BIO 2010- Module 14A and 14B: Isolation and beginning Identification of an Unknown Gram-Negative Bacterial Specimen
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is general/enriched media?
Non selective. Almost every bacteria can grow.
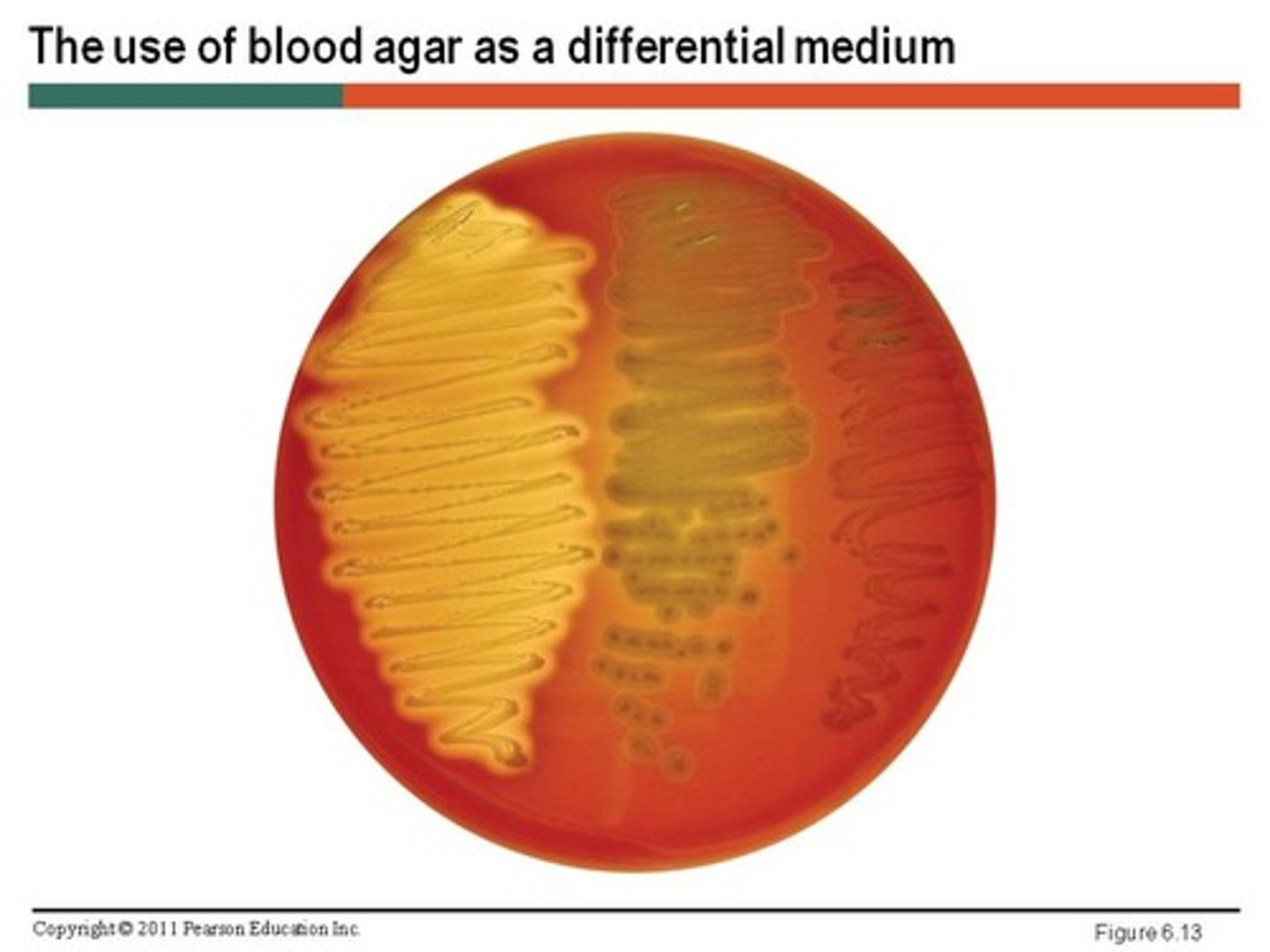
What is differential media?
Contains differential factors, which is used differently by different bacteria, producing visual differences. Provides visual cues (ex. color change, hemolysis) to differentiate organisms.
What is selective media?
Allow growth of specific bacteria, and inhibit others. Contains inhibitory agents (ex. like bile salts, antibiotics, or dyes) that prevent growth of unwanted bacteria.
What are 3 differential stains?
