Chemical Changes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Oxidation
Gain of oxygen, loss of electrons
Reduction
loss of oxygen, gain of electrons
Reactivity of metals with acids
Metals above H2 in reactivity series react with acid to produce H2.
→ The more reactive the metal is, the quicker and more violent reaction with acid occurs.
→ Metals below H2 don't react with acids.
Reactivity of metals with water
Most metals above H2 react with water → aluminium is the exception.
Displacement reaction
A reaction where a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from a compound.
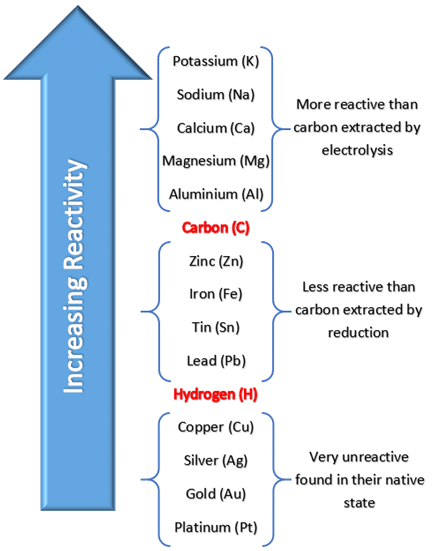
Extraction of metals less reactive than carbon
Reduction with carbon.
→ Carbon displaces the metal in a metal oxide - gets oxidised to carbon oxides.
→ Metal from the metal oxide gets reduced to the pure metal
This is a redox reaction (reduction and oxidation)
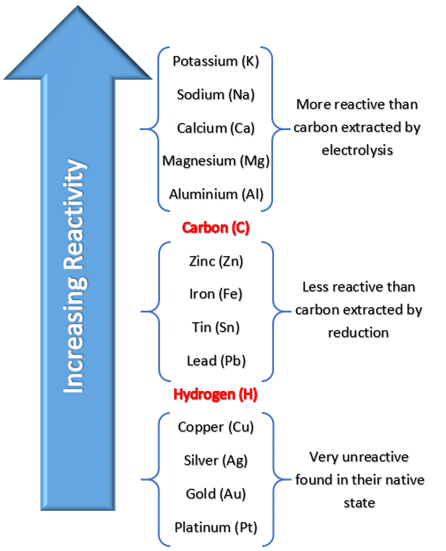
Extraction of metals more reactive than carbon
By electrolysis.
Ionic equation of Neutralisation reactions
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H20(l)
General equations
Metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Metal oxide + acid → salt + water
Base + acid → salt + water (neutralisation)
Metal carbonate + acid → salt + water + carbon dioxide
Metals that react with acid
Those above hydrogen.
Redox reaction
A reaction involving both oxidation and reduction.
Formation of Soluble Salt
React the excess acid with some insoluble chemical (e.g. metal oxide)
filter off the leftovers
crystallise the product.
Products of Acids and Alkalis
Acids produce hydrogen ions (H+)
Alkalis produce hydroxide ions. (OH-)
Definition of Bases, Acids, and Alkalis
Bases are compounds that neutralise acids.
Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions.
Alkalis are soluble bases - produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions.
Strong Acid
Strong acid is completely ionised in aqueous solution.
Weak Acid
Weak acid is only partially ionised in aqueous solution.
Concentrated Acid
Concentrated acid has more particles of acid per unit volume.
Dilute Acid
Dilute acids have less particles of acid per unit volume.
Change in H+ Concentration with pH
As the pH is decreased by one unit, the hydrogen ion concentration increases by a factor of 10.
What is electrolysis?
The passing of an electric current through ionic substances that are molten or in solution to break them down into elements.
→ Ions are discharged (they lose/gain electrons) at electrodes
What is an electrolyte?
The liquid/solution which conducts electricity.
Cathode and Anode
Cathode is the negative electrode.
Anode is the positive electrode.
What occurs at the cathode and what occurs at the anode during electrolysis?
Reduction occurs at the cathode: Ions gain electrons and lose oxygen.
Oxidation occurs at the anode. Ions lose electrons and gain oxgyen.
In aqueous electrolysis, which element is discharged at the cathode?
The less reactive element discharges at the cathode.
→ Hydrogen is produced unless there is a less reactive metal, in which case the said metal is produced.
→ Oxygen is produced at the anode unless the solution contains halide ions, in which case halogen molecules are produced.
How is aluminium manufactured?
Aluminium is made through the electrolysis of aluminium oxide and cryolite.
→ Lots of energy is needed to produce the current in electrolysis which makes this process expensive.
→ Positive electrode needs to be continually replaced → oxygen is formed → reacts with carbon forming CO2 → which burns away
What are the half equations in the extraction of aluminium?
Al3+ + 3 e− → Al (cathode).
2 O2− → O2 + 4 e− (anode).
→ Oxygen reacts with C of the anode producing CO2.
Why is cryolite used in this process?
It lowers the melting point of aluminium oxide.
→ Reducing activation energy needed and therefore energy costs.