Cervonic Acid, Vitamin A in Visual Cycle, Cornea
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is cervonic acid? Where is it found?
an omega-3 fatty acid found in brain, skin, cerebral cortex, and retina
Where is the electrical signal sent to in the brain after photoreceptors transduce light?
area 17 (visual cortex)
What kind of membrane is required to be present in the disks of photoreceptors for phototransduction to occur?
a highly fluid membrane
What is phosphatidylcholine?
most common phospholipid in cell membranes, one of 3 essential phospholipids (other two are phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine)
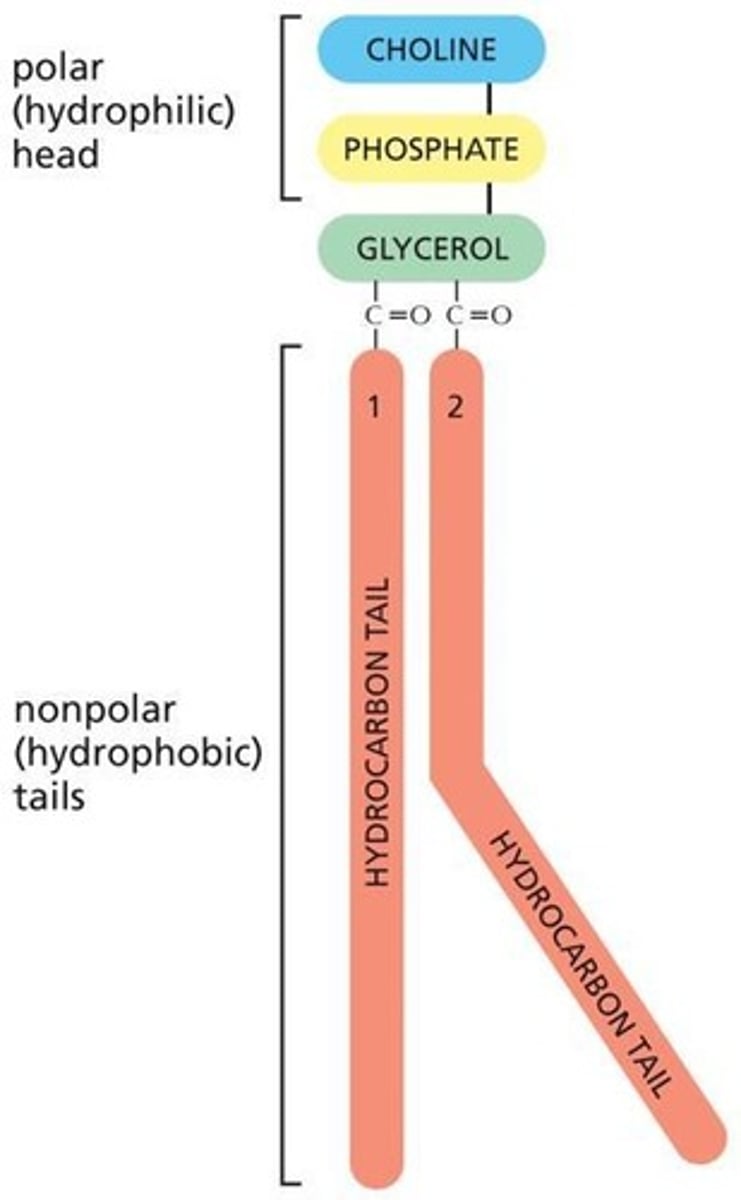
What are the fatty acid tails on phosphatidylcholine? Are they saturated or unsaturated?