Gram stain, endospore stain, acid-fast stain
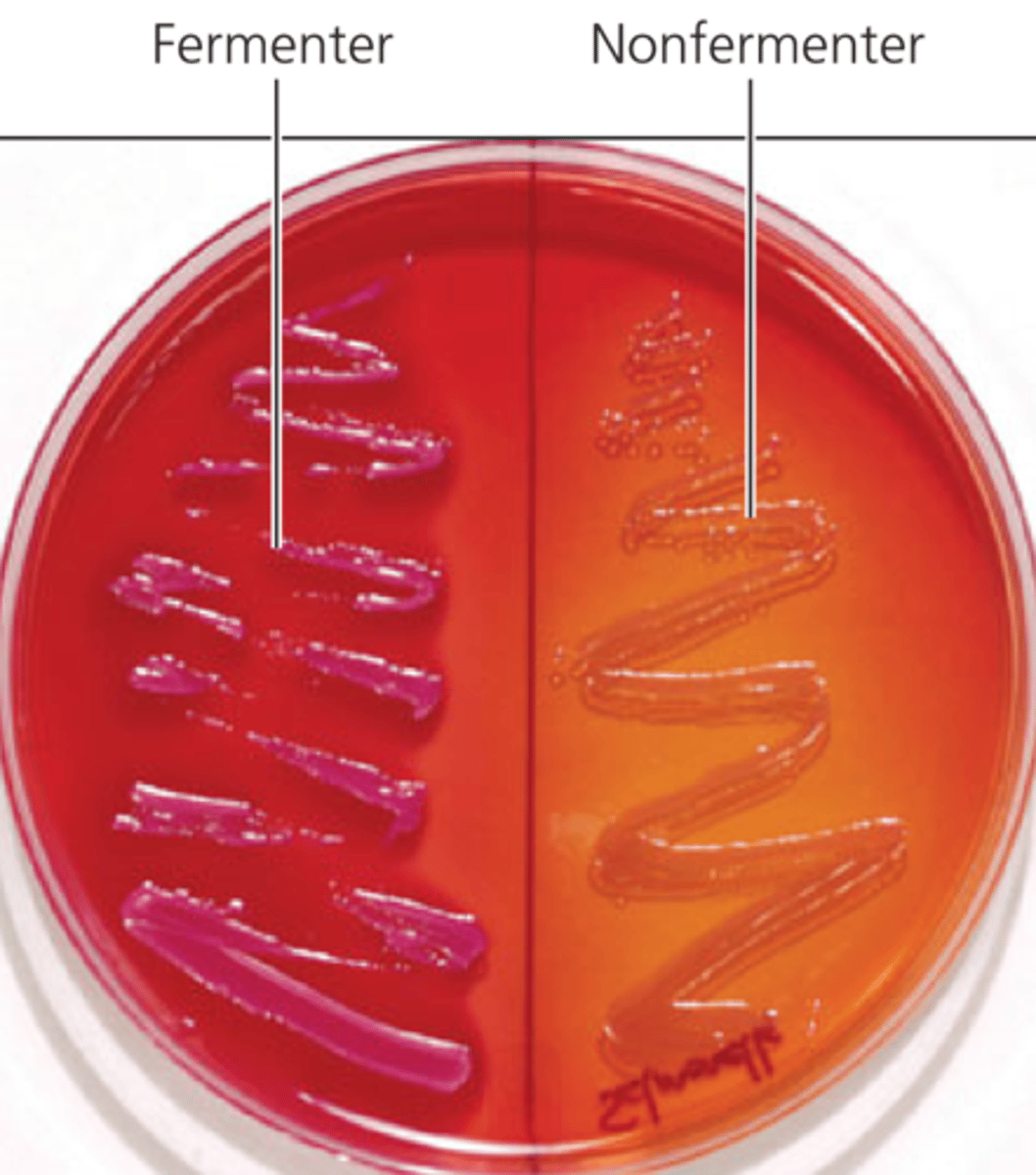
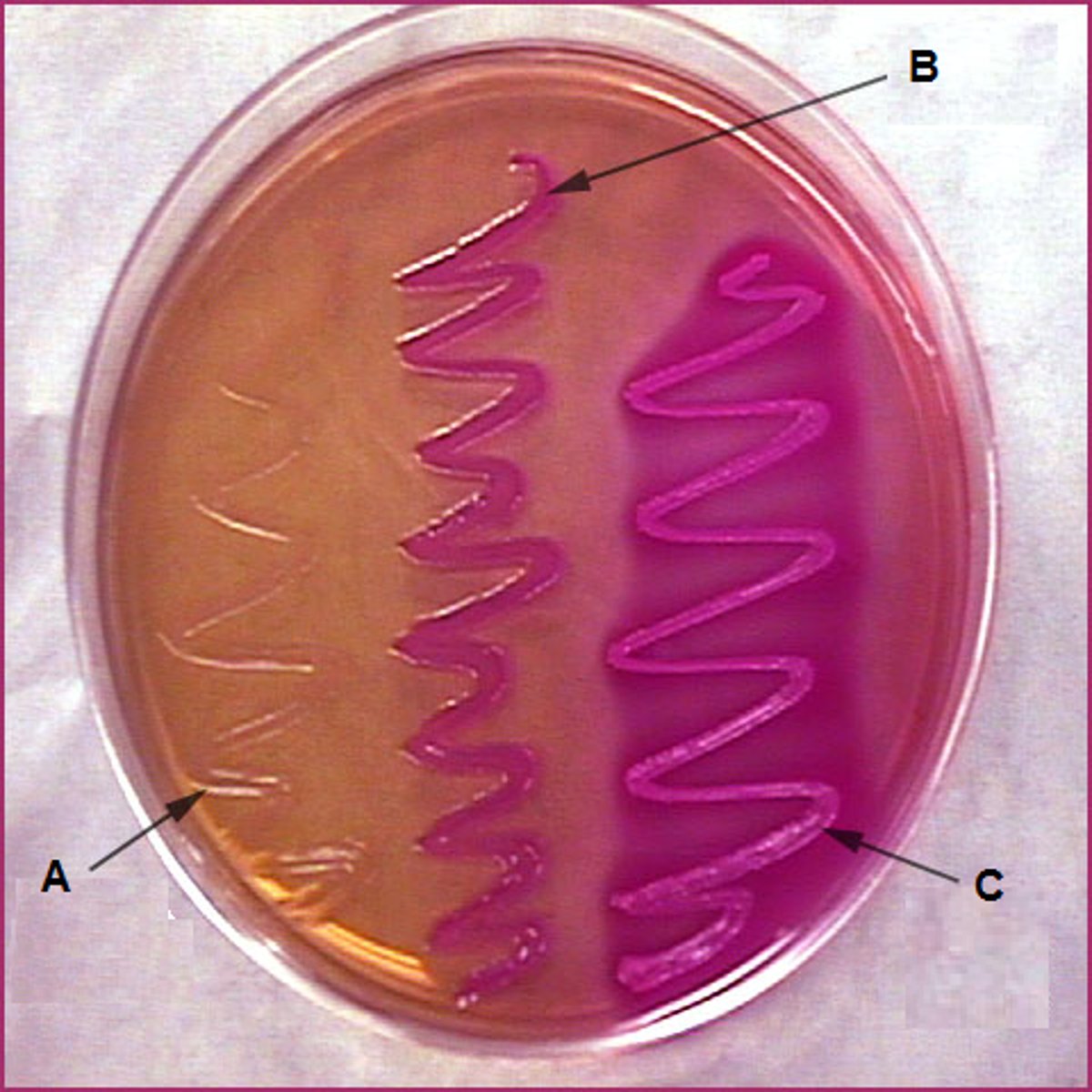
MacConkey Agar (MAC)
This medium is commonly used to select for the growth of gram-negative bacteria and to differentiate those organisms according to their ability to ferment lactose.
What type of media is used for MacConkey?
MacConkey
Which type of technique is used for MacConkey?
Streaking for Isolation
Is MAC selective or differential and why?
both; the bile salt and crystal violet is selective for gram-negative bacteria and the neutral red dye indicates if the bacteria can ferment lactose or not. This differentiates them.
What is the interpretation for MacConkey?
Pink/red colonies: Lactose fermenters → produce acid
Colorless/tan colonies: Non-lactose fermenters → no acid produced
What are the different colors of the MacConkey colonies?
Pink and Red/ Tan
Does gram positive or gram negative grows on MacConkey?
Gram-negative bacteria
Does MacConkey inhibit gram positive or gram negative bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria
What does MacConkey ferment?
Lactose
What qualities does organisms that grow on MacConkey have?
bile-tolerant & crystal violet-tolerant
What is the pH indicator for MacConkey?
neutral red
What are two examples of bacteria that grow on MacConkey?
Escherichia coli and Enterobacter aerogenes
Why does Neisseria sicca not grow on MacConkey despite being gram negative?
It's because Neisseria sicca is found in the respiratory tract, not the intestines, so it cannot tolerate bile and therefore fails to grow on MacConkey agar.
