Economics Unit 4: GDP, Inflation, Unemployment, Business Cycle
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole
US economic goals
growth, price stability & full employment
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
A measurement of the total goods and services produced within a country.
GDP components
consumption, investment, government spending, net exports
secondhand goods
do not count towards GDP. goods that have already been final and then sold as used
non-market transactions
transactions that do not take place in the market and would not be included in GDP
Consumption
spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing. Makes up 70% of GDP
Recession
a period of temporary economic decline during which trade and industrial activity are reduced, generally identified by a fall in GDP in two successive quarters (6 months).
inflation
A general and progressive increase in prices
deflation
a decrease in the general level of prices, which is not a good indication of growth. Occurs in recessions.
1970s Inflation
The inflation at the time was referred to as Stagflation, an unusual period of history in which there was high inflation and stagnant economic growth. The event has been blamed on both oil prices and the monetary policies of the government.
cyclical unemployment
unemployment caused by a business cycle recession
frictional unemployment
unemployment that occurs when people take time to find a job, or quit their job to find something else, or re-enter the workforce
structural unemployment
unemployment that occurs when workers' skills do not match the jobs that are available or their job has been replaced by automation or AI technology
labor force
all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed (unemployed + employed)
Consumer Price Index
The key measure of inflation- the change in the cost of buying a fixed basket of goods and services.
purchasing power
the real goods and services that money can buy; determines how far your money can go
decreased purchasing power
occurs when there is inflation- felt most by people on a fixed income.
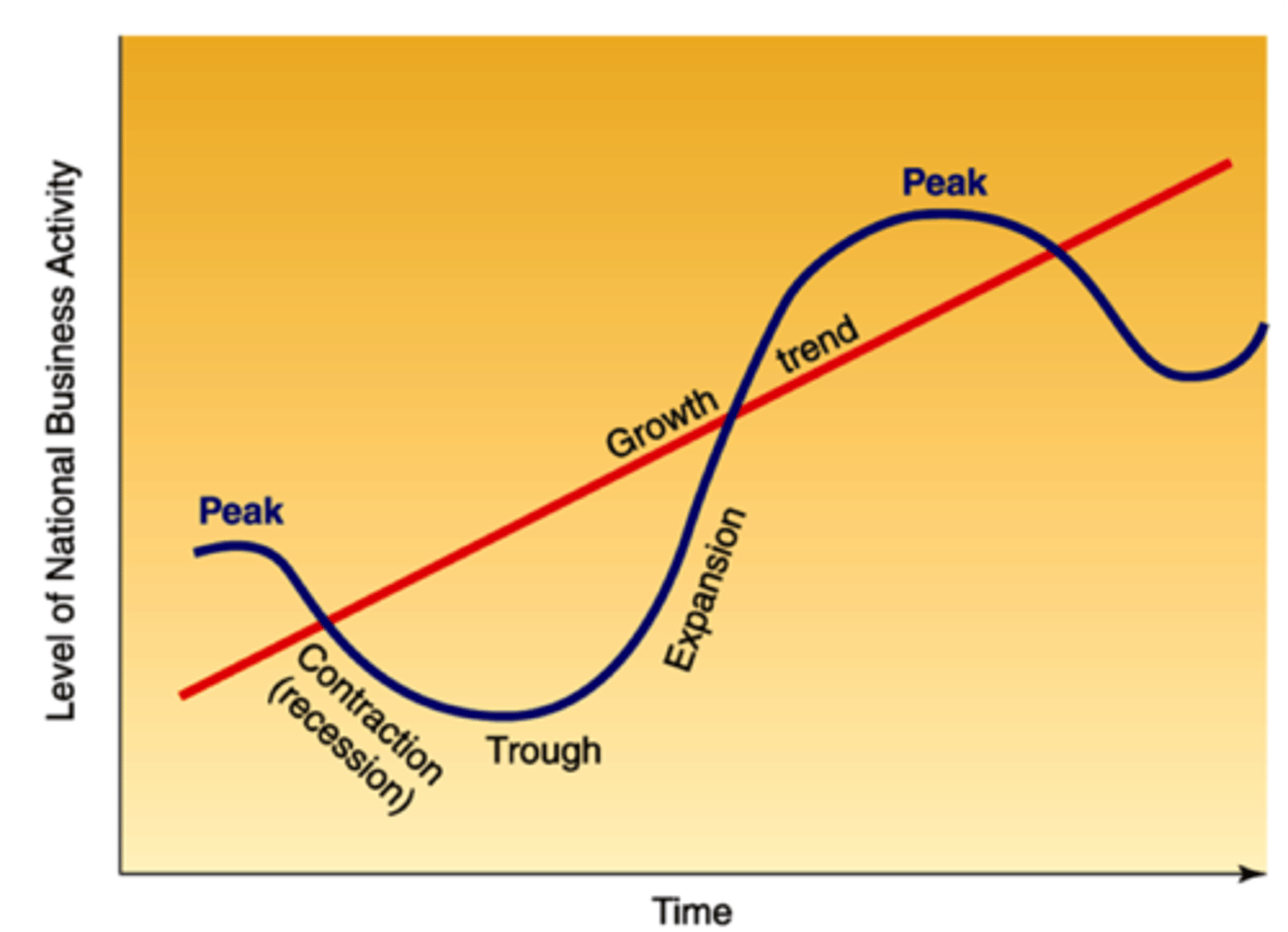
business cycle
Alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession
Demand Pull Inflation
increases in the price level (inflation) resulting from an excess of demand over output at the existing price level, too much money chasing too few goods.
unemployment rate
the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed (unemployed/labor force x 100)
minimum wage
a minimum price that an employer can pay a worker for an hour of labor
Current U.S. federal minimum wage
$7.25 per hour (same in Texas)
business cycle order
peak, contraction, trough, expansion.
When GDP is at it's highest point in the business cycle it is referred to as ______
the peak
natural rate of unemployment
the normal rate of unemployment, consisting of frictional unemployment and structural unemployment
Current US goal for unemployment
Under 5%
discouraged workers
individuals who would like to work but have given up looking for a job
Underemployed
working at a job for which one is overqualified, or working part-time when full-time work is desired