Clover learning 1st mock exam 8/15/23
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Which of the following occurs when a multi-focus image intensifier tube is operated in magnification mode?
A. Larger area of the input phosphor is used
B. Patient dose will be increased
C. Image quality will be reduced
D. Less voltage is applied to the electrostatic lenses
B. Patient dose will be increased
Which radiation measurement is most helpful when comparing biologic damage from different radiation types?
A) Equivalent dose
B) Effective dose
C) Absorbed dose
D) Entrance skin exposure
A) Equivalent dose
This is because it uses the radiation weighting factor to account for the radiation type.
To place the right kidney parallel to the image receptor (IR) during renal tomography, the patient should be placed in what position?
• 30 degree left posterior oblique
• 30 degree right posterior oblique
• AP erect
• Prone
• 30 degree left posterior oblique
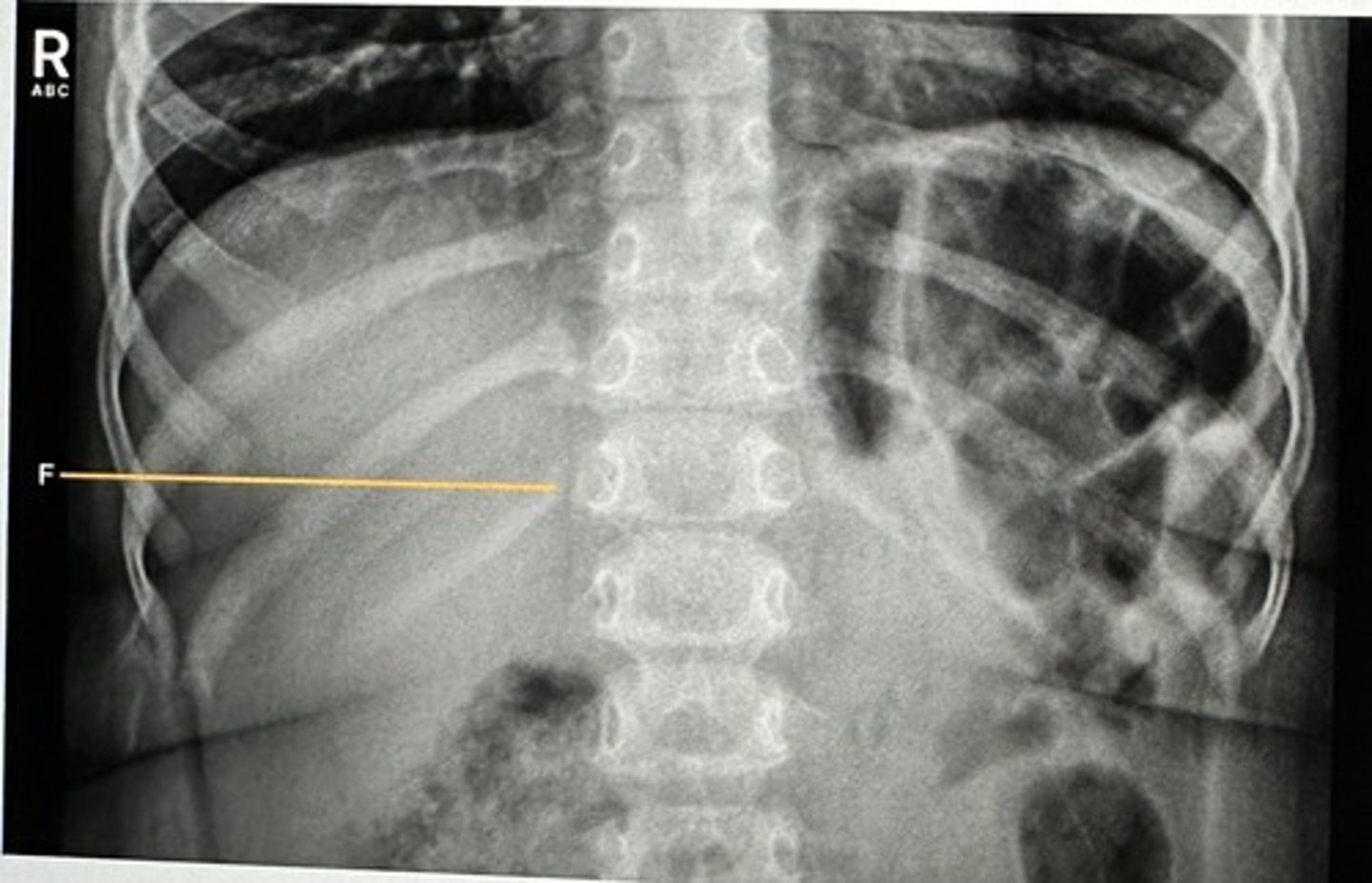
Identify the structure that is represented by the letter (F):
A) Twelfth posterior rib
B) Twelfth anterior rib
C) Ninth posterior rib
D) Tenth anterior rib
A) Twelfth posterior rib
Which of the following automatic exposure control (AEC) detector selections would result in an appropriate exposure level for an anteroposterior (AP)
projection of the lumbar spine?
