Ch. 16 - Species abundance & diversity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Community
Different species that inhabit a defined area
Guild
Group of organisms that make their living in a similar way (ex. birds that live and feed in a specific part of a tree canopy)
Life-form
Classification of structure and growth dynamic of plants
Relative abundance
proportion of a particular species relative to other species in a community.
Preston’s Distribution of Commonness and Rarity
An ecological model that uses a lognormal distribution to show most species are moderately abundant with even fewer species being extremely rare or extremely common.
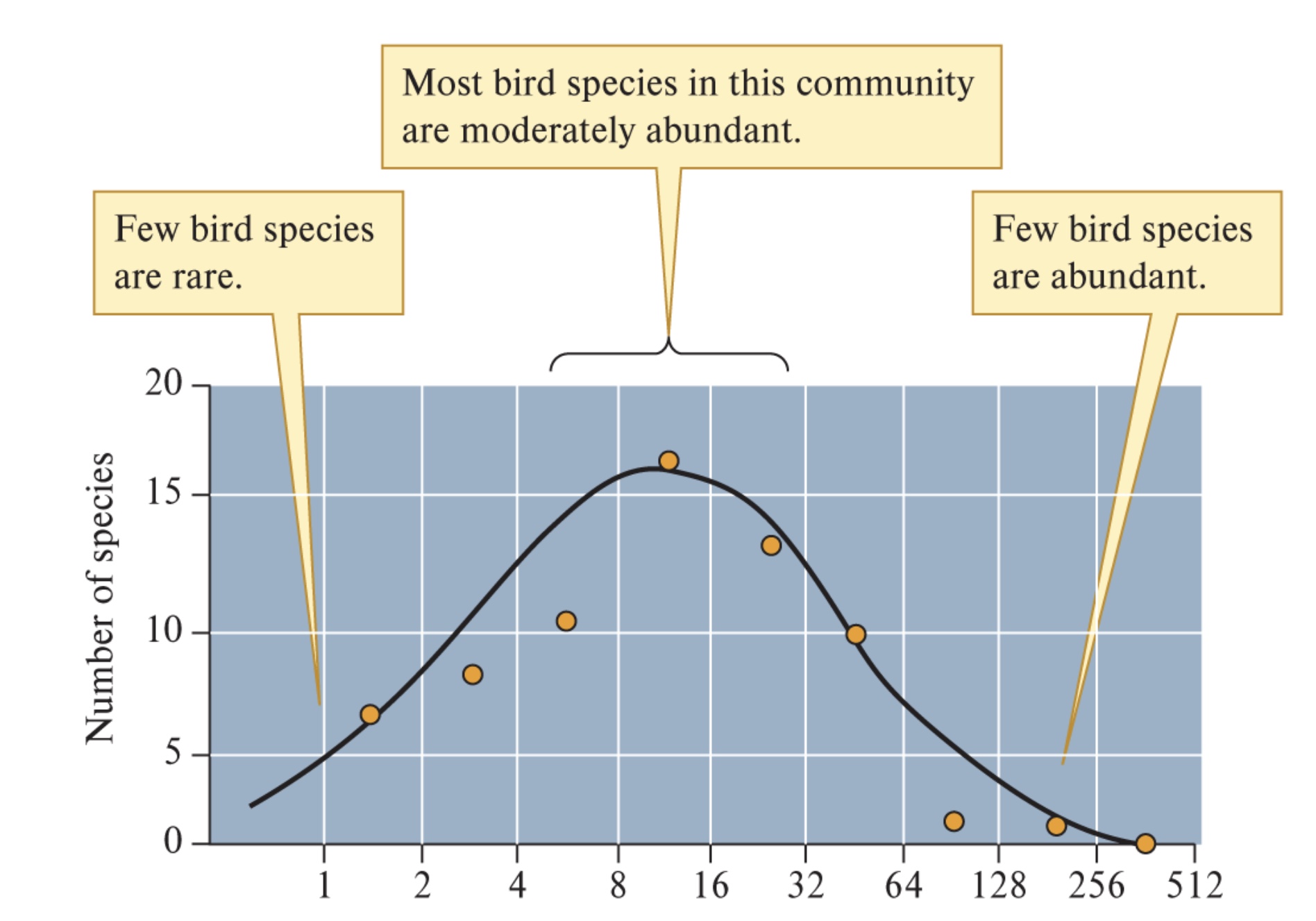
Species diversity is based on two factors:
Species richness & Species evenness
Species richness
the number of different species in a given area.
Species evenness
relative abundance of species in a community.
Shannon Weiner Diversity Index
Method for quantifying species diversity that considers both species richness and species evenness.
Shannon Weiner Value
H’
is always positive
Higher H’ value = higher diversity
Rank Abundance Curve
A plot of relative species abundance against their rank in abundance.
Based on rank abundance curve how can you tell which community has greater species evenness?
a more even slope will have greater species evenness.