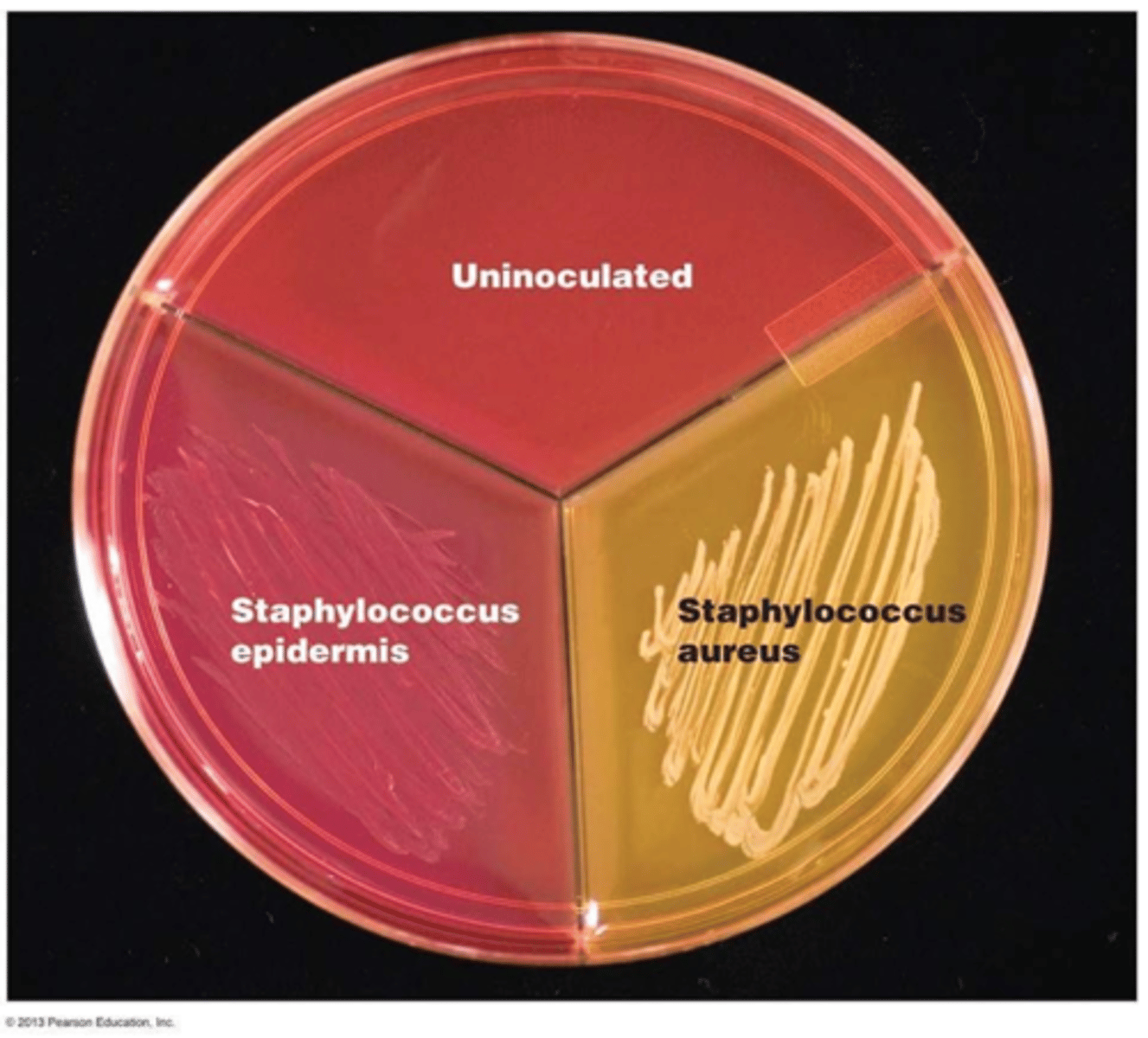
Columbia Blood Agar (CNA)
Is a selective and differential medium used to isolate Gram-positive bacteria.
What type of media is used for CNA?
CNA agar
Which type of technique is used for CNA?
Streak for Isolation
What are the two inhibitory agents for CNA?
the antibiotics colistin and naladixic acid.
Is CNA selective or differential and why?
Both; It is selective because it contains colistin and nalidixic acid, which inhibit the growth of Gram-negative bacteria. It is differential because it contains sheep blood, which allows observation of hemolysis patterns
What is the interpretation for bacterial growth on CNA?
Growth present: Gram-positive bacteria
No growth: Gram-negative
What is the interpretation for hemolysis on CNA?
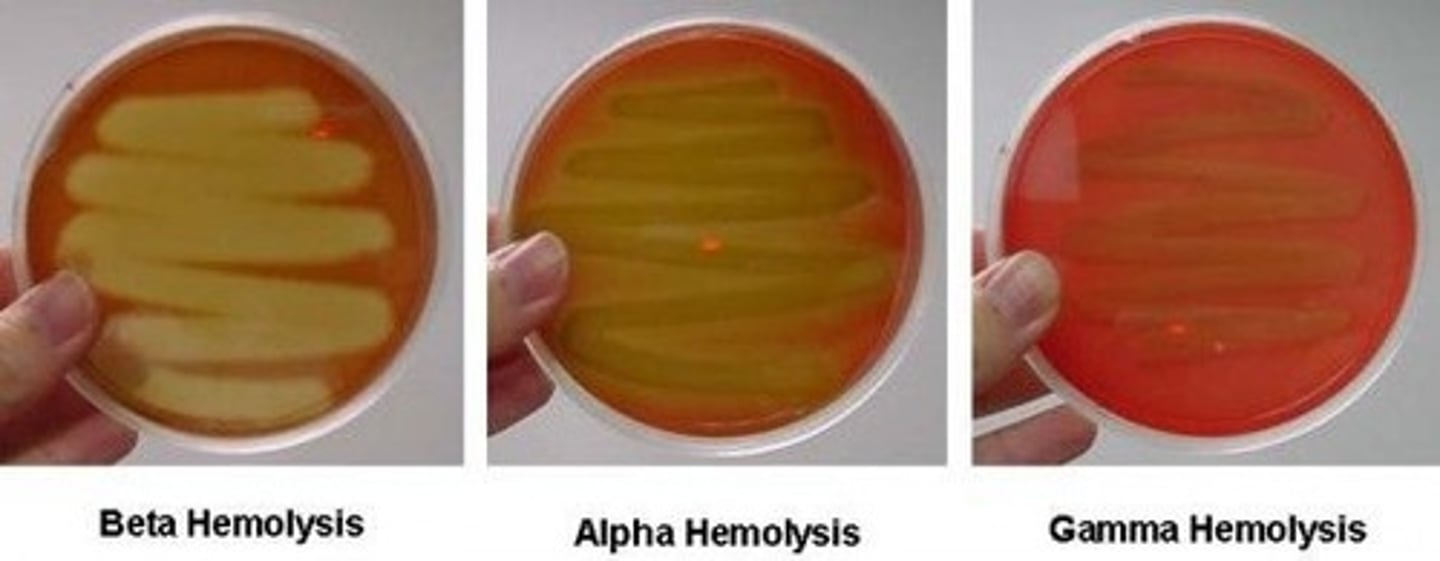
Beta (β) hemolysis: Complete red blood cell→ clear zone around colonies.