A) Center detector only
B) Left detector only
C) Right detector only
D) Right and left detectors only
E) All three detectors
A) Center detector only
because the anatomy of interest is in the center of the collimated beam.
You are preparing to perform a lower gastrointestinal (Gl) procedure on a patient with a suspected perforation of the bowel. What type of contrast media should be prepared?
A) Air
B) Iodinated aqueous
C) Barium
D) Carbon dioxide
B) Iodinated aqueous
What thickness of protective shielding is required in the Bucky slot cover of a fluoroscopic imaging unit?
A) 0.25 mm lead equivalent
B) 0.25 mm aluminum equivalent
C) 0.5 mm lead equivalent
D) 0.5 mm aluminum equivalent
A) 0.25 mm lead equivalent
When using automatic exposure control (AEC), which of the following can be employed to reduce patient motion while maintaining proper image receptor exposure?
A) Decreased back-up timer setting
B) Increased milliamperage setting
C) Decreased kilovoltage peak (kVp) setting
D) Increased grid ratio
B) Increased milliamperage setting
Which of the following is accurate regarding low-pass filtering, or smoothing?
A) Smoothing is a local processing operation
B) Smoothing is a point processing operation
C) Smoothing is a geometric processing operation
A) Smoothing is a local processing operation
Which of the following medications would most likely be given to a patient suffering from angina pectoris?
A) Aspirin
B) Epinephrine
C) Heparin
D) Nitroglycerine
D) Nitroglycerine
Nitroglycerine is a powerful vasodilator that is used to treat angina pectoris
"If you don't hold still, I will have to stick you again with this needle!" is an example of:
A) False imprisonment
B) Battery
C) Assault
D) Negligence
C) Assault
Assault is the threat of touching a person in a harmful manner.
When using fluoroscopy, which of the following is directly proportional to the exposure delivered to the patient?
A) Kilovoltage peak (kVp)
B) Milliamperage (mA)
C) Thickness of the filter
D) Target-to-tabletop distance
B) Milliamperage (mA)
What is the name of the small spur of bone that extends superiorly from the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone?
• Dorsum sellae
• Labyrinth
• Crista galli
• Perpendicular plate
• Crista galli
Cribriform plate = Crista galli
The medical specialization in the study of pregnancy and childbirth is called:
• Family practice
• Gynecology
• Obstetrics
• Pediatrics
Obstetrics is the study of pregnancy and childbirth
Medical asepsis can be defined as a:
. Complete destruction and removal of pathogenic microorganisms in the environment
• Method of encouraging growth of pathogenic microorganisms in the environment
• Method of creating new types of pathogenic microorganisms in the environment
• Reduction in number of pathogenic microorganisms in the environment
• Reduction in number of pathogenic microorganisms in the environment
These processes are put in place to decrease the probability of the spread of infection.
Which of the following would be an acceptable treatment for a patient suffering from epistaxis?
