Thermodynamics Part 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Spontaneous reactions:
NO continuous WHAT assistance is required
May require a “WHAT” but self sufficient after
Not necessarily an WHAT reaction (can be slow but spontaneous)
Can be WHAT or WHAT
Spontaneous reactions:
NO continuous EXTERNAL assistance is required
May require a “JUMP START” but self sufficient after
Not necessarily an INSTANTANEOUS reaction (can be slow but spontaneous)
Can be EXOTHERMIC or ENDOTHERMIC
Non-spontaneous process
Products can still be obtained but continuous WHAT assistance is requires
Non-spontaneous process
Products can still be obtained but continuous EXTERNAL assistance is required (boiling water - applying heat)
If the forward direction is SPONTANEOUS, the reverse reaction is WHAT
If the reverse direction is SPONTANEOUS, the forward reaction is WHAT
If the forward direction is SPONTANEOUS, the reverse reaction is NON-SPONTANEOUS
If the reverse direction is SPONTANEOUS, the forward reaction is NON-SPONTANEOUS
Gibb’s free energy (G)
A property thats analogous to WHAT in chemical system
If spontaneous ΔG WHAT 0KJ
At equilibrium ΔG WHAT 0KJ
Non-spontaneous ΔG WHAT 0KJ
Gibb’s free energy (G)
