Chem Unit 2 - Virginia
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus, which determines its place on the periodic table
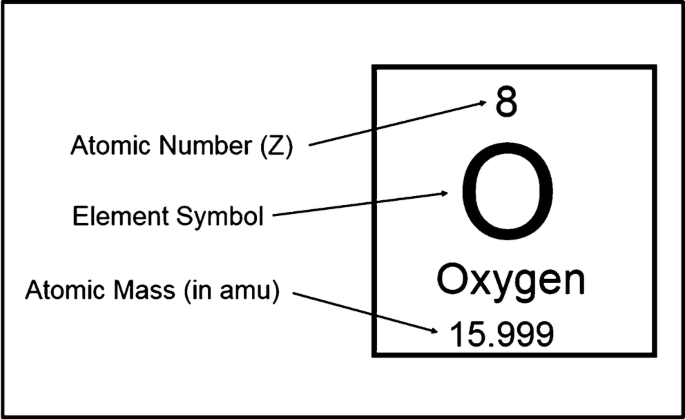
Atomic Mass
The total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus
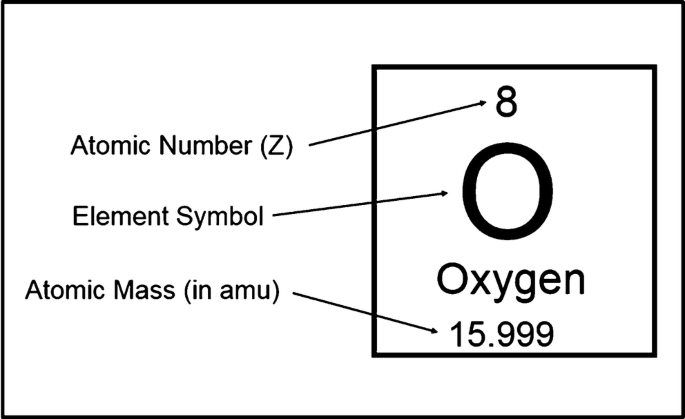
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different masses & different neutrons
Protons and electrons both:
Have an electrical charge
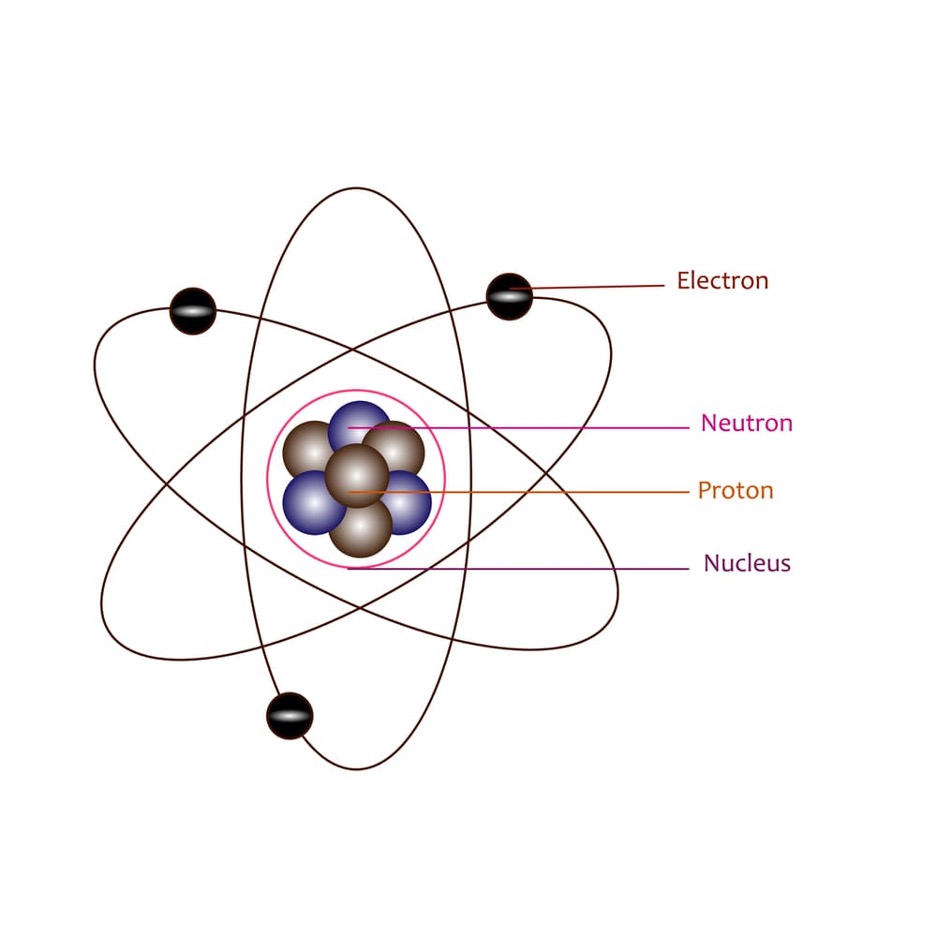
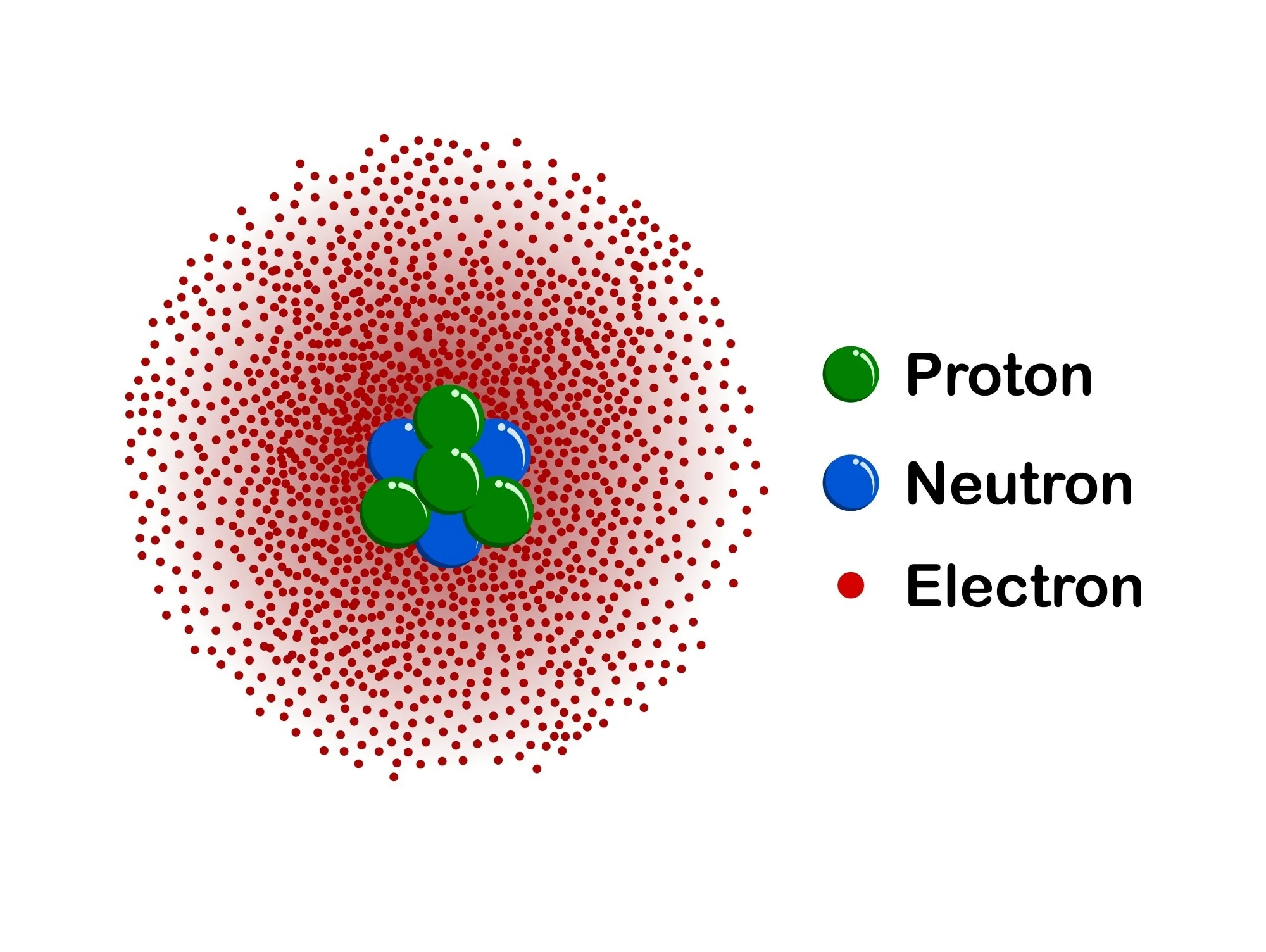
Protons
The subatomic particle that identifies an atom
Valence Electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
Subatomic particle that has no charge:
Neutron
Subatomic particle that has no mass
Electron
Atom
