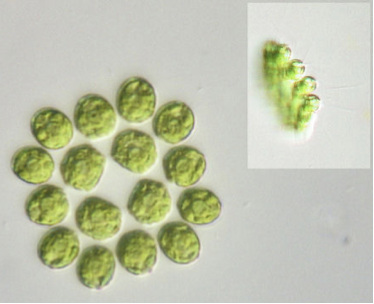
Gonium characteristics
chlorophyta
flattened and held together by gelatinous material
Hydrodictyon characteristics
chlorophyta
non-motile, colonial
multinucleate cells, separated by cross walls
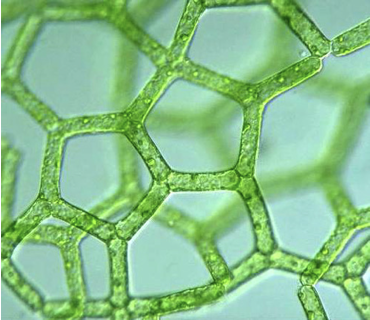
Oedogonium characteristics
chlorophyta
non-motile
filamentous (thread-like); unbranched filaments
life cycle is zygotic meiosis
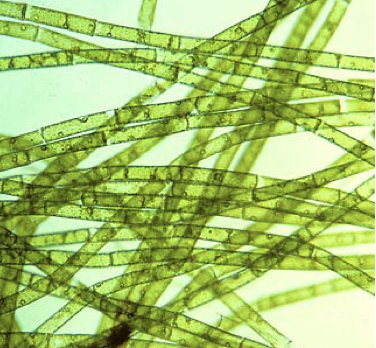
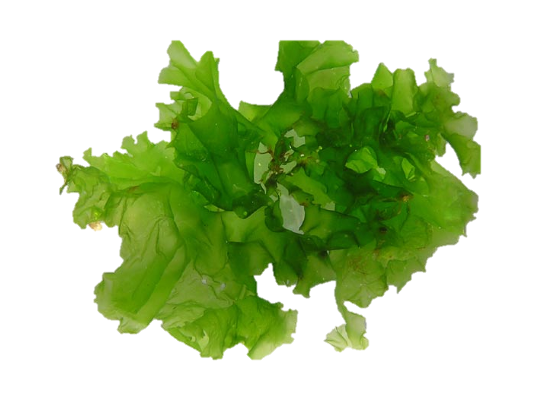
Ulva characteristics
chlorophyta
multicellular; relatively large
mature body is flattened tissue-like sheet
isomorphic alteration of generations
common name is sea lettuce

Kelp characteristics
phaeophyta
large, multicellular complex bodies that form a flattened blade, stipe, and holdfast
found in cool or cold, nutrient rich areas
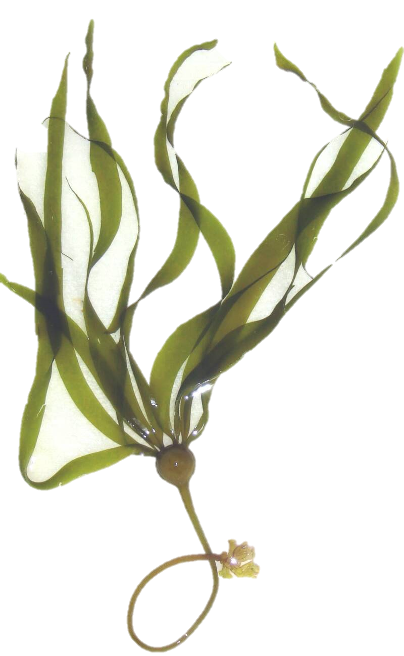

rhodophyta characteristics
multicellular
marine
found in deep waters and tropical waters
contributes to formation if coral reefs
compromised of interwoven cells
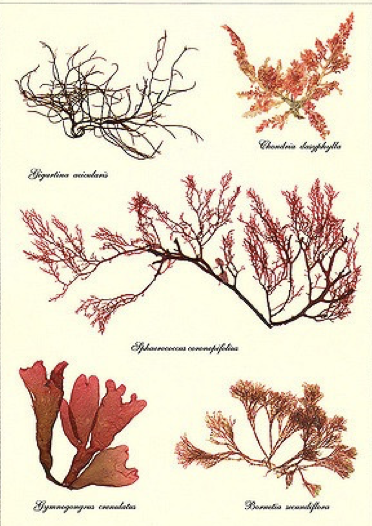

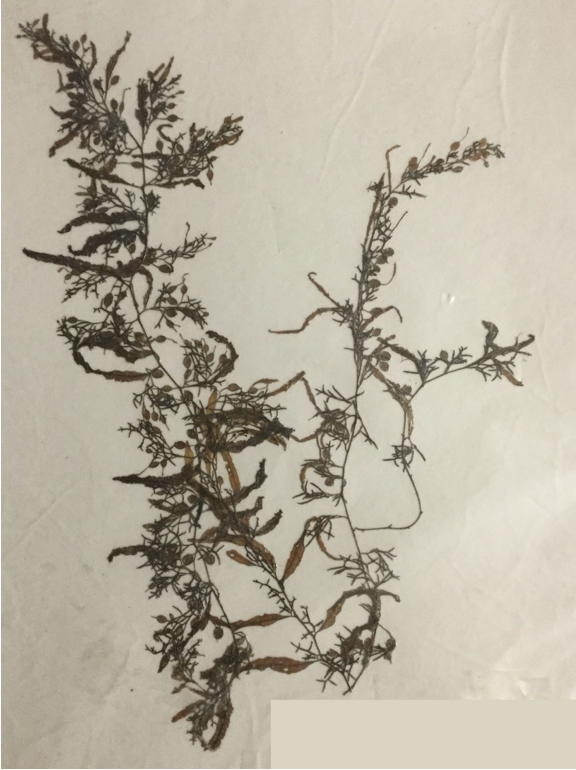
Fucus (pressed specimen)
Phylum phaeophyta

