3.3 fundamentals of data representation
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:28 PM on 6/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
0 + 0
0
2
New cards
1 + 0
1
3
New cards
1 + 1
10 ( put down the 0 and carry the 1 )
4
New cards
1 + 1 + 1
11 ( put down the 1 and carry the other 1 )
5
New cards
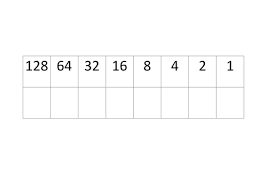
how to convert binary to denary
use the conversion table
6
New cards
how to convert denary to hexadecimal
convert denary to binary
split the conversion table in half
use the split conversion tables both with 8/4/2/1 to convert the binary into what would normally be denary
if the number is above 9 then go into letters
split the conversion table in half
use the split conversion tables both with 8/4/2/1 to convert the binary into what would normally be denary
if the number is above 9 then go into letters
7
New cards
negative binary numbers
work out the denary number in binary if it was positive
reverse the values up until the bit column with a 1 in it.
8
New cards
images
represented using binary numbers
created using a grid of pixels
created using a grid of pixels
9
New cards
pixels
the smallest part of an image
short for picture elements
short for picture elements
10
New cards
1 bit images
can only have 2 possible colours
0 = white 1 = black
0 = white 1 = black
11
New cards
2 bit images
can only have 4 possible colours
00 = white 11 = black 10 = red 01 = blue
00 = white 11 = black 10 = red 01 = blue
12
New cards
how to work out the number of colours
2 to the power of the number of bits
13
New cards
colour depth
the amount of colours available to be used in an image
14
New cards
what will happen if you increase colour depth
* increase the detail of the image
* increase the file size of the image as more bits need to be stored about each pixel
* increase the file size of the image as more bits need to be stored about each pixel
15
New cards
resolution
the ability to distinguish from 2 points
16
New cards
what happens if you increase the resolution
* the clearer the image and the more detail it has
* the larger the file size as data has to be stored about each pixel
* the larger the file size as data has to be stored about each pixel
17
New cards
how do you calculate the image file size
number of pixels(height x width) x colour depth
18
New cards
character set
all the characters that can be represented in a computer system
19
New cards
ASCII
american standard code of information interchange
20
New cards
how many bits did the original ascii account for
7 bits - 128 characters
21
New cards
how many bits did the extended ascii account for
8 bits - 256 characters
22
New cards
what language was ascii used for
english
23
New cards
unicode
universal binary language
Unicode was made because ASCII couldn’t represent all the characters in all the different languages
24
New cards
how many bits does Unicode account for
16 bits - 65,356 characters
25
New cards
analogue sound
waves that are continuously changing in value e.g our voice
they cannot be understood by a computer
they cannot be understood by a computer
26
New cards
digital sound
sound waves which are created from samples of analogue waves,
represented by binary and can be understood by the computer
represented by binary and can be understood by the computer
27
New cards
how do we convert analogue sounds to digital
the analogue sounds can be picked up by a microphone and sent to an ADC (analogue to digital converter)
they are then converted into binary values and stored into the computer
they are then converted into binary values and stored into the computer
28
New cards
sample rate
the number of times a sound is sampled per second measured in hz
29
New cards
sample resolution
number of bits used to represent sound levels
I.e how clear the sound is
30
New cards
bit rate
the space available to store each sample and is measured in kilobits per second
31
New cards
how to calculate sound file size
sample rate x sample resolution x length in seconds
32
New cards
binary shift
when a binary number is shifted one direction
if it is shifted to the left on the binary table the value multiplies by 2
if it is shifted to the right on the binary table the value divides by 2
if it is shifted to the left on the binary table the value multiplies by 2
if it is shifted to the right on the binary table the value divides by 2