The smallest piece of an element that retains the properties of that element
Nucleus
A dense region in the center of an atom; it is made of protons and neutrons and contains almost all of an atom's mass
Electrons live
Outside of the nucleus
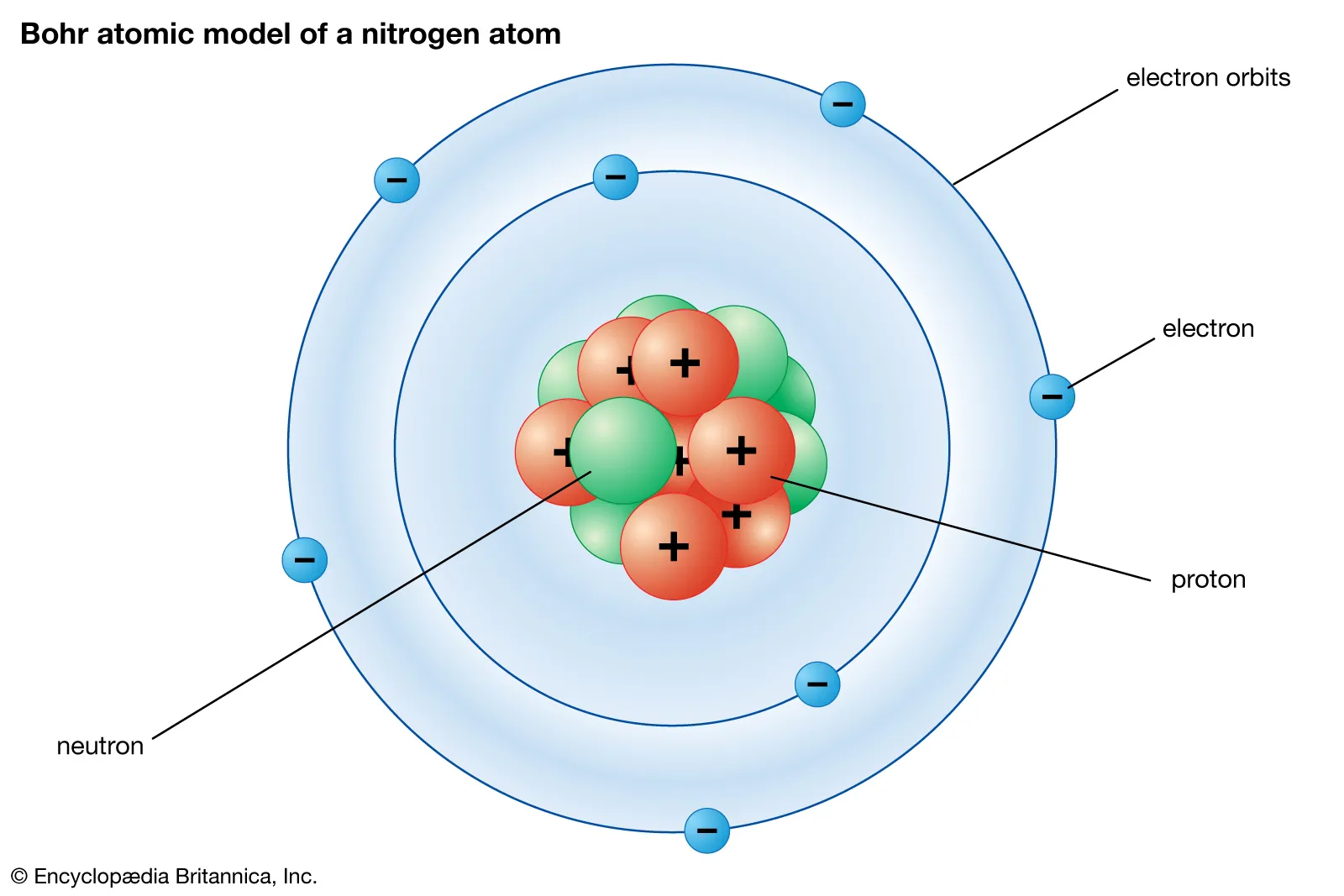
Most of the atom is made up of
Empty space
Atomic number is the__
Number of protons In nucleus of atom
Mass number is the__
Sum of protons and neutrons in an atom
In a neutral atom the__
Number of protons equals the number of electrons
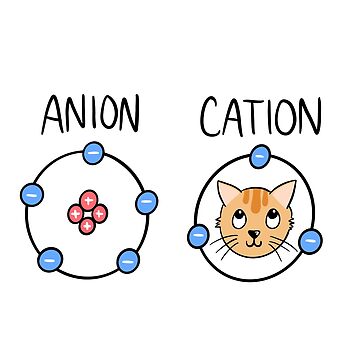
Ions = ___
Charged atoms
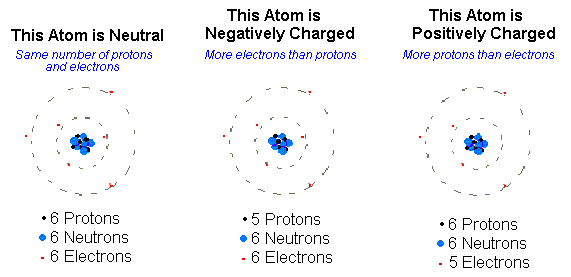
Cation (+ Charge) ….
Lose electrons! (Subtract # of protons w/ atomic #)

Anion (-Charge)
Gain electrons! ( Add # of protons w/ atomic #)
Mass formula =
P+ + n0
Chemical properties of isotopes of the same element are..
The same.. because chemical behavior is associated with electrons not neutrons
Physical properties of isotopes are..
Different because physical properties are based on mass

Atomic mass =
Weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element
Scientist: Dmitri Mendeleev..
Published a table with elements organized by increasing atomic mass
Period Table: Periods (There are 7!!)
The horizontal rows of the table are called (PERIODS OR ENERGY LEVELS)
Elements in the same period have…
The same number of shells/energy levels
Vertical columns of the periodic table are called..
Groups or families
Elements in any group of the periodic table have…
Similar physical and chemical properties
Elements in the same group have..