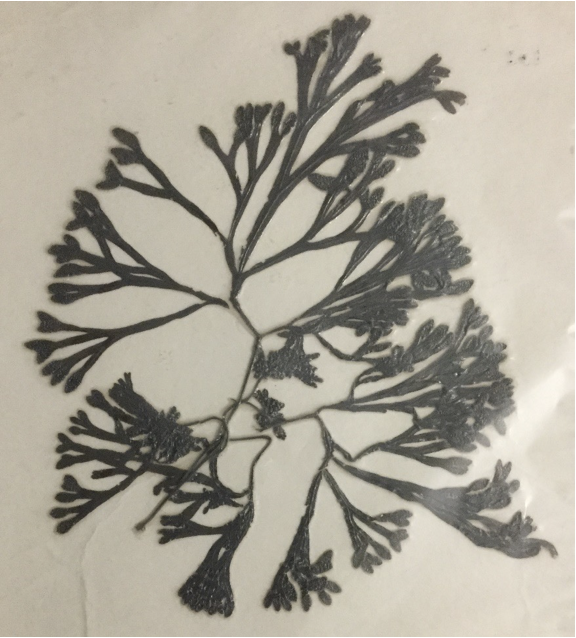
Sargassum (pressed specimen)
phylum phaeophyta
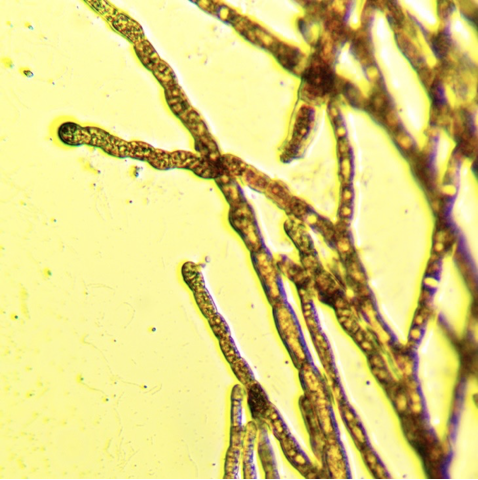
Polysiphonia (micrograph)
phylum phaeophyta
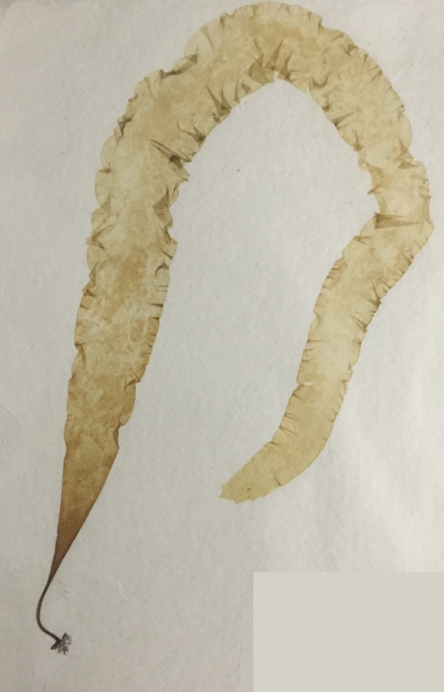

