Pigments
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:01 PM on 2/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
Lipofuscin
An insoluble pigment, also known as lipochrome or wear-and-tear pigment
2
New cards
Lipofuscin is composed of:
Polymers of lipids and phospholipids in complex with protein
3
New cards
melanin
a normal endogenous brown-black pigment formed by enzymatic oxidation of tyrosine to
dihydroxyphenylalanine in melanocytes
dihydroxyphenylalanine in melanocytes
4
New cards
homogentisic acid
a black pigment formed in patients with alkaptouria (lacking homogentisic oxidase) that deposits in skin and connective tissue
5
New cards
anthracosis
accumulations of carbon blacken the tissues of the lungs
6
New cards
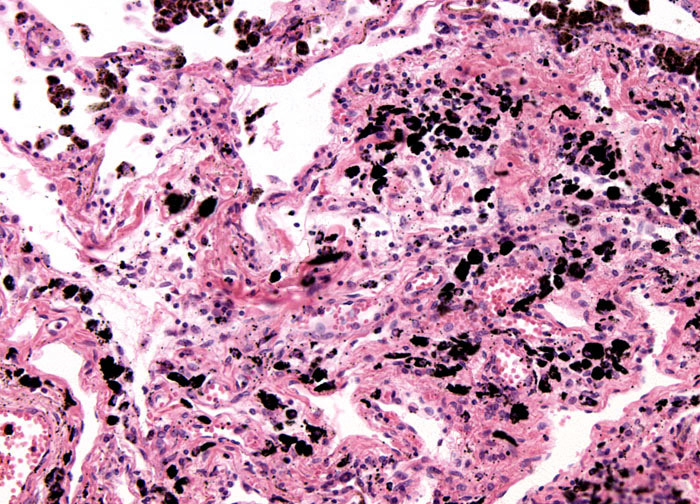
anthracosis
7
New cards
Lipofuscin is a telltale sign of
free radical injury and lipid peroxidation
8
New cards
Lipofuscin is prominent in
the liver and heart of aging patients, or patients with severe malnutrition and cancer cachexia
9
New cards
hemosiderin
a hemoglobin-derived, golden yellow-to-brown, granular, or crystalline pigment is one of the major storage forms of iron
10
New cards
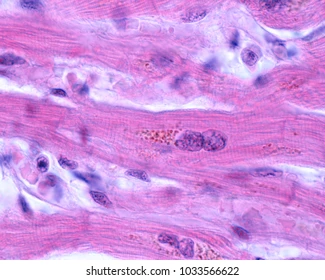
lipofuscin granules in cardiac myocytes
11
New cards
example of localized hemosiderosis
common bruise
12
New cards
main causes of hemosiderosis
1. increased absorption of dietary iron
* due to an inborn error of metabolism called hemochromatosis
2. hemolytic anemia
* excess lysis of red blood cells leads to release of abnormal quantities of iron
3. repeated blood transfusions
13
New cards
hemosiderosis
when there is systemic iron overload, hemosiderin may be deposited in many organs and tissues
14
New cards
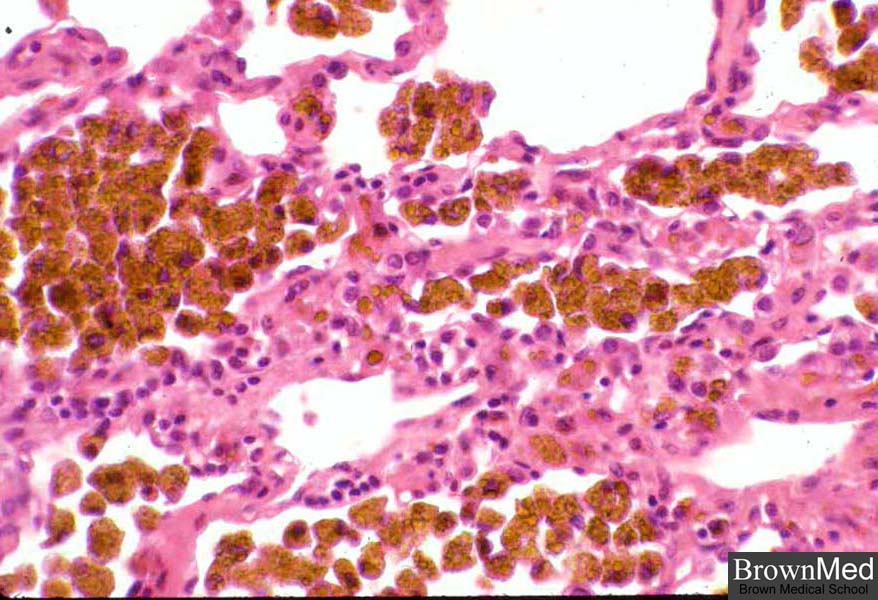
hemosiderosis
15
New cards
pathologic calcification
the abnormal tissue deposition of calcium salts, together with smaller amounts of iron, magnesium, and other mineral salts
16
New cards
forms of pathologic calcification
1. dystrophic calcification
2. metastatic calcification
17
New cards
dystrophic calcification
the deposition of calcium in dead or dying tissue, the serum calcium levels are normal and calcium metabolism is normal
18
New cards
metastatic calcification
the deposition of calcium in normal and healthy tissue. It is seen in hypercalcemia. The serum calcium levels are elevated and the calcium metabolism is abnormal
19
New cards
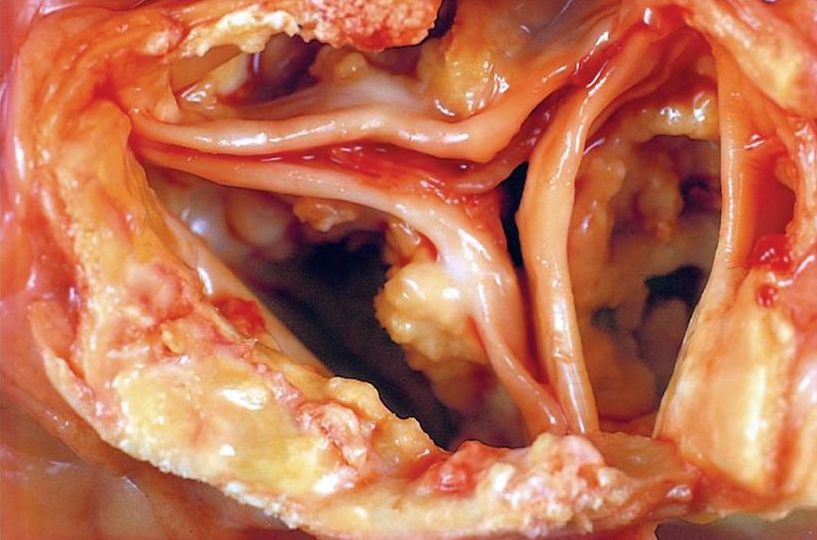
dystrophic calcification of the aortic valve
20
New cards
four principal causes of hypercalcemia
1. elevated parathyroid hormone
2. bone destruction (reabsorption of bone tissue)
3. Vitamin D related disorders
4. Renal failure