Same number of valence electrons
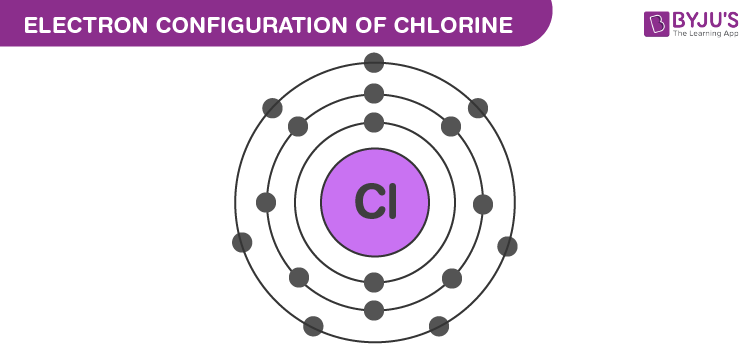
Electron configuration is..
Representation of the arrangement of electrons in the energy levels, sublevels, and orbitals
Abundance formula
(Mass * Abundance %/100) + (Mass * Abundance %/100)
How to calculate neutrons =
mass - atomic
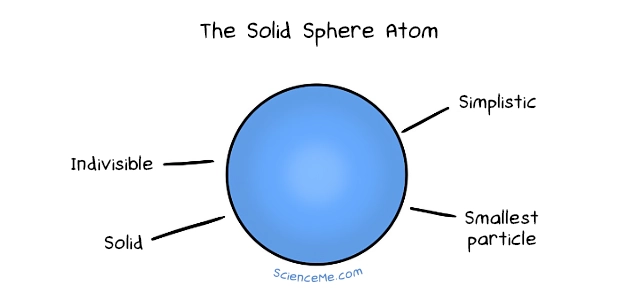
John Dalton developed..
Atomic Theory - Solid Sphere Model
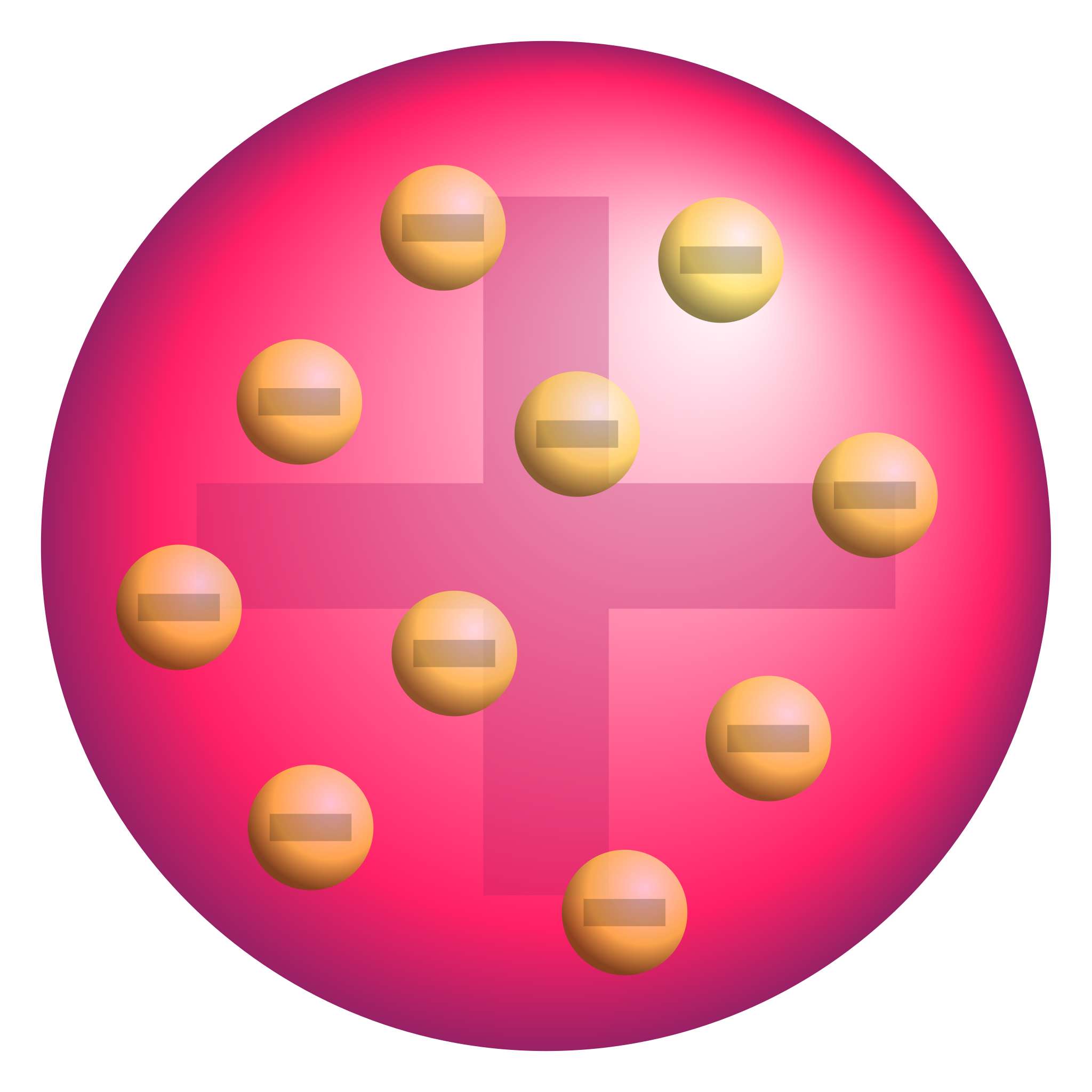
JJ Thomson discovered…
Electrons - Plum Pudding Model
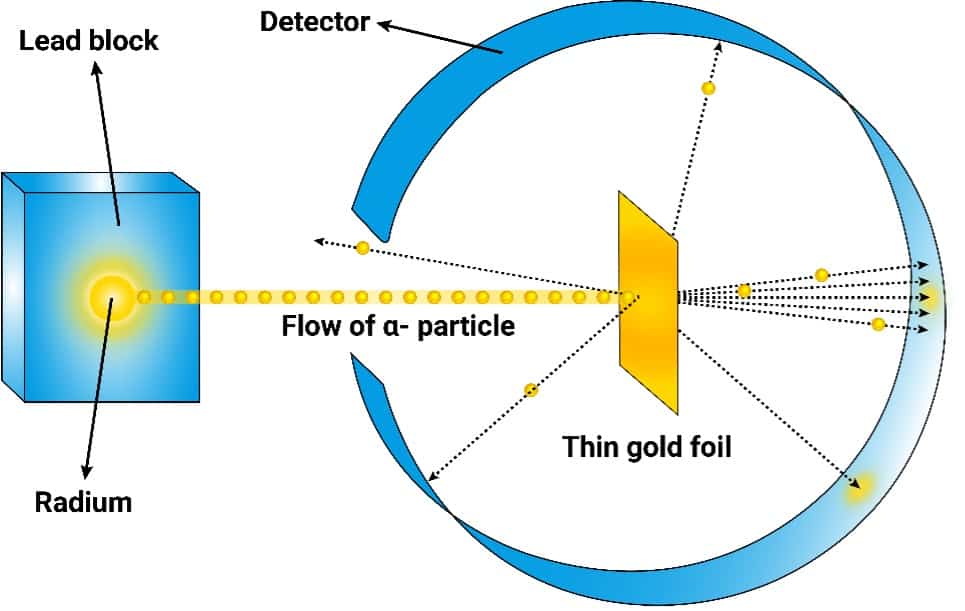
Ernest Rutherford discovered…
Nucleus - Gold Foil Experiment
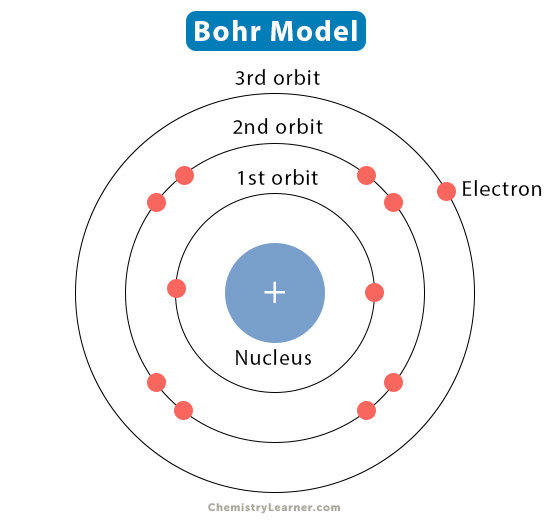
Niels Bohr discovered..
Electrons have a defined path - Bohr Model
how do you find if an isotope is more abundant than another?
by the ratio of the number of neutrons to the number of protons in the nucleus.
James Chadwick discovered…
Neutrons - Quantum mechanical model
Erwin Shrodinger discovered…
Electron cloud - Quantum mechanical model
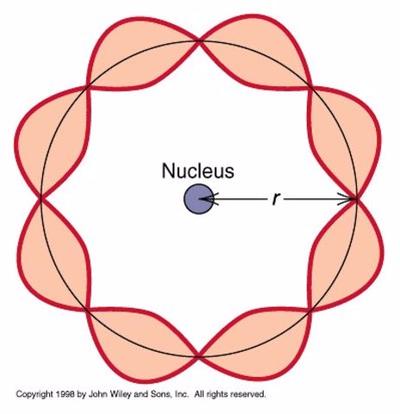
Louis Debroglie discovered…
Particles can have wave like properties…
In the electron cloud, electrons are found & allowed in only certain__
energy levels, in the electron cloud
The electrons further from the nucleus are found in__
higher energy levels
What state are electrons normally found in?
