Integumentary System Wk 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
functions of the skin
protection (barrier), immunity (langerhans), thermoregulation (sweat, evaporation, radiative heat loss)
sensation
(somatosensation)
metabolism
communication
excretion
functions of metabolism includes
excretion, absorption, UV degradation (vitamin d, bilirubin)
Protection: outtermost layer of epidermis
stratum corneum
protect against water loss
BLANK is an acidic coating that delays growth of micoorganisms on skin
Acid Mantle
Disruption or loss of acid mantle on skin surface increases risk of
skin damage and infection
the release of BLANK and trigger of inflammation and angiogenesis
cytokines
When body temperature rises, blood flow increases to the skin causing sweat glands to release heat which is controlled by
hypothalamus
the function of the skin in metabolism includes vitamin d, which is a
Long process that keeps calcium and phosphorous in the blood and bones at normal levels
epidermis is completely
avascular and aneural
what layer are blood vessels at?
dermis
basement membrane zone ?
a zone of complex protein bonds that seperates the epidermis from dermis
5 layers of epidermis
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
what makes up the stratum corneum
dead skin cells that shed daily, protects against water loss
where can the 2nd outtermost layer, the stratum lucidum, be found?
only found in thick skin (palms of hand and soles of feet)
'clear' cells
the stratum granulosum assists with
keratin formation
nucleus of cells begin to die here
stratum spinosum
THICKEST LAYER
MOSTLY LIVING CELLS
produce keratin
spikey cells under microscope
melanin is injected into keratinocytes, and protects nucleus.
Stratum germinativum/basale
melanocytes
outer layer that undergoes mitosis to produce new cells
fluid and cell exchange between layers of skin occurs here
living cells.
MAJORITY of cells in epidermis
keratinocytes (90% ish)
life span of keratinocytes
28 days
Desmosomes bind keratinocytes together to
improve strength
Langerhans cells (2%)
Capture, uptake and processing of antigens
immune response
Recruit T cells to attack pathogens
First line of defense against environment
where are merkel cells found
stratum germinativum
what do merkel cells do
detection of touch
what seperates epidermis from dermis
basement membrane zone
Responsible for communication between skin layers via rete ridges****
where do blisters form?
in basement membrane zone
rete ridges do what?
Rete ridges in epidermis extend downward and interlock with rete ridges from dermis
Helps protect against shear and friction
dermis function
provides nutrients and support to epidermis
what is dermis made of
thick, dense, fibroelastic connective tissue
highly vascularized
base of hair follicle found here***
appearance of dermis
pink/red and appears wet when exposed
more superifical layer of dermis that connects to epidermis
papillary layer
what is within the papillary layer of dermis
blood vessels, lympathics, epipthelial cells, small muscles, neurons
what is papillary layer made up of
connective tissue
extracellular matrix and fibroblasts
LARGEST component of dermis
extracellular matrix
(collagen and elastin)
structural integrity of skin
JOB of ECM
Cell adhesions, lubricates cells and transport system for nutrients and waste products
INNERMOST layer of dermis
reticular layer
Collagen layer arranged in basket-like weave attaching it to the subcutaneous tissue
tensile strength.
where are sweat glands, nerves and hair follicles and blood vessels found within the dermis
reticular layer
cells within the dermis include
macrophages, mast cells, fibroblasts, langerhans
macrophages
front line of defense, ingest dead tissue
mast cells
assist with blood clot in early stage of wound healing
fibroblasts
cells form which connective tissue is developed, improve tensile strength
langerhans (dermis)
first line of defense, assist with epidermal immunity
Structures underneath the dermis include
Subcutaneous tissue
Fascia
Muscle
Tendon
Ligament
Bone
Cartilage
subcutaneous tissue includes
Fat
Loose connective tissue beneath dermal layer of skin
Location of lymphatics and blood vessel supply
cells in the subcutaneous tissue are
adipocytes
layer of padding
appearance in wound in subcutaneous tissue
Pale yellow, waxy, globular, oily substance that glistens if healthy
Dries or turns tan or yellow-brown if more chronic
Fascia layering underneath subcutaneous tissue?