Laminaria (pressed)
phylum phaeophyta
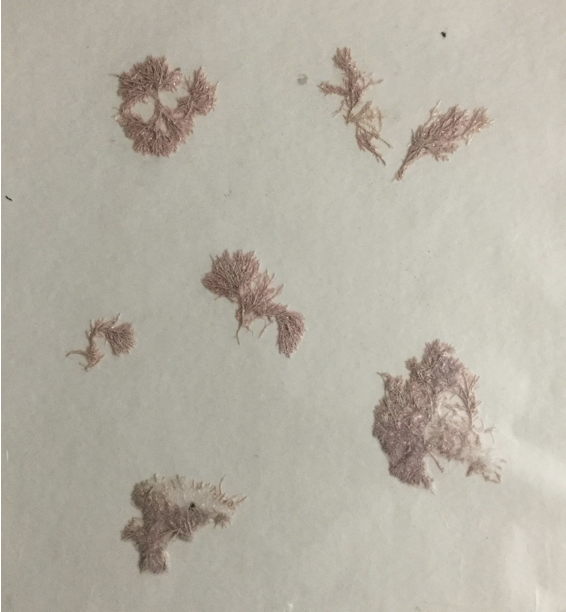

Corallina (pressed)
phylum rhodophyta
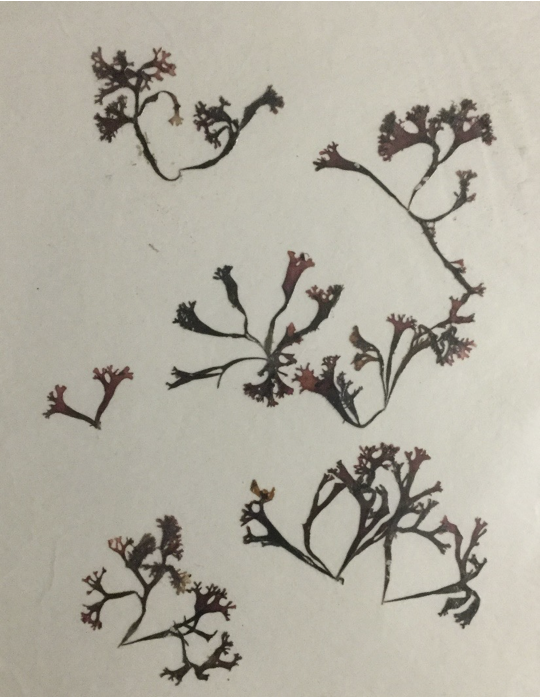

Chondrus (pressed)
phylum rhodophyta

Plasmodial slime molds
phylum myxogastrida
characteristics of myxogastrida
ooze on forest floor
non-walled, multinucleate masses of protoplasm called a plasmodium
plasmodium is a feeding stage
in harsh conditions plasmodium enters an alternate life form in which sporangia (stalked fruiting bodies) are produced
Example of myxogastrida
Physarum (yellow stuff)
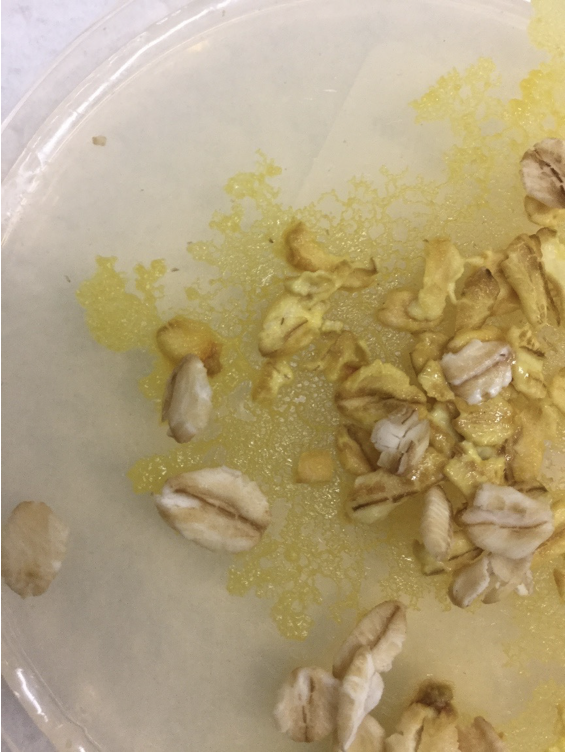

Difference between Plasmodium and plasmodium
Plasmodium = genus of phylum apicomplexa
plasmodium = feeding stage of phylum myxogastrida slime molds
Zygotic meiosis
zygote directly undergoes meiosis
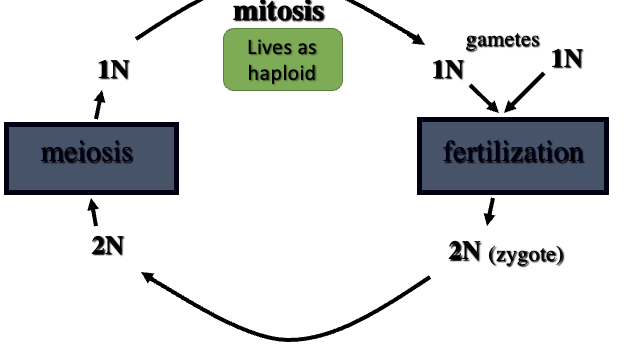
Gametic meiosis
gametes formed directly by meiosis
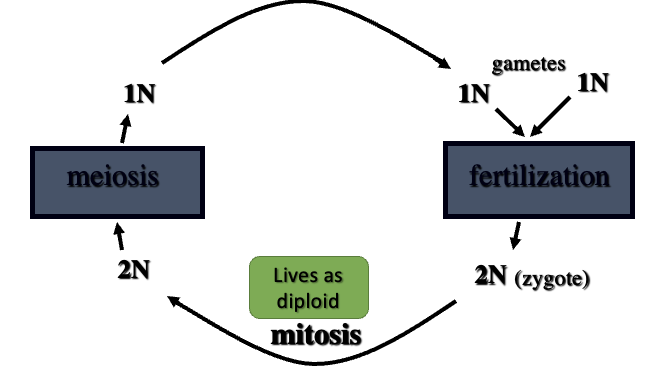
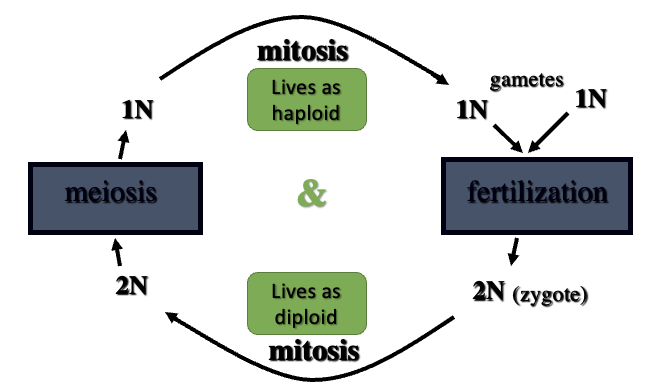
Alteration of generations
mitosis in two positions in life cycle forms 2 distinct multicellular generations; meiosis forms spores
3 phyla of non-vascular plants
Phylum bryophyta
Phylum hepatophyta
Phylum anthocerophyta
Phylum Bryophyta
true mosses

