AP Psych Unit 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Psychology
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes.
Socrates
An ancient Greek philosopher who believed the mind is separable from the body and continues after death, asserting that knowledge is innate
Plato
A student of Socrates who also believed in the separability of mind and body and that knowledge is innate
Aristotle
A student of Plato who derived principles from careful observations and believed knowledge grows from experiences.
Rene Descartes
A philosopher interested in the communication between mind and body, who believed the brain contained 'animal spirits' that provoked movement.
Francis Bacon
A philosopher who advocated for a scientific approach based on experiments, experience, and common sense judgment.
John Locke
A philosopher who proposed the concept of Tabula Rasa, suggesting that personality and knowledge are influenced by experience.
Empiricism
The theory that knowledge is derived from sense-experience
Wilhelm Wundt
The first person to use the scientific method in a psychology experiment, establishing psychology as a scientific discipline.
Scientific Method
A systematic process for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge.
Edward Titchener
A student of Wundt who introduced structuralism and the method of introspection.
Structuralism
An early school of psychology that aimed to identify the structure of the mind through introspection.
Introspection
The examination of one's own conscious thoughts and feelings.
William James
A psychologist who emphasized the functions of the mind over its structure, influenced by Darwin.
Functionalism
A school of psychology that focused on the purpose of consciousness and behavior.
Mary Calkins
A student of William James who became the first female president of the APA, denied a degree because of her gender.
Margaret Floy Washburn
The first woman to earn a PhD in psychology.
Experimental Psychology
The branch of psychology that utilizes experimental methods to study behavior and mental processes.
Sigmund Freud
A psychologist known for developing psychoanalysis and theories about the unconscious mind.
Behaviorism
A theoretical perspective that focuses on observable behaviors and the ways they're learned.
B.F. Skinner
Study of observable behavior, the box.
Humanistic psychology
A psychological perspective that emphasizes the study of the whole person.
Cognitive Neuroscience
The study of the biological processes and aspects that underlie cognition.
Nature - Nurture Issue
The debate regarding the relative contributions of biology and experience to human behavior.
Levels of Analysis
The different perspectives used to understand psychological phenomena.
Biological
Referring to the biological influences on behavior.
Psychological
Referring to the mental processes and behaviors.
Social-cultural
Referring to the social and cultural influences on behavior.
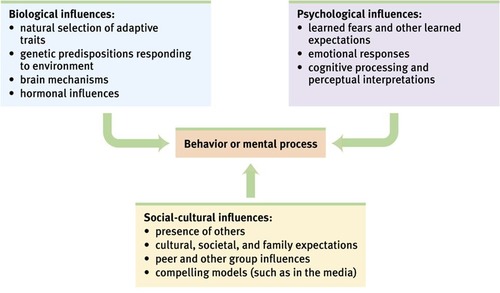
Biopsychosocial Approach
An integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis.
Psychological Approaches/Perspectives
Different ways of viewing psychological phenomena.
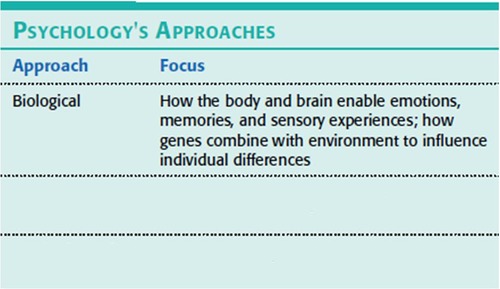
Biological psychology
The study of the relationship between biological processes and psychological phenomena.
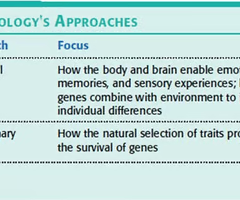
Evolutionary psychology
The study of how evolutionary principles influence human thought and behavior.
Psychodynamic psychology
The study of how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior.

Behavioral psychology
The study of observable behavior and its relationship to environmental stimuli.
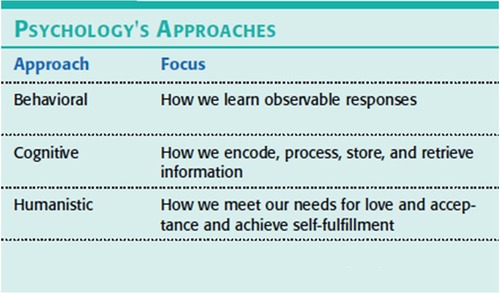
Cognitive psychology
The study of mental processes such as perception, memory, and problem-solving.
Social-cultural psychology
The study of how social and cultural factors influence behavior.
Psychometrics
The field of study concerned with the theory and technique of psychological measurement.
Developmental psychology
The study of how people grow and change throughout the lifespan.
Educational psychology
The study of how people learn and the best practices to teach them.
Personality psychology
The study of individual differences in personality traits.
Social psychology
The study of how individuals influence and are influenced by others.
Industrial/organizational psychology
The application of psychological concepts to workplace environments.
Counseling psychology.
A field that focuses on providing therapeutic treatments to clients
Clinical psychology
The branch of psychology that focuses on diagnosing and treating mental illness.
Psychiatry
A medical specialty focused on the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders.
Nature-Nurture Issue
the longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors. Today's science sees traits and behaviors arising from the interaction of nature and nurture.
Natural Selection
the principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations.
Basic Research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
Applied Research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems.
Industrial-Organizational (I/O) Psychology
the application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplaces.
Human Factors Psychology
the study of how people and machines interact resulting in the design of machines and environments.