Alpha (α) hemolysis: Partial red blood cell→ greenish or brownish zone.
Gamma (γ) hemolysis: No red blood cell→ no color change in the agar.
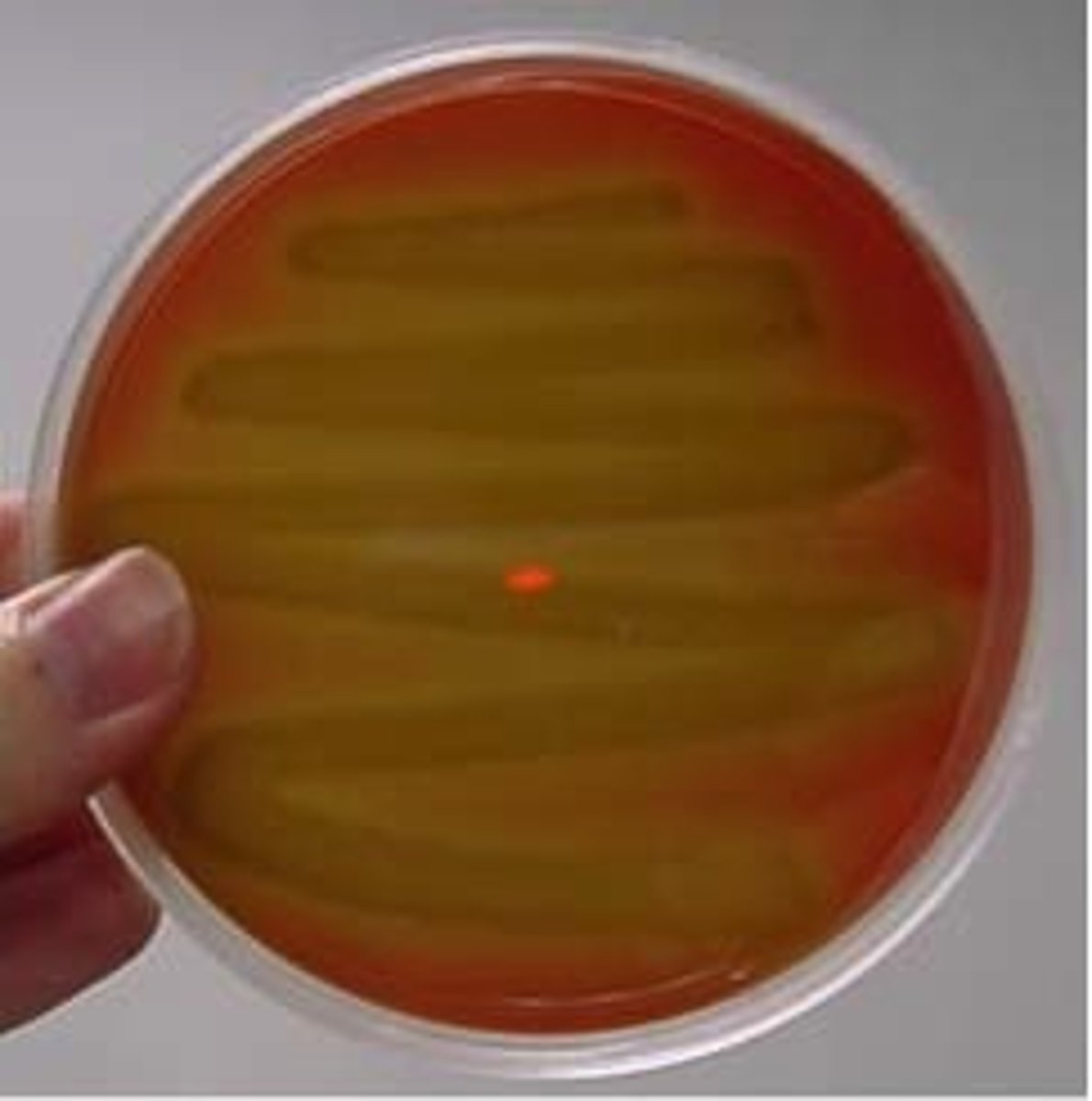
Alpha (α) hemolysis
partial breakdown of hemoglobin
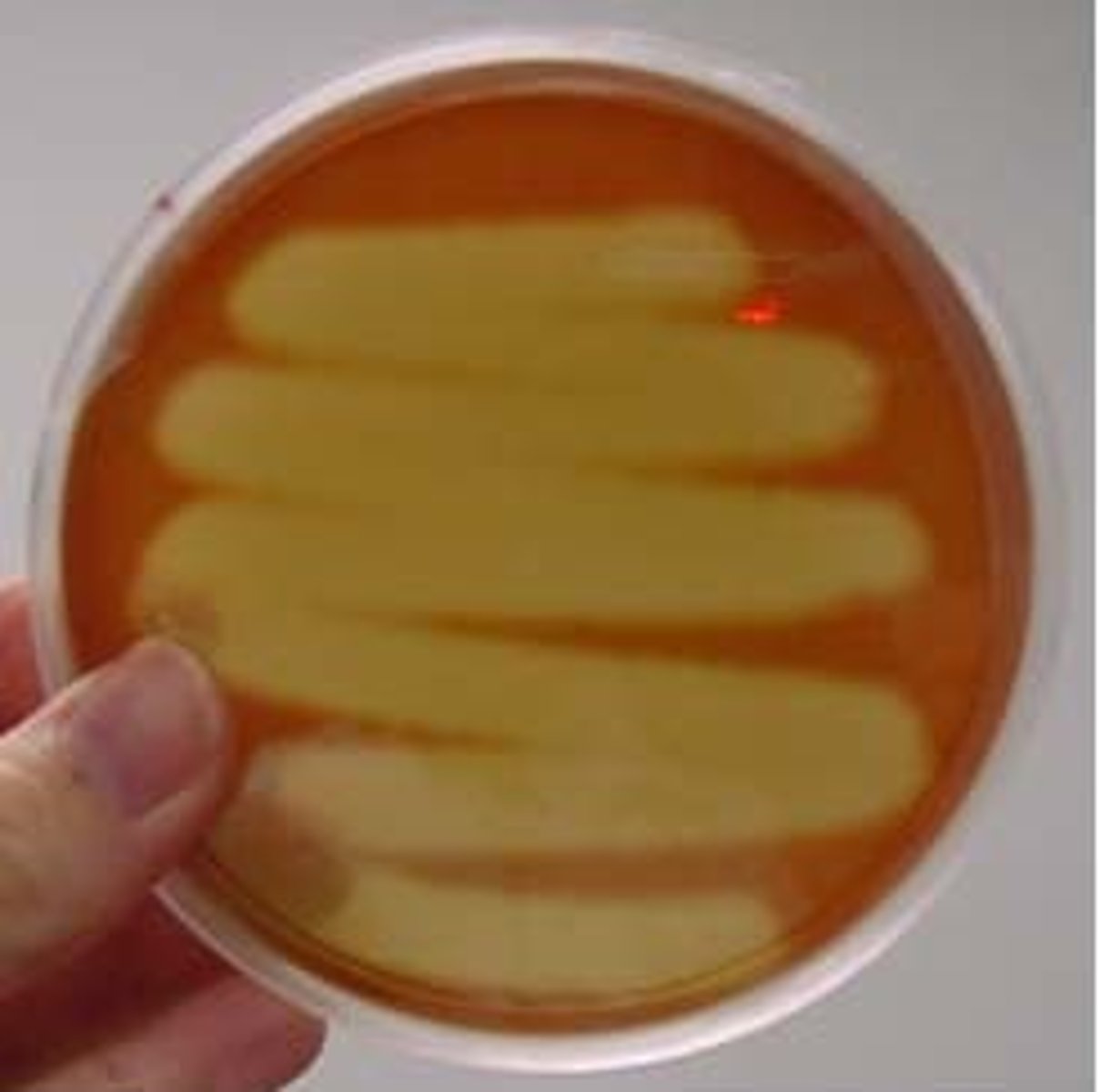
Beta (β) hemolysis
complete breakdown of hemoglobin
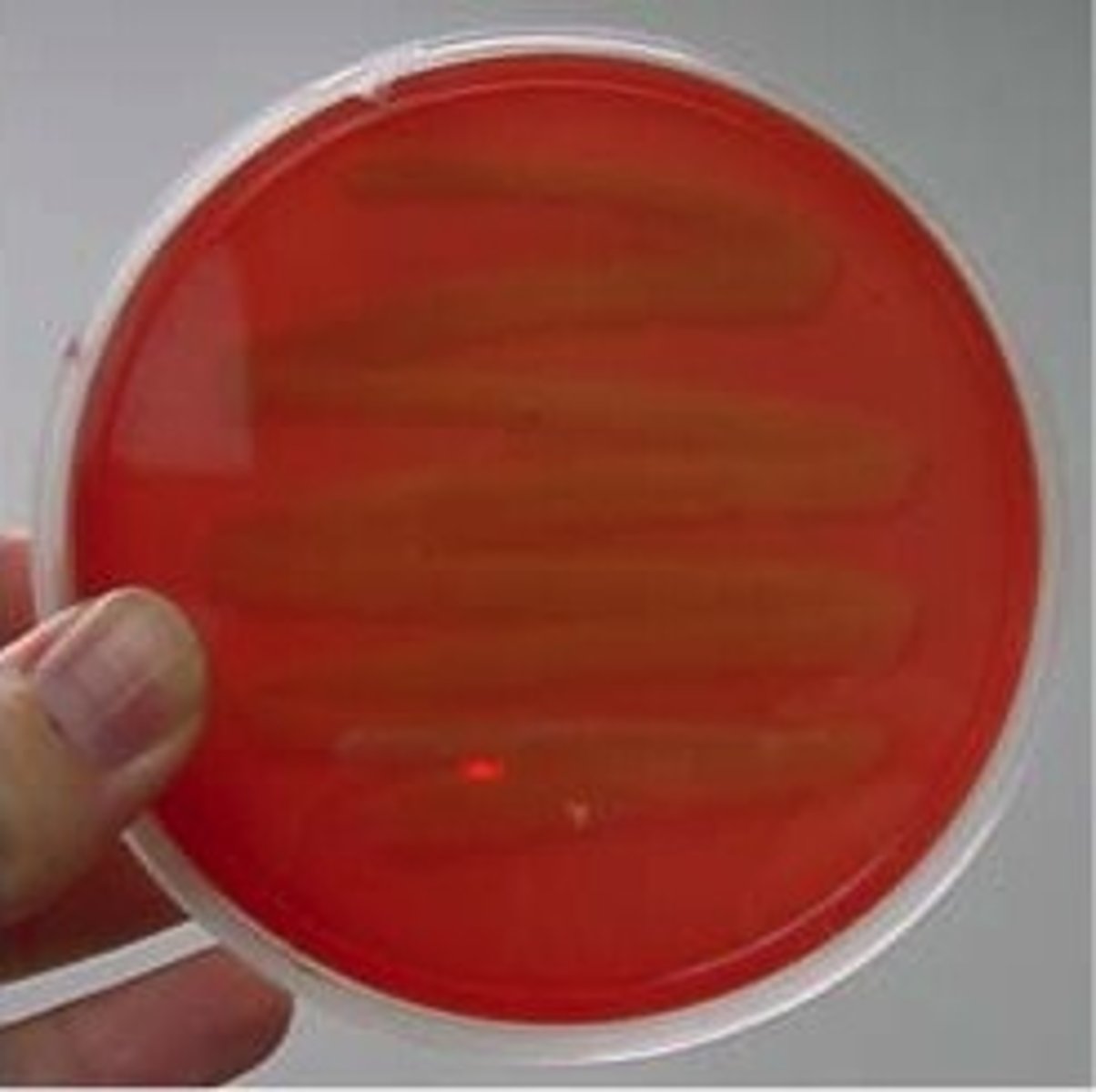
Gamma (γ) hemolysis
no breakdown of hemoglobin
What does Lyse do?
to break down or destroy cells specifically, red blood cells (RBCs) in the agar.
Does gram positive or gram negative grows on CNA?
Gram-positive bacteria
Does CNA inhibit gram positive or gram negative bacteria?
Gram-negative bacteria
Why does Bacillus subtilis inconsistently grow on CNA despite being gram positive?
It is less resistant to the colistin and nalidixic acid used in CNA. In other words, it's sometimes partially inhibited.
What is the only bacteria that has Alpha hemolysis?
Streptococcus pneumonia
What are the two bacteria's that fully grow on CNA and display Beta hemolysis?
Streptococcus pyogenes
Staphylococcus aureus
Carbohydrate Fermentation (CFB)
is a metabolic process in which microorganisms break down sugars (carbohydrates) to produce energy, often resulting in the formation of acid and/or gas as by-products.
What type of media is used for CFB?
liquid (broth) media
Which type of technique is used for CFB?
Inoculation Technique
Is CFB selective or differential and why?
Differential because it allows you to distinguish organisms based on their ability to ferment specific carbohydrates.
What is the interpretation for CFB?
pH indicator (ex. phenol red) changes color:
Red → Yellow = fermentation occurred
Red stays red = no fermentation
What are the 3 broths used for carb fermentation?