Ground state
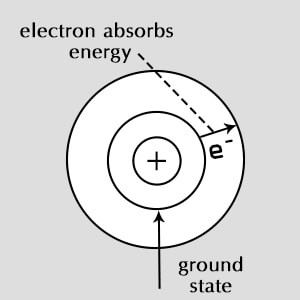
when the electrons in an atom becomes excited by absorbing energy from their surroundings, they jump to__
higher energy levels
the excited state is less__ than the ground state therefore__
LESS STABLE! and FALLS BACK or relaxes to return to the lower energy ground state
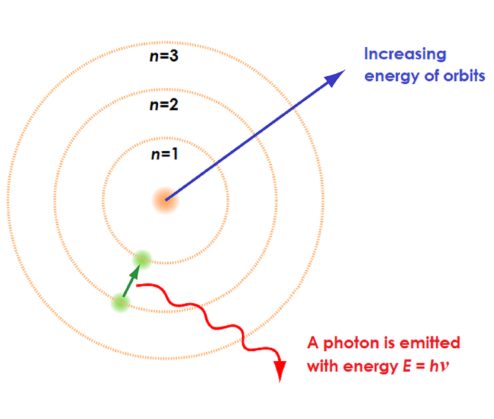
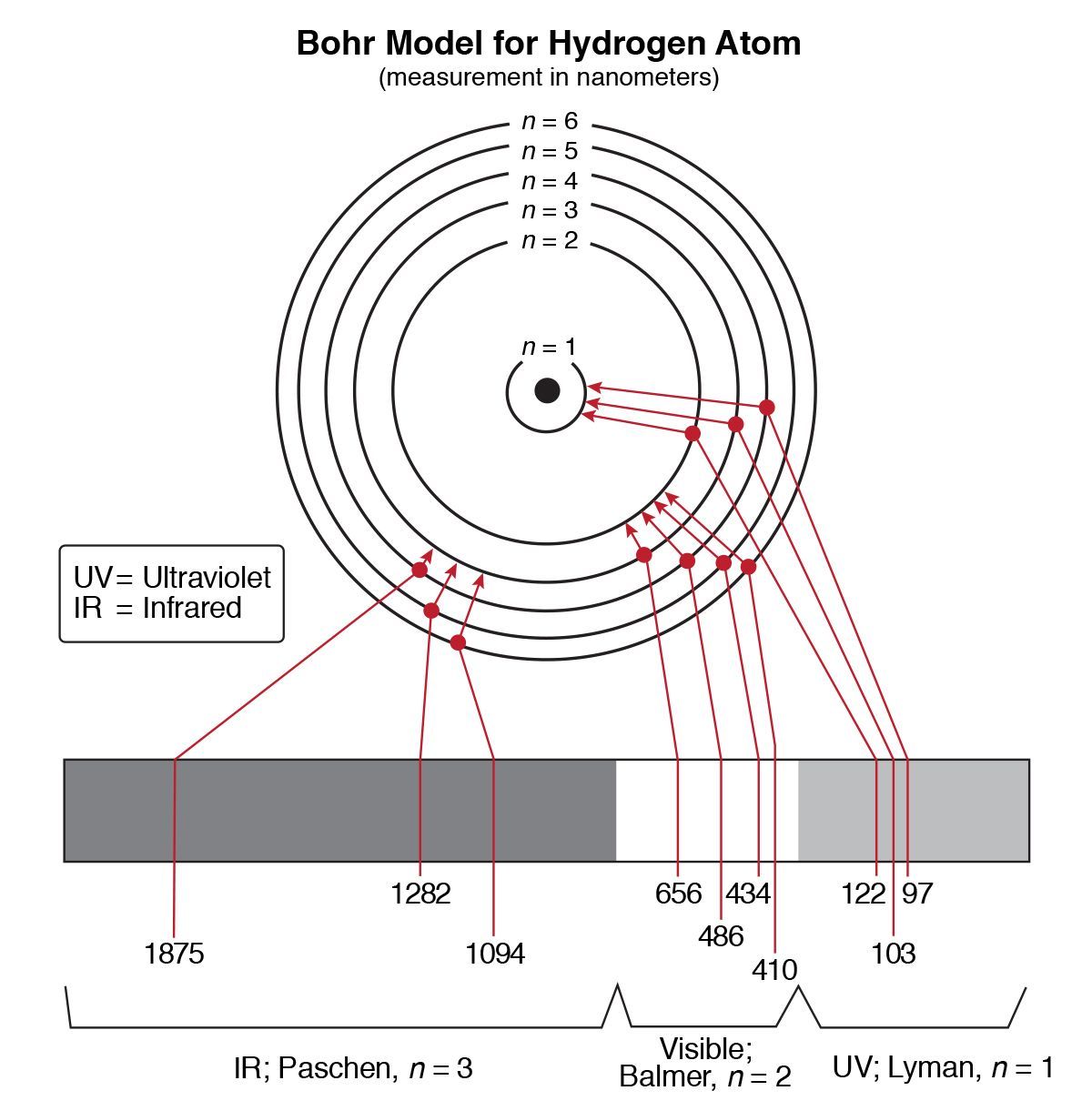
When electrons fall back a specific amount of__
quantum energy is emitted
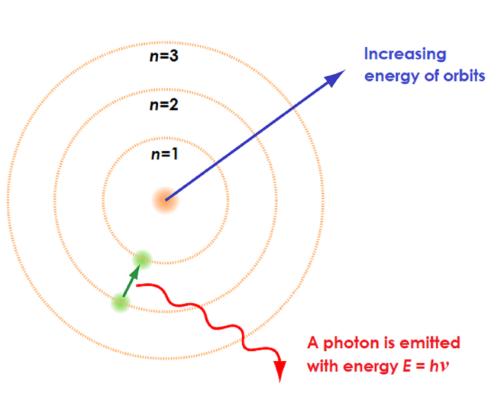
Atomic emission Spectra - the energy is given out in the form of__
a photon of light
