Lokin Headache (Sakit sa Ulo)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Headache is pain or discomfort where… (be specific)
Upper part of head, from orbits to suboccipital area
General mechanisms of headache
Traction on major intracranial vessels
Distension, dilation of intracranial arteries
Inflammation near pain sensitive structures
Direct pressure on cranial or cervical nerves
Sustained contraction of scalp or neck muscles
Stimulation from disease of eye, ear, nose, and sinuses
“SC SI DD, at DT”
Pain sensitive structures found in, or around the head
Cranial venous sinuses
Arteries at the base of brain
Arteries of dura
Dura near base of brain, and large arteries
All extra-cranial structures
Pain-insensitive structures in the cranium
Brain parenchyma
Ependyma
Choroid
Pia
Arachnoid
Dura over convexity of the brain
Skull
What makes a headache primary? Give examples of primary headache
No underlying cause
Migraine, tension, cluster
Examples of underlying causes of secondary headache
CNS infection
Neoplasm (tumors in the brain)
CVD (e.g. strokes)
__ % will have at least one headache/year
__ % will seek physician evaluation, c/c headache
__ % will have emergent secondary cause
60-75%
5-10%
10%
T/F: Migraine is the most common primary HA
False: 69% of PHAs are tension headaches, migraines are 15%, while 0.1% is cluster
Statement T/F: Fever is the most common cause of secondary HA. HAs from disorders of the nose/sinus are a relatively smaller percentage, but are common clinically.
1st statement is false, 2nd statement is true
(note: vascular disorders include stroke)

General clinical presentation of primary headache
Onset
Duration of episodes
Recurrent, non progressive
Positive family history
Normal neurological examinations
HAs that are hereditary
Migraine
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (secondary to brain aneurysm)
Evidence of serious headache disorder by history or physical exam; usually life threatening
Headache alarms

Things to ask for headache history
Reason for consultation
Onset (How did it start)
PMHx (Have you had previous similar headaches, if so when did this type of headache start)
Location
Quality of pain
Associated symptoms
Precipitating/Aggravating factors
Relieving factors
Medical history
Family history
Environment (Carbon monoxide)
Possible reasons for consultation
First HA or worst HA
Accompanied by new or frightening features
Last straw? Has already tried to resolve headache in other ways.
Possible locations of headache
Unilateral/bilateral
Frontal/occipital/facial
Possible qualities of headache pain
Pulsatile, steady, shock-like, tightness
Possible associated symptoms of headache
Nausea, vomiting, LOC, flushing, lacrimation, drop attack, neck stiffness, photophobia, dizziness
Possible precipitating/aggravating factors of HA
Trauma, exertion, noise, position, foods, drugs, weather, anxiety, menstration
Possible relieving factors of HA
Darkroom, position, pressing on scalp, medication
Relevant medical history to HA
Cancer, hypertension, HIV (these conditions can affect the CNS, and lead to headaches)
Recent procedures
Lumbar punctures can cause spinal headache
Change in medications
Nitrates (prevents angina) can cause HA, via vasodilation
Physical exam
Read up

What are bruits? What are they a sign of?
Abnormal pulsations
Abnormal blood flow in the blood vessel
Ear problems causing headache
OM (otitis media) (ear infection)
Hemotympanum
Rash is a sign of
inflammation, and a medical illness which may be causing the HA
Symptoms of Horner’s syndrome
Ptosis, anhidrosis, meiosis
Ataxia can be brought about by
Tumors, abnormal blood vessels
Cause and location of sinus headaches
Sinusitis
Behind browbone, and/or cheekbones — este the frontal and maxillary sinuses
A headache that’s like a band squeezing the head
Tension headache
HA focused around one eye
Cluster headache
HA with unilateral pain, accompanied by nausea, visual changes
Migraine
T/F Migraines can change sides between attacks
True
Migraine vs Tension Headache
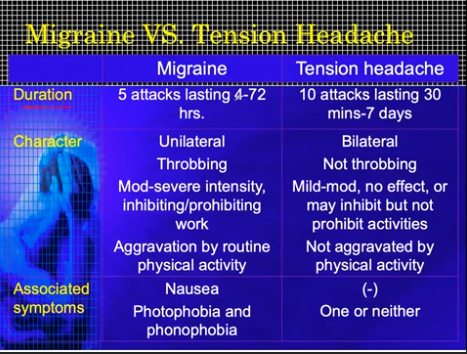
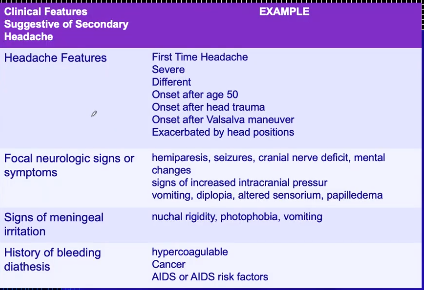
Clinical features suggestive of secondary headache
Common causes of headache
Headache red flags
Sudden/new onset
Wakes patient from sleep
Associated features
Vomiting
Visual symptoms
Weakness/numbness
Meningeal irritation
T/F migraine is associated with anorexia, nausea, and vomiting
True
_% of population have migraines, and suffer more than __ attacks a month
25%, 4
Migraine without aura presentation

Migraine with aura presentation

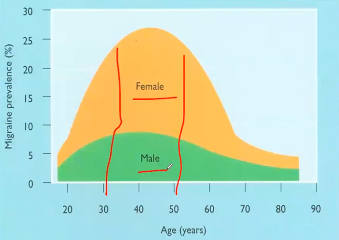
Migraine prevalence (age group, sex)
30-50 yo
Females
Phase of migraine with psychological, neurological, and autonomic symptoms
Premonitory/prodromal phase
> osmophobia is irritability in terms of smell

Phenomenon related to headache phase of migraine
trigeminovascular and neurogenic events
Phenomenon associated with aura
Cortical spreading depression
Trigger for cerebral cortex
Emotion, stress
Trigger for thalamus
Bright lights, noise, smells
Trigger for hypothalamus
Internal bodily environment and mechanisms
Trigger for carotid vessels
Vasodilators