Sheath covering muscle, nerves and blood vessels keeping them in tight bundles as a single unit
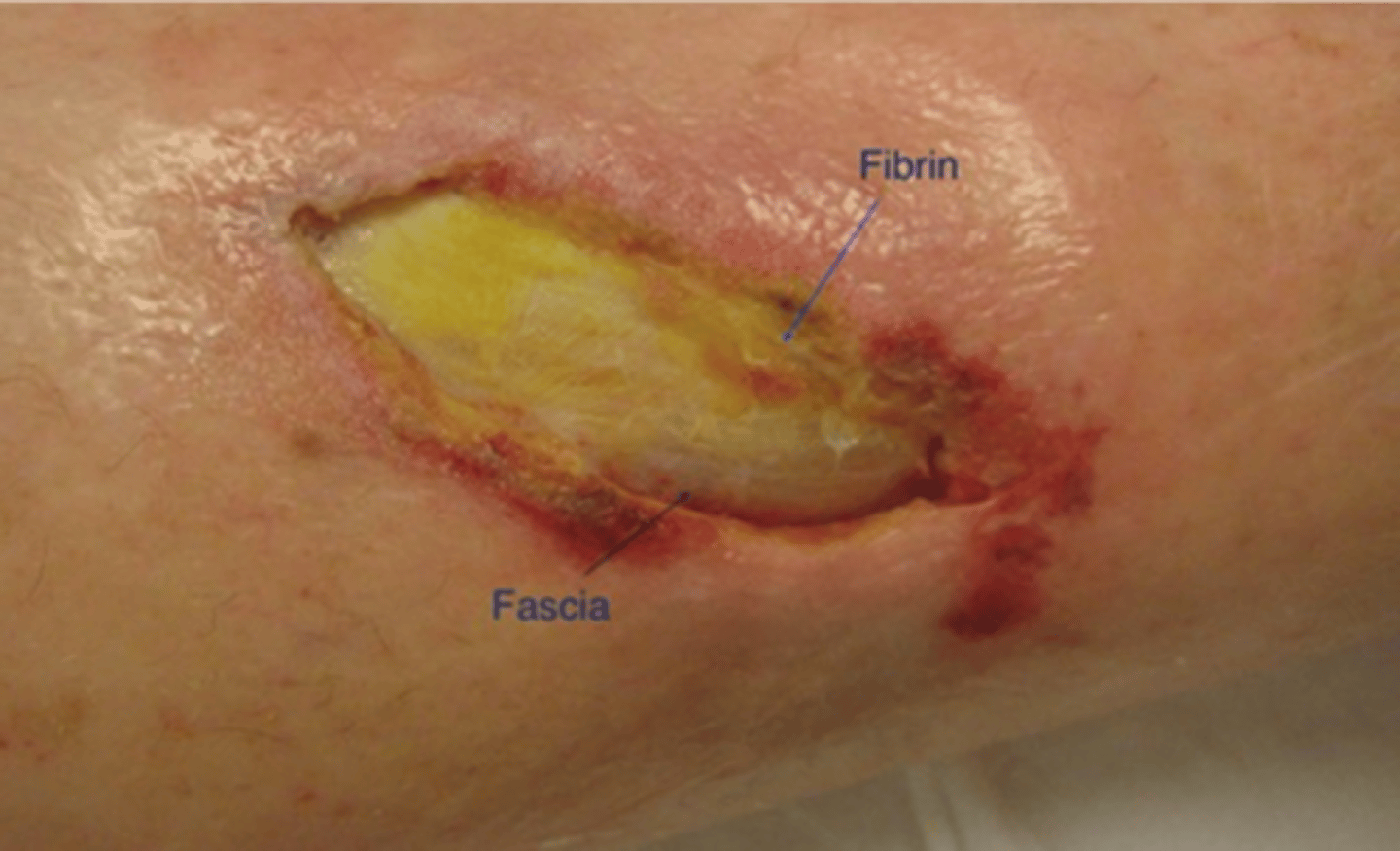
appearance of fascia wound?
White and shiny
Grayish if non-viable
appearance of a muscle wound?
dark red, highly vascularized, striated
will contract if stimulated!
ischemic muscle appearance?
mushy, dull red, cyanotic or pale
necrotic muscle appearance?
will turn liquid causing a dark brown, odorous tissue
BLANK tissue must cover exposed muscle
granulation tissue
required to cover muscle in order to close up wound
why cant epithelial tissue grow over exposed muscle?