Phylum Hepatophyta
Liverworts
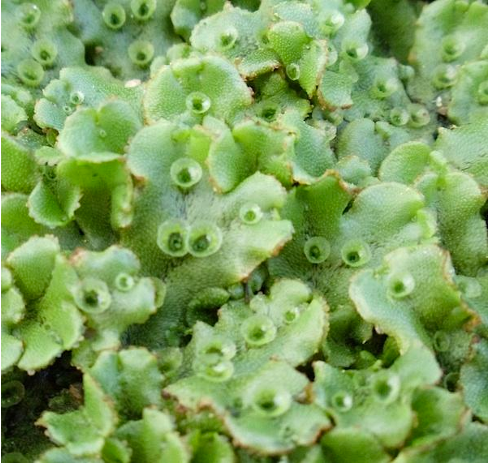

Phylum anthocerophyta
hornworts

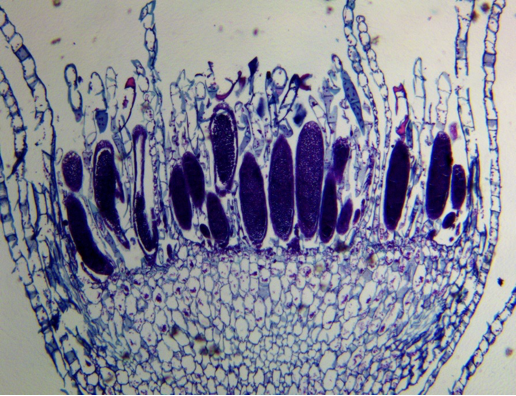
Mnium Antheridial head
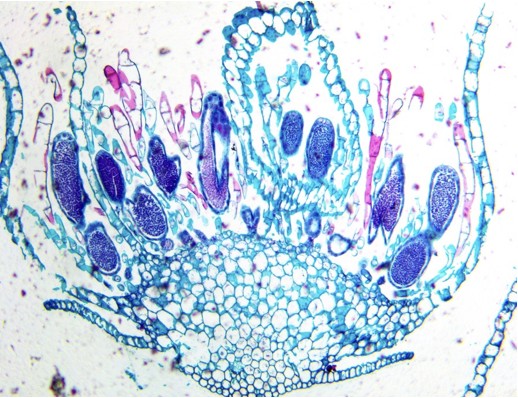
Mnium archegonial head
bryophyta moss example
protonemata


polytrichum
phylum bryophyta
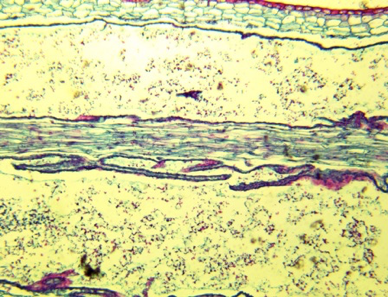
polytrichum mature capsule

polytrichum male gametophyte

polytrichum female gametophyte
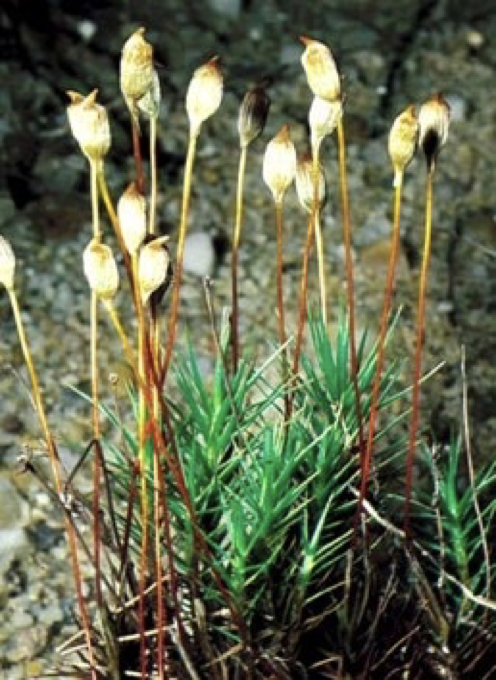

label this sporulating moss
gametophytes: green tissues on bottom
sporophytes: brown/white tissue on top
hepatophyta characteristics
have gemma cups
have antheridiophores (disk shaped)
have archegoniophores (umbrella shaped0