- oleoyl (unsaturated - one or more double bonds)
- palmitoyl (saturated - no double bonds)
What does the insertion of significant quantities of cervonic acid into disks and disk-like membranes do?
provides sufficient flexibility to photoreceptor membranes -> places considerable disorder into the membranes
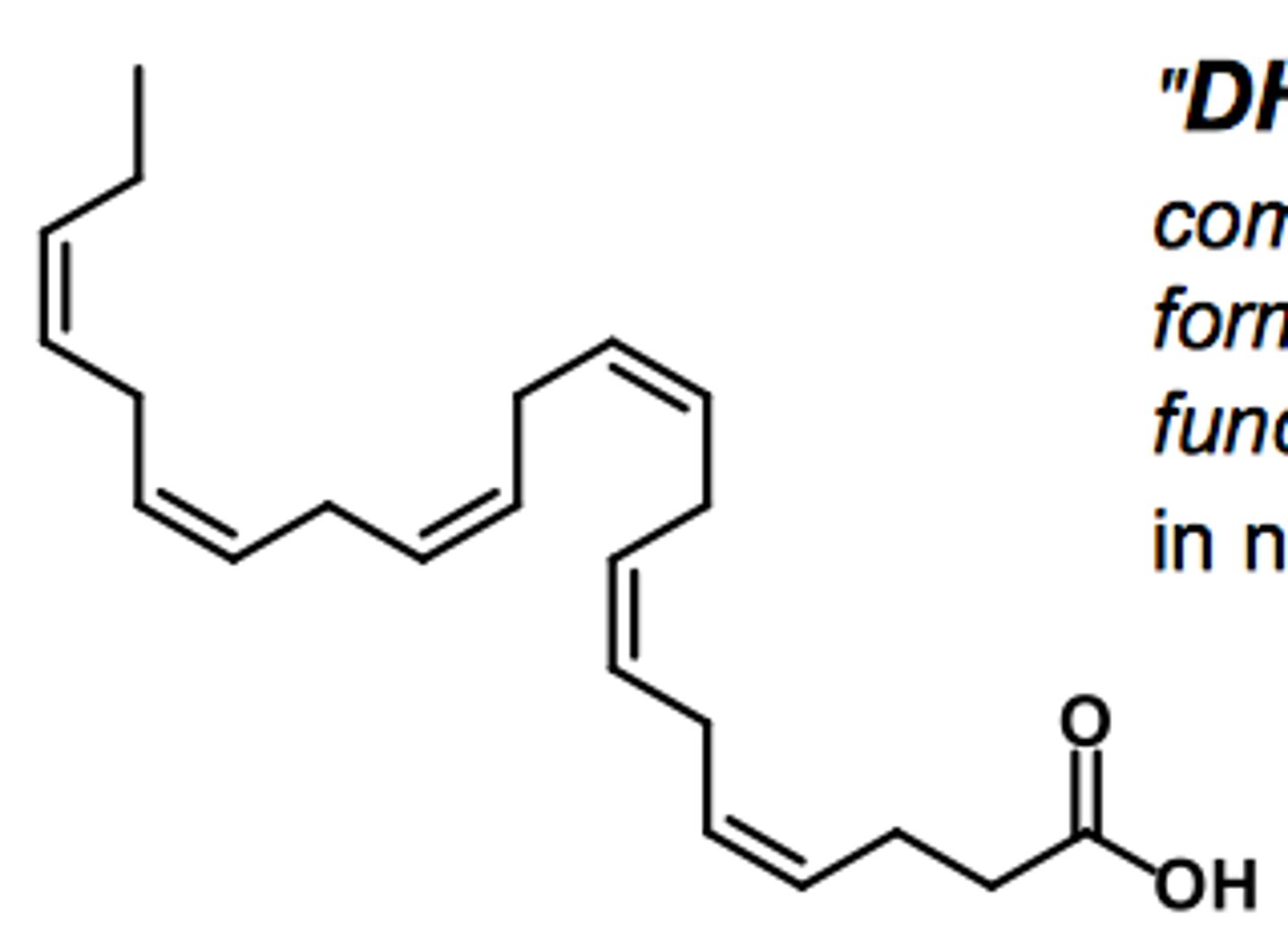
What is another way of writing cervonic acid to indicate the number of carbons in the fatty acid chains and the double bonds it contains?
22:6Δ4,7,10,13,16,19 or 22:6(n-3)
What is cervonic acid synthesized from? What is this precursor obtained from?
linolenic acid (18:3); must be obtained from diet
Describe the general pathway in which cervonic acid is synthesized from linolenate
linolenate (18:3) -> docosapentate (22:5) -> tetracosahexate (24:6) -> cervonate (22:6)
Where does the synthesis of cervonic acid take place? Where is it then transported to?