A property thats analogous to POTENTIAL ENERGY in chemical system
If spontaneous ΔG < 0KJ
At equilibrium ΔG = 0KJ
Non-spontaneous ΔG > 0KJ
How to determine Gibb’s free energy
ΔG = ΔrH - TΔS
Entropy (S)
A measure of WHAT or WHAT in a system resulting from the dispersal of WHAT and/or WHAT
Units = WHAT
The more disordered the system → The WHAT the entropy
Entropy (S)
A measure of RANDOMNESS or DISPERSAL in a system resulting from the dispersal of MATTER and/or ENERGY
Units = J/molK
The more disordered the system → The LARGER the entropy
Entropy of the universe is always WHAT
Entropy of the universe is always INCREASING
What is the equation for entropy
ΔrS = ∑nPΔPS - ∑nRΔRS
ΔS > 0 = WHAT
ΔS = 0 = WHAT
ΔS < 0 = WHAT
ΔS > 0 = Spontaneous
ΔS = 0 = Equilibrium
ΔS < 0 = Non-spontaneous
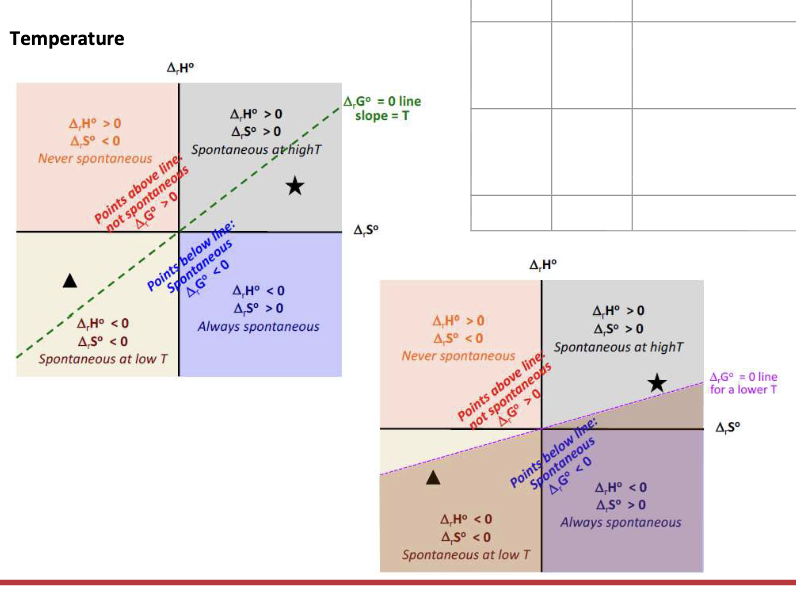
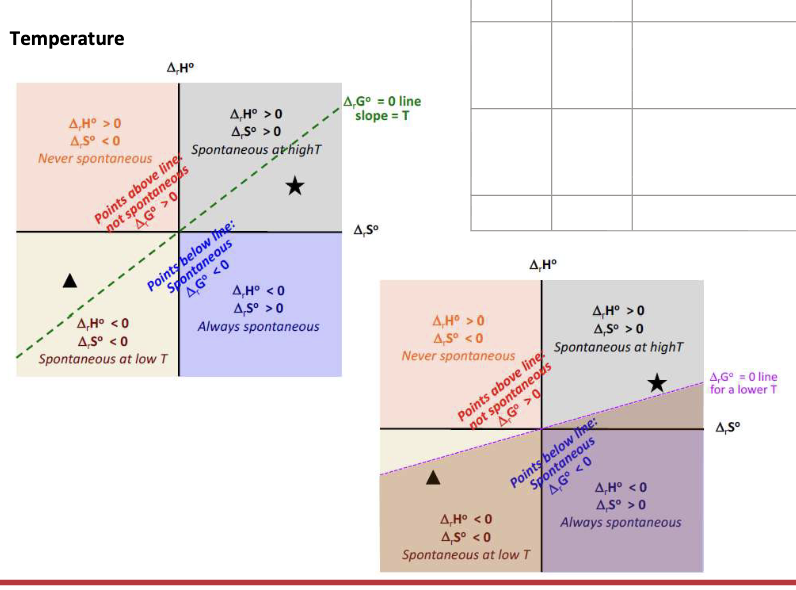
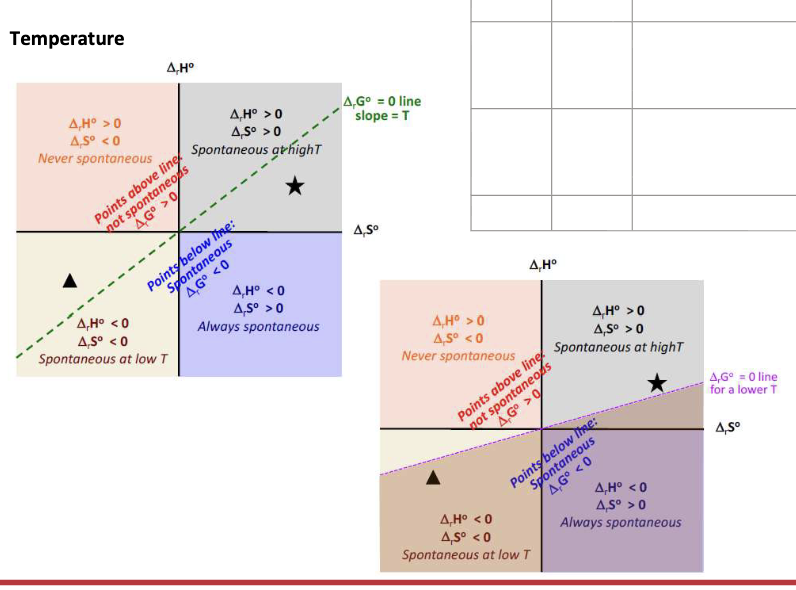
Equation for the spontaneity of a reaction
ΔGrxn = ΔrHrxn - TΔSrxn
What affects the spontaneity of a given reaction:
ΔS and ΔH vary very slightly with WHAT → independent of WHAT
ΔG is strongly WHAT on temp
What affects the spontaneity of a given reaction:
ΔS and ΔH vary very slightly with TEMP → independent of TEMP