Marchantia antheridiophores

Marchantia archegoniophores
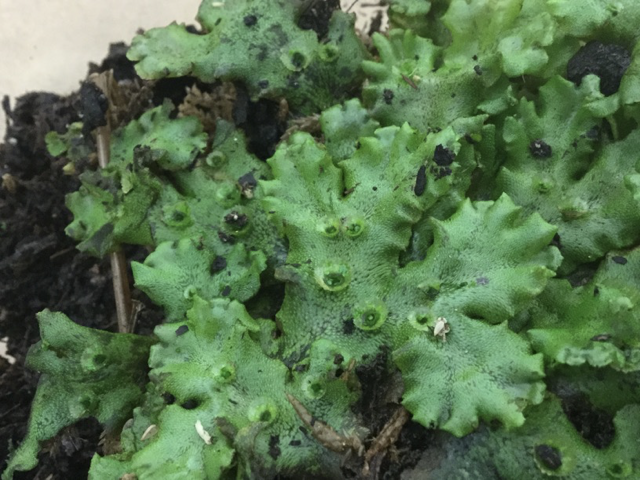

Marchantia with prominent gemma cups
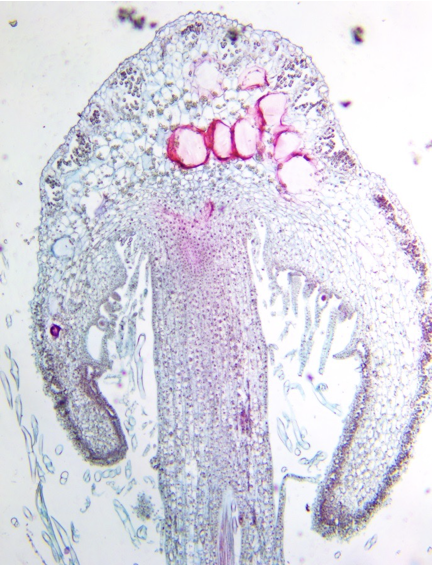
Marchantia archegonial head micrograph
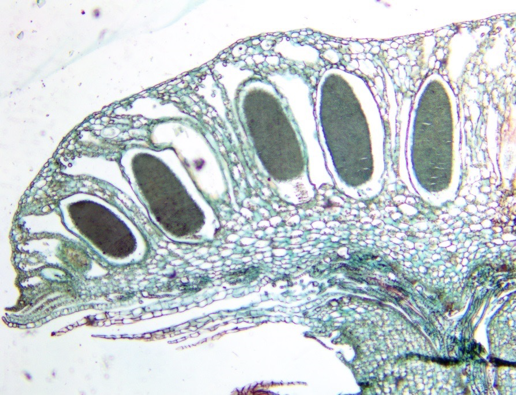
Marchantia antheridial head micrograph
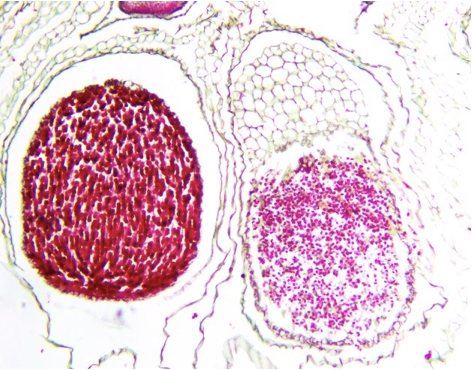
Marchantia spore tetrads micrograph
can sporophytes perform photosynthesis in horworts?
yes

anthoceros
gametophyte is big part
sporophyte is tip/tail looking thing
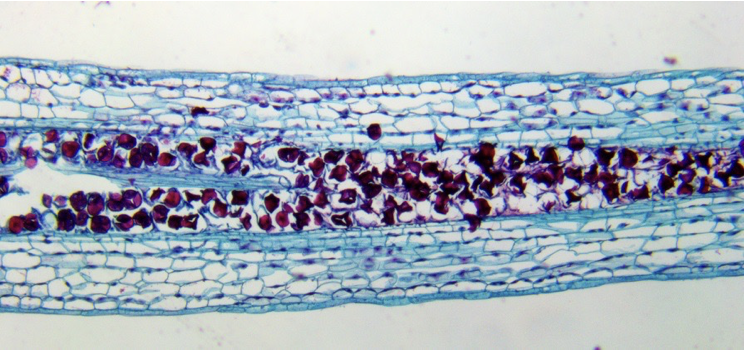
Anthoceros mature sporophyte micrograph
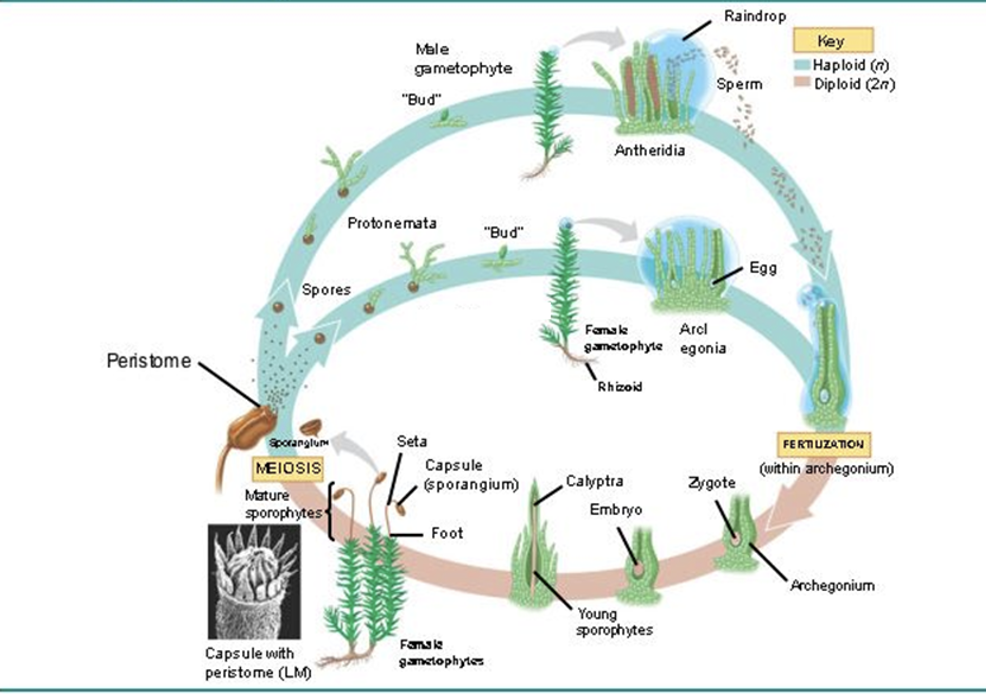
life cycle of a polytrichum moss
alteration of generations
two types of seedless vascular plant tissue
xylem
phloem
function of xylem
carries water and minerals
flow is from roots to rest of the plant
function of phloem
carries carbohydrates and other nutrients
flow is in whatever direction needed
Seedless vascular plant phylums
Phylum lycophyta
Phylum Psilophyta
Phhylum Arthrophyta
Phylum Pterophyta
phylum lycophyta
clubmosses