• Tilt head back while sitting upright in chair and breathe through nose
• Place in the recumbent position and breath through mouth
• Tilt head forward and breath through mouth
• Tilt head forward and blow the nose
• Tilt head forward and breath through mouth
Which two of the following is accomplished with pulsed fluoroscopy? (Select two)
• Decreased patient dose
• Extended tube life
• Continuous activation of the x-ray tube
• Increased signal-to-noise ratio
• Decreased patient dose
• Extended tube life
A decrease in oxygen content is called:
• Anoxia
• Нурохіа
• Deoxia
• Senoxia
• Нурохіа
Every item inside of a sterile kit is considered sterile except for the outer border. The border that is safe to touch is how wide?
• 0.5 inch
• 1 inch
• 1.5 inches
• 2 inches
• 1 inch
Everything within the sterile kit is considered safe to touch up until the 1 inch border, or where it starts to bend down off of the sides of the tray, or the edges.
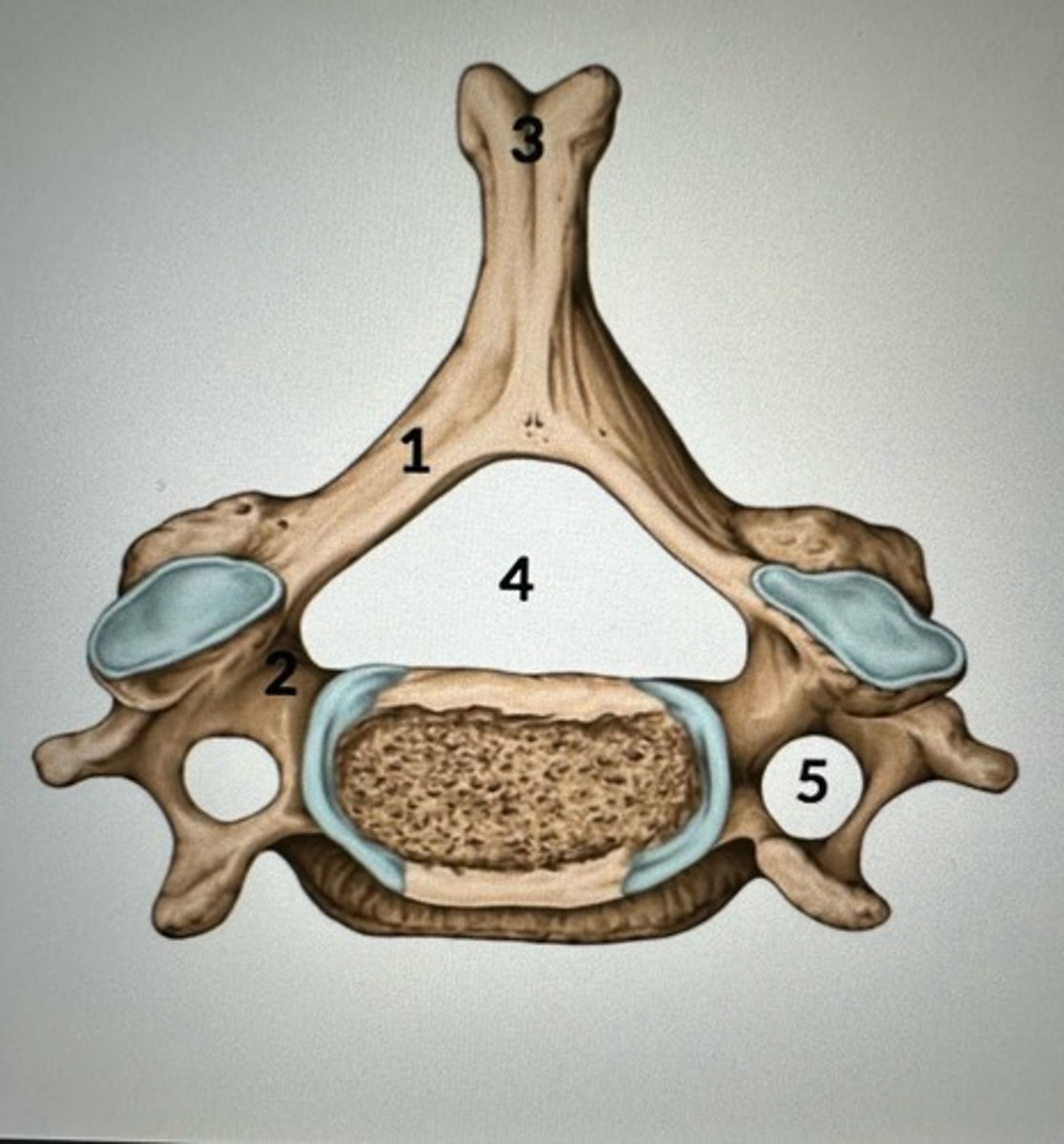
Select the number that represents the lamina on the illustration:
1
2
3
4
1
A technologist takes two exposures using automatic exposure control (AEC) - the first without barium and the second following the introduction of 250 milliliters of oral barium. Which of the following will likely occur to the exposure?