If we see color, then the emission is __
In the visible range
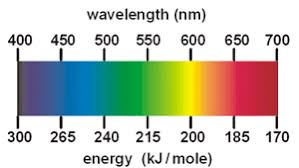
Energy is always ___
Increasing
Wavelength is always__
Increasing
The length of a wave is ____ related to its energy
Inversely
Violet light energy = __ energy, __ wavelength
HIGHER ENERGY, SHORTER WAVELENGTH
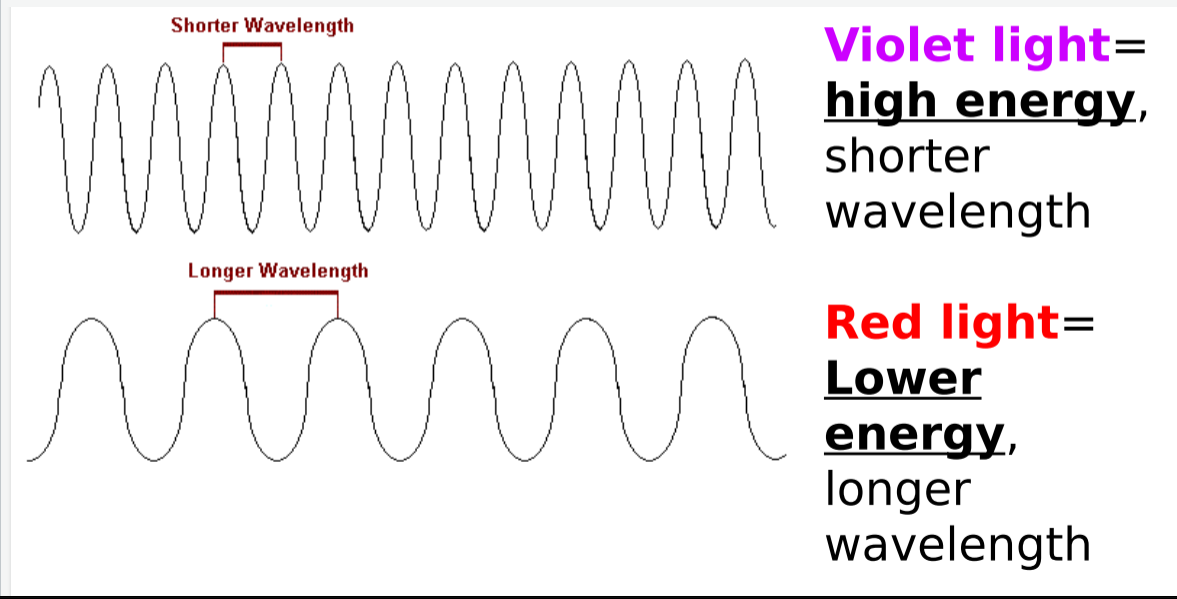
Red light energy = __ energy, __ wavelength
LOWER ENERGY, HIGHER WAVELENGTH
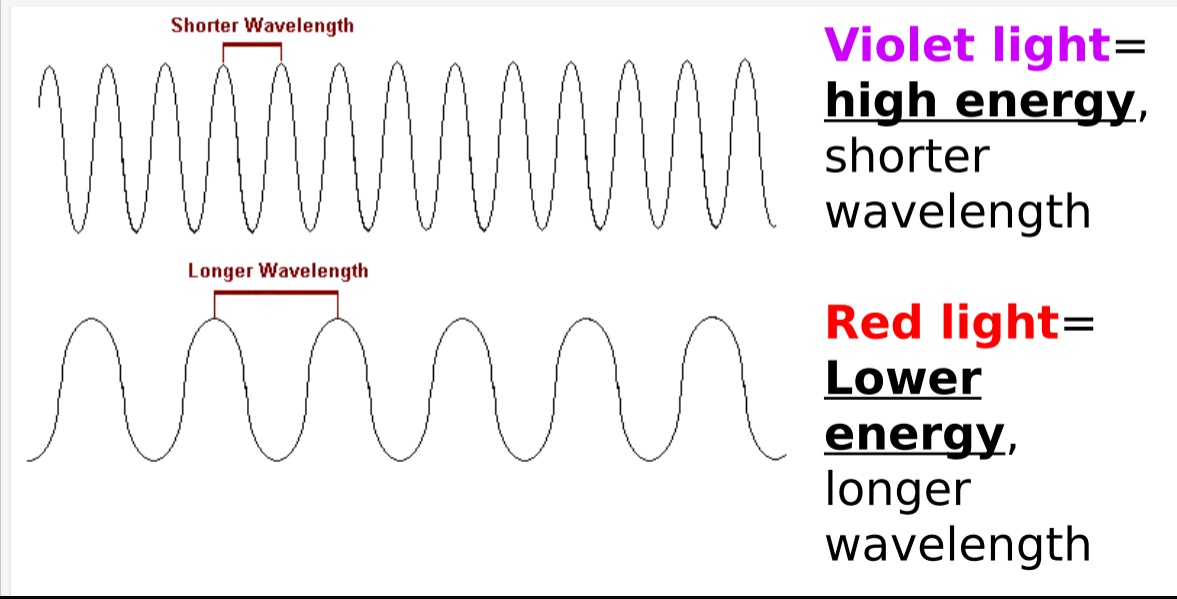
White light is made up of ___
ALL COLORS of the spectrum
Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the longest wavelength?
