Injury and Inflammation
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Acute Reversible Injury
Cell injury that is characterized by:
Swelling
Less efficient mitochondria
Reduced protein synthesis
Undamaged nucleus
Chronic Reversible Injury
Chronic injury with the following adaptations:
Atrophy
Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
Metaplasia
Dysplasia
Atrophy
Reduction in cell/organ size
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell/organ size
Hyperplasia
Increase in # of cells
Metaplasia
Change in cell structure/function
Dysplasia
Increase in cell #s with structural change
Necrosis
Irreversible cell injury, that is a rapid process that includes swelling and the release of intracellular contents, causing inflammation
Apoptosis
Irreversible cell injury that is intentional/programmed cell death. Involves cells shrinking and cellular fragmentation.
Syndactyly
Abnormal apoptosis result
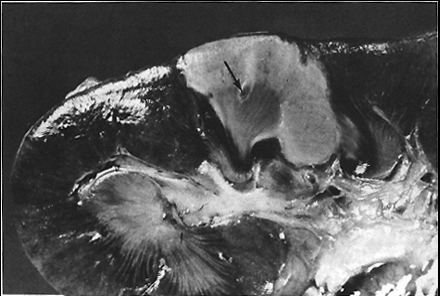
Coagulative necrosis
Necrosis causes by ischemia, in which cell membrane remains intact but organelles dissolve. Found in solid organs (heart, kidney, live)
Ex: early pressure sores
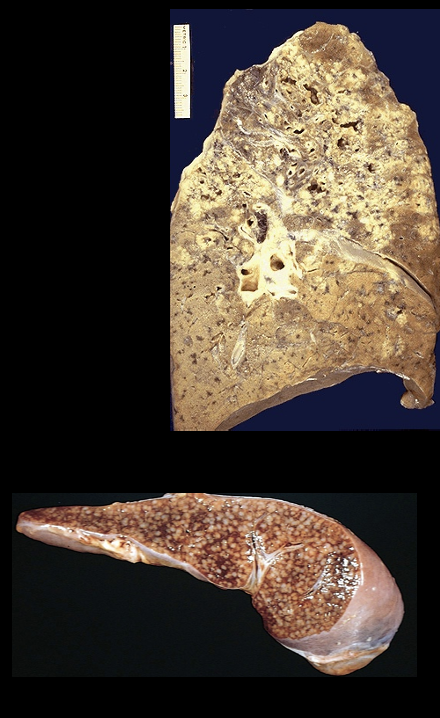
Caseous necrosis
"Cheesy” necrosis found in lungs, bone, and lymph nodes. Cells die, disintegrate and then clump together.
Ex: Miliary tuberculosis, mycobacterioum tuberculosis
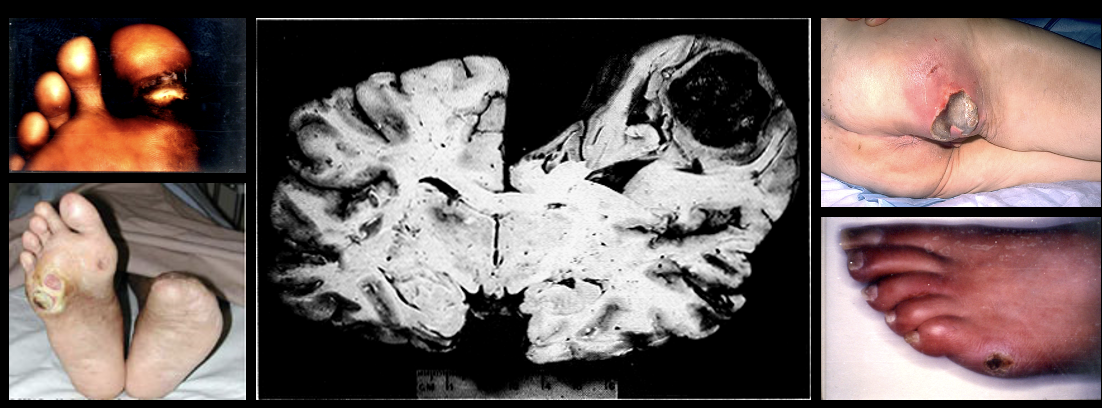
Liqufactive necrosis
Necrosis with abscess formation of tissue by lysosomal enzymes due to infection. Found in brain tissue, skin, wound, joint infections
Ex: late pressure sores
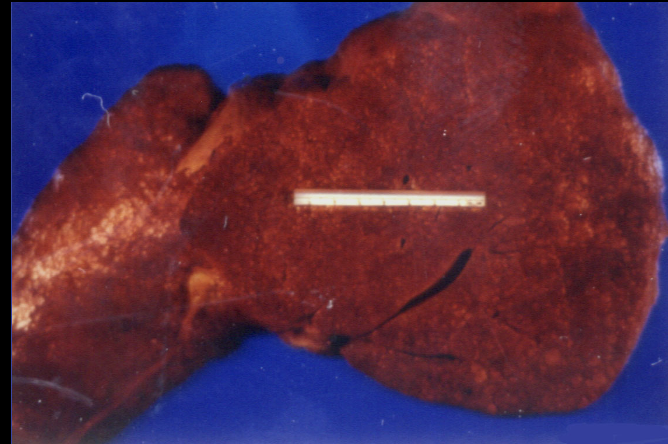
Fatty necrosis
“Chalky” necrosis caused by acute pancreatitis and abdominal trauma, in which tissue is replaced by fat.