• Increased exposure time
• Increased image receptor exposure
• Decreased image receptor exposure
• Increased milliamperage (mA) setting
• Increased exposure time
AC would increase the exposure time to maintain image receptor exposure because barium absorbs more radiation, and therefore, more exposure is needed to produce a quality radiograph.
Which anatomic structure represents the parenchyma of the kidney?
• Minor calyx
• Renal column
• Nephron
• Renal papilla
• Nephron
The nephron represents the parenchyma of the kidney. The parenchyma is the functional tissue of the kidney.
Which exposure technique system uses the rule to double or halve milliampere seconds (mAs) for every 5 centimeters of subject thickness?
A) Fixed kilovoltage peak (kV) system
B) Variable kilovoltage peak (kVp) system
C) Automatic exposure control (AEC)
D) Anatomically programmed technique system
A) Fixed kilovoltage peak (kV) system
A patient with pertussis, whooping cough, or influenza needing transmission-based precautions would most likely be placed in which of the following?
• Airborne infection isolation
• Contact precautions
• Droplet precautions
• Strict isolation
• Droplet precautions
Which of the following may be used when anatomy or the area of interest is too large to fit on one image receptor?
• Stitching
• Appending
• Volume rendering
• Multiplanar reconstructions
• Stitching
Images are processed in computer programs that nearly seamlessly join the anatomy for display as one single image.
The duct that connects with the proximal gallbladder is known as the:
• Common hepatic duct
• Common Bile duct
• Cystic duct
• Left/right hepatic duct
• Cystic duct
When using an automatic exposure control (AEC), which of the following changes will result in increased image receptor exposure?
• Decrease in the milliamperage (mA) setting
• Increase in the grid ratio
• Increase in the kilovoltage (kV) setting
• Increase in the exposure adjustment (density control)
• Increase in the exposure adjustment (density control)
What is the correct central ray entrance point for the lateral projection of the foot?
• At the center of the longitudinal arch
• At the subtalar joint
• Entering the medial cuneiform, and through the base of the third metatarsal
• Through the head of the first metatarsal
• Entering the medial cuneiform, and through the base of the third metatarsal
If a radiographer produced an image using an x-ray exposure that is below the dynamic range, the resulting image is expected to display:
A) Quantum mottle
B) Saturation artifact
C) Excessive contrast
D) Shape distortion
A) Quantum mottle
Where is the technique chart of anatomically programmed technique systems stored?
• In the microprocessor of the control unit
• On the secondary side of the high-voltage transformer
• In the software application of the control unit
• On the primary side of the high-voltage transformer
• In the microprocessor of the control unit
Which of the following allows the free flow of electrons?
• Insulator
• Battery
• Capacitor
• Conductor
• Conductor
Which of the following technical factor adjustments should be made when negative contrast media agents are used?