phylum pterophyta
true ferns

phylum psilophyta
whisk ferns

phylum arthrophyta
horsetails

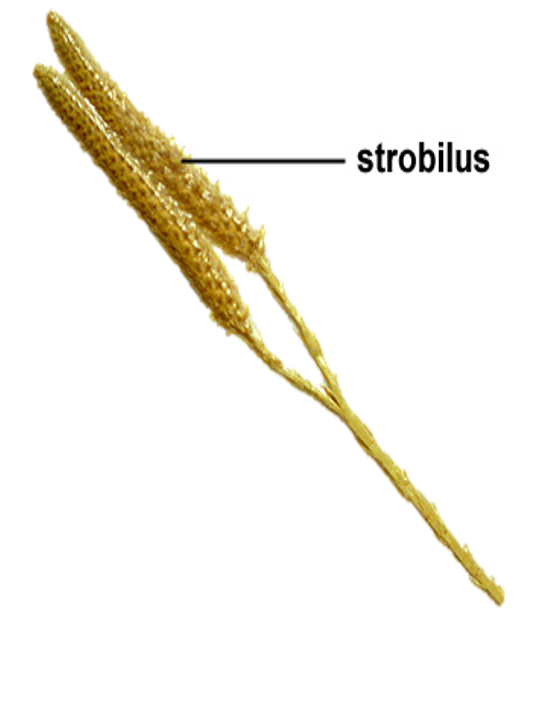
strobilus
cone-like structure that consists of a cluster of sporophylls
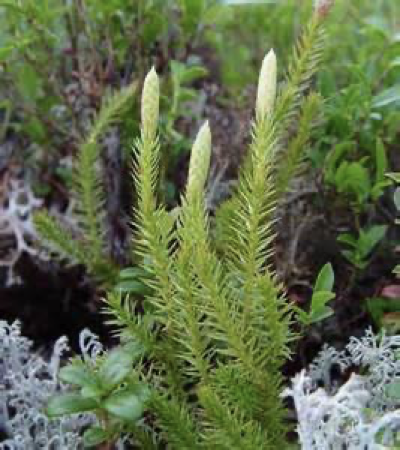