Fibrinoid necrosis
Necrosis caused by trauma in blood vessel walls, where the boy attacks blood vessels through autoimmune response.
Ex: organ transplant rejection
Ischemia
Cell injury characterized by the lack of blood flow leading to oxygen deprivations
Infectious agents
Cell injury that invades tissue and releases toxins leading to cell death and lysis. Spreads infection
Genetic factors
Cell injury, examples are chromosomal abnormalities and gene mutations
Down syndrome, Huntington’s chorea, sickle cell anemia
Examples of genetic factors that can result in cellular injury
Nutritional factors
Malnutrition and obesity causing reduced protein synthesis and amino acid deficiencies
Physical factors
Trauma, such as motor vehicle accident, gunshot wounds, extreme temperatures (burns), radiation
Chemical factors
Factors that include heavy metals and medications that can cause cellular damage.
Free radicals
Unpaired electrons latching onto things and disrupting cells
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Chemical factors that fight inflammation, kill bacteria, regulate autonomic nervous system
Caused by prolonged exercise, irradiation, ultraviolet/fluorescent light, pollutants, tobacco, and pesticides.
Create oxidative stresses that lead to diseases/conditions
Antioxidants
Chemical factors of cellular injury that neutralize free radials by binding
Endogenous : enzymatic and nonenzymatic defense systems within cells
Exogenous: Vitamin C and E
Nitric Oxide
Chemical factors of cellular injury that relax blood vessels and decreased levels are associated with cardiovascular disease
Exercise & Free Radicals
Chemical factors of cellular injury that increase NO production.
Improved antioxidant defense and regulation or repair systems
Overtraining
___________ can lead to reduced ability to fight infection
Inflammation
Our response to restore tissue to the injury state
Injurious agent
Inflammation ends when when the ____________ _________ is removed
Purpose of inflammation
To be a protective response
To get rid of the cause and consequences of an injury
Initiate healing
Signs/Symptoms
Redness, swelling, increased temperature, pain, decreased function of affected site
Vasodilation
Increased capillary permeability
Loss of fluid
Increased fibrinogen
Migration of leukocytes
Effects of vasodilation in inflammation
Increases blood flow → causing heat and redness (erythema)
Effects of increased capillary permeability in inflammation
Movement of plasma proteins and leukocytes which causing swelling (edema)
Causes fluid loss
Effects of fluid loss in inflammation
Slows blood flow, increase red blood cell concentration, and increases blood viscosityE
Effects of leukocyte migration in inflammation
Increases swelling of cells, as leukocytes move into cell
Effects of increased fibrinogen in inflammation
Clotting of fluid
Role of vascular changes during inflammation
Movement of plasma/cells from intracellular space to the injury site
Exudation
Transudation
Exudation
Escape of fluid, protein, and blood from vasculature system into tissue/body cavities (pu
Hemorrhagic/Sanguineous exudate
Exudate or discharge that is bright red or bloody, presence of RBCs
Serosanguineous exudate
Exudate or discharge that is blood tinged yellow or pink
Serous exudate
Exudate or discharge that is thin clear yellow
Ex: blisters
Purulent exudate
Exudate or discharge that is viscous cloudy pus
Catarrhal exudate
Exudate or discharge that is thin clear mucus
Transudation
Occurs when fluid leaks into a space
Binding (LA)
1st step of leukocyte accumulations
Occurs when leukocytes bind to endothelial cells at the site of inflammation
Migration
2nd step of leukocyte accumulations
Occurs when leukocytes move out of the vessels and into the problem area (process called diapedesis)
Attraction
3rd step of leukocyte accumulations
Occurs when chemostatic agents pull leukocytes closer to inflammation site
Clean up
4th step of leukocyte accumulations
Occurs when macrophages clean up debris IF inflammatory stimulus subsides
Acetylated Lysophospholipid
Type of acid arachidonic acid derivative and chemical mediator that acts as a platelet activating factor
Cyclooxygenase Pathway
Type of acid arachidonic acid derivative that involves prostaglandins modulating vasomotor tone and platelets; helps with restructuring and stopping the bleeding
Lipooxygenase Pathway
Type of acid arachidonic acid derivative and chemical mediator that involves the creation of leukotrienes that produce smooth muscle contraction, increased vascular permeability, migrations of leukocytes.
Phagocytosis
Ingesting microorganisms, killing, or deactivating them
Coating
1st step of Phagocytosis
“Harpoon gun”
Leukocytes attaching identifying signals to cell/agent
Binding (P)
2nd step of Phagocytosis
Enfolding
3rd step of Phagocytosis
Engulfing of the cell/agent
Infusion of lysosome to kill/degrade
4th and final step of Phagocytosis
May manifest or leave the body as pus