• Decreased kilovoltage peak (kVp)
• Increased kilovoltage peak (kV)
• Increased milliampere seconds (mAs)
• Decreased milliampere seconds (mAs)
• Decreased kilovoltage peak (kVp)
You are performing an anteroposterior (AP) projection of the abdomen using 70 kilovoltage peak (kV) and 40 milliampere-seconds (mAs). What exposure time should be used if you select the 200 milliampere (mA) station?
• 5 seconds
• 2 seconds
• 0.5 seconds
• 0.2 seconds
• 0.2 seconds
What International System of Units (SI) is used to express exposure?
• Coulombs/kilogram
• Gray
• Sievert
• Becquerel
• Coulombs/kilogram
Which of the following is the most common cause of esophageal varices?
• Eating spicy food
• Cardiovascular disease
• Portal hypertension
• Long term gastritis
• Portal hypertension
A condition of dilated and tortuous veins in the middle and distal esophagus is called varices, which is secondary to long term portal hypertension where blood does not easily circulate through the liver and must find an alternate path to return to the heart.
Values of interest (VOI) are determined during:
• Histogram analysis
• Grayscale analysis
• Analog data analysis
• Value analysis
• Histogram analysis
Which of the following describes the sternoclavicular joint?
• Synarthroidial
• Synovial, gliding
• Amphiarthroidial
• Synovial, condylar
• Synovial, gliding
Sternoclavicular joints are freely movable, gliding joints that allow elevation and depression of the shoulders along with other movements.
For an arthrogram, a combination of which imaging modalities is most commonly utilized?
• Diagnostic radiography and fluoroscopy
• Fluoroscopy and nuclear medicine
• Fluoroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT)
• Fluoroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Where should the central ray enter for a posteroanterior (PA) projection of the finger?
• Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint
• Distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint
• Metacarpophalangeal joint
• Carpometacarpal joint
• Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint
A patient with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) had imaging in the emergency department (ED) and the technologist touched the affected area on the patient without using protective equipment or proper hand hygiene. The technologist later developed an infectious lesion on the hand. How was the MRSA transmitted in this case?
• Fomite, indirect
• Airborne contact
• Vector, indirect
• Direct contact
• Direct contact
If the primary beam area is doubled by opening the collimator, patient dose and exposure to the operator will:
• Increase by a factor of 4
• Increase by a factor of 3
• Increase by a factor of 2
• Remain the same
• Increase by a factor of 2
Which three of the following structures are located on the tibia? (Select three)
• Lateral condyle
• Intercondylar eminence
• Apex
• Adductor tubercle
• Medial condyle
• Lateral condyle
• Intercondylar eminence
• Medial condyle
When performing a double-contrast barium study of the colon, what is the recommended product density?
• 75 - 95% weight/volume
• 15 - 20% weight/volume
• 50 - 60% weight/volume
• 25 - 35% weight/volume
• 75 - 95% weight/volume
During digital image formation, quantization occurs in the:
• Technologist's control console
• Analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
• Detector assembly
• X-ray tube housing
• Analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
Quantization is the process through which analog electrical signals are assigned a numerical value, which determines the shades of gray in the digital image.
Which of the following should be avoided if possible when imaging morbidly obese patients using direct radiography (DR) image receptors?
• The use of full 17×17" radiation field
• The use of a grid
• The use of automatic exposure control (AEC)
• The use of positive beam limitation
• The use of full 17×17" radiation field
Which of the following devices collects the light signal released by photostimulable phosphors (PSP) in the plate reader?
A) Thin-film transistor (TFT)
B) Photomultiplier tube (PMT)
C) Scintillator
D) Analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
B) Photomultiplier tube (PMT)
Which of the following is an indication for retrograde urography?
• Renal calculus
• Renal insufficiency
• Benign prostatic hyperplasia
• Cystitis
• Renal insufficiency
Which of the following medications would be given to a patient suffering from angina pectoris?
• Nitroglycerine
• Benadryl
• Epinephrine
• Lidocaine
• Nitroglycerine
Nitroglycerine is a powerful vasodilator that is used to treat angina pectoris (chest pain).