Glucose, Lactose, Sucrose
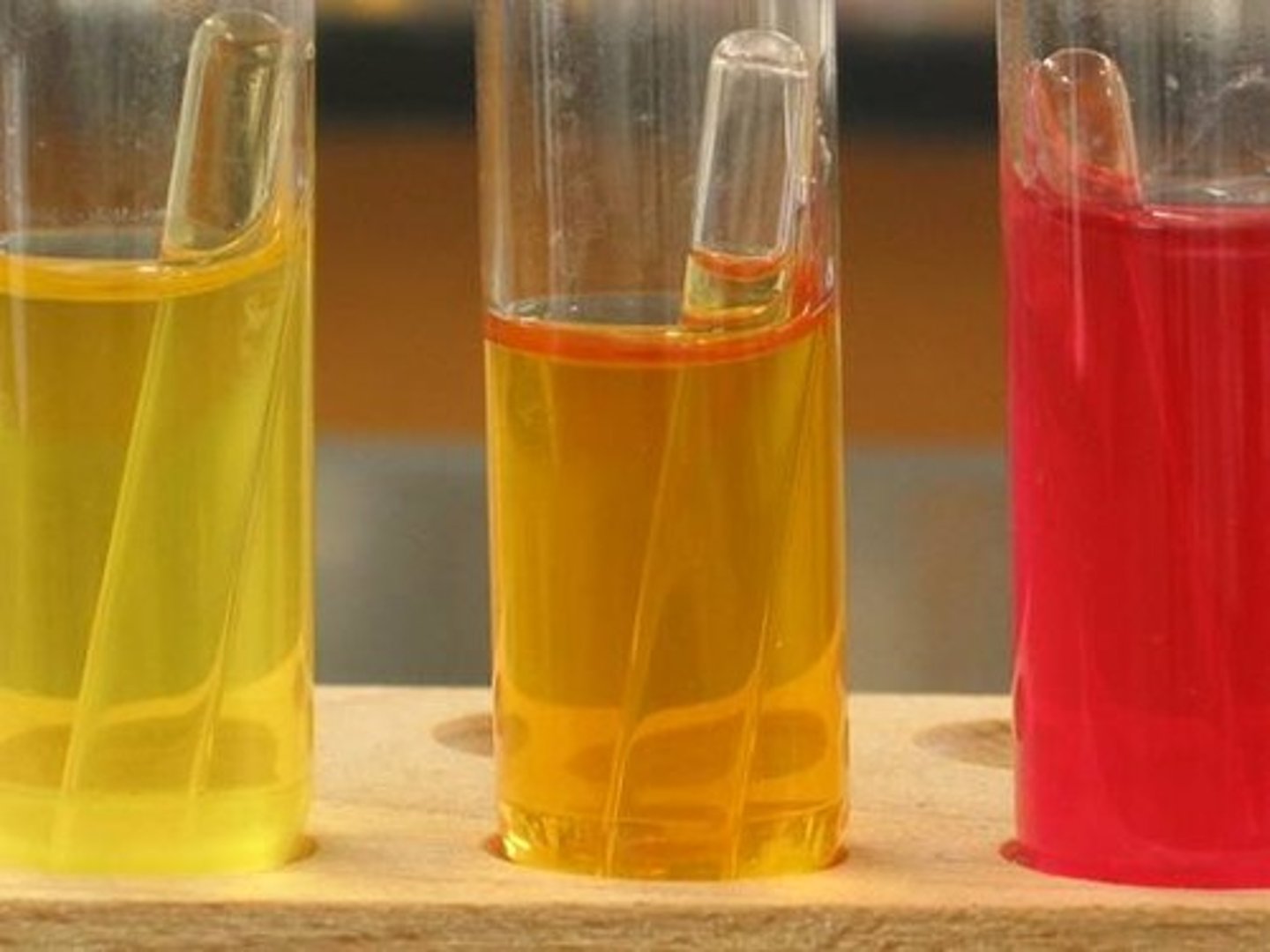

What is the pH indicator for CFB?
phenol red
What are the two different colors of the CFB colonies?
Red: pH is neutral or alkaline.
Yellow: acid is produced, lowering the pH.
Does gram positive or gram negative grows on CFB?
Both; CFB is not selective, it does not contain inhibitory agents.
It's purpose is to differentiate bacteria based on their ability to ferment specific sugars
Does CFB inhibit gram positive or gram negative bacteria?
Neither
Durham tube
a small inverted (upside down) glass tube found in the broth tube to trap gas bubbles produced in fermentation.
What is the purpose of the durham tube being inverted inside of the broth tube?
The gas rises and gets trapped at the top of the inverted tube, forming a visible bubble.
What does it mean when there's a bubble present in the Durham tube?
A bubble in the Durham tube means that the organism has produced gas (usually during the carbon dioxide (CO₂)) during carbohydrate fermentation.
Which bacteria is negative for all sugars?
Pseudomonas