Borrowing costs (IAS23) and Government grants (IAS20)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What does IAS23 define borrowing costs as?
Interest and other costs that an entity incurs in connection with the borrowing of funds.
Interest expense
Amortisation of discounts or premiums on borrowings
Finance charges on lease liabilities
Exchange differences on foreign currency borrowings
What is a qualifying asset?
An asset that takes a substantial period of time to get ready for its intended use or sale.
What are some examples of qualifying assets?
Certain types of inventory (must take a substantial period of time for its intended use)
PPE
Intangibles
Investment Property
Bearer plants
When are borrowing costs capitalised?
Borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualifying asset are capitalised when:
Probable future economic benefits
The costs can be measured reliably
What happens to the other borrowing costs when they don’t meet the criteria to be capitalised?
They are recognised as an expense in profit or loss in the period in which they are incurred
What are the two types of borrowing costs?
Specific borrowings
General borrowings
What are specific borrowings?
If funds are borrowed specifically for a qualifying asset.
Capitalise actual borrowing costs incurred less any investment income on temporary investment of the borrowings
What are general borrowings?
If funds are borrowed generally to obtain a qualifying asset
Apply a capitalisation rate ( weighted average rate on outstanding general borrowings)
The amount of borrowing costs that an entity capitalises during a period shall not exceed the amount of borrowing costs it incurred during that period
What is the formula for the capitalisation rate?

When does capitalisation start?
Only during the construction period, which is governed by three stages:
Commencement of Capitalisation
Suspension of Capitalisation
Cessation of Capitalisation
What is the commencement period of capitalisation?
This is the point when capitalisation of borrowing costs start. Begins when these conditions are met:
Expenditure on the qualifying asset has been incurred
Borrowing costs are being incurred
Activities necessary to prepare the asset for use or sale are in progress
What is the suspension period of capitalisation?
This is a temporary stop in capitalisation during the construction period.
DO NOT Suspend if the delay is short or if it is long but necessary
What is the cessation period of capitalisation?
This is the point where capitalisation permanently stops.
It ceases when substantially all activities necessary to prepare the asset for its intended use or sale are complete.
What must an entity disclose for borrowing costs?
The amount of borrowing costs capitalised during the accounting period
The capitalisation rate used to calculate the amount of general borrowing costs that are eligible for capitalisation
Explain the term government.
Refers to government, government agencies and similar bodies whether local, national or international
Explain the term government assistance.
Is action by government designed to provide an economic benefit specific to an entity or range of entities qualifying under certain criteria.
What are government grants?
Assistance by government in the form of transfers of resources to an entity in return for past or future compliance with certain conditions relating to the operating activities of the entity.
What are the two types of government assistance?
Government grants- recognise + disclose
Other government assistance- only disclose
What are the two types of government grants?
Grants related to assets
Grants related to income
When can we recognise government grants? (2 step criteria)
The entity will comply with the conditions attaching to them
The grant will be received
How are government grants recognised in profit or loss?
On a systematic basis over the periods in which the entity recognises as expenses the related costs for which the grants are intended to compensate
When is a grant recognised as income?
A grant receivable as compensation for costs already incurred or for immediate financial support with no future related costs
What is IAS23 concerned with borrowing costs in connection with?
The purchase and/or development of “qualifying asset”
Are inventories produced in bulk in a short period of time a qualifying asset?
No, they do not take a substantial period of time to get ready for intended use.
Are inventories that requires a significant time to reach its intended use or saleable condition a qualifiable asset?
Yes, it tells us they do take a substantial period of time to get ready for intended use/sale
How do we determine if the borrowing costs are directly attributable?
Borrowed specifically
Would have been avoided - e.g. if project cancelled we wouldn’t have to borrow anything
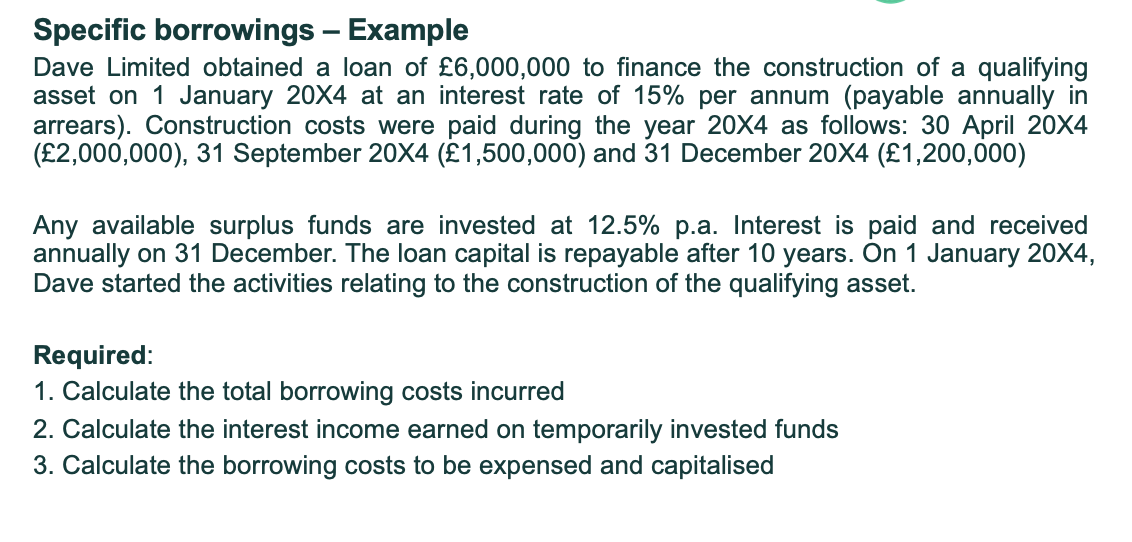

When calculating mixed borrowings whats the rule?
Specific borrowings
Then general borrowings
Explain capitalisation of borrowing costs on a qualifying asset would begin.
Expenditures for the asset are being incurred
Borrowing costs are being incurred
Activities necessary to prepare the asset for its intended use or sale are in progress
Explain when capitalisation of borrowing costs on a qualifying asset would cease.
During the cessation period when all necessary activities are complete.
Explain how one accounts for the receipt of a government grant in the form of cash.
The grant is not recognised immediately in profit or loss
Initially recognised as deferred income ( a liability)
The grant is then recognised in profit or loss systematically over the periods in which the related expenditure is incurred
Presented as other income or deducted from the related expense
How do we find the borrowing cost to be capitalised for specific borrowings?
The total borrowing costs - investment income on temporary borrowings
Can all forms of government assistance be recognised as a government grant in the financial statements of the reporting entity?
No
What is the disclosure for government grants?
The accounting policy adopted
The nature and extent of government grants recognised in the financial statements and an indication of other forms of government assistance from which the entity has directly benefited
Unfulfilled conditions and other contingencies attaching to government assistance that has been recognised.
Can the amount of borrowing costs capitalised exceed the total borrowing costs incurred?
No
In terms of IAS23 the capitalisation of borrowing costs ceases when the asset is substantially completed.
True