The International System of Units (SI) for absorbed dose is:
• Gray (Gy)
• Sievert (Sv)
• Becquerel (Bq)
• Coulombs per kilogram (C/kg)
• Gray (Gy)
A cumulative timer must be provided and used with each fluoroscopic unit.
This resettable device times the x-ray beam-on time and sounds an audible alarm or temporarily interrupts the exposure after the fluoroscope has been activated for:
• 1 minute
• 3 minutes
• 5 minutes
• 10 minutes
• 5 minutes
What is the medical term for fever?
• Apnea
• Hypertension
• Orthostatic hypotension
• Pyrexia
• Pyrexia
The medical term for elevated body temperature is pyrexia or hyperthermia.
Patients with elevated body temperatures can also be described as febrile or having a fever.
The following image has a low spatial resolution as a result of a small:
• Pixel size
• Detector size
• Matrix size
• Bit depth
• Matrix size
The image has a low spatial resolution as a result of a small matrix
size. Small matrix size results in fewer pixels that are larger,
resulting in a poor spatial resolution.
Expectant mothers who are technologists should wear a fetal dosimeter at what location?
• At the collar
• At the thyroid
• At the waist
• Outside the apron
• At the waist
Expectant mothers who are technologists should wear a fetal dosimeter at the waist.
This dosimeter should be worn underneath the lead apron, in addition to the radiation monitoring device that is worn at the collar over the lead apron.
Blur and spatial resolution share what relationship?
• Direct
• Inverse
• There is no relationship between blur and spatial resolution
• Inverse
A patient requests a paper copy of their radiology report. If the paper report is provided directly to the patient, is this a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) violation?
• This is a HIPAA violation
• This is not a HIPAA violation
• This is not a HIPAA violation as long as the report is anonymized
• This is a HIPAA violation only if the patient discloses the report to third parties
• This is not a HIPAA violation
When performing images of the stomach after a double-contrast upper gastrointestinal series, barium will fill the fundus of the stomach in which of the following positions?
• Erect AP
• Supine AP
• Recumbent RAO
• Erect PA
• Supine AP
Since the fundus is more posterior than the body of the stomach, it will fill with barium in the supine position.
Which three of the following are included in a personnel monitoring report?
(Select three)
• Total effective dose equivalent
• Quarterly accumulated dose equivalent
• Year to date dose equivalent
• Lifetime dose equivalent
Quarterly accumulated dose equivalent
• Year to date dose equivalent
• Lifetime dose equivalent
The bones of the forearm are crossed when the hand is:
• Flexed
• Extended
• Supinated
• Pronated
• Pronated
A contaminated object, such as a Foley catheter, acting as a source of disease transmission is called a/an:
• Vector
• Parasite
• Host
• Fomite
• Fomite
A contaminated object
Which two of the following are controlled by kilovoltage peak (kVp)? (Select two)
• Electric potential
• Beam quality
• Tube current
• Electron production
• Electric potential
• Beam quality
The burden of proof for medical negligence rests with the:
• Physician
• Plaintiff
• Radiographer
• Defendant
• Plaintiff
In litigation, the patient is the plaintiff (the suing party).
Which of the following describes a dermoid cyst?
• Benign smooth muscle tumor of the uterus
• Malignant tumor of the ovarian follicles
• Benign tumor filled with material such as hair and teeth
• Malignant tumor of the uterine muscle
• Benign tumor filled with material such as hair and teeth
Which three of the following parts are used in making a transformer?
(Select three)
• Transfer capacitor
• Core
• Primary coil
• Secondary coil
• Core
• Primary coil
• Secondary coil
Which of the following is needed to move electrons through a circuit?
• Amperes
• Ohms
• Volts
• Coulombs
• Volts
There needs to be a source of electric potential (voltage), which pushes electrons from a point of low potential energy to higher potential energy.