- synthesis occurs in the liver
- transported to inner segment of photoreceptors, incorporated into phospholipids
How is cervonic acid "spared" in photoreceptors?
it is preserved after removal from photoreceptor membranes and taken back up again into inner segments
Due to the high metabolic rate of photoreceptors, the disks of the outer segments are replaced about every __ days
10 days
Describe the turnover of disk membranes in photoreceptors
1) initial precursor assembly at the inner segment
2) incorporation into disk membranes
3) transport to the distal end of the rod outer segment
4) shedding to a PE organelle
What are two reasons that photoreceptors naturally preserve and re-use as many fatty acids as possible?
1) their synthesis is limited and metabolically complicated
2) retina has significant supply of anti-oxidants (vitamin E)
To determine the path of cervonic acid through the retina, what did researchers use?
[3H] 22:6n3, a tritiated form of cervonic acid (radiolabeled)
The experiment with [3H] 22:6n3 cervonic acid determined that cone/rod cells had a slower turnover. What was this shown by?
cone cells had a slower turnover -> no uptake into cone cells after 4 hours
The incorporation of cervonic acid into which segment of the photoreceptors occurs first?
incorporation in the inner segments precedes outer segments
Describe the pathway from when cervonic acid is synthesized in the liver to incorporation in the photoreceptors
- dietary 18:3 is incorporated into the liver where 22:6PL is synthesized and transported to the photoreceptor inner segments
- 22:6PL is incorporated into outer segment disks and removed with disk shedding
- 22:6PL is returned to the inner segment via the interphotoreceptor matrix or the liver for re-transport to the retina
What kind of vitamin is Vitamin A? What is it involved in?
lipid-soluble vitamin; involved in visual transduction and protein synthesis at the level of a nucleic acid promoter
Which other vitamins are lipid-soluble?
D, E, K
What is the role of vitamin D?
acts to promote calcium metabolism and bone growth
What is the role of vitamin E?
antioxidant; in the retina it prevents oxidation of cervonic acid and other highly unsaturated fatty acids found on photoreceptors
What is the role of vitamin K?
blood clotting factor
List the most common forms of Vitamin A and their roles
1) retinyl ester: storage
2) retinol: transport, hormonal
3) retinal: visual transduction
4) retinoic acid: synthesis, regulating gene transcription
In which form must retinal exist in order to be triggered by light while bound to opsin (as rhodopsin)?
11-cis retinal form
What are opsin and retinal bound to each other by?
through a protonated Schiff base
Before release from its protein, 11-cis retinal is isomerized to the all-trans form. A conformational change is induced in the opsin portion of rhodopsin and achieves which two things?
1) conformational change in opsin allows it to interact with the G-protein, transducin
2) forced separation of the two molecules (protein and chromophore)
What is Vitamin A taken up as? What is it ultimately converted to and where does this conversion occur?
- vitamin A is taken up as beta-carotene (from vegetables) or retinyl esters (from animals)
- ultimately converted to retinol
- re-esterified in the intestine and incorporated into chylomicrons for transport to the liver
Which 2 proteins is vitamin A bound to when leaving the liver?
1) a retinol binding protein (RBP)
2) a prealbumin (PA) (also called transthyretin)
Failure of vitamin A to bind to the protein carriers RBP and PA as it leaves the liver does NOT solve what?
vitamin A deficiency -> you need these protein carriers! deficiency of binding proteins leads to deficiency of vitamin A
Aside from needing binding proteins to solve vitamin deficiency, why would you not want free vitamin A in the body?
free vitamin A is toxic
What is vitamin A bound to when it arrives at its target cells (including pigment epithelial cells)? What is it stored as?
- when vitamin A arrives at its target cell, vitamin is bound to a cellular retinol binding protein (CRBP)
- stored as either an ester or converted to a useful form such as retinoic acid
What is the pigmented epithelium located between?
between Bruch's membrane and photoreceptors
Do photoreceptors extend from the pigment epithelium's apical or basal membrane?
apical
Where is vitamin A transported to be converted from 11-cis retinol to 11-cis retinal before it is transported to the photoreceptors?