phylum lycophyta example 1
Selaginella

phylum lycophyta example 2
lycopodium
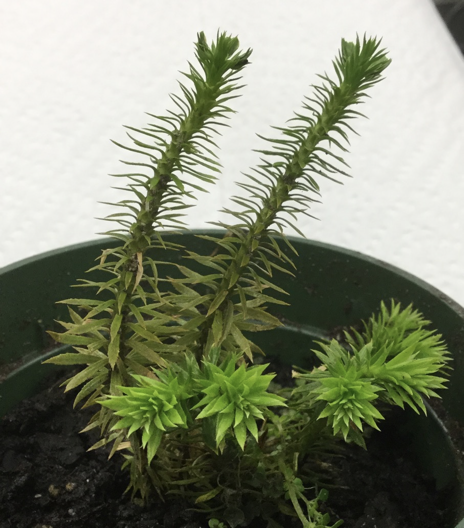

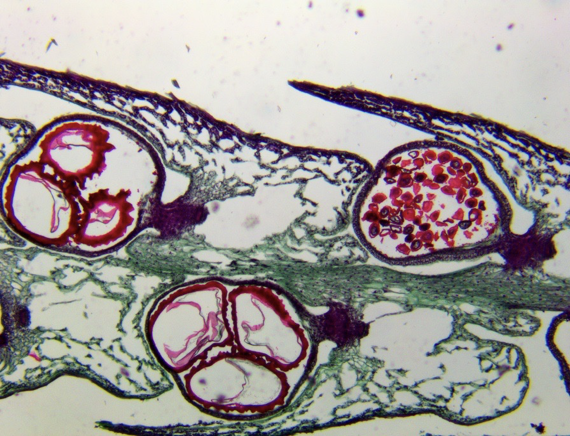
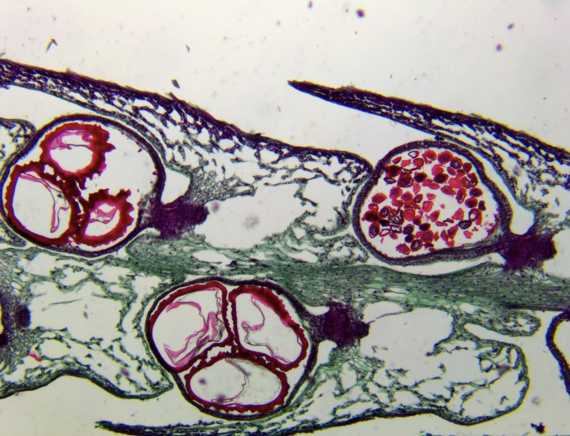
Selaginella strobilus (micrograph)
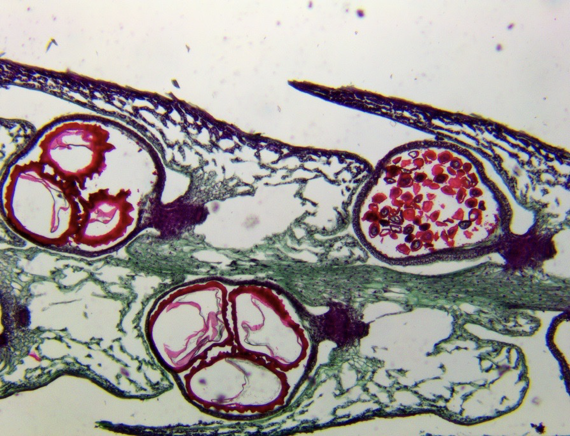
Label the megaspores and microspores on this Selaginella strobilus
megaspores are the larger female ones (farthest left)
microspores are the smaller male ones (farthest right)

Resurrection plant
phylum lycophyta
Phylum psilophyta characteristics
most “primitive” vascular plants
no true leaves
aka whisk ferns
Psilophyta example
Psilotum
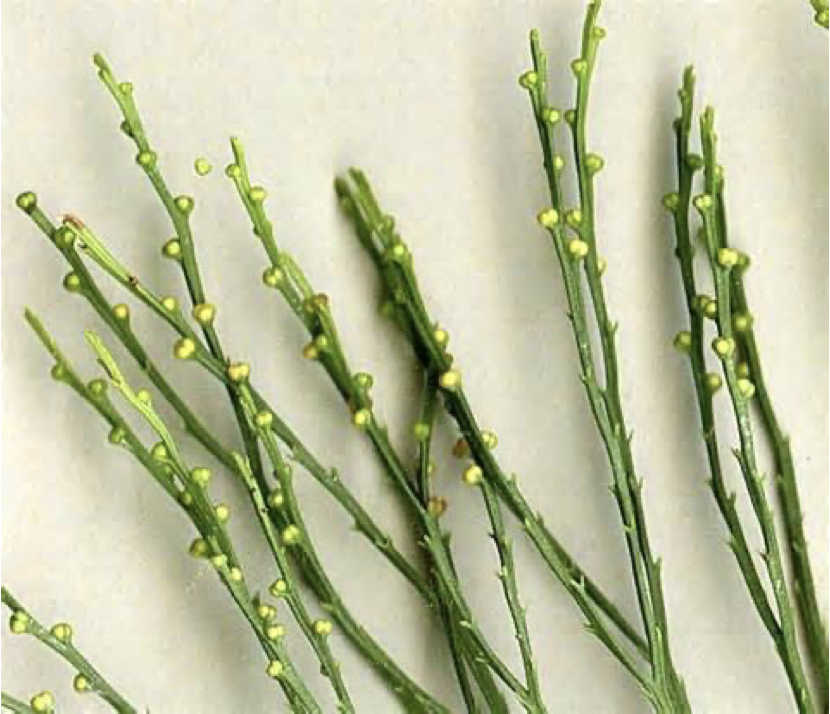
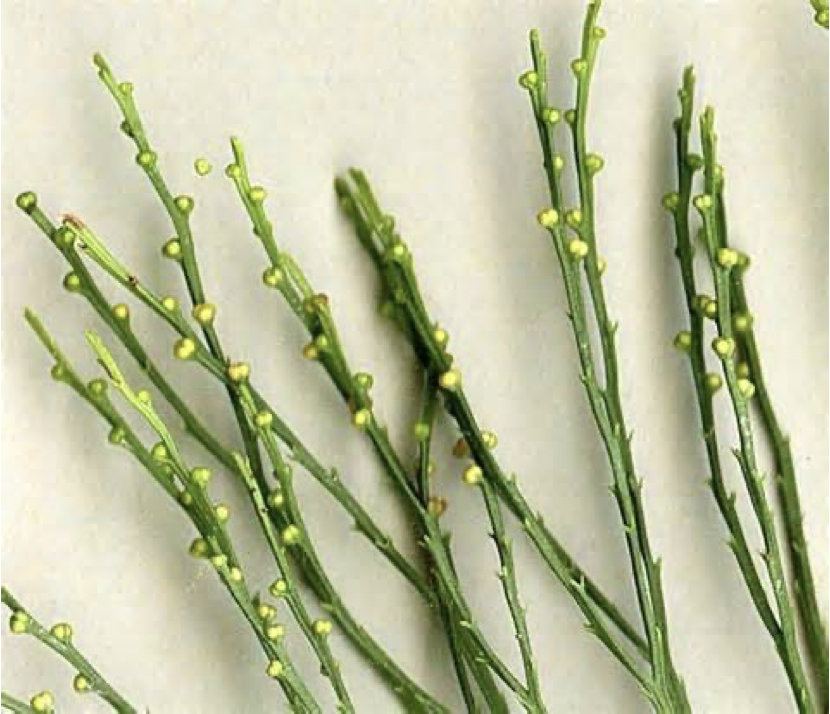


