PFT INTERPRETATION
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
volume of air that can be inhaled after normal inspiration
3,100 ml
Normal Volume for Inspiratory Reserve Volume
Expiratory Reserve Volume
Volume of air that can be exhaled after normal expiration
1,200ml
Normal Volume for Expiratory Reserve volume
Tidal Volume
volume of air moves normally in and out of the lungs.
5-8 ml/kg
Normal value for Tidal Volume
Residual Volume
amount of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal expiration
Inspiratory Capacity
Maximum volume of air that can be inhaled from the normal resting end-expiratory level
VT + IRV
Formula for Inspiratory Capacity
Functional Residual Capacity
Volume of air remaining in the lungs at the resting end-expiratory level
ERV + RV
Formula for Functional Residual Capacity
Vital Capacity
Maximum volume of air that can be exhaled following a maximum inspiration
IRV + VT + ERV
Formula for Vital Capacity
Total Lung Capacity
Total amount of air inside the lungs after maximum inspiration
VT x F
formula for Ventilation
Direct Spirometry
Involves the use of a spirometer to measure the volumes of air moving into and out of a subject’s lungs during breathing
Indirect Spirometry
It is used to determine lung volumes that are not measurable by direct spirometry. These volumes are RV, FRC, and TLC
0.5 - 1 Hz
Normal Acceptable panting for Indirect Spirometry
Gas Dilution
Operate on Boyle's law except that the fractional concentration of a known gas is used instead of its partial pressure
Can only measure lung volumes in communication with conducting airways
Nitrogen washout
Used to determine the anatomical deadspace in the lungs
This technique can only measure gas that is in communication with the mouth
3-7 minutes
How many minutes of breathing 100% O2 to washout N2 from the lungs
less than 1.5%
Test is successfully completed when the N2 Levels decrease to become less than ___for at least 3 successive breaths
3-4 minutes
Healthy subjects should washout N2 completely in
Tissot Spirometer
Collects the nitrogen that is exhaled after inhaling 100% oxygen
Helium Dilution
A technique for measuring functional residual capacity and residual volume
It is based on the principle that if a known volume and concentration of helium are added to a patient's respiratory system, the helium will be diluted in proportion to the lung volume to which it is added.
7 minutes
How many minutes until Helium is stable during Helium Dilution
less than 0.02% over a 30 second interval
during helium dilution, A state of equilibrium is defined as helium concentration changes of___, indicates that the test is succesful
Body Plethysmograph
The amount of CHANGE in air pressure inside the box and CHANGE in volume during breathing is measured and used in the equation
sinusoidal pump, 30ml
What pump is used for calibrating the body pleth and how much ml
Ellipsoid Volume Method
Assumes that the lungs, in cross section through the chest, are basically elliptical in shape
Measurements are made on the x-rays that divide the thorax into a series of five vertical segments Its volume is determined on the basis of height, width and depth dimensions
Planimetry Method
Uses regression equations to correlate the lung surface areas measured on chest X rays to TLC measurements made by body plethysmographs
Obstructive Pattern
v Increase FRC is considered pathologic
v FRC values >120% of predicted represent air trapping
v Emphysematous changes
v Obstruction caused by asthma or bronchitis
Normal, Decreased, Increased, >35%+
n TLC ____
n VC ____
n FRC AND RV _____
n RV/TLC% _____
DURING OBSTRUCTIVE PATTERN
Restrictive Pattern
v FRC, RV and TLC typically decreased
v Usually lung volumes are decreased equally
v When TLC is <80% a restrictive process is present
v RV/TLC is relatively norma
Sarcoidosis, Tuberculosis, Pneumonectomy, Pneumonia
Intrinsic Restrictive Lung Disorders
Scoliosis/Kyphosis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Pleural Effusion, Pregnancy, Gross Obesity, Tumors/Ascite
Extrinsinct Restrictive Lung Disorders
Generalized Weakness, Paralysis of the diaphragm, Myasthenia Gravis, Muscular Dystrophy, Poliomyelitis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Neuromuscular Restrictive Lung Disorders
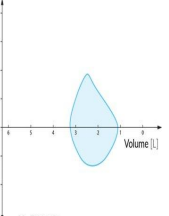
Normal
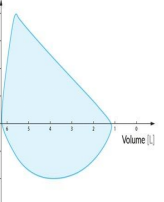
Acute Asthma
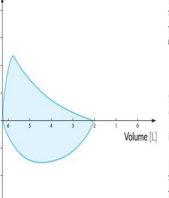
Emphysema
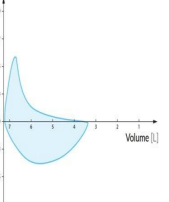
Fixed Upper Airway Obstruction
Fibrosis