RPE
Which sources does RPE receive vitamin A from?
blood and photoreceptor
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction of 11-cis retinol to 11-cis retinal?
11-RDH
Once 11-cis retinal is created in the RPE and transported to the outer segment of the photoreceptor, what does it convert to?
11-cis retinal binds to opsin to create rhodopsin
Which active intermediate is formed from 11-cis retinal for about a second when light activates rhodopsin?
metarhodopsin II
Which bond is broken during isomerization of 11-cis retinal in rhodopsin? What does it do to the rhodopsin molecule?
Schiff bond at 296 Lys in the lumen of the rod outer segment disk -> all-trans retinal released from opsin
Once the retinal in rhodopsin is converted to all-trans, what converts the it to all-trans retinol? What then transports it back to the RPE?
- retinol dehydrogenase (RDH) converts all-trans retinal to all-trans retinol as it passes out of the lumen through the ABCR transporter
- interphotoreceptor retinal binding protein (IRBP) needed for transport to RPE
Once the all-trans retinol binds to IRBP and is carried to the RPE cell, where is it transferred to?
transferred to CRBP in RPE cell
All-trans retinol from the blood can also enter the RPE and transfer to CRBP. Which protein carriers are needed for transport?
transthyretin (prealbumin) and retinol binding protein (RBP)
How does all-trans retinol from the blood enter the RPE?
the RBP-TTR-all-trans retinol complex binds to the RPE cell surface through RBP binding to a specific receptor and the all-trans retinol is transferred to CRBP in the RPE cell
Which enzyme converts all-trans retinol to all-trans retinyl ester?
LRAT (lecithin retinol acyl transferase)
Which enzyme converts all-trans retinyl ester to 11-cis retinol?
retinol isomerohydrolase (RPE65)
What carries 11-cis retinol to 11-RDH (11-cis retinol dehydrogenase)?
a CRALBP
What does 11-RDH convert 11-cis retinol to? Where is it then transported?
- 11-RDH converts 11-cis retinol to 11-cis retinal
- a CRALBP transports 11-cis retinal to IRBP and transported back into the rod outer segment
What happens to 11-cis retinal once transported back into the rod outer segment?
11-cis retinal can be covalently joined in a Schiff base linkage back to opsin at 296 Lys, thus regenerating a functional rhodopsin that can initiate phototransduction
In the visual cycle, is the concentration of 11-cis retinal in the retina highest during light or dark adaptation?
dark adaptation
In the visual cycle, is the concentration of all-trans retinol in the RPE highest during light or dark adaptation?
light adaptation
What is keratomalacia?
hardened, weakened, cloudy or "melting" cornea due to vitamin A deficiency
What are the specific proteins/mucins lacking in malnutrition related to vitamin A deficiency?
MUC 1, 4, 16
What properties do oligosaccharides on mucins give the protein?
give the proteins a viscous property while allowing the surface to remain moist
What is xerosis? Can it be treated?
- drying of the ocular surface due to mild vitamin A deficiency
- treatment with vitamin A restores normal smooth, lubricated surface
What is a descemetocele?
herniation of/in descemet's membrane, can occur from progression of keratomalacia
Vitamin A stimulates protein synthesis in the same manner as steroid hormones and T3-T4. Where does the vitamin bind to in the cell nucleus?
binds to a protein located exclusively in the cell nucleus
What happens after vitamin A binds to a protein in the cell nucleus?
the protein binds to the enhancer region of DNA, meanwhile RNA polymerase binds to its promoter region
How is the signal for transcription initiated once RNA polymerase binds to the promoter?
the long region of the binding protein (vitamin A-protein complex) binds to RNA polymerase and signal for the beginning of transcription
What are some symptoms of vitamin A toxicity?
nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, hair loss, anemia
What effect is caused in the retina when levels of vitamin A are decreased?
11-cis retinal regeneration would be slow or halted, leading to retinal damage & degeneration and blindness