ΔG is strongly DEPENDENT on temp
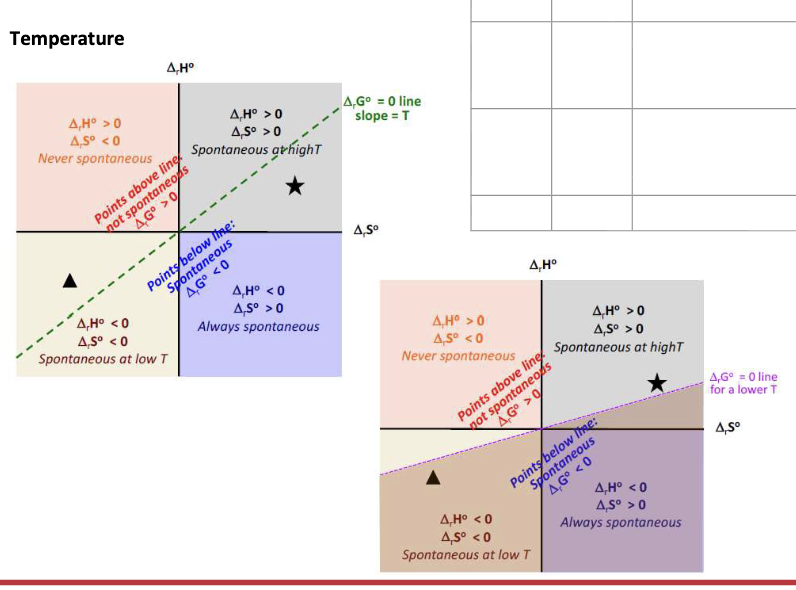
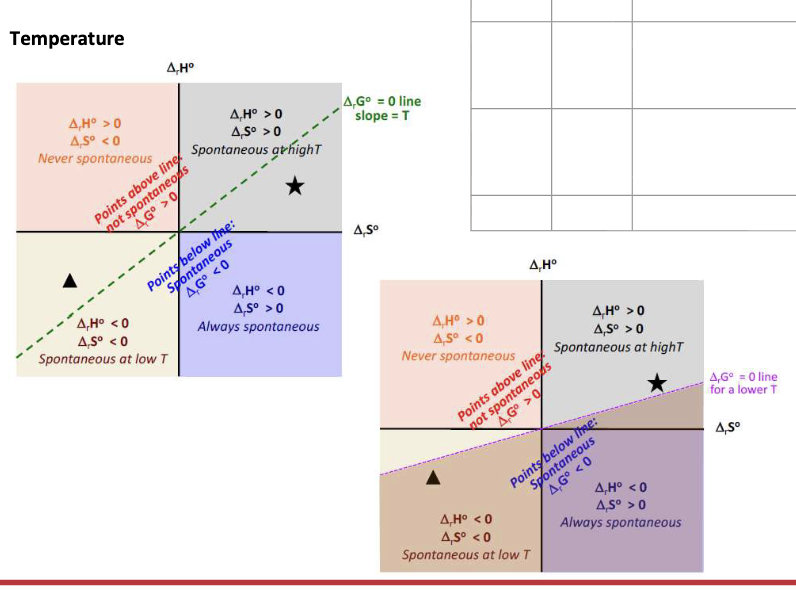
ΔH = negative
ΔS = Positive
ΔG = WHAT
ΔH = negative
ΔS = Positive
ΔG = <0 at all temperature → SPONTANEOUS at all temperatures
ΔH = Positive
ΔS = Negative
ΔG = WHAT
ΔH = Positive
ΔS = Negative
ΔG = >0 at all temps → NON-SPONTANEOUS at all temperatures
ΔH = Negative
ΔS = Negative
ΔG = WHAT
ΔH = Negative
ΔS = Negative
ΔG = Change from NEGATIVE to POSITIVE when temp increases (T>ΔH/ΔS) → Only spontaneous at LOW temperature
ΔH = Positive
ΔS = Positive
ΔG = WHAT
ΔH = Positive
ΔS = Positive
ΔG = Change from POSITIVE to NEGATIVE when temp increases (T>ΔH/ΔS) → Only spontaneous at HIGH temperature
Third law of thermodynamics:
The entropies of all perfect WHAT substances are the same at T = WHAT
At absolute zero all the substances have no WHAT
This means that a system will have perfect order at T= 0K → ΔS = WHAT
Third law of thermodynamics:
The entropies of all perfect CRYSTALLINE substances are the same at T = 0K
At absolute zero all the substances have no KINETIC ENERGY
This means that a system will have perfect order at T= 0K → ΔS = 0
Which factors can affect the entropy of the system:
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
Which factors can affect the entropy of the system:
Physical state
Temperature
Number of particles in the sample
Complexity and size of molecules
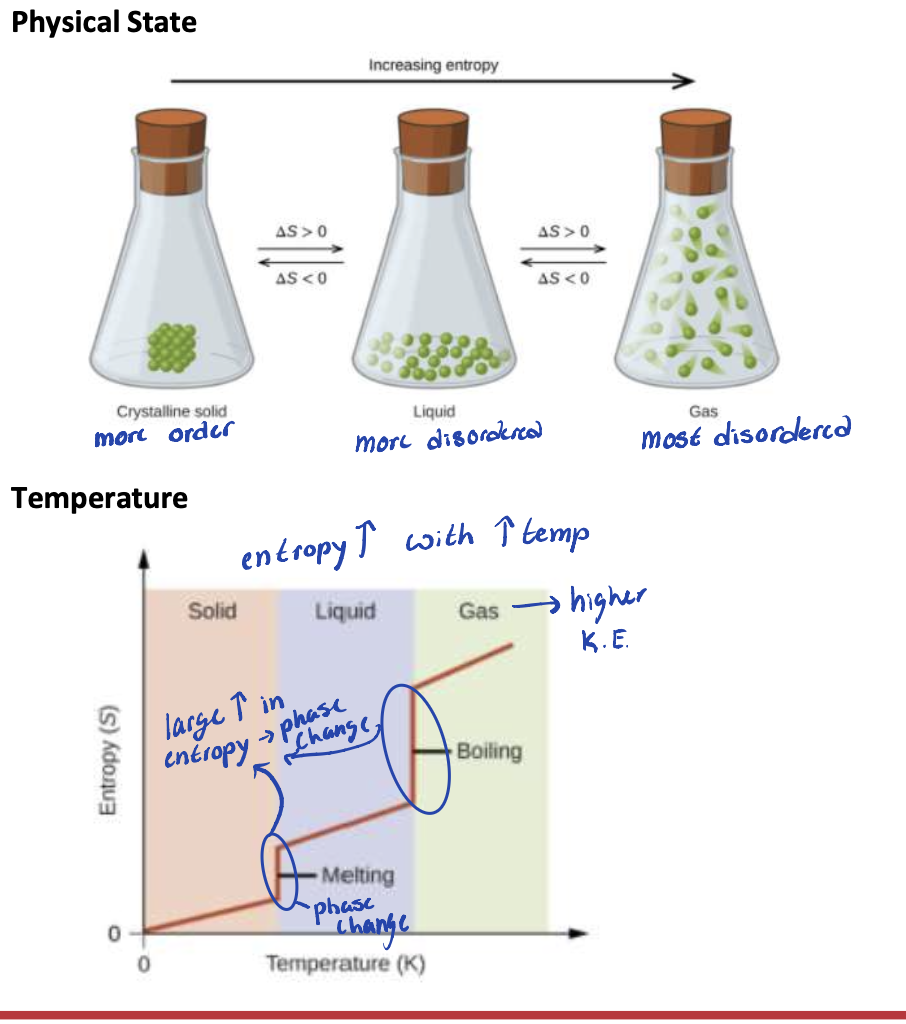
Large increase in entropy = WHAT
Large increase in entropy = PHASE CHANGE
Number of particles in the sample
Less particles → WHAT → WHAT
More particles → WHAT → WHAT
Solid particles dissolve in H2O → freedom in WHAT → Increase in WHAT
Additional WHAT/WHAT in a mixture
Number of particles in the sample
Less particles → Less disorder → smaller
More particles → More disorder → Larger
Solid particles dissolve in H2O → freedom in MOVEMENT → Increase in S
Additional ORIENTATION/INTERACTION in a mixture
Complexity and size of molecules
WHAT molecules have higher S → more WHAT → Randomness is through WHAT and WHAT within the molecule
Complexity and size of molecules
LARGER molecules have higher S → more ATOMS → Randomness is through VIBRATION and ROTATION within the molecule
Change in the concentration use din a reaction
WHAT equation for Q
WHAT equation for K
Change in the concentration use din a reaction
ΔGrxn = ΔG°rxn + RTln(Q) equation for Q
ΔG°rxn = -RTln(Q) equation for K → ΔGrxn = 0