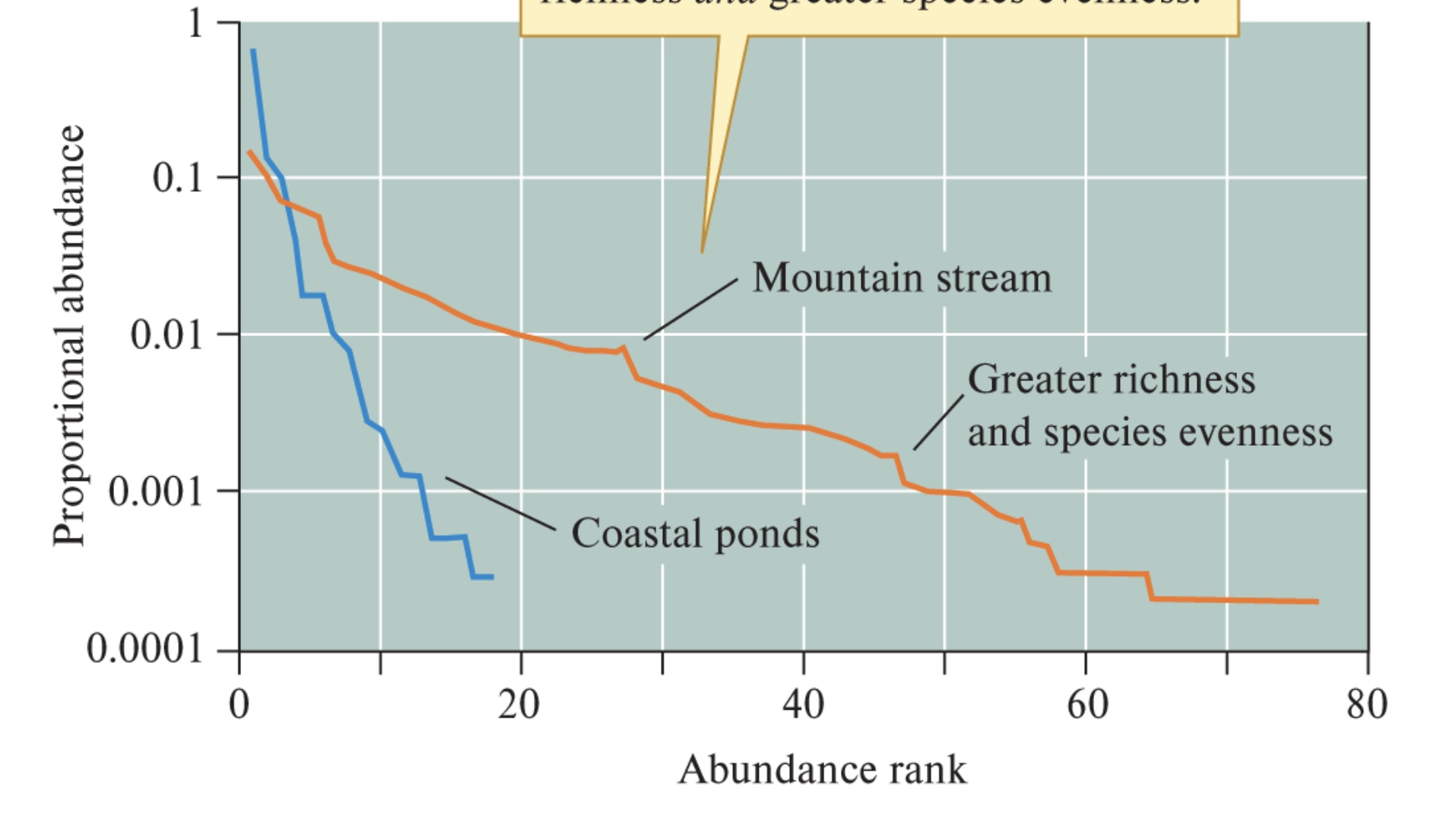
According to this rank abundance curve which community is more diverse?
The mountain stream community
Why is it important to quantify diversity within a community?
it allows scientist to measure the health, stability, and track the impacts that any environmental changes have on a community
provides a baseline for comparison
provide a numerical representation of a community's structure and how this may be impacted by disease, climate change, pollution, etc.
Help us better understand ecological roles that impact communities: such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and decomposition.
Environmental complexity creates more
Species diversity
Examples of environmental complexity supporting greater diversity
Robert and John MacArthur found that greater foliage height supported more diverse bird communities
David Tilman found that greater variation of nutrients in lakes supports more diverse phytoplankton communities
Equilibrium
State of community/ecosystem when environmental conditions remain reasonably stable.
opposing forces cancel each other out
Disturbance
Any event that removes all or part of a community.
Potential sources of disturbance:
abiotic (fire, hurricanes, floods)
biotic (disease, predation, competition, parasitism, invasives)
human-caused (pollution, climate change, agriculture)
What factors must be considered when looking at the impacts of disturbance on communities
impacts vary with organisms and environments
spatial and temporal scales
frequency and intensity
Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis
Predicts that intermediate levels of disturbance promote higher levels of species diversity.
Examples of intermediate disturbance hypothesis.
in the intertidal zone boulders of medium size that experience intermediate disturbance have greater diversity of algae and marine organisms compared to the smaller and larger ones.
Prairie dogs disturb the vegetation around the areas they create burrows however this disturbance has a positive effect on plant diversity by creating open patches for new plants to colonize.
Urban Ecology
Study of ecology in urban settings
landscapes exposed to some degree of human land use can have a positive impact on species diversity.