lack of basal lamina to allow for epithelial cell migration
appearance of tendon wound
Gleaming yellow or white, shiny
appearance of bone wound
Shiny, hard, milky white
Slick to touch
Flaky with a gray, brown or black color if necrosing
Mushy or rough, falling apart if osteomyelitis present
ligament appearance of wound
ribbon-like, striated, pearly white
difference in wound appearance between ligament and tendon
broader, flatter, more loosely woven compared to tendon
appearance of cartilage wound
very white and shiny, POOR VASCULAR SUPPLY
total time for a wound to repair is BLANK weeks
4-6 weeks
4 major steps of wound repair
hemostasis
inflammation
proliferation
remodeling
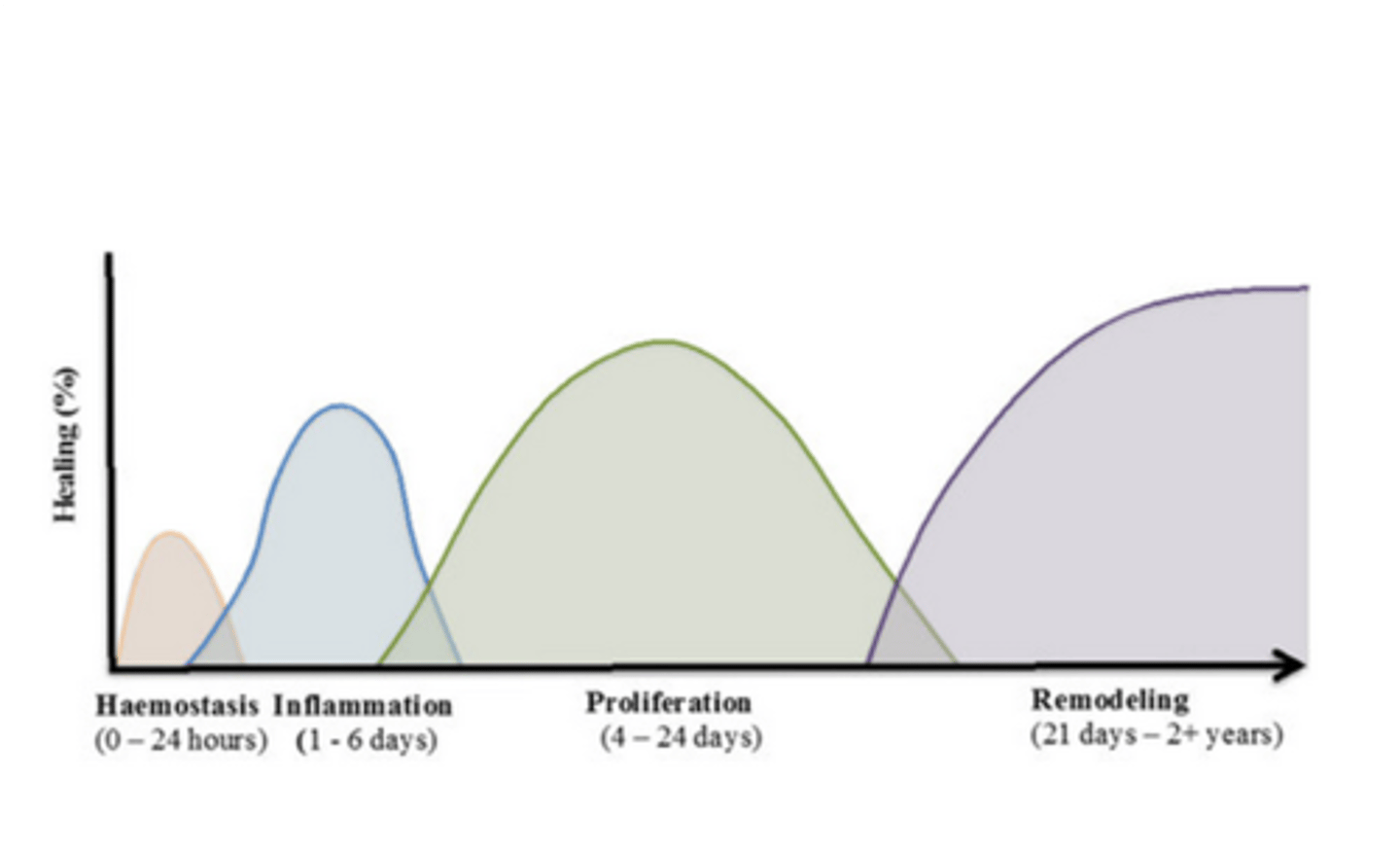
what two main things will limit wound repair?
anything that promotes necrosis or limited vascularization will extend this time