Radio
Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the shortest wavelength?
Gamma ray
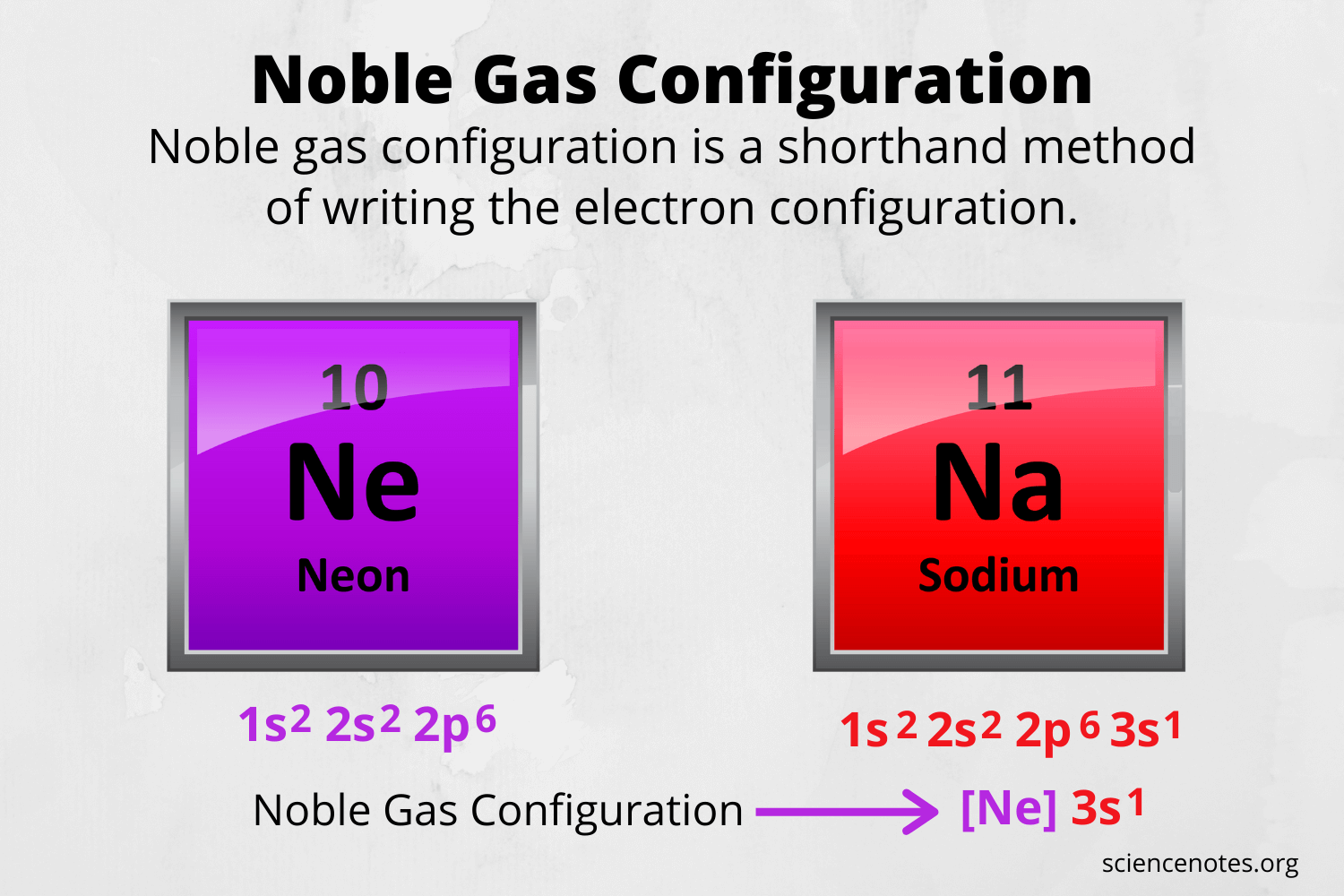
For noble gas notation - How to find noble gas using electron configuration?
By the FAR RIGHT of the periodic table.