While examining an anteroposterior (AP) axial projection of the barium-filled large intestine, at what point does the central ray enter the midsagittal plane:
• Level of the iliac crests
• Top of the pubic symphysis
• Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
• Two inches (5cm) inferior to the level of the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
• Two inches (5cm) inferior to the level of the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
A cancer patient may have which three devices inserted to aid in the delivery of strong chemotherapy medication? (Select three)
• Power Port
• Swan-Ganz line
• Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line
• Hickman line
• Power Port
• Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line
• Hickman line
How can paralanguage be used to improve the quality of communication with one's patient?
• Make sure to speak distinctly when giving instructions for positioning
• Maintain appropriate eye contact during the entire procedure
• Repeat the patient's comment to ensure understanding
• Use the appropriate terminology when explaining the procedure
• Make sure to speak distinctly when giving instructions for positioning
Which two of the following is measured by the light field-radiation field alignment test? (Select two)
• How well the collimator regulates the radiation field size
• Whether the area illuminated by the positioning light and the area exposed by x-rays are the same
• Accuracy of the positive beam limitation (PBL)
• Illuminator bulb brightness
• How well the collimator regulates the radiation field size
• Whether the area illuminated by the positioning light and the area exposed by x-rays are the same
Which of the following is NOT an appropriate use of electronic annotation during digital radiographic imaging?
• Indicating laterality (R/L)
• Indicating patient position
• Indicating time of the exam
• Indicating sequencing of the projections
• Indicating laterality (R/L)
The gray is a unit of absorbed dose defined as being equal to:
• Joule/kilogram
• Joule x kilogram
• Kerma/kilogram
• (Joule/kilogram) × 100
• Joule/kilogram
Which of the following joints is often assessed using arthrography?
• Metacarpalphalangeal joint (MCP)
• Interphalangeal joint (IP)
• Shoulder joint
• Sacroiliac joint
• Shoulder joint
Which two of the following devices may an oncology patient have for the delivery of chemotherapy medication? (Select two)
• Chest tube pigtail catheter
• Central venous catheter (CVC)
• Swan-Ganz catheter
• Implantable venous access port (PORT)
• Central venous catheter (CVC)
• Implantable venous access port (PORT)
Which two of the following are included in the total filtration of the x-ray beam? (Select two)
• Added filtration
• Inherent filtration
• Collimation
• Gravity filtration
• Added filtration
• Inherent filtration
The majority of the x-ray photons are produced at the anode by which interaction?
• Bremsstrahlung
• Characteristic
• Compton
• Photoelectric
• Bremsstrahlung
In the context of a digital matrix, 1,024 × 1,024 refers to the:
• Number of pixels in the matrix
• Size of pixels in the matrix
• Number of brightness levels displayed in the matrix
• Physical measurement of the matrix
• Number of pixels in the matrix
Which of the following structures is located at the level of the interspace between T4 and T5?
• Jugular notch
• Sternal angle
• Manubrium
• Xiphoid
• Sternal angle
Digital image receptors with a large detector element (DEL) pitch will have:
• Low spatial resolution
• High spatial resolution
• Low contrast resolution
• High contrast resolution
• Low spatial resolution
Which of the following would cause excessive image receptor (IR) exposure while using automatic exposure control (AEC)?
• Milliamperage (mA) setting
• Incorrect radiation detector selection
• Source-to-image distance (SID)
• Kilovoltage (kV) setting
• Incorrect radiation detector selection
For a parietoacanthial projection, Waters method, the first step in positioning is to have which body parts) resting against the image receptor (IR)?
• Chin
• Nose
• Forehead
• Nose and forehead
• Chin
During Compton interactions, the incident x-ray photon interacts with what portion of an atom?
• Inner-shell electron
• Outer-shell electron
• K-shell electron
• Atomic nucleus
• Outer-shell electron
At what point is a person at risk of irreversible brain damage if they develop cerebral hypoxia?
• 2 to 3 minutes
• 4 to 6 minutes
• 7 to 10 minutes
• Cerebral hypoxia does not lead to brain injury or death
• 4 to 6 minutes
Cerebral hypoxia or loss of oxygen to the brain is an extremely serious condition.
In which of the following positions or projections are the cuboid articulations, sinus tarsi, and tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal best demonstrated?