label the parts of this psilotum
yellow: sporangia
Phylum anthrophyta example
Equisetum
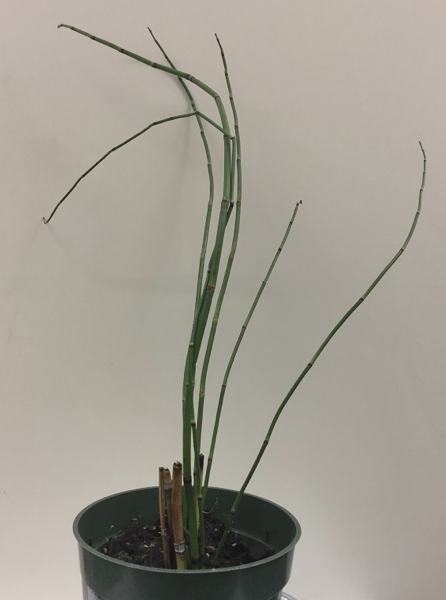


Equisetum pressed specimen

Equisetum strobilus close up
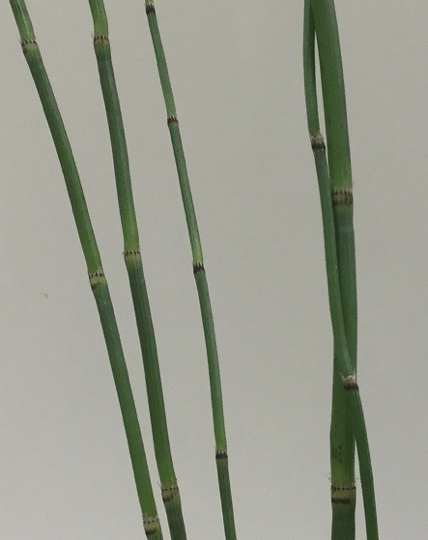

Equisetum close look at nodes/internodes
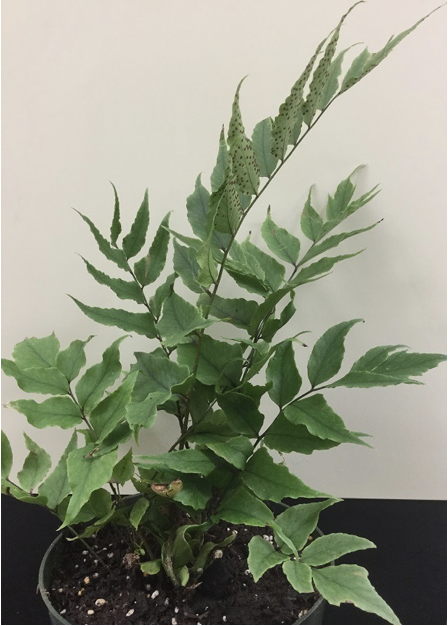
largest group of seedless vascular plants
phylum pterophyta
rhizomes
horizontal underground stems
fronds
large leaves of ferns
sori
clusters of sporangia
prothallus
flat, heart shaped, thalloid structure
(gametophyte)
fiddleheads
tightly coiled fronds
protonemata
filament of cells
sporangium
structures in which spores are produced
archegonia
produced on underside of archegoniophore
female gametophyte
antheridia
produced in cavities connected by pores to the upper surface
(male gametophyte)
lifecycle of ferns
alteration of generations
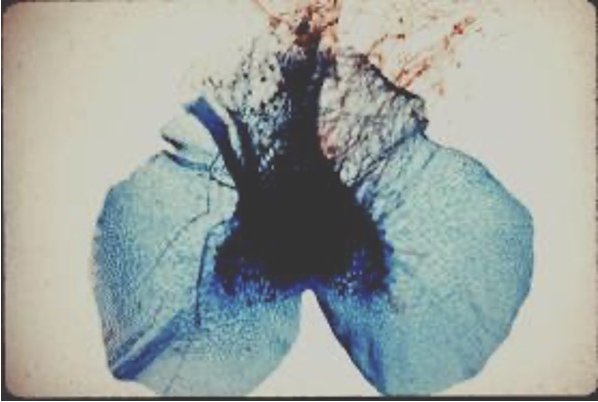
fern prothallus
(gametophyte stage)
phylum pterophyta example