• Lateral foot
• Anteroposterior (AP) oblique foot with lateral rotation
• Anteroposterior (AP) oblique foot with medial rotation
• Anteroposterior (AP) weight-bearing foot
• Anteroposterior (AP) oblique foot with medial rotation
Which of the following patient positions would best demonstrate the right sacroiliac joint?
• 25-30 degree right posterior oblique (RPO)
• 25-30 degree left posterior oblique (LPO)
• 10-15 degree right posterior oblique (RPO)
• 10-15 degree left posterior oblique (LPO)
• 25-30 degree left posterior oblique (LPO)
Which of the following projections would best demonstrate a dislocation of the lunate?
• Anteroposterior (AP) wrist
• Posteroanterior (PA) oblique wrist
• Posteroanterior (PA) wrist
• Lateral wrist
• Lateral wrist
Another name for radiation tissue reactions is:
• Non-linear effects
• Stochastic effects
• Deterministic effects
• Heritable effects
• Deterministic effects
The overall ability of an image intensifier to increase image illumination is called:
• Minification gain
• Flux gain
• Brightness gain
• Illumination gain
• Brightness gain
As the angle of the anode decreases, what happens to the heat loading capacity of the x-ray tube?
• Increases
• Decreases
• The angle of the anode is not related to heat loading capacity
• There is no heat change due to the angle of the anode
• Decreases
When performing the parietoacanthial projection of the sinuses open-mouth,
Waters method, where should the central ray exit?
• Nasion
• Glabella
• Acanthion
• Mental point
Acanthion
When performing a lateral image of the sternum, what source-to-image receptor distance (SID) should be used?
• 30 inches
• 40 inches
• 72 inches
• 100 inches
72 inches
Which of the following describes eversion of the foot?
• Pointing the toe downward
• Abnormal movement when the sole of the foot is bent inward
• Decreasing the angle between the top of the foot and the lower leg
• Outward or lateral stress motion of the foot
• Outward or lateral stress motion of the foot
What effect would changing the x-ray tube filtration from 3.5 mm to 4.0 mm
have on the x-ray beam quality?
• Decreased quality
• Increased quality
• No change in quality
• Increased quality
The document in which patients identify the type and amount of nutritional and life-sustaining treatments desired at the end of life is referred to as which of the following?
• Living will
• Do not resuscitate (DNR) order
• Patient's Bill of Rights
• Durable power of attorney
• Living will
Current federal standards limit entrance skin exposure rates of general-purpose intensified fluoroscopic units to a maximum of:
• 10 milligrays (mGy) per hour
• 10 milligrays (mGy) per minute
• 100 milligrays (my) per minute
• 100 milligrays (mGy) per hour
• 100 milligrays (my) per minute
The brightness of the image on a viewing monitor is the result of:
• A monitor function
• Image receptor exposure
• Tissue composition
• Part thickness
• A monitor function
Which of the following is the appropriate formula to calculate heat units for a 3-phase 12-pulse machine?
• Kilovoltage peak (kVp) × milliamperage (mA) x exposure time
• Kilovoltage peak (kVp) × milliamperage (mA) × exposure time × 1.35
• Kilovoltage peak (kVp) x milliamperage (mA) x exposure time × 1.41
• Kilovoltage peak (kVp) x milliamperage (mA) x exposure time x 1.45
• Kilovoltage peak (kVp) x milliamperage (mA) x exposure time × 1.41
How is a gross overexposure error demonstrated in a digital image?
• Overall graininess
• Missing data points
• Increased contrast
• Increased brightness
• Missing data points
Diminished sperm count can occur with a dose of at least:
• 100 milligray (mGy)
• 10 milligray (mGy)
• 25 milligray (mGy)
• 50 milligray (mGy)
• 100 milligray (mGy)
The dorsum sellae is projected within the foramen magnum in which projection of the skull?
• PA skull
• PA axial skull (Caldwell method)
• AP axial skull (Towne method)
• Lateral skull
• AP axial skull (Towne method)
How many facial bones are there?
• 8
• 9
• 14
• 15
14